Intracellular Conformation of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis-Causative TDP-43
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
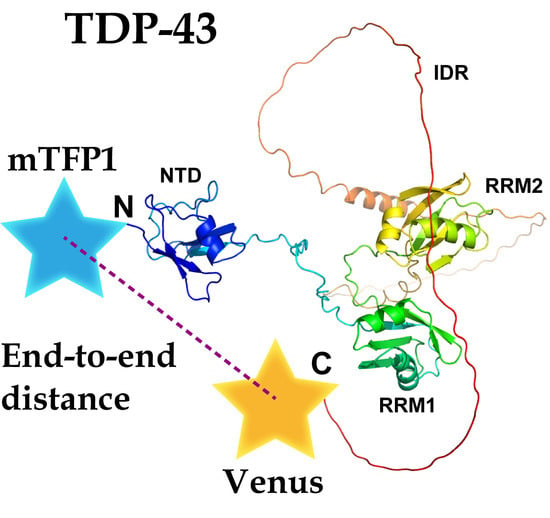
2.1. The End-To-End Distance of TDP-43 between N- and C-Termini Using FRET
2.2. Possible Conformation of ALS-Associated Mutants and Wild Type of TDP-43
2.3. Molecular Shape Estimation of T43V Using Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy
2.4. Diffusion Coefficient of T43V in Live Cells Using Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy
2.5. ALS-Associated Mutants of TDP-43 Strongly Interact with hnRNP A1
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plasmids
3.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
3.3. Confocal Fluorescence Microscopy
3.4. Acceptor Photobleaching FRET
3.5. Protein Structure Analysis
3.6. Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy
3.7. Fluorescence Cross-Correlation Spectroscopy
3.8. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neumann, M.; Sampathu, D.M.; Kwong, L.K.; Truax, A.C.; Micsenyi, M.C.; Chou, T.T.; Bruce, J.; Schuck, T.; Grossman, M.; Clark, C.M.; et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2006, 314, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Chalabi, A.; Jones, A.; Troakes, C.; King, A.; Al-Sarraj, S.; van den Berg, L.H. The genetics and neuropathology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagier-Tourenne, C.; Polymenidou, M.; Cleveland, D.W. TDP-43 and FUS/TLS: Emerging roles in RNA processing and neurodegeneration. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, R46–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Bharathi, V.; Sivalingam, V.; Girdhar, A.; Patel, B.K. Molecular Mechanisms of TDP-43 Misfolding and Pathology in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedharan, J.; Blair, I.P.; Tripathi, V.B.; Hu, X.; Vance, C.; Rogelj, B.; Ackerley, S.; Durnall, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Buratti, E.; et al. TDP-43 mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 2008, 319, 1668–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziortzouda, P.; Van Den Bosch, L.; Hirth, F. Triad of TDP43 control in neurodegeneration: Autoregulation, localization and aggregation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 22, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirulli, E.T.; Lasseigne, B.N.; Petrovski, S.; Sapp, P.C.; Dion, P.A.; Leblond, C.S.; Couthouis, J.; Lu, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Krueger, B.J.; et al. Exome sequencing in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis identifies risk genes and pathways. Science 2015, 347, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deshaies, J.E.; Shkreta, L.; Moszczynski, A.J.; Sidibe, H.; Semmler, S.; Fouillen, A.; Bennett, E.R.; Bekenstein, U.; Destroismaisons, L.; Toutant, J.; et al. TDP-43 regulates the alternative splicing of hnRNP A1 to yield an aggregation-prone variant in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain A J. Neurol. 2018, 141, 1320–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Cruz, S.; Cleveland, D.W. Understanding the role of TDP-43 and FUS/TLS in ALS and beyond. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2011, 21, 904–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polymenidou, M.; Lagier-Tourenne, C.; Hutt, K.R.; Huelga, S.C.; Moran, J.; Liang, T.Y.; Ling, S.C.; Sun, E.; Wancewicz, E.; Mazur, C.; et al. Long pre-mRNA depletion and RNA missplicing contribute to neuronal vulnerability from loss of TDP-43. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tollervey, J.R.; Curk, T.; Rogelj, B.; Briese, M.; Cereda, M.; Kayikci, M.; Konig, J.; Hortobagyi, T.; Nishimura, A.L.; Zupunski, V.; et al. Characterizing the RNA targets and position-dependent splicing regulation by TDP-43. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Babinchak, W.M.; Surewicz, W.K. Cryo-EM structure of amyloid fibrils formed by the entire low complexity domain of TDP-43. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francois-Moutal, L.; Perez-Miller, S.; Scott, D.D.; Miranda, V.G.; Mollasalehi, N.; Khanna, M. Structural Insights Into TDP-43 and Effects of Post-translational Modifications. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, T.; Sato, N.; Ueyama, M.; Fujikake, N.; Sellier, C.; Kanegami, A.; Tokuda, E.; Zamiri, B.; Gall-Duncan, T.; Mirceta, M.; et al. Regulatory Role of RNA Chaperone TDP-43 for RNA Misfolding and Repeat-Associated Translation in SCA31. Neuron 2017, 94, 108–124 e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, A.; Shibasaki, A.; Takeda, K.; Suno, R.; Kinjo, M. Analysis of the substrate recognition state of TDP-43 to single-stranded DNA using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2018, 14, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.L.; Zhao, J.; Yin, X.F.; He, W.T.; Yang, H.; Che, M.X.; Hu, H.Y. Two mutations G335D and Q343R within the amyloidogenic core region of TDP-43 influence its aggregation and inclusion formation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; p. xxvi. 954p. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Baek, I.Y.; Seong, J. Genetically encoded fluorescent biosensors for GPCR research. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1007893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyuk, A.I.; Demidovich, A.D.; Kotova, D.A.; Belousov, V.V.; Bilan, D.S. Circularly Permuted Fluorescent Protein-Based Indicators: History, Principles, and Classification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagai, T.; Yamada, S.; Tominaga, T.; Ichikawa, M.; Miyawaki, A. Expanded dynamic range of fluorescent indicators for Ca(2+) by circularly permuted yellow fluorescent proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10554–10559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, A.; Inada, N.; Kubota, H.; Matsumoto, G.; Kinjo, M.; Morimoto, R.I.; Nagata, K. Dysregulation of the proteasome increases the toxicity of ALS-linked mutant SOD1. Genes Cells Devoted Mol. Cell. Mech. 2014, 19, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.A.; Heinze, K.G.; Schwille, P. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy in living cells. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, A.; Nakayama, Y.; Shibasaki, A.; Taki, A.; Yuno, S.; Takeda, K.; Yahara, M.; Tanabe, N.; Kinjo, M. Interaction of RNA with a C-terminal fragment of the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-associated TDP43 reduces cytotoxicity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, A.; Kinjo, M. State-of-the-Art Fluorescence Fluctuation-Based Spectroscopic Techniques for the Study of Protein Aggregation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bacia, K.; Kim, S.A.; Schwille, P. Fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy in living cells. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasset-Rosa, F.; Lu, S.; Yu, H.; Chen, C.; Melamed, Z.; Guo, L.; Shorter, J.; Da Cruz, S.; Cleveland, D.W. Cytoplasmic TDP-43 De-mixing Independent of Stress Granules Drives Inhibition of Nuclear Import, Loss of Nuclear TDP-43, and Cell Death. Neuron 2019, 102, 339–357 e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Duan, Y.; Duan, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, K.; Deng, X.; Qian, B.; Gu, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, S.; et al. Stress Induces Dynamic, Cytotoxicity-Antagonizing TDP-43 Nuclear Bodies via Paraspeckle LncRNA NEAT1-Mediated Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 443–458 e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evers, T.H.; van Dongen, E.M.; Faesen, A.C.; Meijer, E.W.; Merkx, M. Quantitative understanding of the energy transfer between fluorescent proteins connected via flexible peptide linkers. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 13183–13192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patterson, G.H.; Piston, D.W.; Barisas, B.G. Forster distances between green fluorescent protein pairs. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 284, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukavsky, P.J.; Daujotyte, D.; Tollervey, J.R.; Ule, J.; Stuani, C.; Buratti, E.; Baralle, F.E.; Damberger, F.F.; Allain, F.H. Molecular basis of UG-rich RNA recognition by the human splicing factor TDP-43. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.L.; Xue, W.; Hong, J.Y.; Zhang, J.T.; Li, M.J.; Yu, S.N.; He, J.H.; Hu, H.Y. The N-terminal dimerization is required for TDP-43 splicing activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Conicella, A.E.; Schmidt, H.B.; Martin, E.W.; Rhoads, S.N.; Reeb, A.N.; Nourse, A.; Ramirez Montero, D.; Ryan, V.H.; Rohatgi, R.; et al. A single N-terminal phosphomimic disrupts TDP-43 polymerization, phase separation, and RNA splicing. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e97452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekas, A.; Alattia, J.R.; Nagai, T.; Miyawaki, A.; Ikura, M. Crystal structure of venus, a yellow fluorescent protein with improved maturation and reduced environmental sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 50573–50578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ai, H.W.; Henderson, J.N.; Remington, S.J.; Campbell, R.E. Directed evolution of a monomeric, bright and photostable version of Clavularia cyan fluorescent protein: Structural characterization and applications in fluorescence imaging. Biochem. J. 2006, 400, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asakawa, K.; Handa, H.; Kawakami, K. Optogenetic modulation of TDP-43 oligomerization accelerates ALS-related pathologies in the spinal motor neurons. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, H.B.; Barreau, A.; Rohatgi, R. Phase separation-deficient TDP43 remains functional in splicing. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buratti, E.; Brindisi, A.; Giombi, M.; Tisminetzky, S.; Ayala, Y.M.; Baralle, F.E. TDP-43 binds heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B through its C-terminal tail: An important region for the inhibition of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator exon 9 splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37572–37584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, A.; Fujimoto, A.; Kawashima, R.; Lyu, Y.; Moriya, K.; Kurata, A.; Takahashi, K.; Brielmann, R.; Bott, L.C.; Morimoto, R.I.; et al. Hetero-oligomerization of TDP-43 carboxy-terminal fragments with cellular proteins contributes to proteotoxicity. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, A.; Kubota, H.; Pack, C.G.; Matsumoto, G.; Hirayama, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Kimura, H.; Kinjo, M.; Morimoto, R.I.; Nagata, K. Cytosolic chaperonin prevents polyglutamine toxicity with altering the aggregation state. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Protein | DFast (μm2/s; Mean ± SD) | Fast Components (%; Mean ± SD) | MFCS (kDa) | MTheo (kDa) | DTheo (μm2/s) | Perrin Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eGFP | 91 ± 0.2 | 97 ± 0.3 | - | 27.0 † | - | - |
| 43G | 42 ± 0.3 | 97 ± 0.4 | 270 ⁋ | 72.6 † | 66 * | 1.6 |
| T43V | 30 ± 0.6 | 93 ± 2.2 | 500 ⁋ | 100 † | 52 * | 1.7 |
| Protein | Mutant | DFast (μm2/s; Mean ± SD) | Fast Components (%; Mean ± SD) | DSlow (μm2/s; Mean ± SD) | Slow Components (%; Mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Venus | - | 43 ± 0.5 | 96 ± 0.3 | 0.7 ± 0.07 | 3.8 ± 0.3 |
| T43V | WT | 34 ± 0.5 | 66 ± 0.5 | 0.4 ± 0.01 | 34 ± 0.5 |
| T43V | A315T | 36 ± 0.3 | 63 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.01 | 37 ± 0.3 |
| T43V | Q331K | 37 ± 0.7 | 65 ± 0.5 | 0.4 ± 0.01 | 35 ± 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kitamura, A.; Yuno, S.; Kawamura, R.; Kinjo, M. Intracellular Conformation of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis-Causative TDP-43. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065513
Kitamura A, Yuno S, Kawamura R, Kinjo M. Intracellular Conformation of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis-Causative TDP-43. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065513
Chicago/Turabian StyleKitamura, Akira, Sachiko Yuno, Rintaro Kawamura, and Masataka Kinjo. 2023. "Intracellular Conformation of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis-Causative TDP-43" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065513
APA StyleKitamura, A., Yuno, S., Kawamura, R., & Kinjo, M. (2023). Intracellular Conformation of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis-Causative TDP-43. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065513