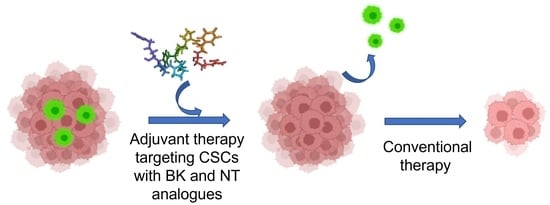
Bradykinin and Neurotensin Analogues as Potential Compounds in Colon Cancer Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Peptides
2.2. Stability Test
2.3. In Vitro Preliminary Studies
2.4. Analysis of CRC Cell Phenotype with Flow Cytometry
2.5. Colonosphere Formation and Quantification
2.6. Analysis of CRC Cell Viability
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptide Synthesis
4.2. Characterization of the Peptides
4.3. Stability Test in Human Plasma
- A.
- TCA procedure for peptides: BK, BK-1, BK-2, BK-5, BK-7, NT, and NT analogues.
- B.
- Formic acid/urea procedure for the peptides: BK-1, BK-2, BK-3, and BK-4.
4.4. Expansions of HCT116 and HT29 Cell Lines
4.5. Cell Treatment
4.6. Analysis of CRC Cell Phenotype with Flow Cytometry
4.7. Cell Death Assay (7AAD)
4.8. Proliferation Assay
4.9. Colonosphere Formation and Quantification
4.10. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and Real-Time PCR Experiments
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the Global Cancer Incidence and Mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN Sources and Methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaroszyńska, Z.; Wiśniewska, K. Epidemiologia Raka Jelita Grubego (C18-C21) w Polsce. J. Educ. Health Sport 2021, 11, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, N.G.; Predes, D.; Moreno, M.M.; Carvalho, I.O.; Mendes, F.A.; Abreu, J.G. Flavonoids and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling: Potential Role in Colorectal Cancer Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12094–12106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Cancer Report 2008. Cancer Research for Cancer Prevention; International Agency for Research on-World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 199, ISBN 9789283204237.
- Manhas, J.; Bhattacharya, A.; Agrawal, S.K.; Gupta, B.; Das, P.; Deo, S.V.S.; Pal, S.; Sen, S. Characterization of Cancer Stem Cells from Different Grades of Human Colorectal Cancer. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 14069–14081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeb-Lundberg, L.M.F.; Marceau, F.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Pettibone, D.J.; Zuraw, B.L. International Union of Pharmacology. XLV. Classification of the Kinin Receptor Family: From Molecular Mechanisms to Pathophysiological Consequences. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 27–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandell, A.G.; Larson, N.; Laxmikanthan, G.; Panos, M.; Blaber, S.I.; Blaber, M.; Scarisbrick, I.A. Protease-Activated Receptor Dependent and Independent Signaling by Kallikreins 1 and 6 in CNS Neuron and Astroglial Cell Lines. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofman, Z.L.M.; Relan, A.; Zeerleder, S.; Drouet, C.; Zuraw, B.; Hack, C.E. Angioedema Attacks in Patients with Hereditary Angioedema: Local Manifestations of a Systemic Activation Process. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nokkari, A.; Abou-El-Hassan, H.; Mechref, Y.; Mondello, S.; Kindy, M.S.; Jaffa, A.A.; Kobeissy, F. Implication of the Kallikrein-Kinin System in Neurological Disorders: Quest for Potential Biomarkers and Mechanisms. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 165, 26–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofman, Z.; de Maat, S.; Hack, C.E.; Maas, C. Bradykinin: Inflammatory Product of the Coagulation System. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 51, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marceau, F.; Bachelard, H.; Bouthillier, J.; Fortin, J.P.; Morissette, G.; Bawolak, M.T.; Charest-Morin, X.; Gera, L. Bradykinin Receptors: Agonists, Antagonists, Expression, Signaling, and Adaptation to Sustained Stimulation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 82, 106305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couture, R.; Harrisson, M.; Vianna, R.M.; Cloutier, F. Kinin Receptors in Pain and Inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 429, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, F.; Bader, M. Kinin B1 Receptors as a Therapeutic Target for Inflammation. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marceau, F.; Sabourin, T.; Houle, S.; Fortin, J.