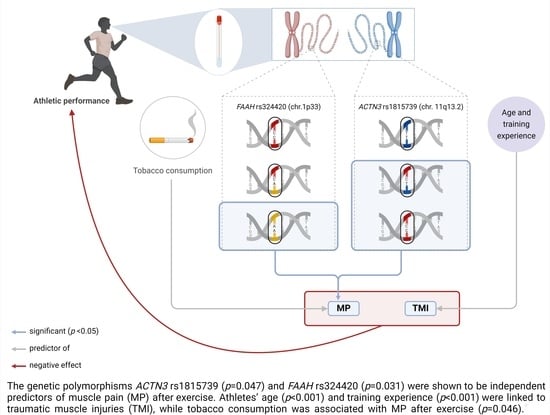
Genetic Variations in Susceptibility to Traumatic Muscle Injuries and Muscle Pain among Brazilian High-Performance Athletes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Study Population
2.2. Distribution of SNP Genotypes
2.3. Associations between the SNPs and the Athletes’ Characteristics
2.4. Associations of the SNPs with TMI and MP after Exercise
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Athlete Recruitment
4.2. SNP Selection
4.3. Sample Collection, Genomic DNA Extraction, and SNP Genotyping
4.4. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ni, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yao, J. Introduction to musculoskeletal system. In Biomechanical Modelling and Simulation on Musculoskeletal System; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Knudson, D. Mechanics of the musculoskeletal system. In Fundamentals of Biomechanics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 55–78. [Google Scholar]
- Søgaard, K.; Sjøgaard, G. Physical activity as cause and cure of muscular pain: Evidence of underlying mechanisms. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2017, 45, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, W. Musculoskeletal pain and its socioeconomic implications. Clin. Rheumatol. 2002, 21, S2–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Graven-Nielsen, T. Basic aspects of musculoskeletal pain: From acute to chronic pain. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2011, 19, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, S. Musculoskeletal structure and physiology. In Canine Sports Medicine and Rehabilitation, 2nd ed.; Zink, C., Van Dyke, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 43–71. [Google Scholar]
- Greising, S.M.; Corona, B.T.; Call, J.A. Musculoskeletal regeneration, rehabilitation, and plasticity following traumatic injury. Int. J. Sports Med. 2020, 41, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, Z.J.; Reumann, M.K.; Gruen, R.L.; Mayer-Kuckuk, P.; Schuetz, M.A.; Harris, I.A.; Gabbe, B.J.; Bhandari, M. Advances and future directions for management of trauma patients with musculoskeletal injuries. Lancet 2012, 380, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimigliano, F.; Resmini, G.; Moretti, A.; Aulicino, M.; Gargiulo, F.; Gimigliano, A.; Liguori, S.; Paoletta, M.; Iolascon, G. Epidemiology of musculoskeletal injuries in adult athletes: A scoping review. Medicina 2021, 57, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goes, R.A.; Lopes, L.R.; Cossich, V.R.A.; de Miranda, V.A.R.; Coelho, O.N.; do Carmo Bastos, R.; Domenis, L.A.M.; Guimarães, J.A.M.; Grangeiro-Neto, J.A.; Perini, J.A. Musculoskeletal injuries in athletes from five modalities: A cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020, 21, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teyhen, D.S.; Shaffer, S.W.; Goffar, S.L.; Kiesel, K.; Butler, R.J.; Rhon, D.I.; Plisky, P.J. Identification of risk factors prospectively associated with musculoskeletal injury in a warrior athlete population. Sports Health 2020, 12, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisman, P.J.; de la Motte, S.J.; Gribbin, T.C.; Jaffin, D.P.; Murphy, K.; Deuster, P.A. A Systematic Review of the Association between Physical Fitness and Musculoskeletal Injury Risk: Part 1-Cardiorespiratory Endurance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 1744–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yard, E.E.; Schroeder, M.J.; Fields, S.K.; Collins, C.L.; Comstock, R.D. The epidemiology of United States high school soccer injuries 2005–2007. Am. J. Sports Med. 2008, 36, 1930–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromley, S.J.; Drew, M.K.; Talpey, S.; McIntosh, A.S.; Finch, C.F. A systematic review of prospective epidemiological research into injury and illness in Olympic combat sport. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toohey, L.A.; Drew, M.K.; Finch, C.F.; Cook, J.L.; Fortington, L.V. A 2-Year Prospective Study of Injury Epidemiology in Elite Australian Rugby Sevens: Exploration of Incidence Rates, Severity, Injury Type, and Subsequent Injury in Men and Women. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.