On the Diversity of Phyllodocida (Annelida: Errantia), with a Focus on Glyceridae, Goniadidae, Nephtyidae, Polynoidae, Sphaerodoridae, Syllidae, and the Holoplanktonic Families
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Species List
2.2. Occurrence Records
2.3. Biogeographic Distribution
2.4. Non-Indigenous Species
2.5. Data Mining and BOLD Dataset Creation
2.6. Data Processing and Analyses
2.7. Analyses at the Family Level
3. Results and Discussion
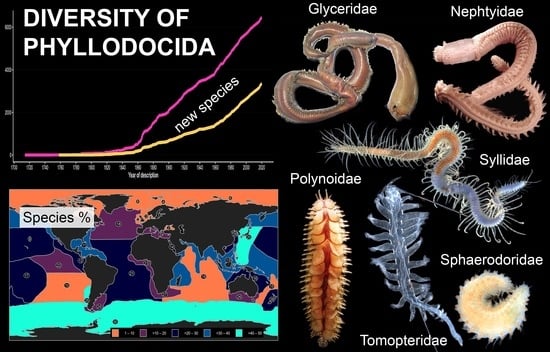
3.1. Species Diversity Trends among Phyllodocida
3.1.1. Biogeographic Distribution Patterns
3.1.2. Global Gap-Analysis
3.2. Selected Taxa
3.2.1. Glyceriformia
3.2.2. Holoplanktonic Taxa
Alciopini
Iospilidae
Lopadorrhynchidae
Pontodoridae
Tomopteridae
Typhloscolecidae
Yndolaciidae
3.2.3. Nephtyidae
3.2.4. Polynoidae
3.2.5. Sphaerodoridae
3.2.6. Syllidae
4. Conclusions
- The highest numbers of species of Phyllodocida have been reported from European, North American, and Australian waters, although these numbers are biased by an increased sampling effort in these regions and do not reflect true species richness. DNA barcode data show similar patterns, but also similar bias.
- At the family level, the highest number of distribution records are for Nephtyidae, Phyllodocidae, Syllidae, Nereididae, and Polynoidae and widest distribution ranges were for Phyllodocidae, Polynoidae, Nereididae, Syllidae, and Lopadorrhynchidae.
- Overall, there is a weak latitudinal gradient in species richness, with a rather uniformly high diversity across tropical and temperate latitudes and a drop only in extreme latitudes.
- Antarctic and Pacific coasts of America and Asia, together with the circumtropical areas worldwide show the highest level of endemism, while the lowest numbers occur in temperate Atlantic areas and in the Arctic Ocean.
- Most records of Phyllodocida and the highest species number and barcode data come from the high subtidal, where Nereididae, Syllidae, and Nephtyidae dominate. However, members of Phyllodocida seems to be well adapted to deep waters, particularly polynoids.
- Less than 3% of the known species have been reported as occurring non-natively in certain parts of the world, most of them in Mediterranean waters, and more than half belong to Nereididae and Syllidae. However, many “non-native” or “introduced” species, particularly those belonging to critic species-complexes, turned to be native species with locally restricted populations when carefully examined. None of them has been considered as invasive or as pest to date.
- There is a still unknown number of possible cryptic species complexes, this being a recurrent trend in most examined families.
- Most examined families except to some extent Glyceridae and Goniadidae, show no traces of stabilization of the accumulative curve of species description, indicating that more new species are expected to be described in the coming years. Sources of new species diversity are mainly related with cryptic species complexes, but also with sampling in poorly explored regions and environments, with the deep-sea being particularly promising.
- Only 620 species of Phyllodocida have sequences published in BOLD, for 1215 BINS as a consequence of having sequences (1) assigned to higher taxonomic ranks (genus or family), and (2) with wrong taxonomy assignments, the latter representing 22% and including sequences either misidentified and/or with invalid, misspelled, or synonymized names.
- Our analyses show the key importance of keeping barcode libraries adequately curated, together with the need of adding metadata, while highlighting the apparent difficulty of having molecular data with correct identifications among Phyllodocida, with less than 60% of the records being usable at the species-level in statistical analysis.
- Despite the amount of knowledge on the systematics of Phyllodocida, we would like to stress that there are still many open questions regarding the correct phylogenetic placement of most taxa (at different levels) so that further efforts must be dedicated to collecting new materials, allowing precise morphological descriptions in parallel with sequences.
- We would like to highlight that there is a similar lack of knowledge with respect to the ecology of most species of Phyllodocida, as well as on their functional role in marine ecosystems all over the world oceans.