-P.; Petitclerc, E.; Molinaro, G.; Adam, A. Kinin Receptors: Functional Aspects. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2002, 2, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschöpe, C.; Schultheiss, H.-P.; Walther, T. Multiple Interactions between the Renin-Angiotensin and the Kallikrein-Kinin Systems: Role of ACE Inhibition and AT1 Receptor Blockade. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2002, 39, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, F.; Fischetti, F.; Regoli, D.; Durigutto, P.; Frossi, B.; Gobeil, F.J.; Ghebrehiwet, B.; Peerschke, E.I.; Cicardi, M.; Tedesco, F. Novel Pathogenic Mechanism and Therapeutic Approaches to Angioedema Associated with C1 Inhibitor Deficiency. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 1303–1310.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaffa, M.A.; Kobeissy, F.; Al Hariri, M.; Chalhoub, H.; Eid, A.; Ziyadeh, F.N.; Jaffa, A.A. Global Renal Gene Expression Profiling Analysis in B2-Kinin Receptor Null Mice: Impact of Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naffah-Mazzacoratti, M.d.G.; Gouveia, T.L.F.; Simões, P.S.R.; Perosa, S.R. What Have We Learned about the Kallikrein-Kinin and Renin-Angiotensin Systems in Neurological Disorders? World J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 5, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotsch, C.; Biddlecome, G.; Biswas, K.; Chen, J.J.; D’Amico, D.C.; Groneberg, R.D.; Han, N.B.; Hsieh, F.-Y.; Kamassah, A.; Kumar, G.; et al. A New Class of Bradykinin 1 Receptor Antagonists Containing the Piperidine Acetic Acid Tetralin Core. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 2071–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolewski, D.; Prahl, A. Bradykinin Analogues Acylated on Their N-Terminus—Some Recent Development. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 611, 353–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoli, D.; Nsa Allogho, S.; Rizzi, A.; Gobeil, F.J. Bradykinin Receptors and Their Antagonists. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 348, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawidowska, O.; Prahl, A.; Wierzba, T.; Nowakowski, L.; Kowalczyk, W.; Slaninová, J.; Lammek, B. New Acylated Bradykinin Analogues: Effect on Rat Blood Pressure and Rat Uterus. J. Pept. Sci. 2005, 11, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labudda, O.; Wierzba, T.; Sobolewski, D.; Kowalczyk, W.; Sleszyńska, M.; Gawiński, L.; Plackova, M.; Slaninová, J.; Prahl, A. New Bradykinin Analogues Substituted in Positions 7 and 8 with Sterically Restricted 1-Aminocyclopentane-1-Carboxylic Acid. J. Pept. Sci. 2006, 12, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleszyńska, M.; Wierzba, T.H.; Malinowski, K.; Tůmová, T.; Lammek, B.; Slaninová, J.; Prahl, A. Novel Bradykinin Analogues Modified in the N-Terminal Part of the Molecule with a Variety of Acyl Substituents. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2012, 18, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, J.M.; Gera, L.; Chan, D.C.; Bunn, P.A.J.; York, E.J.; Simkeviciene, V.; Helfrich, B. Bradykinin-Related Compounds as New Drugs for Cancer and Inflammation. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2002, 80, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steranka, L.R.; Manning, D.C.; DeHaas, C.J.; Ferkany, J.W.; Borosky, S.A.; Connor, J.R.; Vavrek, R.J.; Stewart, J.M.; Snyder, S.H. Bradykinin as a Pain Mediator: Receptors Are Localized to Sensory Neurons, and Antagonists Have Analgesic Actions. PNAS 1988, 85, 3245–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lammek, B.; Wang, Y.X.; Gavras, I.; Gavras, H. A Novel Bradykinin Antagonist with Improved Properties. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1991, 43, 887–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammek, B.; Wang, Y.X.; Gavras, I.; Gavras, H. A New Highly Potent Antagonist of Bradykinin. Peptides 1990, 11, 1041–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavrek, R.J.; Stewart, J.M. Competitive Antagonists of Bradykinin. Peptides 1985, 6, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proniewicz, E.; Burnat, G.; Domin, H.; Iłowska, E.; Roman, A.; Prahl, A. Spectroscopic Characterization and in vitro Studies of Biological Activity of Bradykinin Derivatives. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.; Gera, L.; Stewart, J.; Helfrich, B.; Verella-Garcia, M.; Johnson, G.; Baron, A.; Yang, J.; Puck, T.; Bunn, P. Bradykinin Antagonist Dimer, CU201, Inhibits the Growth of Human Lung Cancer Cell Lines by a “Biased Agonist” Mechanism. PNAS 2002, 99, 4608–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, D.C.; Gera, L.; Stewart, J.M.; Helfrich, B.; Zhao, T.L.; Feng, W.Y.; Chan, K.K.; Covey, J.M.; Bunn, P.A.J. Bradykinin Antagonist Dimer, CU201, Inhibits the Growth of Human Lung Cancer Cell Lines in vitro and in vivo and Produces Synergistic Growth Inhibition in Combination with Other Antitumor Agents. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Bunn, P.A.J.; Chan, D.; Dienhart, D.G.; Tolley, R.; Tagawa, M.; Jewett, P.B. Neuropeptide Signal Transduction in Lung Cancer: Clinical Implications of Bradykinin Sensitivity and Overall Heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barki-Harrington, L.; Daaka, Y. Bradykinin Induced Mitogenesis of Androgen Independent Prostate Cancer Cells. J. Urol. 2001, 165, 2121–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleczkowska, P.; Lipkowski, A.W. Neurotensin and Neurotensin Receptors: Characteristic, Structure-Activity Relationship and Pain Modulation—A Review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 716, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.F.; Noinaj, N.; Shibata, Y.; Love, J.; Kloss, B.; Xu, F.; Gvozdenovic-jeremic, J.; Shah, P.; Shiloach, J.; Tate, C.G.; et al. Structure of the Agonist-Bound Neurotensin Receptor. Nature 2012, 490, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barber, D.L.; Cacace, A.M.; Raucci, D.T.; Ganz, M.B. Fatty Acids Stereospecifically Stimulate Neurotensin Release and Increase [Ca2+] in Enteric Endocrine Cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 261, G497–G503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, J.; Zaytseva, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.; Rychahou, P.; Jiang, K.; Starr, M.E.; Kim, J.T.; Harris, J.W.; Yiannikouris, F.B.; et al. An Obligatory Role for Neurotensin in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity. Nature 2016, 533, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evers, B.M. Neurotensin and Growth of Normal and Neoplastic Tissues. Peptides 2006, 27, 2424–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafatakis, K.; Triantafyllou, K. Contribution of Neurotensin in the Immune and Neuroendocrine Modulation of Normal and Abnormal Enteric Function. Regul. Pept. 2011, 170, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.T.; Weiss, H.L.; Evers, B.M. Diverse Expression Patterns and Tumorigenic Role of Neurotensin Signaling Components in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boules, M.; Li, Z.; Smith, K.; Fredrickson, P.; Richelson, E. Diverse Roles of Neurotensin Agonists in the Central Nervous System. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, D.; Pothoulakis, C. Effects of NT on Gastrointestinal Motility and Secretion, and Role in Intestinal Inflammation. Peptides 2006, 27, 2434–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rock, S.A.; Jiang, K.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Weiss, H.L.; Wang, C.; Jia, J.; Gao, T.; Evers, B.M. Neurotensin Regulates Proliferation and Stem Cell Function in the Small Intestine in a Nutrient-Dependent Manner. Cmgh 2022, 13, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maoret, J.J.; Anini, Y.; Rouyer-Fessard, C.; Gully, D.; Laburthe, M. Neurotensin and a Non-Peptide Neurotensin Receptor Antagonist Control Human Colon Cancer Cell Growth in Cell Culture and in Cells Xenografted into Nude Mice. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, K.; Evers, B.M.; Izukura, M.; Parekh, D.; Uchida, T.; Townsend, C.M.J.; Thompson, J.C. Neurotensin Stimulates Growth of Colon Cancer. Surg. Oncol. 