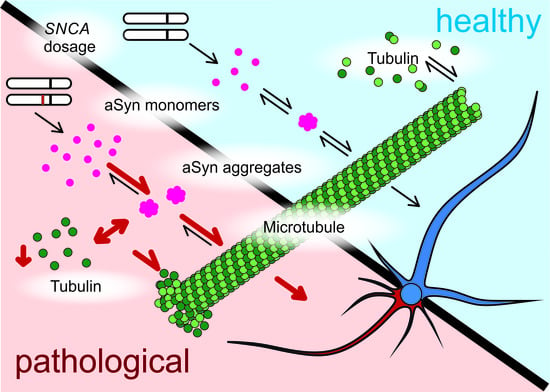
Interaction of Alpha Synuclein and Microtubule Organization Is Linked to Impaired Neuritic Integrity in Parkinson’s Patient-Derived Neuronal Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. aSyn Overexpression Leads to Its Aggregation and Promotes Its Interaction with Microtubule Elements
2.2. Insoluble aSyn Is Associated with the Redistribution of Microtubule Elements
2.3. SNCA Duplication Leads to an Increased aSyn Protein Level in hiPSC-Derived NPCs and Neuronal Cells
2.4. The Level of Tubulins Is Decreased in mDANs Carrying SNCADupl
2.5. bTubIII Is Redistributed in SNCADupl mDANs
2.6. Increased aSyn Perturbs Neurite Morphology Already in an Early Differentiation Stage
3. Discussion
3.1. aSyn Overload and Its Aggregation
3.2. aSyn and Microtubule Organization
3.3. aSyn and Neuritic Integrity
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. H4 Cell Lines
4.2. Human iPSC
4.3. Differentiation of mDANs
4.4. Dot Blot
4.5. Western Blot (WB)
4.6. Immunoprecipitation and LC-MS Analysis
4.7. In-Cell Fractionation
4.8. Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
4.9. Analysis of Neuronal and Neurite Morphology
4.10. Antibodies
4.11. Statistical Methods
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | ammonium bicarbonate |
| ACN | acetonitrile |
| aSyn | alpha synuclein |
| aTub | alpha tubulin |
| bActin | beta actin |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| bTub | beta tubulin |
| bTubIII | beta tubulin, class III |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CPN | cortical projection neuron |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidin-2-phenylindol |
| DDC | DOPA decarboxylase |
| EBs | embryoid bodies |
| FA | formic acid |
| hiPSCs | human induced pluripotent stem cells |
| ICC | immunocytochemistry |
| LC-MS | liquid chromatography coupled mass spectrometry |
| mDAN | midbrain dopaminergic neuronal cell |
| NPC | neural precursor cell |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PFA | paraformaldehyde |
| RT | room temperature |
| RT-PCR | reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| SNCA | aSyn gene |
| SNCADupl | SNCA gene duplication |
| SNpc | substantia nigra pars compacta |
| TBS | Tris-buffered saline |
| TFA | trifluoroacetic acid |
| TH | tyrosine hydroxylase |
| WB | Western blot |
References
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. 100 Years of Lewy Pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahmoradian, S.H.; Lewis, A.J.; Genoud, C.; Hench, J.; Moors, T.E.; Navarro, P.P.; Castano-Diez, D.; Schweighauser, G.; Graff-Meyer, A.; Goldie, K.N.; et al. Lewy Pathology in Parkinson’s Disease Consists of Crowded Organelles and Lipid Membranes. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. Alpha-Synuclein in Lewy Bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroteaux, L.; Campanelli, J.T.; Scheller, R.H. Synuclein: A Neuron-Specific Protein Localized to the Nucleus and Presynaptic Nerve Terminal. J. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 2804–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, C.; Schlossmacher, M.G. The Genetics of Parkinson‘s Disease: Implications for Neurological Care. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2006, 2, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadores, N.; Sanhueza, M.; Manque, P.; Court, F.A. Axonal Degeneration during Aging and Its Functional Role in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, Y.C.; Luk, K.; Purtell, K.; Burke Nanni, S.; Stoessl, A.J.; Trudeau, L.E.; Yue, Z.; Krainc, D.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.A.; et al. Neuronal Vulnerability in Parkinson‘s Disease: Should the Focus Be on Axons and Synaptic Terminals? Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1406–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, J.C.; Bitow, F.; Haack, J.; d‘Hedouville, Z.; Zhang, J.N.; Tonges, L.; Michel, U.; Oliveira, L.M.; Jovin, T.M.; Liman, J.