DNA Nanoflowers’ Amelioration of Lupus Symptoms in Mice via Blockade of TLR7/9’s Signal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
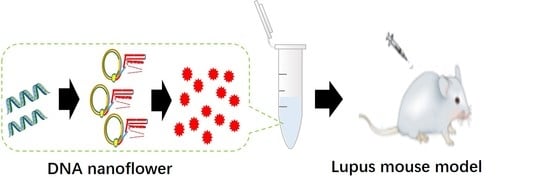
2.1. Characterization of the Prepared DNA Nanoflowers
2.2. Body Weight and Organ Indexes
2.3. The Treatment Attenuated ANA Antibodies in the IRS-661-Treated and IRS-869-Nanoflower-Treated Groups and Significantly Reduced dsDNA Antibodies in the IRS-661-Nanoflower-Treated Group
2.4. Proteinuria Was Down-Regulated in All the Nanoflower-Treated Groups, Especially IRS-661-Treated and IRS-869-Nanoflower-Treated Groups
2.5. Lupus Nephritis Was Ameliorated after Nanoflower Treatment but Not in the IRS 954 Group
2.6. Immune Complexes Reduced in the CTR-Treated-, IRS-661-Treated-, and IRS-869-Nanoflower-Treated Groups
2.7. The Serum Level of IL-17 in IRS-661-Treated and IRS-869-Nanoflower-Treated Groups Significantly Reduced; IFNα Levels Decreased Markedly in All Nanoflower-Treated Groups
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation and Characterization of the DNA Nanoflower
4.2. Animal Grouping and DNA Nanoflower Administration
4.3. ANA Analysis
4.4. Quantification of ANA and Anti-dsDNA Antibodies
4.5. Detection of Proteinuria
4.6. Histological Evaluation
4.7. Immune Complex (IC) Detection
4.8. Quantitative Detection of the Level of Cytokines IFNα and IL-17
4.9. Statistical Processing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avihingsanon, Y.; Hirankarn, N. Major lupus organ involvement: Severe lupus nephritis. Lupus 2010, 19, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakonas, E.; Joseph, L.; Esdaile, J.M.; Choquette, D.; Senécal, J.L.; Cividino, A.; Danoff, D.; Osterland, C.K.; Yeadon, C.; Smith, C.D. A Long-Term Study of Hydroxychloroquine Withdrawal on Exacerbations in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Lupus 1998, 7, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Celhar, T.; Magalhes, R.; Fairhurst, A.M. TLR7 and TLR9 in SLE: When sensing self goes wrong. Immunol. Res. 2012, 53, 58–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillatreau, S.; Manfroi, B.; Dörner, T. Toll-like receptor signalling in B cells during systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colonna, M. TLR pathways and IFN-regulatory factors: To each its own. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kader, M.; Smith, A.P.; Guiducci, C.; Wonderlich, E.R.; Normolle, D.; Watkins, S.C.; Barrat, F.J.; Barratt-Boyes, S.M. Blocking TLR7- and TLR9-mediated IFN-alpha Production by Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Does Not Diminish Immune Activation in Early SIV Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, K.; Du, W.; Wang, X.; Yuan, S.; Cai, X.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Lu, L. Multiple Functions of B Cells in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rommler, F.; Jurk, M.; Uhlmann, E.; Hammel, M.; Waldhuber, A.; Pfeiffer, L.; Wagner, H.; Vollmer, J.; Miethke, T. Guanine modification of inhibitory oligonucleotides potentiates their suppressive function. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3240–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steinhagen, F.; Zillinger, T.; Peukert, K.; Fox, M.; Thudium, M.; Barchet, W.; Putensen, C.; Klinman, D.; Latz, E.; Bode, C. Suppressive oligodeoxynucleotides containing TTAGGG motifs inhibit cGAS activation in human monocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2018, 48, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenert, P.S. Classification, Mechanisms of Action, and Therapeutic Applications of Inhibitory Oligonucleotides for Toll-Like Receptors (TLR) 7 and 9. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 986596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S.R.; Shupe, J.; Nickerson, K.; Kashgarian, M.; Flavell, R.A.; Shlomchik, M.J. Toll-like Receptor 7 and TLR9 Dictate Autoantibody Specificity and Have Opposing Inflammatory and Regulatory Roles in a Murine Model of Lupus. Immunity 2006, 25, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Summers, S.A.; Steinmetz, O.M.; Ooi, J.D.; Gan, P.Y.; O”Sullivan, K.M.; Visvanathan, K.; Akira, S.; Kitching, A.R.; Holdsworth, S.R. Toll-Like Receptor 9 Enhances Nephritogenic Immunity and Glomerular Leukocyte Recruitment, Exacerbating Experimental Crescentic Glomerulonephritis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 2234–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrat, F.; Meeker, T.; Chan, J.; Guiducci, C.; Coffman, R. Treatment of lupus-prone mice with a dual inhibitor of TLR7 and TLR9 leads to reduction of autoantibody production and amelioration of disease symptoms. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 37, 3582–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnopp, T.E.; Chapacais, G.F.; Freitas, E.C.; Monticielo, O.A. Lupus animal models and neuropsychiatric implications. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 40, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meas, R.; Burak, M.J.; Sweasy, J.B. DNA repair and systemic lupus erythematosus. DNA Repair 2017, 56, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashman, R.F.; Goeken, J.A.; Latz, E.; Lenert, P. Optimal oligonucleotide sequences for TLR9 inhibitory activity in human cells: Lack of correlation with TLR9 binding. Int. Immunol. 2011, 23, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenert, P. Inhibitory oligodeoxynucleotides-therapeutic promise for systemic autoimmune diseases? Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 140, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallin, H.; Perers, A.; Alm, G.V.; Rönnblom, L. Anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies and immunostimulatory plasmid DNA in combination mimic the endogenous IFN-alpha inducer in systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 6306–6313. [Google Scholar]
- Matesic, D.; Lenert, A.; Lenert, P. Modulating toll-like receptor 7 and 9 responses as therapy for allergy and autoimmunity. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012, 12, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenert, P.; Stunz, L.; Yi, A.K.; Krieg, A.M.; Ashman, R.F. CpG stimulation of primary mouse B cells is blocked by inhibitory oligodeoxyribonucleotides at a site proximal to NF-kappaB activation. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 2001, 11, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Ito, S.; Ishii, K.J.; Klinman, D.M. Suppressive oligodeoxynucleotides delay the onset of glomerulonephritis and prolong survival in lupus-prone NZB x NZW mice. Arthritis Rheum 2005, 52, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Fukui, R.; Tanaka, R.; Motoi, Y.; Kanno, A.; Sato, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Amano, H.; Furukawa, Y.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Anti-TLR7 Antibody Protects Against Lupus Nephritis in NZBWF1 Mice by Targeting B Cells and Patrolling Monocytes. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 777197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patole, P.S.; Zecher, D.; Pawar, R.D.; Grone, H.J.; Schlondorff, D.; Anders, H.J. G-rich DNA suppresses systemic lupus. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3273–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lau, C.M.; Tabor, A.S.; Akira, S.; Flavell, R.A.; Mamula, M.J.; Christensen, S.R.; Shlomchik, M.J.; Viglianti, G.A.; Rifkin, I.R.; Marshak-Rothstein, A. RNA-associated autoantigens activate B cells by combined B cell antigen receptor/Toll-like receptor 7 engagement. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Raber, M.L.; Dunand-Sauthier, I.; Wu, T.; Li, Q.Z.; Uematsu, S.; Akira, S.; Reith, W.; Mohan, C.; Kotzin, B.L.; Izui, S. Critical role of TLR7 in the acceleration of systemic lupus erythematosus in TLR9-deficient mice. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summers, S.A.; Hoi, A.; Steinmetz, O.M.; O’Sullivan, K.M.; Ooi, J.D.; Odobasic, D.; Akira, S.; Kitching, A.R.; Holdsworth, S.R. TLR9 and TLR4 are required for the development of autoimmunity and lupus nephritis in pristane nephropathy. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 35, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.D.; Ramanjaneyulu, A.; Kulkarni, O.P.; Lech, M.; Segerer, S.; Anders, H.J. Inhibition of Toll-like receptor-7 (TLR-7) or TLR-7 plus TLR-9 attenuates glomerulonephritis and lung injury in experimental lupus. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nickerson, K.M.; Christensen, S.R.; Shupe, J.; Kashgarian, M.; Kim, D.; Elkon, K.; Shlomchik, M.J. TLR9 Regulates TLR7-and MyD88-Dependent Autoantibody Production and Disease in a Murine Model of Lupus. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1840–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rnnblom, L.; Alm, G.V. A Pivotal Role for the Natural Interferon α–producing Cells (Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells) in the Pathogenesis of Lupus. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, f59–f63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lövgren, T.; Eloranta, M.