Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Genes in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci—Stability, Expression, and Genomic Context
Abstract
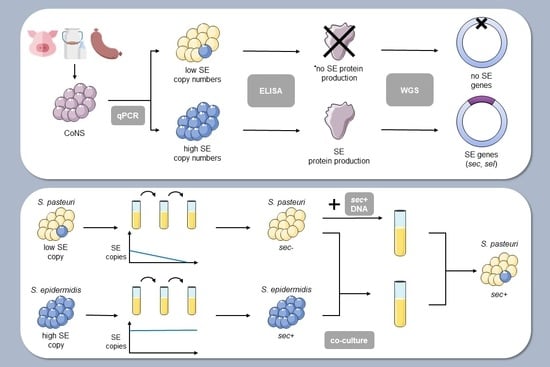
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Enterotoxigenic Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in Food Products and Livestock Animals
2.2. Determination of the Relative Copy Numbers of SE Genes in CoNS Isolates
2.3. Determination of Stability of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Genes
2.4. Mixed Culture of Bacterial Isolates and Incubation of Bacterial Culture with Genomic DNA
2.5. Genome Sequencing and Analysis of Selected Bacterial Isolates
2.6. Production of SEs by CoNS Isolates
3. Discussion
3.1. Origin, Stability, Abundance, and Genomic Context of CoNS Enterotoxin Genes
3.2. Food Safety Hazards and Clinical Relevance of CoNS Enterotoxins
3.3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains’ Isolation and Staphylococcal Species’ Identification
4.2. Genomic DNA Extraction
4.3. PCR Amplification
4.4. Determination of Relative Gene Copy Numbers in the Tested Staphylococcal Isolates
4.5. Determination of Stability of Enterotoxin Genes in CoNS Isolates
4.6. Mixed Culture of Bacterial Isolates and Incubation of Bacterial Culture with Genomic DNA
4.7. Growth Curve Determination and Sandwich ELISA of Selected Bacterial Isolates
4.8. Genome Sequencing and Analysis of Bacterial Isolates
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Argudín, M.Á.; Mendoza, M.C.; Rodicio, M.R. Food Poisoning and Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins. Toxins 2010, 2, 1751–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omori, G.; Kato, Y. A Staphylococcal Food-Poisoning Caused by a Coagulase-Negative Strain. Biken’s J. 1959, 2, 92. [Google Scholar]
- Breckinridge, J.C.; Bergdoll, M.S. Outbreak of Food-Borne Gastroenteritis Due to a Coagulase-Negative Enterotoxin-Producing Staphylococcus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 284, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crass, B.A.; Bergdoll, M.S. Involvement of coagulase-negative staphylococci in toxic shock syndrome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1986, 23, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bautista, L.; Gaya, P.; Medina, M.; Nuñez, M. A quantitative study of enterotoxin production by sheep milk staphylococci. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valle, J.; Vadillo, S.; Piriz, S.; Gomez-Lucia, E. Detection of antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins in the serum and milk of healthy goats. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1991, 76, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroishi, T.; Komine, K.-I.; Kai, K.; Itagaki, M.; Kobayashi, J.; Ohta, M.; Kamata, S.-I.; Kumagai, K. Concentrations and Specific Antibodies to Staphylococcal Enterotoxin-C and Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 in Bovine Mammary Gland Secretions, and Inflammatory Response to the Intramammary Inoculation of These Toxins. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2003, 65, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Cunha, M.D.L.R.D.S.; Calsolari, R.A.O.; Júnior, J.P.A. Detection of Enterotoxin and Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin 1 Genes in Staphylococcus, with Emphasis on Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Microbiol. Immunol. 