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein Affects Neurite Morphology, Autophagy, Vesicle Transport and Axonal Degeneration in CNS Neurons. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prots, I.; Grosch, J.; Brazdis, R.M.; Simmnacher, K.; Veber, V.; Havlicek, S.; Hannappel, C.; Krach, F.; Krumbiegel, M.; Schutz, O.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers Induce Early Axonal Dysfunction in Human iPSC-Based Models of Synucleinopathies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7813–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janke, C.; Magiera, M.M. The Tubulin Code and its Role in Controlling Microtubule Properties and Functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prots, I.; Veber, V.; Brey, S.; Campioni, S.; Buder, K.; Riek, R.; Bohm, K.J.; Winner, B. Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers Impair Neuronal Microtubule-Kinesin Interplay. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21742–21754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cartelli, D.; Aliverti, A.; Barbiroli, A.; Santambrogio, C.; Ragg, E.M.; Casagrande, F.V.; Cantele, F.; Beltramone, S.; Marangon, J.; De Gregorio, C.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein is a Novel Microtubule Dynamase. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brazdis, R.M.; Alecu, J.E.; Marsch, D.; Dahms, A.; Simmnacher, K.; Lorentz, S.; Brendler, A.; Schneider, Y.; Marxreiter, F.; Roybon, L.; et al. Demonstration of Brain Region-Specific Neuronal Vulnerability in Human iPSC-Based Model of Familial Parkinson’s Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.T.; Jagannath, S.; Francois, C.; Vanderstichele, H.; Stoops, E.; Lashuel, H.A. How Specific Are the Conformation-Specific Alpha-Synuclein Antibodies? Characterization and Validation of 16 Alpha-Synuclein Conformation-Specific Antibodies Using Well-Characterized Preparations of Alpha-Synuclein Monomers, Fibrils and Oligomers with Distinct Structures and Morphology. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 146, 105086. [Google Scholar]
- Carnwath, T.; Mohammed, R.; Tsiang, D. The Direct and Indirect Effects of Alpha-Synuclein on Microtubule Stability in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson‘s Disease. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsetos, C.D.; Draberova, E.; Smejkalova, B.; Reddy, G.; Bertrand, L.; de Chadarevian, J.P.; Legido, A.; Nissanov, J.; Baas, P.W.; Draber, P. Class III Beta-Tubulin and Gamma-Tubulin Are Co-Expressed and Form Complexes in Human Glioblastoma Cells. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, P.; Glatza, M.; Hemmer, K.; Tsytsyura, Y.; Thiel, C.S.; Hoing, S.; Moritz, S.; Parga, J.A.; Wagner, L.; Bruder, J.M.; et al. Derivation and Expansion Using Only Small Molecules of Human Neural Progenitors for Neurodegenerative Disease Modeling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmnacher, K.; Krach, F.; Schneider, Y.; Alecu, J.E.; Mautner, L.; Klein, P.; Roybon, L.; Prots, I.; Xiang, W.; Winner, B. Unique Signatures of Stress-Induced Senescent Human Astrocytes. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 334, 113466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, A.; Maxreiter, F.; Krach, F.; Fadler, T.; Grosch, J.; Maroni, M.; Graef, D.; Eberhardt, E.; Riemenschneider, M.J.; Yeo, G.W.; et al. Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal Cell Death in a Human iPSC-Based Model of Parkinson‘s Disease. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 123–131.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klein, C.; Westenberger, A. Genetics of Parkinson‘s Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a008888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stojkovska, I.; Wani, W.Y.; Zunke, F.; Belur, N.R.; Pavlenko, E.A.; Mwenda, N.; Sharma, K.; Francelle, L.; Mazzulli, J.R. Rescue of Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation in Parkinson‘s Patient Neurons by Synergistic Enhancement of ER Proteostasis and Protein Trafficking. Neuron 2021, 110, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.C.; Minakaki, G.; Menges, S.; Salvi, R.; Savitskiy, S.; Kazman, A.; Vicente Miranda, H.; Mielenz, D.; Klucken, J.; Winkler, J.; et al. Extracellular Aggregated Alpha Synuclein Primarily Triggers Lysosomal Dysfunction in Neural Cells Prevented by Trehalose. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huarcaya, S.P.; Drobny, A.; Marques, A.R.A.; Spiezio, A.D.; Dobert, J.P.; Balta, D.; Werner, C.; Rizo, T.; Gallwitz, L.; Bub, S.; et al. Recombinant Pro-Cathepsin D Enhances a-Synuclein Degradation in a-Synucleinopathy Models. Autophagy, 2022; (Accepted). [Google Scholar]