-H.; Silva, M.; Cerqueira, F.; Tavares, V.; Medeiros, R. Genomic profile in association with sport-type, sex, ethnicity, psychological traits and sport injuries of elite athletes. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2021, 62, 418–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornett, E.M.; Carroll Turpin, M.A.; Pinner, A.; Thakur, P.; Sekaran, T.S.G.; Siddaiah, H.; Rivas, J.; Yates, A.; Huang, G.J.; Senthil, A. Pharmacogenomics of pain management: The impact of specific biological polymorphisms on drugs and metabolism. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogan, M.; Aslan, B.T.; Ulucan, K. Comparison of potential biomarker, ACTN3 rs1815739 polymorphism, for athletic performance of Turkish athletes. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2022, 68, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digre, A.; Lindskog, C. The human protein atlas—Spatial localization of the human proteome in health and disease. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, C.; Kiely, J. ACTN3: More than just a gene for speed. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongdem, J.T.; Helegbe, G.K.; Opare-Asamoah, K.; Wezena, C.A.; Ocloo, A. Assessment of NSAIDs as potential inhibitors of the fatty acid amide hydrolase I (FAAH-1) using three different primary fatty acid amide substrates in vitro. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 23, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.-H.; Tavares, V.; Silva, M.-R.G.; Neto, B.V.; Cerqueira, F.; Medeiros, R. FAAH rs324420 Polymorphism Is Associated with Performance in Elite Rink-Hockey Players. Biology 2022, 11, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.-H.; Tavares, V.; Silva, M.-R.G.; Neto, B.V.; Cerqueira, F.; Medeiros, R. Association of FAAH rs324420 (C385A) Polymorphism with High-Level Performance in Volleyball Players. Genes 2023, 14, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, H.-H.; Tavares, V.; Neto, B.V.; Cerqueira, F.; Medeiros, R.; Silva, M.-R.G. FAAH rs324420 Polymorphism: Biological Pathways, Impact on Elite Athletic Performance and Insights for Sport Medicine. Genes 2023, 14, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Handschin, C.; Spiegelman, B.M. Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription coactivators. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, K.L.; Achuthan, P.; Allen, J.; Allen, J.; Alvarez-Jarreta, J.; Amode, M.R.; Armean, I.M.; Azov, A.G.; Bennett, R.; Bhai, J. Ensembl 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D884–D891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharabenjasin, P.; Pabalan, N.; Jarjanazi, H. Association of PPARGC1A Gly428Ser (rs8192678) polymorphism with potential for athletic ability and sports performance: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0200967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Mittal, D.; Iadarola, M.; Dionne, R. Genetic predictors for acute experimental cold and heat pain sensitivity in humans. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsianos, G.I.; Evangelou, E.; Boot, A.; Carola Zillikens, M.; van Meurs, J.B.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Ioannidis, J.P. Associations of polymorphisms of eight muscle-or metabolism-related genes with performance in Mount Olympus marathon runners. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhmetov, I.; Popov, D.; Mozhaĭskaia, I.; Missina, S.; Astratenkova, I.; Vinogradova, O.; Rogozkin, V. Association of regulatory genes polymorphisms with aerobic and anaerobic performance of athletes. Ross. Fiziol. Zhurnal Im. IM Sechenova 2007, 93, 837–843. [Google Scholar]
- Sessa, F.; Chetta, M.; Petito, A.; Franzetti, M.; Bafunno, V.; Pisanelli, D.; Sarno, M.; Iuso, S.; Margaglione, M. Gene polymorphisms and sport attitude in Italian athletes. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2011, 15, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, H.; Miller, B.; Kim, S.-J.; Leelaprachakul, N.; Kikuchi, N.; Yen, K.; Cohen, P. Novel Insights into Mitochondrial DNA: Mitochondrial Microproteins and mtDNA Variants Modulate Athletic Performance and Age-Related Diseases. Genes 2023, 14, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varley, I.; Hughes, D.C.; Greeves, J.P.; Stellingwerff, T.; Ranson, C.; Fraser, W.D.; Sale, C. The association of novel polymorphisms with stress fracture injury in Elite Athletes: Further insights from the SFEA cohort. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2018, 21, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, S.D.; Di Pietro, G.; Fuchshuber-Moraes, M.; Genro, J.P.; Hutz, M.H.; Kehdy, F.d.S.G.; Kohlrausch, F.; Magno, L.A.V.; Montenegro, R.C.; Moraes, M.O. The genomic ancestry of individuals from different geographical regions of Brazil is more uniform than expected. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.; Nelson-Filho, P.; Marañón-Vásquez, G.A.; de Carvalho Ramos, A.G.; Dantas, B.; Sebastiani, A.M.; Silvério, F.; Omori, M.A.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Teixeira, E.C. Genetic variants in ACTN3 and MYO1H are associated with sagittal and vertical craniofacial skeletal patterns. Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 97, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.J.d.M.; Genelhu, V.; Pimentel, M.M.G.; Celoria, B.M.J.; Mangia, R.F.; Aveta, T.; Silvestri, C.; Di Marzo, V.; Francischetti, E.A. Circulating endocannabinoids and the polymorphism 385C> A in fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) gene may identify the obesity phenotype related to cardiometabolic risk: A study conducted in a Brazilian population of complex interethnic admixture. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Queiroz, E.M.; Cândido, A.P.C.; Castro, I.d.M.; Bastos, A.Q.A.; Machado-Coelho, G.; Freitas, R.N.d. IGF2, LEPR, POMC, PPARG, and PPARGC1 gene variants are associated with obesity-related risk phenotypes in Brazilian children and adolescents. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2015, 48, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, K.; Rosado, E.L.; da Fonseca, A.C.P.; Belfort, G.P.; da Silva, L.B.G.; Ribeiro-Alves, M.; Zembrzuski, V.M.; Martínez, J.A.; Saunders, C. FTO and ADRB2 Genetic Polymorphisms Are Risk Factors for Earlier Excessive Gestational Weight Gain in Pregnant Women with Pregestational Diabetes Mellitus: Results of a Randomized Nutrigenetic Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, T.M.; Rocha, A.V.; Lacchini, R.; Marques, C.R.; Silva, E.S.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Rios-Santos, F. Association of polymorphisms of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) gene with the risk of primary open angle glaucoma in a Brazilian population. Gene 2012, 502, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, R.S.; Silva, C.S.; Cavalcante, G.C.; de Queiroz, N.N.; Felício, K.M.; Felício, J.S.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, Â. Variants in the VDR Gene May Influence 25 (OH) D Levels in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in a Brazilian Population. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, M.; Vanni, D.; Pantalone, A.; Salini, V. Cigarette smoking and musculoskeletal disorders. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2013, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, K.T.; Syddall, H.; Cooper, C.; Coggon, D. Smoking and musculoskeletal disorders: Findings from a British national survey. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, A.C.; Young, P.W. The actinin family of actin cross-linking proteins–a genetic perspective. Cell Biosci. 2015, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; MacArthur, D.G.; Gulbin, J.P.; Hahn, A.G.; Beggs, A.H.; Easteal, S.; North, K. ACTN3 genotype is associated with human elite athletic performance. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 73, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.X.; Houweling, P.J.; North, K.N.; Quinlan, K.G. How does α-actinin-3 deficiency alter muscle function? Mechanistic insights into ACTN3, the ‘gene for speed’. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, B.; De Bock, K.; Ramaekers, M.; Van den Eede, E.; Van Leemputte, M.; Hespel, P.; Thomis, M.A. ACTN3 (R577X) genotype is associated with fiber type distribution. Physiol. Genom. 2007, 32, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacArthur, D.G.; North, K.N. A gene for speed? The evolution and function of α-actinin-3. Bioessays 2004, 26, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, N.; Gotoda, Y.; Hatakeyama, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Miyatake, Y.; Kuroda, M.; Masumoto, S.; Tsutsumi, R.; Nakaya, Y.; Sakaue, H. Differential regulation of Actn2 and Actn3 expression during unfolded protein response in C2C12 myotubes. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2020, 41, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Coso, J.; Rodas, G.; Buil, M.Á.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J.; López, P.; González-Ródenas, J.; Gasulla-Anglés, P.; López-Samanes, Á.; Hernández-Sánchez, S.; Iztueta, A. Association of the ACTN3 rs1815739 Polymorphism with Physical Performance and Injury Incidence in Professional Women Football Players. Genes 2022, 13, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, B.; Bulgay, C.; Ceylan, H.İ.; Öztürk, M.E.; Öztürk, D.; Kazan, H.H.; Ergun, M.A.; Cerit, M.; Semenova, E.A.; Larin, A.K. Association of ACTN3 R577X Polymorphism with Elite Basketball Player Status and Training Responses. Genes 2023, 14, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Coso, J.; Hiam, D.; Houweling, P.; Pérez, L.M.; Eynon, N.; Lucía, A. More than a ‘speed gene’: ACTN3 R577X genotype, trainability, muscle damage, and the risk for injuries. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massidda, M.; Voisin, S.; Culigioni, C.; Piras, F.; Cugia, P.; Yan, X.; Eynon, N.; Calò, C.M. ACTN3 R577X polymorphism is associated with the incidence and severity of injuries in professional football players. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2019, 29, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Coso, J.; Valero, M.; Salinero, J.J.; Lara, B.; Díaz, G.; Gallo-Salazar, C.; Ruiz-Vicente, D.; Areces, F.; Puente, C.; Carril, J.C. ACTN3 genotype influences exercise-induced muscle damage during a marathon competition. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peplonska, B.; Safranow, K.; Adamczyk, J.; Boguszewski, D.; Szymański, K.; Soltyszewski, I.; Barczak, A.; Siewierski, M.; Ploski, R.; Sozanski, H. Association of serotoninergic pathway gene variants with elite athletic status in the Polish population. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, B.; Marsicano, G.; Maldonado, R.; Hillard, C.J. The endocannabinoid system in guarding against fear, anxiety and stress. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slivicki, R.A.; Saberi, S.A.; Iyer, V.; Vemuri, V.K.; Makriyannis, A.; Hohmann, A.G. Brain-permeant and-impermeant inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase synergize with the opioid analgesic morphine to suppress chemotherapy-induced neuropathic nociception without enhancing effects of morphine on gastrointestinal transit. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2018, 367, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwosu, B.U.; Kum-Nji, P. Tobacco smoke exposure is an independent predictor of vitamin D deficiency in US children. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Ni, J. The association between tobacco smoke exposure and vitamin D levels among US general population, 2001–2014: Temporal variation and inequalities in population susceptibility. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 32773–32787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küchler, E.C.; Tannure, P.N.; Falagan-Lotsch, P.; Lopes, T.S.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Amorim, L.M.F. Buccal cells DNA extraction to obtain high quality human genomic DNA suitable for polymorphism genotyping by PCR-RFLP and Real-Time PCR. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2012, 20, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assis, J.; Pereira, D.; Gomes, M.; Marques, D.; Marques, I.; Nogueira, A.; Catarino, R.; Medeiros, R. Influence of CYP3A4 genotypes in the outcome of serous ovarian cancer patients treated with first-line chemotherapy: Implication of a CYP3A4 activity profile. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 6, 552. [Google Scholar]

| Characteristics | Athletes | χ2 p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| With TMI (N = 172) N (%) | Without TMI (N = 173) N (%) | Total (N = 345) N (%) | ||
| Age (years) * | 25.5 ± 5.9 | 22.4 ± 4.5 | 23.9 ± 5.4 | <0.001 |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 49 (28.5) | 59 (34.1) | 108 (31.3) | 0.261 |