2007, 51, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Fox, L.K.; Seo, K.S.; McGuire, M.A.; Park, Y.H.; Rurangirwa, F.R.; Sischo, W.M.; Bohach, G.A. Detection of classical and newly described staphylococcal superantigen genes in coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from bovine intramammary infections. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 147, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Freitas Guimarães, F.; Nóbrega, D.; Richini-Pereira, V.; Marson, P.M.; de Figueiredo Pantoja, J.C.; Langoni, H. Enterotoxin genes in coagulase-negative and coagulase-positive staphylococci isolated from bovine milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 2866–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mello, P.L.; Riboli, D.F.M.; Pinheiro, L.; de Almeida Martins, L.; Brito, M.A.V.P.; da Cunha, M.D.L.R.D.S. Detection of Enterotoxigenic Potential and Determination of Clonal Profile in Staphylococcus aureus and Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Bovine Subclinical Mastitis in Different Brazilian States. Toxins 2016, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osman, K.M.; da Silva Pires, Á.; Franco, O.L.; Orabi, A.; Hanafy, M.H.; Marzouk, E.; Hussien, H.; Alzaben, F.A.; Almuzaini, A.M.; Elbehiry, A. Enterotoxigenicity and Antibiotic Resistance of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Raw Buffalo and Cow Milk. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podkowik, M.; Seo, K.S.; Schubert, J.; Tolo, I.; Robinson, D.A.; Bania, J.; Bystroń, J. Genotype and enterotoxigenicity of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolate from ready to eat meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 229, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Novick, R.P. Mobile genetic elements and bacterial toxinoses: The superantigen-encoding pathogenicity islands of Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid 2003, 49, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallent, S.M.; Langston, T.B.; Moran, R.G.; Christie, G.E. Transducing Particles of Staphylococcus aureus Pathogenicity Island SaPI1 Are Comprised of Helper Phage-Encoded Proteins. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 7520–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Úbeda, C.; Maiques, E.; Barry, P.; Matthews, A.; Tormo, M.Á.; Lasa, Í.; Novick, R.P.; Penadés, J.R. SaPI mutations affecting replication and transfer and enabling autonomous replication in the absence of helper phage. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 67, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Novick, R.P. Phage-Mediated Intergeneric Transfer of Toxin Genes. Science 2009, 323, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madhusoodanan, J.; Seo, K.S.; Remortel, B.; Park, J.Y.; Hwang, S.Y.; Fox, L.K.; Park, Y.H.; Deobald, C.F.; Wang, D.; Liu, S.; et al. An Enterotoxin-Bearing Pathogenicity Island in Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naushad, S.; Naqvi, S.A.; Nobrega, D.; Luby, C.; Kastelic, J.P.; Barkema, H.W.; de Buck, J. Comprehensive Virulence Gene Profiling of Bovine Non-aureus Staphylococci Based on Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. mSystems 2019, 4, e00098-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Cao, C.-C.; Feng, M.-Q.; Xu, X.-L.; Zhou, G.