- Minakaki, G.; Menges, S.; Kittel, A.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Schaeffner, I.; Barkovits, K.; Bergmann, A.; Rockenstein, E.; Adame, A.; Marxreiter, F.; et al. Autophagy Inhibition Promotes SNCA/Alpha-Synuclein Release and Transfer via Extracellular Vesicles with a Hybrid Autophagosome-Exosome-Like Phenotype. Autophagy 2018, 14, 98–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poehler, A.M.; Xiang, W.; Spitzer, P.; May, V.; Meixner, H.; Rockenstein, E.; Chutna, O.; Outeiro, T.; Winkler, J.; Masliah, E.; et al. Autophagy Modulates SNCA/Alpha-Synuclein Release, thereby Generating a Hostile Microenvironment. Autophagy 2014, 10, 2171–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, L.M.; Falomir-Lockhart, L.J.; Botelho, M.G.; Lin, K.H.; Wales, P.; Koch, J.C.; Gerhardt, E.; Taschenberger, H.; Outeiro, T.F.; Lingor, P.; et al. Elevated Alpha-Synuclein Caused by SNCA Gene Triplication Impairs Neuronal Differentiation and Maturation in Parkinson‘s Patient-Derived Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calogero, A.M.; Mazzetti, S.; Pezzoli, G.; Cappelletti, G. Neuronal Microtubules and Proteins Linked to Parkinson‘s Disease: A Relevant Interaction? Biol. Chem. 2019, 400, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.E.; O‘Malley, K. Axon Degeneration in Parkinson‘s Disease. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 246, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halliday, G.M.; Li, Y.W.; Blumbergs, P.C.; Joh, T.H.; Cotton, R.G.; Howe, P.R.; Blessing, W.W.; Geffen, L.B. Neuropathology of Immunohistochemically Identified Brainstem Neurons in Parkinson‘s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 1990, 27, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosch, J.; Winkler, J.; Kohl, Z. Early Degeneration of Both Dopaminergic and Serotonergic Axons-A Common Mechanism in Parkinson‘s Disease. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2016, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, Y.; Morfini, G.A.; Langhamer, L.B.; He, Y.; Brady, S.T.; Kordower, J.H. Alterations in Axonal Transport Motor Proteins in Sporadic and Experimental Parkinson‘s Disease. Brain 2012, 135, 2058–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kordower, J.H.; Olanow, C.W.; Dodiya, H.B.; Chu, Y.; Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Halliday, G.M.; Bartus, R.T. Disease Duration and the Integrity of the Nigrostriatal System in Parkinson‘s Disease. Brain 2013, 136 Pt 8, 2419–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Politis, M.; Wu, K.; Loane, C.; Brooks, D.J.; Kiferle, L.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Bain, P.; Molloy, S.; Piccini, P. Serotonergic Mechanisms Responsible for Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias in Parkinson‘s Disease Patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, V.L.; Bellani, S.; Giannandrea, M.; Yousuf, M.; Valtorta, F.; Meldolesi, J.; Chieregatti, E. α-Synuclein and its A30P Mutant Affect Actin Cytoskeletal Structure and Dynamics. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 3725–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rub, U.; de Vos, R.A.; Jansen Steur, E.N.; Braak, E. Staging of Brain Pathology Related to Sporadic Parkinson‘s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Rub, U.; Gai, W.P.; Del Tredici, K. Idiopathic Parkinson‘s Disease: Possible Routes by Which Vulnerable Neuronal Types May Be Subject to Neuroinvasion by an Unknown Pathogen. J. Neural. Transm. 