PAK1 Is Involved in the Spindle Assembly during the First Meiotic Division in Porcine Oocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Dynamic Distribution and Expression of p-PAK1 during Meiotic Maturation in Porcine Oocytes
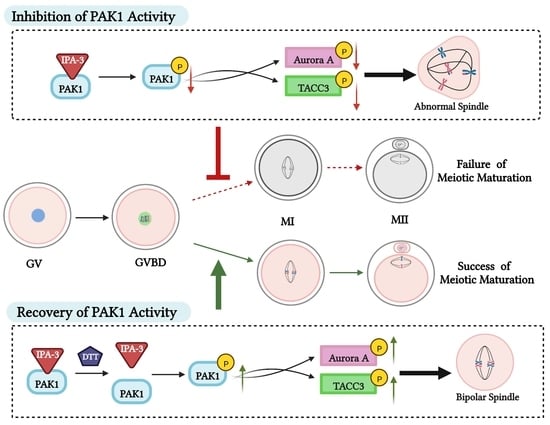
2.2. Inhibition of PAK1 Activity Affected Porcine Oocyte Maturation
2.3. Inhibition of PAK1 Activity Resulted in Disorganized Spindles in Porcine Oocytes
2.4. Dithiothreitol(DTT) Restored Oocytes Maturation and Normal Spindle Formation
2.5. Inhibition of PAK1 Decreased the Activity of Aurora A and TACC3
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antibodies and Chemicals
4.2. Collection and In Vitro Maturation of Oocytes
4.3. Experimental Design
4.3.1. Effects of PAK1 Inhibition on the Meiotic Division of Porcine Oocytes
4.3.2. Effects of DTT on the Meiotic Division of IPA-3 Inhibited Porcine Oocytes
4.4. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.5. Immunoblotting
4.6. Co-Immunoprecipitation
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anjur-Dietrich, M.I.; Kelleher, C.P.; Needleman, D.J. Mechanical mechanisms of chromosome segregation. Cells 2021, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chircop, M. Rho GTPases as regulators of mitosis and cytokinesis in mammalian cells. Small GTPases 2014, 5, e29770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, D.; Pan, D.; Zhen, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; He, Z. Ferulin C triggers potent PAK1 and p21-mediated anti-tumor effects in breast cancer by inhibiting Tubulin polymerization in vitro and in vivo. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvrckova, F.; De Virgilio, C.; Manser, E.; Pringle, J.R.; Nasmyth, K. Ste20-like protein kinases are required for normal localization of cell growth and for cytokinesis in budding yeast. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1817–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, H.; Nicholas, N.S.; Wells, C.M. Role of p-21-activated kinases in cancer progression. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 309, 347–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffer, Z.M.; Chernoff, J. P21-activated kinases: Three more join the PAK. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 34, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernohorska, M.; Sulimenko, V.; Hajkova, Z.; Sulimenko, T.; Sladkova, V.; Vinopal, S.; Draberova, E.; Draber, P. GIT1/βPIX signaling proteins and PAK1 kinase regulate microtubule nucleation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 1282–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.S.; Lim, J.P.; Ng, Y.W.; Lim, L.; Manser, E. The GIT-associated kinase PAK targets to the centrosome and regulates Aurora-A. Mol. Cell 2005, 20, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, J.; Bompard, G.; Rabeharivelo, G.; Cau, J.; Delsert, C.; Morin, N. PAK1 regulates MEC-17 acetyltransferase activity and microtubule acetylation during proplatelet extension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet, S.; Verlhac, M.H. Positioning to get out of meiosis: The asymmetry of division. Hum. Reprod. Update 2011, 17, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pederson, T. The centriole mystique. Trends. Cell Biol. 2020, 30, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihajlovic, A.I.; FitzHarris, G. Segregating chromosomes in the mammalian oocyte. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R895–R907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.-L.; Qi, S.-T.; Sun, S.-C.; Wang, Y.-P.; Schatten, H.; Sun, Q.-Y. PAK1 regulates spindle microtubule organization during oocyte meiotic maturation. Front. Biosci. Elite 2010, 2, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Du, J.; Weng, J.; Ma, W. P21-activated kinase 1 activity is required for histone H3 Ser(10) phosphorylation and chromatin condensation in mouse oocyte meiosis. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2017, 29, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Viveiros, M.M. Error-prone meiotic division and subfertility in mice with oocyte-conditional knockdown of pericentrin. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, W.; Viveiros, M.M. Depletion of pericentrin in mouse oocytes disrupts microtubule organizing center function and meiotic spindle organization. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2014, 81, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.H.; Lee, I.W.; Jo, Y.J.; Kim, N.H.; Namgoong, S. Acentriolar microtubule organization centers and Ran-mediated microtubule formation pathways are both required in porcine oocytes. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2019, 86, 972–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deacon, S.W.; Beeser, A.; Fukui, J.A.; Rennefahrt, U.E.; Myers, C.; Chernoff, J.; Peterson, J.R. An isoform-selective, small-molecule inhibitor targets the autoregulatory mechanism of p21-activated kinase. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pakala, S.B.; Nair, V.S.; Reddy, S.D.; Kumar, R. Signaling-dependent phosphorylation of mitotic centromere-associated kinesin regulates microtubule depolymerization and its centrosomal localization. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40560–40569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabrielli, B.; Chau, Y.Q.; Giles, N.; Harding, A.; Stevens, F.; Beamish, H. Caffeine promotes apoptosis in mitotic spindle checkpoint-arrested cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 6954–6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, K.W.; Leung, J.W.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Feng, L.; Ma, W.; Liu, D.; Songyang, Z.; Chen, J. MTR120/KIAA1383, a novel microtubule-associated protein, promotes microtubule stability and ensures cytokinesis. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittmann, T.; Wilm, M.; Karsenti, E.; Vernos, I. TPX2, A novel Xenopus MAP involved in spindle pole organization. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 149, 1405–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Worth, D.; Prowse, D.M.; Nikolic, M. PAK1 phosphorylation on T212 affects microtubules in cells undergoing mitosis. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vadlamudi, R.K.; Barnes, C.J.; Rayala, S.; Li, F.; Balasenthil, S.; Marcus, S.; Goodson, H.V.; Sahin, A.A.; Kumar, R. P21-activated kinase 1 regulates microtubule dynamics by phosphorylating tubulin cofactor B. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viaud, J.; Peterson, J.R. An allosteric kinase inhibitor binds the p21-activated kinase autoregulatory domain covalently. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Azayzih, A.; Missaoui, W.N.; Cummings, B.S.; Somanath, P.R. Liposome-mediated delivery of the p21 activated kinase-1 (PAK-1) inhibitor IPA-3 limits prostate tumor growth in vivo. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rudolph, J.; Crawford, J.J.; Hoeflich, K.P.; Chernoff, J. p21-activated kinase inhibitors. Enzymes 2013, 34, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.L.; Lam, I.P.; Wong, T.Y.; Lai, W.L.; Liu, H.F.; Yeung, L.L.; Ching, Y.P. IPA-3 inhibits the growth of liver cancer cells by suppressing PAK1 and NF-κB activation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuzelova, K.; Grebenova, D.; Holoubek, A.; Roselova, P.; Obr, A. Group I PAK inhibitor IPA-3 induces cell death and affects cell adhesivity to fibronectin in human hematopoietic cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyano, T.; Lee, J.; Fulka, J., Jr. G2/M transition of pig oocytes: How do oocytes initiate maturation? Reprod. Med. Biol. 2003, 2, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.J.; Choi, C.K.; Lee, C.S.; Park, M.H.; Tian, X.; Kim, N.D.; Lee, K.I.; Choi, J.K.; Ahn, J.H.; Shin, E.Y.; et al. Small molecules that allosterically inhibit p21-activated kinase activity by binding to the regulatory p21-binding domain. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Baumann, C.; De La Fuente, R.; Viveiros, M.M. Loss of acentriolar MTOCs disrupts spindle pole Aurora A and assembly of the liquid-like meiotic spindle domain in oocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2021, 134, jcs256297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabritius, A.S.; Ellefson, M.L.; McNally, F.J. Nuclear and spindle positioning during oocyte meiosis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2011, 23, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drutovic, D.; Duan, X.; Li, R.; Kalab, P.; Solc, P. RanGTP and importin beta regulate meiosis I spindle assembly and function in mouse oocytes. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e101689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, K.; Noetzel, T.L.; Pelletier, L.; Mechtler, K.; Drechsel, D.N.; Schwager, A.; Lee, M.; Raff, J.W.; Hyman, A.A. Aurora A phosphorylation of TACC3/maskin is required for centrosome-dependent microtubule assembly in mitosis. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 170, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeRoy, P.J.; Hunter, J.J.; Hoar, K.M.; Burke, K.E.; Shinde, V.; Ruan, J.; Bowman, D.; Galvin, K.; Ecsedy, J.A. Localization of human TACC3 to mitotic spindles is mediated by phosphorylation on Ser558 by Aurora A: A novel pharmacodynamic method for measuring Aurora A activity. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5362–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgess, S.G.; Peset, I.; Joseph, N.; Cavazza, T.; Vernos, I.; Pfuhl, M.; Gergely, F.; Bayliss, R. Aurora-A-dependent control of TACC3 influences the rate of mitotic spindle assembly. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mori, D.; Yano, Y.; Toyo-oka, K.; Yoshida, N.; Yamada, M.; Muramatsu, M.; Zhang, D.; Saya, H.; Toyoshima, Y.Y.; Kinoshita, K.; et al. NDEL1 phosphorylation by Aurora-A kinase is essential for centrosomal maturation, separation, and TACC3 recruitment. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 352–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asteriti, I.A.; De Mattia, F.; Guarguaglini, G. Cross-talk between AURKA and Plk1 in mitotic entry and spindle assembly. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lieu, A.-S.; Cheng, T.-S.; Chou, C.-H.; Wu, C.-H.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Huang, C.-Y.F.; Chang, L.-K.; Loh, J.-K.; Chang, C.-S.; Hsu, C.-M.; et al. Functional characterization of AIBp, a novel Aurora-A binding protein in centrosome structure and spindle formation. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cotteret, S.; Chernoff, J. Pak GITs to Aurora-A. Dev. Cell 2005, 9, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, S.; Peng, X.; Yang, X.; Sozar, S.; Muneri, C.W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, C.; Cui, P.; Xu, W.; Rui, R. Aurora B inhibitor barasertib prevents meiotic maturation and subsequent embryo development in pig oocytes. Theriogenology 2016, 86, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Hou, Y.; Sun, Q.Y.; Sun, X.F.; Wang, W.H. Localization of centromere proteins and their association with chromosomes and microtubules during meiotic maturation in pig oocytes. Reproduction 2003, 126, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Artham, S.; Alwhaibi, A.; Adil, M.S.; Cummings, B.S.; Somanath, P.R. PAK1 inhibitor IPA-3 mitigates metastatic prostate cancer-induced bone remodeling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 113943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.J.; Shan, M.M.; Wan, X.; Liu, J.C.; Zhang, K.H.; Ju, J.Q.; Xing, C.H.; Sun, S.C. Kinesin KIF15 regulates tubulin acetylation and spindle assembly checkpoint in mouse oocyte meiosis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, L.; He, Y.; Wang, W.; Chu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Rui, R.; Li, Q.; Ju, S. PAK1 Is Involved in the Spindle Assembly during the First Meiotic Division in Porcine Oocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021123
Peng L, He Y, Wang W, Chu Y, Lin Q, Rui R, Li Q, Ju S. PAK1 Is Involved in the Spindle Assembly during the First Meiotic Division in Porcine Oocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(2):1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021123
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Lei, Yijing He, Weihan Wang, Yajie Chu, Qixin Lin, Rong Rui, Qiao Li, and Shiqiang Ju. 2023. "PAK1 Is Involved in the Spindle Assembly during the First Meiotic Division in Porcine Oocytes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 2: 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021123
APA StylePeng, L., He, Y., Wang, W., Chu, Y., Lin, Q., Rui, R., Li, Q., & Ju, S. (2023). PAK1 Is Involved in the Spindle Assembly during the First Meiotic Division in Porcine Oocytes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(2), 1123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24021123