-H. Technological and safety characterization of coagulase-negative staphylococci with high protease activity isolated from Traditional Chinese fermented sausages. LWT 2019, 114, 108371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banaszkiewicz, S.; Calland, J.K.; Mourkas, E.; Sheppard, S.K.; Pascoe, B.; Bania, J. Genetic Diversity of Composite Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus epidermidis Pathogenicity Islands. Genome Biol. Evol. 2019, 11, 3498–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argemi, X.; Nanoukon, C.; Affolabi, D.; Keller, D.; Hansmann, Y.; Riegel, P.; Baba-Moussa, L.; Prévost, G. Comparative Genomics and Identification of an Enterotoxin-Bearing Pathogenicity Island, SEPI-1/SECI-1, in Staphylococcus epidermidis Pathogenic Strains. Toxins 2018, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C. BIGSdb: Scalable analysis of bacterial genome variation at the population level. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valle, J.; Gomez-Lucia, E.; Piriz, S.; Goyache, J.; Orden, J.A.; Vadillo, S. Enterotoxin production by staphylococci isolated from healthy goats. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1323–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zell, C.; Resch, M.; Rosenstein, R.; Albrecht, T.; Hertel, C.; Götz, F. Characterization of toxin production of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from food and starter cultures. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 127, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Cunha, M.D.L.R.D.S.; de Souza Rugolo, L.M.S.; de Magalhães Lopes, C.A. Study of virulence factors in coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from newborns. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2006, 101, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rall, V.L.M.; Sforcin, J.M.; de Deus, M.F.R.; de Sousa, D.C.; Camargo, C.H.; Godinho, N.C.; Galindo, L.A.; Soares, T.C.S.; Araújo, J.P. Polymerase Chain Reaction Detection of Enterotoxins Genes in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Brazilian Minas Cheese. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 1121–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holtfreter, S.; Bröker, B.M. Staphylococcal Superantigens: Do They Play a Role in Sepsis? Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2005, 53, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.-L.; Li, S.; Fang, R.; Ono, H.K. Update on molecular diversity and multipathogenicity of staphylococcal superantigen toxins. Anim. Dis. 2021, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argemi, X.; Hansmann, Y.; Prola, K.; Prévost, G. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Pathogenomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabiś, A.; Gonet, M.; Schubert, J.; Miazek, A.; Nowak, M.; Tomaszek, A.; Bania, J. Analysis of enterotoxigenic effect of Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis enterotoxins C and L on mice. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 258, 126979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, A.; Loeffler, A.; Witney, A.; Gould, K.; Lloyd, D.H.; Lindsay, J.A. Extensive Horizontal Gene Transfer during Staphylococcus aureus Co-colonization In Vivo. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 2697–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, J.; Podkowik, M.; Bystroń, J.; Bania, J. Production of staphylococcal enterotoxins in microbial broth and milk by Staphylococcus aureus strains harboring seh gene. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 235, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis, E.; Podkowik, M.; Bystroń, J.; Stefaniak, T.; Bania, J. Temporal Expression of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin H in Comparison with Accessory Gene Regulator–Dependent and –Independent Enterotoxins. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoe, K.; Hu, D.-L.; Ono, H.K.; Shimizu, S.; Takahashi-Omoe, H.; Nakane, A.; Uchiyama, T.; Shinagawa, K.; Imanishi, K. Emetic Potentials of Newly Identified Staphylococcal Enterotoxin-Like Toxins. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 3627–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| No. | Isolate | Species | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 5–8 | S. saprophyticus | smoked meat |