| Male | 123 (71.5) | 114 (65.9) | 237 (68.7) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) * | 24.8 ± 3.5 | 24.4 ± 3.4 | 24.6 ± 3.4 | 0.294 |
| Tobacco consumption ** | 11 (6.4) | 8 (4.6) | 19 (5.5) | 0.471 |
| Alcohol consumption ** | 98 (57.0) | 97 (56.1) | 195 (56.5) | 0.865 |
| Age at sports practice initiation (years) | 13.4 ± 6.5 | 14.3 ± 6.0 | 13.8 ± 6.2 | 0.190 |
| Training experience (years)* | 11.2 ± 6.6 | 8.1 ± 5.7 | 9.7 ± 6.4 | <0.001 |
| Training frequency (hours/week) * | 13.5 ± 9.0 | 12.4 ± 6.6 | 13.0 ± 7.9 | 0.214 |
| Level of sports competition | ||||
| School/university | 19 (11.0) | 25 (14.5) | 44 (12.8) | 0.343 |
| Professional | 153 (89.0) | 148 (85.5) | 301 (87.2) | |
| MP after exercise | 87 (50.6) | 53 (30.6) | 140 (40.6) | <0.001 |
| Polymorphism Genotype | Study Population a | Previous Studies with Brazilian Population | χ2 p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype Frequency | Failed Genotyping | MAF (MA) | Genotype Frequency | MAF (MA) | Reference b | ||
| ACTN3 rs1815739 | |||||||
| TT | 56 (16.2) | 1 (0.3) | 40.9 (T) | 120 (19.9) | 41.9 (T) | [35] | 0.313 |
| CT | 165 (47.8) | 265 (44.0) | |||||
| CC | 123 (35.7) | 217 (36.0) | |||||
| FAAH rs324420 | |||||||
| AA | 31 (9.0) | 1 (0.3) | 26.9 (A) | 14 (7.0) | 25.0 (A) | [36] | 0.708 |
| AC | 123 (35.7) | 72 (36.0) | |||||
| CC | 190 (55.1) | 114 (57.0) | |||||
| PPARGC1A rs8192678 | |||||||
| TT | 31 (9.0) | 2 (0.6) | 27.1 (T) | 15 (6.0) | 25.1 (T) | [37] | 0.409 |
| CT | 124 (35.9) | 94 (38.1) | |||||
| CC | 188 (54.5) | 138 (55.9) | |||||
| ADRB2 rs1042713 | |||||||
| AA | 69 (20.0) | 3 (0.9) | 43.4 (A) | 8 (11.4) | 37.9 (A) | [38] | 0.226 |
| AG | 159 (46.1) | 37 (52.9) | |||||
| GG | 114 (33.0) | 25 (35.7) | |||||
| NOS3 rs1799983 | |||||||
| TT | 28 (8.1) | 1 (0.3) | 26.9 (T) | 13 (6.1) | 23.0 (T) | [39] | 0.414 |
| GT | 129 (37.4) | 73 (34.3) | |||||
| GG | 187 (54.2) | 127 (59.6) | |||||
| VDR rs731236 | |||||||
| GG | 36 (10.4) | 1 (0.3) | 34.7 (G) | 12 (8.1) | 29.7 (G) | [40] | 0.271 |
| AG | 167 (48.4) | 64 (43.2) | |||||
| AA | 141 (40.9) | 72 (48.6) | |||||
| Variable | Adjusted OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age (≥23 vs. <23 years 1) * | 0.93 | (0.60–1.45) | 0.756 |
| Sex (male vs. female 1) | 0.94 | (0.58–1.50) | 0.779 |
| Tobacco consumption (yes vs. no 1) | 2.74 | (1.04–7.27) | 0.042 |
| ACTN3 rs1815739 (CC/CT vs. TT 1) | 1.90 | (1.01–3.57) | 0.047 |
| Variable | Adjusted OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Age (≥23 vs. <23 years 1) * | 0.95 | (0.61–1.47) | 0.804 |
| Sex (male vs. female 1) | 0.92 | (0.57–1.48) | 0.729 |
| Tobacco consumption (yes vs. no 1) | 2.82 | (1.07–7.45) | 0.037 |
| FAAH rs324420 (AA vs. AC/CC 1) | 2.30 | (1.08–4.91) | 0.031 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marques, I.S.; Tavares, V.; Vieira Neto, B.; Lopes, L.R.; Goes, R.A.; Guimarães, J.A.M.; Perini, J.A.; Medeiros, R. Genetic Variations in Susceptibility to Traumatic Muscle Injuries and Muscle Pain among Brazilian High-Performance Athletes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063300
Marques IS, Tavares V, Vieira Neto B, Lopes LR, Goes RA, Guimarães JAM, Perini JA, Medeiros R. Genetic Variations in Susceptibility to Traumatic Muscle Injuries and Muscle Pain among Brazilian High-Performance Athletes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(6):3300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063300
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarques, Inês Soares, Valéria Tavares, Beatriz Vieira Neto, Lucas Rafael Lopes, Rodrigo Araújo Goes, João António Matheus Guimarães, Jamila Alessandra Perini, and Rui Medeiros. 2024. "Genetic Variations in Susceptibility to Traumatic Muscle Injuries and Muscle Pain among Brazilian High-Performance Athletes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 6: 3300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063300
APA StyleMarques, I. S., Tavares, V., Vieira Neto, B., Lopes, L. R., Goes, R. A., Guimarães, J. A. M., Perini, J. A., & Medeiros, R. (2024). Genetic Variations in Susceptibility to Traumatic Muscle Injuries and Muscle Pain among Brazilian High-Performance Athletes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(6), 3300. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25063300