-L.; Båve, U.; Alm, G.V.; Rönnblom, L. Induction of interferon-α production in plasmacytoid dendritic cells by immune complexes containing nucleic acid released by necrotic or late apoptotic cells and lupus IgG. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1861–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Hertzog, P.J.; Ravasi, T.; Hume, D.A. Interferon-γ: An overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2004, 75, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satterthwaite, A.B. TLR7 Signaling in Lupus B Cells: New Insights into Synergizing Factors and Downstream Signals. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2021, 23, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J. IFN-γ Mediates the Development of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7176515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trieu, A.; Roberts, T.L.; Dunn, J.A.; Sweet, M.J.; Stacey, K.J. DNA motifs suppressing TLR9 responses. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 26, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paquissi, F.C.; Abensur, H. The Th17/IL-17 Axis and Kidney Diseases, With Focus on Lupus Nephritis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 654912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, S.A.; Odobasic, D.; Khouri, M.B.; Steinmetz, O.M.; Yang, Y.; Holdsworth, S.R.; Kitching, A.R. Endogenous interleukin (IL)-17A promotes pristane-induced systemic autoimmunity and lupus nephritis induced by pristane. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 176, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, P.S.; Aggarwal, R.; Levesque, M.C.; Maers, K.; Ramani, K. Type I interferon and T helper 17 cells co-exist and co-regulate disease pathogenesis in lupus patients. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 18, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Groups | Body Weight | Heart | Liver | Spleen | Lung | Kidney |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model Group | 35.64 ± 5.30 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 1.93 ± 0.42 | 0.64 ± 0.17 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | 0.57 ± 0.13 |
| CTR-treated | 36.49 ± 1.01 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 2.31 ± 0.60 | 0.60 ± 0.08 | 0.31 ± 0.07 | 0.54 ± 0.13 |
| IRS-661-treated | 36.39 ± 1.58 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 2.11 ± 0.19 | 0.61 ± 0.10 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.55 ± 0.05 |
| IRS-869-treated | 37.33 ± 4.26 | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 2.18 ± 0.25 | 0.71 ± 0.19 | 0.28 ± 0.04 | 0.58 ± 0.07 |
| IRS-954-treated | 34.97 ± 1.99 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 2.06 ± 0.32 | 0.62 ± 0.20 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.49 ± 0.07 |
| Groups | Heart Index | Liver Index | Spleen Index | Lung Index | Kidney Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model Group | 0.52 ± 0.09% | 5.36 ± 0.48% | 1.76 ± 0.29% | 0.76 ± 0.18% | 1.58 ± 0.19% |
| CTR-treated | 0.51 ± 0.07% | 6.29 ± 0.47% | 1.64 ± 0.18% | 0.84 ± 0.17% | 1.47 ± 0.32% |
| IRS-661-treated | 0.49 ± 0.08% | 5.81 ± 0.64% | 1.66 ± 0.24% | 0.65 ± 0.10% | 1.52 ± 0.17% |
| IRS-869-treated | 0.51 ± 0.11% | 5.86 ± 0.59% | 1.88 ± 0.31% | 0.75 ± 0.19% | 1.59 ± 0.33% |
| IRS-954-treated | 0.46 ± 0.06% | 5.88 ± 0.74% | 1.77 ± 0.56% | 0.68 ± 0.06% | 1.39 ± 0.15% |
| ODN | Deoxynucleotide Sequence |
|---|---|
| IRS 661 | 5′- GACTATGGTGACTCAATGCTTGCAAGCTTGCAAGCAGACTGTGATGACAAG-3′ |
| IRS 869 | 5′-GACTATGGTGACTCTCCTGGAGGGGTTGTGCAACTGTGATGACAAG-3′ |
| IRS 954 | 5′-GACTATGGTGACTCTGCTCCTGGAGGGGTTGTGCAACTGTGATGACAAG3′ |
| CTR | 5′-GACTATGGTGACTCAGGTTGACTTCCACTCTACTCAGACTGTGATGACAAG-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Gan, M. DNA Nanoflowers’ Amelioration of Lupus Symptoms in Mice via Blockade of TLR7/9’s Signal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232416030
Wang J, Gan M. DNA Nanoflowers’ Amelioration of Lupus Symptoms in Mice via Blockade of TLR7/9’s Signal. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(24):16030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232416030
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jing, and Mingzhe Gan. 2022. "DNA Nanoflowers’ Amelioration of Lupus Symptoms in Mice via Blockade of TLR7/9’s Signal" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 24: 16030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232416030
APA StyleWang, J., & Gan, M. (2022). DNA Nanoflowers’ Amelioration of Lupus Symptoms in Mice via Blockade of TLR7/9’s Signal. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(24), 16030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232416030