| 2. | WS08.1 | S. xylosus | maturing sausage |
| 3. | 29 | S. epidermidis | jamón ibérico ham |
| 4. | 34 | S. epidermidis | dried sausage with wild boar meat |
| 5. | 34.1.3 | S. pasteuri | dried sausage with wild boar meat |
| 6. | 34.30 | S. pasteuri | dried sausage with wild boar meat |
| 7. | 65.2 | S. epidermidis | dried sausage with wild boar meat |
| 8. | 65.1 | S. pasteuri | dried sausage with wild boar meat |
| 9. | 51.2 | S. saprophyticus | Schwarzwald ham |
| 10. | 54.1 | S. epidermidis | fuet sausage |
| 11. | 70.1 | S. warneri | smoked meat |
| 12. | 72.3 | S. vitulinus | dried sausage |
| 13. | 210.1 | S. epidermidis | swine nasal swab |
| 14. | 210.3 | S. chromogenes | swine nasal swab |
| 15. | 231.4 | S. chromogenes | swine nasal swab |
| 16. | 206D1 | S. epidermidis | raw cow’s milk |
| 17. | 275lp | S. epidermidis | raw cow’s milk |
| 18. | 424C1 | S. epidermidis | raw cow’s milk |
| 19. | 17B | S. borealis | raw cow’s milk |
| 20. | 263D | S. haemolyticus | raw cow’s milk |
| 21. | 325C | S. haemolyticus | raw cow’s milk |
| 22. | 3A | S. borealis | raw cow’s milk |
| 23. | 11D2 | S. borealis | raw cow’s milk |
| 24. | 321C | S. borealis | raw cow’s milk |
| 25. | 424A | S. borealis | raw cow’s milk |
| 26. | 9541D | S. borealis | raw cow’s milk |
| 27. | 41B | S. borealis | raw cow’s milk |
| 28. | 23JK | S. haemolyticus | raw cow’s milk |
| 29. | 18C | S. haemolyticus | raw cow’s milk |
| No. | Species | Number of Isolates | Number of Isolates Containing Enterotoxin Genes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sea | seb | sec | seh | |||
| 1. | S. chromogenes | 2 | - | - | - | 2 |
| 2. | S. epidermidis | 8 | - | - | 3 | 5 |
| 3. | S. haemolyticus | 4 | - | - | - | 4 |
| 4. | S. pasteuri | 3 | - | - | 3 | - |
| 5. | S. saprophyticus | 2 | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| 6. | S. vitulinus | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| 7. | S. warneri | 1 | - | - | - | 1 |
| 8. | S. xylosus | 1 | - | 1 | - | - |
| 9. | S. borealis | 7 | - | - | - | 7 |
| No. | Isolate | Species | Enterotoxin Genes | BLAST Parameters | Sequence Lenght [bp] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Score | Total Score | Query Cover | E Value | % Identity | Accession Number | |||||
| 1. | 5–8 | S. saprophyticus | sea | 640 | 640 | 100% | 1.00 × 10−179 | 100.00% | LR134093.1 | 346 |
| 2. | WS08.1 | S. xylosus | seb | 651 | 651 | 99% | 0.0 | 100.00% | CP039157.1 | 353 |
| 3. | 29 | S. epidermidis | sec | 1480 | 1480 | 100% | 0.0 | 100.00% | CP024437.1 | 812 |
| 4. | 34 | S. epidermidis | 1480 | 1480 | 100% | 0.0 | 100.00% | CP024437.1 | 812 | |
| 5. | 34.1.3 | S. pasteuri | 1480 | 1480 | 100% | 0.1 | 100.00% | CP024437.2 | 812 | |
| 6. | 34.30 | S. pasteuri | 470 | 470 | 99% | 1.00 × 10−128 | 100.00% | LR134088.1 | 255 | |
| 7. | 65.2 | S. epidermidis | 1480 | 1480 | 100% | 0.0 | 100.00% | CP024437.1 | 812 | |
| 8. | 65.1 | S. pasteuri | 390 | 390 | 100% | 9.00 × 10−105 | 100.00% | CP024437.1 | 211 | |
| 9. | 51.2 | S. saprophyticus | seh | 656 | 656 | 99% | 0.0 | 99.72% | AY345144.1 | 359 |
| 10. | 54.1 | S. epidermidis | 656 | 656 | 99% | 0.0 | 99.72% | AY345144.1 | 359 | |