2003, 110, 517–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Englund, E.; Widner, H.; Mattsson, B.; van Westen, D.; Latt, J.; Rehncrona, S.; Brundin, P.; Bjorklund, A.; Lindvall, O.; et al. Extensive Graft-Derived Dopaminergic Innervation Is Maintained 24 Years after Transplantation in the Degenerating Parkinsonian Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 6544–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luk, K.C.; Kehm, V.; Carroll, J.; Zhang, B.; O‘Brien, P.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Pathological Alpha-Synuclein Transmission Initiates Parkinson-Like Neurodegeneration in Nontransgenic Mice. Science 2012, 338, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uemura, N.; Yagi, H.; Uemura, M.T.; Hatanaka, Y.; Yamakado, H.; Takahashi, R. Inoculation of Alpha-Synuclein Preformed Fibrils into the Mouse Gastrointestinal Tract Induces Lewy Body-Like Aggregates in the Brainstem via the Vagus Nerve. Mol. Neurodegener. 2018, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jan, A.; Goncalves, N.P.; Vaegter, C.B.; Jensen, P.H.; Ferreira, N. The Prion-Like Spreading of Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson‘s Disease: Update on Models and Hypotheses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freundt, E.C.; Maynard, N.; Clancy, E.K.; Roy, S.; Bousset, L.; Sourigues, Y.; Covert, M.; Melki, R.; Kirkegaard, K.; Brahic, M. Neuron-to-Neuron Transmission of Alpha-Synuclein Fibrils through Axonal Transport. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamberts, J.T.; Hildebrandt, E.N.; Brundin, P. Spreading of Alpha-Synuclein in the Face of Axonal Transport Deficits in Parkinson’s Disease: A Speculative Synthesis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 77, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Pritzkow, S.; Mendez, N.; Rabadia, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, B.; Schmeichel, A.; Singer, W.; Wu, G.; et al. Discriminating Alpha-Synuclein Strains in Parkinson‘s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy. Nature 2020, 578, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanudjojo, B.; Shaikh, S.S.; Fenyi, A.; Bousset, L.; Agarwal, D.; Marsh, J.; Zois, C.; Heman-Ackah, S.; Fischer, R.; Sims, D.; et al. Phenotypic Manifestation of Alpha-Synuclein Strains Derived from Parkinson‘s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy in Human Dopaminergic Neurons. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Gathagan, R.J.; Covell, D.J.; Medellin, C.; Stieber, A.; Robinson, J.L.; Zhang, B.; Pitkin, R.M.; Olufemi, M.F.; Luk, K.C.; et al. Cellular Milieu Imparts Distinct Pathological Alpha-Synuclein Strains in Alpha-Synucleinopathies. Nature 2018, 557, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Woerman, A.L.; Mordes, D.A.; Watts, J.C.; Rampersaud, R.; Berry, D.B.; Patel, S.; Oehler, A.; Lowe, J.K.; Kravitz, S.N.; et al. Evidence for Alpha-Synuclein Prions Causing Multiple System Atrophy in Humans with Parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5308–E5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, N.; Gram, H.; Sorrentino, Z.A.; Gregersen, E.; Schmidt, S.I.; Reimer, L.; Betzer, C.; Perez-Gozalbo, C.; Beltoja, M.; Nagaraj, M.; et al. Multiple System Atrophy-Associated Oligodendroglial Protein p25alpha Stimulates Formation of Novel Alpha-Synuclein Strain with Enhanced Neurodegenerative Potential. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 142, 87–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avazzadeh, S.; Baena, J.M.; Keighron, C.; Feller-Sanchez, Y.; Quinlan, L.R. Modelling Parkinson’s Disease: iPSCs towards Better Understanding of Human Pathology. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, B.; Feng, J. Modeling Parkinson’s Disease Using Patient-specific Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. J. Parkinson‘s Dis. 2018, 8, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menges, S.; Minakaki, G.; Schaefer, P.M.; Meixner, H.; Prots, I.; Schlotzer-Schrehardt, U.; Friedland, K.; Winner, B.; Outeiro, T.F.; Winklhofer, K.F.