- Taking into account that we are entering in the 2020s Oceans Decade, during which marine ecosystems have to be re-evaluated from many different points of view (from basic science to sustainable ecosystem services and derived benefits), having a real and accurate picture of the world oceans emerges as a strategic pillar, with the knowledge on the diversity they hold being keystone.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dales, R.P. The polychaete stomodeum and the inter-relationships of the families of Polychaeta. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1962, 139, 389–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, G.W.; Fauchald, K. Cladistics and polychaetes. Zool. Scr. 1997, 26, 139–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, G.W.; Pleijel, F. Polychaetes; Oxford University Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Weigert, A.; Bleidorn, C. Current status of annelid phylogeny. Org. Divers. Evol. 2016, 16, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struck, T.H.; Paul, C.; Hill, N.; Hartmann, S.; Hosel, C.; Kube, M.; Lieb, B.; Meyer, A.; Tiedemann, R.; Purschke, G.; et al. Phylogenomic analyses unravel annelid evolution. Nature 2011, 471, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, G.; Fauchald, K. World Polychaeta Database. 2020. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org/polychaeta (accessed on 6 September 2020).
- Parry, L.; Tanner, A.; Vinther, J. The origin of annelids. Palaeontology 2014, 57, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, U.C.; Briggs, D.E. A pyritized polychaete from the Devonian of Ontario. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, B.C.; Martínez, A.; Borda, E.; Iliffe, T.M.; Eibye-Jacobsen, D.; Worsaae, K. Phylogeny and systematics of Aphroditiformia. Cladistics 2018, 34, 225–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parapar, J.; Caramelo, C.; Candás, M.; Cunha-Veira, X.; Moreira, J. An integrative approach to the anatomy of Syllis gracilis Grube, 1840 (Annelida) using micro-computed X-ray tomography. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watson, C.; Faulwetter, S. Stylet jaws of Chrysopetalidae (Annelida). J. Nat. Hist. 2017, 51, 2863–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumars, P.A.; Dorgan, K.M.; Lindsay, S.M. Diet of worms emended: An update of polychaete feeding guilds. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 497–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Zhan, Z.; Xu, K. Two new and two rarely known species of Branchinotogluma (Annelida: Polynoidae) from deep-sea hydrothermal vents of the Manus Back-Arc basin, with remarks on the diversity and biogeography of vent polynoids. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2019, 149, 103051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Qiu, J.-W. Sexually dimorphic scale worms (Annelida: Polynoidae) from hydrothermal vents in the Okinawa Trough: Two new species and two new sex morphs. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCowin, M.F.; Rouse, G.W. Phylogeny of hydrothermal vent Iphionidae, with the description of a new species (Aphroditiformia, Annelida). ZooKeys 2018, 779, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.; Britayev, T.A. Symbiotic polychaetes revisited: An update of the known species and relationships (1998–2017). Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2018, 56, 371–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Britayev, T.A. Symbiotic polychaetes: Review of known species. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1998, 36, 217–340. [Google Scholar]
- Nygren, A. Cryptic polychaete diversity: A review. Zool. Scr. 2014, 43, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravara, A.; Ramos, D.; Teixeira, M.A.L.; Costa, F.O.; Cunha, M.R. Taxonomy, distribution and ecology of the order Phyllodocida (Annelida, Polychaeta) in deep-sea habitats around the Iberian margin. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2017, 137, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borja, A.; Franco, J.; Pérez, V. A marine biotic index to establish the ecological quality of soft-bottom benthos within European estuarine and coastal environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 1100–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, E. DNA barcodes jump-start search for new species. Science 2019, 364, 920–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leese, F.; Bouchez, A.; Abarenkov, K.; Altermatt, F.; Borja, Á.; Bruce, K.; Ekrem, T.; Čiampor, F.; Čiamporová-Zaťovičová, Z.; Costa, F.O.; et al. Chapter Two—Why We Need Sustainable Networks Bridging Countries, Disciplines, Cultures and Generations for Aquatic Biomonitoring 2.0: A Perspective Derived From the DNAqua-Net COST Action. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2018, 58, 63–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Lopez, J.; Bourne, S.; Holman, L.; Seymour, M.; Grey, E.K.; Lacoursière, A.; Li, Y.; Renshaw, M.A.; Pfrender, M.E.; et al. Optimising the detection of marine taxonomic richness using environmental DNA metabarcoding: The effects of filter material, pore size and extraction method. Metabarcoding Metagenom. 2018, 2, e28963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigand, H.; Beermann, A.J.; Čiampor, F.; Costa, F.O.; Csabai, Z.; Duarte, S.; Geiger, M.F.; Grabowski, M.; Rimet, F.; Rulik, B.; et al. DNA barcode reference libraries for the monitoring of aquatic biota in Europe: Gap-analysis and recommendations for future work. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygren, A.; Pleijel, F. From one to ten in a single stroke--resolving the European Eumida sanguinea (Phyllodocidae, Annelida) species complex. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2011, 58, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delić, T.; Trontelj, P.; Rendoš, M.; Fišer, C. The importance of naming cryptic species and the conservation of endemic subterranean amphipods. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fišer, C.; Robinson, C.T.; Malard, F. Cryptic species as a window into the paradigm shift of the species concept. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. Barcoding: Bold: The Barcode of Life Data System (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horton, T.; Kroh, A.; Ahyong, S.; Bailly, N.; Boyko, C.B.; Brandão, S.N.; Gofas, S.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Hernandez, F.; Holovachov, O.; et al. World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS). 2021. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org (accessed on 7 January 2021).