| 11. | 70.1 | S. warneri | ||||||||
| 12. | 72.3 | S. vitulinus | ||||||||
| 13. | 210.1 | S. epidermidis | 662 | 662 | 99% | 0.0 | 100.00% | AY345144.1 | 359 | |
| 14. | 210.3 | S. chromogenes | ||||||||
| 15. | 231.4 | S. chromogenes | ||||||||
| 16. | 206D1 | S. epidermidis | 645 | 645 | 100% | 0.0 | 100.00% | CP034441.1 | 349 | |
| 17. | 275lp | S. epidermidis | ||||||||
| 18. | 424C1 | S. epidermidis | 664 | 664 | 100% | 0.0 | 100.00% | AY345144.1 | 359 | |
| 19. | 17B | S. borealis | 645 | 645 | 100% | 0.0 | 100.00% | AY345144.1 | 349 | |
| 20. | 263D | S. haemolyticus | ||||||||
| 21. | 325C | S. haemolyticus | ||||||||
| 22. | 3A | S. borealis | ||||||||
| 23. | 11D2 | S. borealis | ||||||||
| 24. | 321C | S. borealis | ||||||||
| 25. | 424A | S. borealis | ||||||||
| 26. | 9541D | S. borealis | ||||||||
| 27. | 41B | S. borealis | 658 | 658 | 100% | 0.0 | 99.72% | CP034441.1 | 359 | |
| 28. | 23JK | S. haemolyticus | ||||||||
| 29. | 18C | S. haemolyticus | ||||||||
| Gene | Isolate | Species | Relative Gene Copy Number | SD | Mean Ct | SD (Ct) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sea | 5–8 | S. saprophyticus | 0.0000016059 | 0.0000003 | 30.27 | 0.23 |
| FRI913 | S. aureus | 1 | 0.2348314 | 11.51 | 0.03 | |
| seb | CCM5757 | S. aureus | 1 | 0.1075083 | 17.5 | 0.14 |
| WS08.1 | S. xylosus | 0.0000019868 | 0.0000004 | 33.34 | 0.25 | |
| sec | 34.1.3 | S. pasteuri | 0.0000922401 | 0.0000958 | 27.38 | 1.42 |
| 34.30 | S. pasteuri | n/d | - | n/d | - | |
| 65.1 | S. pasteuri | 0.0001387956 | 0.0001296 | 28.25 | 1.41 | |
| 29 | S. epidermidis | 1 | 0.2141541 | 15.26 | 0.03 | |
| 34 | S. epidermidis | 0.3779972882 | 0.0459499 | 15.93 | 0.17 | |
| 65.2 | S. epidermidis | 0.6169930460 | 0.1108341 | 14.42 | 0.23 | |
| 4S | S. epidermidis | 0.6340004893 | 0.1377956 | 14.36 | 0.26 | |
| FRI913 | S. aureus | 0.5515770501 | 0.0360212 | 17.36 | 0.02 | |
| seh | 11D2 | S. borealis | 0.0000013360 | 0.0000005 | 34.46 | 0.56 |
| 17B | S. borealis | 0.0000016867 | 0.0000006 | 34.87 | 0.51 | |
| 206D1 | S. epidermidis | 0.0000138600 | 0.0000025 | 32.39 | 0.27 | |
| 23JK | S. haemolyticus | n/d | - | n/d | - | |
| 263D | S. haemolyticus | 0.0000002889 | 0.0000001 | 33.21 | 0.37 | |
| 275lp | S. epidermidis | 0.0000106355 | 0.0000016 | 31.40 | 0.17 | |
| 325C | S. haemolyticus | n/d | - | n/d | - | |
| 3A | S. borealis | 0.0000026664 | 0.0000013 | 33.95 | 0.71 | |
| 424A | S. borealis | 0.0000219215 | 0.0000147 | 33.84 | 0.90 | |
| 424C1 | S. epidermidis | 0.0000271405 | 0.0000104 | 32.01 | 0.47 | |
| 51.2 | S. saprophyticus | 0.0009528300 | 0.0003784 | 26.52 | 0.21 | |
| 54.1 | S. epidermidis | 0.0006245173 | 0.0004667 | 28.31 | 1.11 | |
| 70.1 | S. warneri | n/d | - | n/d | - | |
| 72.3 | S. vitulinus | 0.0000873649 | 0.0000553 | 33.45 | 0.86 | |
| 210.1 | S. epidermidis | n/d | - | n/d | - | |
| 210.3 | S. chromogenes | n/d | - | n/d | - | |
| 231.4 | S. chromogenes | n/d | - | n/d | - | |
| 321C | S. borealis | n/d | - | n/d | - | |
| 9541D | S. borealis | n/d | - | n/d | - | |
| 41B | S. borealis | n/d | - | n/d | - | |
| 18C | S. haemolyticus | n/d | - | n/d | - | |
| FRI137 | S. aureus | 1 | 0.1672767 | 13.28 | 0.15 |
| Gene | Isolate | No. of Passage | Relative Gene Copy Number | SD | Mean Ct | SD (Ct) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sea | S. saprophyticus 5–8 | 1 | 0.0000016059 | 0.0000003 | 30.27 | 0.23 |
| 2 | 0.0000062828 | 0.0000009 | 29.09 | 0.05 | ||
| 3 | 0.0000019716 | 0.0000003 | 31.45 | 0.23 | ||
| 4 | 0.0000003002 | 0.0000001 | 34.03 | 0.33 | ||