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein Prevents the Formation of Spherical Mitochondria and Apoptosis under Oxidative Stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzulli, J.R.; Xu, Y.H.; Sun, Y.; Knight, A.L.; McLean, P.J.; Caldwell, G.A.; Sidransky, E.; Grabowski, G.A.; Krainc, D. Gaucher Disease Glucocerebrosidase and Alpha-Synuclein Form a Bidirectional Pathogenic Loop in Synucleinopathies. Cell 2011, 146, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Havlicek, S.; Kohl, Z.; Mishra, H.K.; Prots, I.; Eberhardt, E.; Denguir, N.; Wend, H.; Plotz, S.; Boyer, L.; Marchetto, M.C.; et al. Gene Dosage-Dependent Rescue of HSP Neurite Defects in SPG4 Patients‘ Neurons. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 2527–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.-Y.; Yoo, G.-S.; Choi, J.-K. Detection of Proteins on Blots Using Direct Blue 71. In The Protein Protocols Handbook, 2nd ed.; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]






| 1st Antibody | Host | Company | Order No. | Dilution | WB/ICC |
| Acet aTub | Mouse | Sigma-Aldrich | T7451 | 1:1000 | WB |
| aSyn (Syn1) | Mouse | BD Biosciences | 610786 | 1:1000 | WB |
| bTubIII | Rabbit | Abcam | ab18207 | 1:1000 | WB |
| bTubIII (TUJ1) | Mouse | BioLegend | 801201 | 1.1000 | WB/ICC |
| DDC | Rabbit | Abcam | ab3905 | 1:500 | WB |
| MJFR-14-6-4-2 | Rabbit | Abcam | ab209538 | 1:1000 | Dot blot |
| Nestin (10C2) | Mouse | EMD Millipore Corp. | MAB5326 | 1:300 | ICC |
| Sox-2 (Y-17) | Goat | Santa Cruz Biotech. | Sc-17320 | 1:300 | ICC |
| Synapsin1 | Mouse | Synaptic Systems | SySy106011 | 1:1000 | WB |
| Tau | Rabbit | Abcam | ab64193 | 1:1000 | WB |
| TH | Rabbit | EMD Millipore Corp. | AB152 | 1:300 | WB/ICC |
| 2nd Antibody | Host | Company | Order No. | Dilution | WB/ICC |
| Goat Alexa-488 | Donkey | Thermo Fisher Sci. | A-11055 | 1:1000 | ICC |
| Mouse Alexa-568 | Donkey | Thermo Fisher Sci. | A10037 | 1:1000 | ICC |
| Mouse Alexa-647 | Donkey | Thermo Fisher Sci. | A-31571 | 1:1000 | ICC |
| Mouse HRP | Goat | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 11-035-146 | 1:20,000 | WB |
| Rabbit Alexa-488 | Donkey | Thermo Fisher Sci. | A21206 | 1:1000 | ICC |
| Rabbit IRDye 800CW | Donkey | LI-COR Biosciences | 926-32214 | 1:10,000 | Dot blot |
| Rabbit HRP | Donkey | Thermo Fisher Sci. | SA1-200 | 1:5000 | WB |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seebauer, L.; Schneider, Y.; Drobny, A.; Plötz, S.; Koudelka, T.; Tholey, A.; Prots, I.; Winner, B.; Zunke, F.; Winkler, J.; et al. Interaction of Alpha Synuclein and Microtubule Organization Is Linked to Impaired Neuritic Integrity in Parkinson’s Patient-Derived Neuronal Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031812
Seebauer L, Schneider Y, Drobny A, Plötz S, Koudelka T, Tholey A, Prots I, Winner B, Zunke F, Winkler J, et al. Interaction of Alpha Synuclein and Microtubule Organization Is Linked to Impaired Neuritic Integrity in Parkinson’s Patient-Derived Neuronal Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(3):1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031812
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeebauer, Lukas, Yanni Schneider, Alice Drobny, Sonja Plötz, Tomas Koudelka, Andreas Tholey, Iryna Prots, Beate Winner, Friederike Zunke, Jürgen Winkler, and et al. 2022. "Interaction of Alpha Synuclein and Microtubule Organization Is Linked to Impaired Neuritic Integrity in Parkinson’s Patient-Derived Neuronal Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 3: 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031812
APA StyleSeebauer, L., Schneider, Y., Drobny, A., Plötz, S., Koudelka, T., Tholey, A., Prots, I., Winner, B., Zunke, F., Winkler, J., & Xiang, W. (2022). Interaction of Alpha Synuclein and Microtubule Organization Is Linked to Impaired Neuritic Integrity in Parkinson’s Patient-Derived Neuronal Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(3), 1812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031812