1992, 1, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugni, J.M.; Rabadi, L.A.; Jubbal, K.; Karagiannides, I.; Lawson, G.; Pothoulakis, C. The Neurotensin Receptor-1 Promotes Tumor Development in a Sporadic but Not an Inflammation-Associated Mouse Model of Colon Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 1798–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Ives, K.L.; Evers, B.M. Curcumin Inhibits Neurotensin-Mediated Interleukin-8 Production and Migration of HCT116 Human Colon Cancer Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5346–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dal Farra, C.; Sarret, P.; Navarro, V.; Botto, J.M.; Mazella, J.; Vincent, J.P. Involvement of the Neurotensin Receptor Subtype NTR3 in the Growth Effect of Neurotensin on Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 92, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, F.; Devader, C.; Lacas-Gervais, S.; Béraud-Dufour, S.; Coppola, T.; Mazella, J. Impairement of HT29 Cancer Cells Cohesion by the Soluble Form of Neurotensin Receptor-3. Genes Cancer 2014, 5, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massa, F.; Devader, C.; Béraud-Dufour, S.; Brau, F.; Coppola, T.; Mazella, J. Focal Adhesion Kinase Dependent Activation of the PI3 Kinase Pathway by the Functional Soluble form of Neurotensin Receptor-3 in HT29 Cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Danielsen, S.A.; Eknæs, M.; Hektoen, M.; Lind, G.E.; Lothe, R.A. Epigenetic and Genetic Features of 24 Colon Cancer Cell Lines. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olejniczak-Kęder, A.; Szaryńska, M.; Wrońska, A.; Siedlecka-Kroplewska, K.; Kmieć, Z. Effects of 5-FU and Anti-EGFR Antibody in Combination with ASA on the Spherical Culture System of HCT116 and HT29 Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 223–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olejniczak, A.; Szaryńska, M.; Kmieć, Z. In vitro Characterization of Spheres Derived from Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petrie, K.A.; Bubser, M.; Casey, C.D.; Davis, M.D.; Roth, B.L.; Deutch, A.Y. The Neurotensin Agonist PD149163 Increases Fos Expression in the Prefrontal Cortex of the Rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 1878–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubuc, I.; Sarret, P.; Labbé-Jullié, C.; Botto, J.M.; Honoré, E.; Bourdel, E.; Martinez, J.; Costentin, J.; Vincent, J.P.; Kitabgi, P.; et al. Identification of the Receptor Subtype Involved in the Analgesic Effect of Neurotensin. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eiselt, E.; Gonzalez, S.; Martin, C.; Chartier, M.; Betti, C.; Longpré, J.M.; Cavelier, F.; Tourwé, D.; Gendron, L.; Ballet, S.; et al. Neurotensin Analogues Containing Cyclic Surrogates of Tyrosine at Position 11 Improve NTS2 Selectivity Leading to Analgesia without Hypotension and Hypothermia. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 4535–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Park, S.-M.; Tumanov, A.V.; Hau, A.; Sawada, K.; Feig, C.; Turner, J.R.; Fu, Y.-X.; Romero, I.L.; Lengyel, E.; et al. CD95 Promotes Tumour Growth. Nature 2010, 465, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Fabrizi, E.; Palio, E.; De Maria, R. Colon Cancer Stem Cells. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 87, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Lombardi, D.G.; Pilozzi, E.; Biffoni, M.; Todaro, M.; Peschle, C.; De Maria, R. Identification and Expansion of Human Colon-Cancer-Initiating Cells. Nature 2007, 445, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szarynska, M.; Olejniczak, A.; Wierzbicki, P.; Kobiela, J.; Laski, D.; Sledzinski, Z.; Adrych, K.; Guzek, M.; Kmiec, Z. FasR and FasL in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Śleszyńska, M.; Kwiatkowska, A.; Sobolewski, D.; Wierzba, T.H.; Katarzyńska, J.; Zabrocki, J.; Borovickova, L.; Slaninová, J.; Prahl, A. New Bradykinin B2 Receptor Antagonists—Influence of C-Terminal Segment Modifications on Their Pharmacological Properties. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2009, 56, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bironaite, D.; Gera, L.; Stewart, J.M. Characterization of the B2 Receptor and Activity of Bradykinin Analogs in SHP-77 Cell Line by Cytosensor Microphysiometer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2004, 150, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, J.; Naran, A.; Misso, N.L.; Thompson, P.J.; Bhoola, K.D. Expression of Tissue and Plasma Kallikreins and Kinin B1 and B2 Receptors in Lung Cancer. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Huang, Y.; Yao, W.; Tao, F.; Chen, Y. Novel Bradykinin Receptor Inhibitors Inhibit Proliferation and Promote the Apoptosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Inhibiting the ERK Pathway. Molecules 2021, 26, 3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubuc, C.; Savard, M.; Bovenzi, V.; Lessard, A.; Côté, J.; Neugebauer, W.; Geha, S.; Chemtob, S.; Gobeil, F.J. Antitumor Activity of Cell-Penetrant Kinin B1 Receptor Antagonists in Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 2851–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Martinez-Fong, D.; Trédaniel, J.; Forgez, P. Neurotensin and Its High Affinity Receptor 1 as a Potential Pharmacological Target in Cancer Therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falciani, C.; Brunetti, J.; Pagliuca, C.; Menichetti, S.; Vitellozzi, L.; Lelli, B.; Pini, A.; Bracci, L. Design and in vitro Evaluation of Branched Peptide Conjugates: Turning Nonspecific Cytotoxic Drugs into Tumor-Selective Agents. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falciani, C.; Lelli, B.; Brunetti, J.; Pileri, S.; Cappelli, A.; Pini, A.; Pagliuca, C.; Ravenni, N.; Bencini, L.; Menichetti, S.; et al. Modular Branched Neurotensin Peptides for Tumor Target Tracing and Receptor-Mediated Therapy: A Proof-of-Concept. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2010, 10, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Chau, J.K.; Perry, N.A.; de Boer, L.; Zaat, S.A.J.; Vogel, H.J. Serum Stabilities of Short Tryptophan- and Arginine-Rich Antimicrobial Peptide Analogs. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Peptide ID | Sequence | MW | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0′ | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
| BK | Arg | Pro | Pro | Gly | Phe | Ser | Pro | Phe | Arg | 1060.66 | ||
| BK-1 | d-Arg | Arg | Pro | Hyp | Gly | Thi | Ser | Apc | Thi | Arg | 1258.59 | |
| BK-2 | d-Arg | Arg | Pro | Hyp | Gly | Thi | Ser | d-Phe | Apc | Arg | 1252.76 | |
| BK-3 | Aaa | d-Arg | Arg | Pro | Hyp | Gly | Thi | Ser | Acc | Thi | Arg | 1448.87 |
| BK-4 | Aaa | d-Arg | Arg | Pro | Hyp | Gly | Thi | Ser | d-Phe | Acc | Arg | 1442.89 |
| BK-5 | d-Arg | Arg | Pro | Hyp | Gly | Thi | Ser | d-Phe | l-Pip | Arg | 1252.65 | |
| BK-6 | Aaa | d-Arg | Arg | Pro | Hyp | Gly | Thi | Ser | d-Pip | l-Pip | Arg | 1428.75 |
| BK-7 | d-Arg | Arg | Pro | Hyp | Gly | Thi | Ser | d-Pip | Thi | Arg | 1258.58 | |
| BK-8 | Aaa | d-Arg | Arg | Pro | Hyp | Gly | Thi | Ser | d-Pip | Thi | Arg | 1434.70 |
| Peptide ID | Sequence | MW | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | ||
| NT | Glu | Leu | Tyr | Glu | Asn | Lys | Pro | Arg | Arg | Pro | Tyr | Ile | Leu | 1690.23 |
| NT-9 | Arg | Arg | Pro | Tyr | Ile | Leu | 817.46 | |||||||
| NT-10 | Arg | Arg | Pro | Ala | Ile | Leu | 725.43 | |||||||
| NT-11 | Arg | Arg | Pro | Tyr | Ala | Leu | 775.41 | |||||||
| NT-12 | Pro | Glu | Gly | Arg | Lys | Pro | Tyr | Tle | Leu | 1072.58 | ||||
| NT-13 | Pro | Glu | Gly | Lys | Arg | Pro | Tyr | Tle | Leu | 1072.58 | ||||
| NT-14 | Pro | Glu | Gly | Lys | Lys | Pro | Tyr | Tle | Leu | 1044.58 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szaryńska, M.; Olejniczak-Kęder, A.; Podpłońska, K.; Prahl, A.; Iłowska, E. Bradykinin and Neurotensin Analogues as Potential Compounds in Colon Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119644
Szaryńska M, Olejniczak-Kęder A, Podpłońska K, Prahl A, Iłowska E. Bradykinin and Neurotensin Analogues as Potential Compounds in Colon Cancer Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(11):9644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119644
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzaryńska, Magdalena, Agata Olejniczak-Kęder, Kamila Podpłońska, Adam Prahl, and Emilia Iłowska. 2023. "Bradykinin and Neurotensin Analogues as Potential Compounds in Colon Cancer Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 11: 9644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119644
APA StyleSzaryńska, M., Olejniczak-Kęder, A., Podpłońska, K., Prahl, A., & Iłowska, E. (2023). Bradykinin and Neurotensin Analogues as Potential Compounds in Colon Cancer Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(11), 9644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119644