| 5 | 0.0000004322 | 0.0000001 | 33.78 | 0.49 | ||
| seb | S. xylosus WS08.1 | 1 | 0.0000019868 | 0.0000004 | 33.34 | 0.25 |
| 2 | n/d | - | n/d | - | ||
| sec | S. pasteuri 65.1 | 1 | 0.0000005755 | 0.0000001 | 37.52 | 0.06 |
| 2 | n/d | - | n/d | - | ||
| 3 | 0.0000000322 | 0.0000001 | 37.85 | 1.13 | ||
| 4 | 0.0000001303 | 0.0000001 | 35.88 | 0.37 | ||
| 5 | n/d | - | n/d | - | ||
| S. epidermidis 29 | 1 | 1 | 0.2141541 | 15.26 | 0.03 | |
| 2 | 0.6902912192 | 0.0312809 | 13.11 | 0.03 | ||
| 3 | 0.7780831151 | 0.1391411 | 16.16 | 0.04 | ||
| 4 | 1.0812638900 | 0.1415436 | 11.86 | 0.04 | ||
| 5 | 0.8365744160 | 0.1012565 | 13.22 | 0.18 | ||
| seh | S. epidermidis 275lp | 1 | 0.0000563722 | 0.0000226 | 31.67 | 0.53 |
| 2 | 0.0000061340 | 0.0000063 | 34.87 | 0.85 | ||
| 3 | 0.0000127956 | 0.0000006 | 34.96 | 0.06 | ||
| 4 | 0.0000003596 | 0.0000002 | 35.72 | 0.89 | ||
| 5 | 0.0000028244 | 0.0000015 | 34.33 | 0.71 |
| Days of Culture | Colony Symbol | Relative Gene Copy Number | SD | Mean CT | SD (Ct) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | I 16 | 0.0000001141 | 0.00000003 | 36.31 | 0.38 |
| 5 | I 7 | 0.0000001724 | 0.0000001 | 36.70 | 0.30 |
| I 8 | 0.0000018644 | 0.0000008 | 34.11 | 0 | |
| I 10 | 0.0000002251 | 0.00000002 | 36.93 | 0 | |
| I 13 | n/d | - | n/d | - | |
| II 7 | 0.0000016132 | 0.0000014 | 33.54 | 1.26 | |
| II 8 | 0.0000007944 | 0.0000004 | 33.54 | 0.75 | |
| 8 | I 8 | 0.0000012647 | 0.0000010 | 34.25 | 0 |
| I 9 | 0.0000001023 | 0.00000004 | 35.74 | 0.56 | |
| I 10 | 0.0000002328 | 0.0000002 | 34.90 | 0.11 | |
| II 2 | 0.0000003608 | 0.0000004 | 34.56 | 1.77 | |
| II 7 | 0.0000003394 | 0.00000003 | 34.03 | 0.13 | |
| II 8 | 0.0000001604 | 0.0000002 | 35.58 | 1.46 | |
| II 9 | 0.0000020119 | 0.0000007 | 32.87 | 0.55 |
| Days of Culture | Colony Symbol | Relative Gene Copy Number | SD | Mean CT | SD (Ct) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 0.0000014947 | 0.0000006 | 33.87 | 0.57 |
| 4 | 0.0000043783 | 0.0000020 | 31.78 | 0.71 | |
| 5 | 0.0000079241 | 0.0000047 | 31.25 | 0.80 | |
| 6 | 0.0000023815 | 0.0000002 | 32.64 | 0.06 | |
| 7 | 0.0000011681 | 0.0000009 | 34.04 | 1.16 | |
| 5 | 1 | 0.0000129606 | 0.0000001 | 32.05 | 0.02 |
| 2 | 0.0000412559 | 0.0000029 | 29.56 | 0.11 | |
| 3 | 0.0000063897 | 0.0000041 | 31.71 | 0.99 | |
| 4 | 0.0000037225 | 0.0000009 | 32.51 | 0.36 | |
| 6 | 0.0000046248 | 0.0000006 | 31.86 | 0.07 | |
| 7 | 0.0000077427 | 0.0000026 | 31.18 | 0.35 | |
| 8 | 0.0000066784 | 0.0000007 | 31.55 | 0 | |
| 8 | 1 | 0.0000085114 | 0.0000026 | 32.15 | 0.46 |
| 4 | 0.0000023988 | 0.0000004 | 33.16 | 0.19 |
| No. | Isolate | Species | No. of Contigs | Sequence Length [bp] | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 29 | S. epidermidis | 58 | 2,543,747 | [21] * |
| 2. | 34 | S. epidermidis | 83 | 2,558,976 | [21] * |
| 3. | 65.1 | S. pasteuri | 146 | 2,618,483 | This study |
| 4. | 65.2 | S. epidermidis | 48 | 2,536,954 | [21] * |
| Staphylococcal Enterotoxin | Isolates Tested | Positive Control | Negative Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| SEA | S. saprophyticus 5–8 | S. aureus FRI913 | S. aureus CCM5757 |
| SEB | S. xylosus WS08.1 | S. aureus CCM5757 | - |
| SEC and SEL | S. epidermidis 29 | S. aureus FRI913 | S. aureus CCM5757 |
| S. epidermidis 34 | S. epidermidis 4S | ||
| S. epidermidis 65.2 | |||
| S. pasteuri 65.1 | |||
| SEH | S. saprophyticus 51.2 | S. aureus FRI137 | S. aureus CCM5757 |
| S. epidermidis 54.1 |
| SE | Isolate | Bacterial Growth | SE Concentration [ng/mL] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [log CFU/ml] | |||||
| 6 h | 24 h | 6 h | 24 h | ||
| SEA | S. saprophyticus 5–8 | 4.3 ± 0.3 | 8.8 ± 0.2 | 0 | 0 |
| S. aureus FRI913 | 8.0 ± 0.2 | 8.7 ± 0.3 | 36.7 ± 3.9 | 54.6 ± 9.9 | |
| S. aureus CCM5757 | 9.4 ± 0.3 | 9.2 ± 0.2 | 0 | 0 | |
| SEB | S. xylosus WS08.1 | 8.2 ± 0.2 | 8.7 ± 0.3 | - | - |
| S. aureus CCM5757 | 9.4 ± 0.3 | 9.2 ± 0.2 | + | + | |
| SEC | S. epidermidis 29 | 9.0 ± 0.1 | 9.4 ± 0.3 | 476.1 ± 91.7 | 1180.0 ± 79.6 |
| S. epidermidis 34 | 9.2 ± 0.2 | 9.6 ± 0.1 | 337.7 ± 17.4 | 933.8 ± 65.1 | |
| S. pasteuri 65.1 | 8.0 ± 0.1 | 9.1 ± 0.1 | 0 | 0 | |
| S. epidermidis 65.2 | 9.2 ± 0.2 | 9.5 ± 0.1 | 235.6 ± 29.3 | 1023.7 ± 100.5 | |
| S. epidermidis 4S | 9.3 ± 0.2 | 9.5 ± 0.2 | 881.0 ± 59.9 | 4094.9 ± 559.4 | |
| S. aureus FRI913 | 9.4 ± 0.1 | 9.7 ± 0.2 | 1392.7 ± 90.1 | 2530.9 ± 136.9 | |
| S. aureus CCM5757 | 9.4 ± 0.3 | 9.2 ± 0.2 | 0 | 0 | |
| SEH | S. saprophyticus 51.2 | 4.8 ± 0.1 | 8.9 ± 0.2 | 0 | 0 |
| S. epidermidis 54.1 | 8.7 ± 0.1 | 9.6 ± 0.1 | 0 | 0 | |
| S. aureus FRI137 | 8.6 ± 0.1 | 10.0 ± 0.1 | 418.5 ± 72.8 | 761.0 ± 85.5 | |
| S. aureus CCM5757 | 9.4 ± 0.3 | 9.2 ± 0.2 | 0 | 0 | |
| SEL | S. epidermidis 29 | 9.0 ± 0.1 | 9.4 ± 0.3 | 57.6 ± 24.1 | 222.9 ± 58.8 |
| S. epidermidis 34 | 9.2 ± 0.2 | 9.6 ± 0.1 | 17.9 ± 1.9 | 75.8 ± 17.9 | |
| S. pasteuri 65.1 | 8.0 ± 0.1 | 9.1 ± 0.1 | 0 | 0 | |
| S. epidermidis 65.2 | 9.2 ± 0.2 | 9.5 ± 0.1 | 16.6 ± 0.2 | 20.4 ± 5.9 | |
| S. epidermidis 4S | 9.3 ± 0.2 | 9.5 ± 0.2 | 13.7 ± 2.2 | 44.6 ± 5.2 | |
| S. aureus FRI913 | 9.4 ± 0.1 | 9.7 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 26.8 ± 2.2 | |
| S. aureus CCM5757 | 9.4 ± 0.3 | 9.2 ± 0.2 | 0 | 0 | |
| No. | Strain | Control for Genes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | S. aureus FRI913 | sea, sec, sel |
| 2 | S. aureus CCM5757 | seb |
| 3 | S. aureus FRI1151m | sed |
| 4 | S. aureus FRI137 | seh, nuc, clf |
| 5 | S. epidermidis 4S | sec, sel |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banaszkiewicz, S.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Schubert, J.; Tabiś, A.; Król, J.; Stefaniak, T.; Węsierska, E.; Bania, J. Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Genes in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci—Stability, Expression, and Genomic Context. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052560
Banaszkiewicz S, Wałecka-Zacharska E, Schubert J, Tabiś A, Król J, Stefaniak T, Węsierska E, Bania J. Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Genes in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci—Stability, Expression, and Genomic Context. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(5):2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052560
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanaszkiewicz, Sylwia, Ewa Wałecka-Zacharska, Justyna Schubert, Aleksandra Tabiś, Jarosław Król, Tadeusz Stefaniak, Ewelina Węsierska, and Jacek Bania. 2022. "Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Genes in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci—Stability, Expression, and Genomic Context" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 5: 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052560
APA StyleBanaszkiewicz, S., Wałecka-Zacharska, E., Schubert, J., Tabiś, A., Król, J., Stefaniak, T., Węsierska, E., & Bania, J. (2022). Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Genes in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci—Stability, Expression, and Genomic Context. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(5), 2560. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052560