- Chamberlain, S. Worrms: World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) Client. R Package Version 0.4.0. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=worrms (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- OBIS. Ocean Biodiversity Information System. Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO. 2020. Available online: http://www.iobis.org (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Provoost, P.; Bosch, S. “Robis: R Client to access data from the OBIS API.” Ocean Biogeographic Information System. Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO. R Package Version 2.1.8. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=robis (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- “GBIF.org”. GBIF Occurrence Download. 2020. Available online: https://doi.org/10.15468/dl.yntzgf (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Provoost, P.; Bosch, S. “Obistools: Tools for Data Enhancement and Quality Control.” Ocean Biogeographic Information System. Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO. R Package Version 0.0.9. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=obistools (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Costello, M.J.; Tsai, P.; Wong, P.S.; Cheung, A.K.L.; Basher, Z.; Chaudhary, C. Marine biogeographic realms and species endemicity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnes, R. DggridR: Discrete Global Grids. R Package Version 2.0.4. 2020. Available online: https://github.com/r-barnes/dggridR/ (accessed on 20 April 2020).
- Hurlbert, S.H. The nonconcept of species diversity: A critique and alternative parameters. Ecology 1971, 52, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahyong, S.; Costello, M.J.; Galil, B.S.; Gollasch, S.; Hutchings, P.A.; Katsanevakis, S.; Lejeusne, C.; Marchini, A.; Occhipinti, A.; Pagad, S.; et al. World Register of Introduced Marine Species (WRiMS). 2020. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org/introduced (accessed on 6 September 2020). [CrossRef]
- Çinar, M.E. Alien polychaete species worldwide: Current status and their impacts. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2013, 93, 1257–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulwetter, S.; Simboura, N.; Katsiaras, N.; Chatzigeorgiou, G.; Arvanitidis, C. Polychaetes of Greece: An updated and annotated checklist. Biodivers. Data J. 2017, 5, e20997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keppel, E.; Keith, I.; Ruiz, G.M.; Carlton, J.T. New records of native and non-indigenous polychaetes (Annelida: Polychaeta) in the Galapagos Islands. Aquat. Invasions 2019, 14, 59–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppel, E.; Tovar-Hernandez, A.M.; Ruiz, G. First record and establishment of Branchiomma coheni (Polychaeta: Sabellidae) in the Atlantic Ocean and review of non–indigenous species of the genus. Zootaxa 2015, 4058, 499–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langeneck, J.; Lezzi, M.; Del Pasqua, M.; Musco, L.; Gambi, M.C.; Castelli, A.; Giangrande, A. Non-indigenous polychaetes along the coasts of Italy: A critical review. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2020, 238–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, E.; Richter, A. Non-indigenous species (NIS) of polychaetes (Annelida: Polychaeta) from the Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts of the Iberian Peninsula: An annotated checklist. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2017, 71, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanders Marine Institute. MarineRegions.org. 2020. Available online: www.marineregions.org (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- Olenin, S.; Alemany, F.; Cardoso, A.C.; Gollasch, S.; Goulletquer, P.; Lehtiniemi, M.; McCollin, T.; Minchin, D.; Miossec, L.; Occhipinti-Ambrogi, A.O.H.; et al. Marine Strategy Framework Directive–Task Group 2 Report. Non-Indigenous Species; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, EU/ICES: Luxembourg, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravara, A.; Carvalho, S. Nephtyidae (Polychaeta, Phyllodocida) from the Red Sea, with record of a new species. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2017, 97, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, C.M.; Hardy, S.M.; Brown, T.M.; Macdonald, T.A.; Hebert, P.D.N. A tri-oceanic perspective: DNA barcoding reveals geographic structure and cryptic diversity in Canadian polychaetes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reish, D.J.; Anderson, F.E.; Horn, K.M.; Hardege, J. Molecular phylogenetics of the Neanthes acuminata (Annelida: Nereididae) species complex. Mem. Mus. Vic. 2014, 71, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fauvel, P. Mission Robert Ph. Dollfus en Egypte. Annélides Polychètes. Mémoires Présentes A L’institut D’egypte Et Publes Sous Les Auspices De Sa Majesté Fouad Ierroi D’egypte 1933, 21, 31–83. [Google Scholar]
- Wehe, T. Revision of the scale worms (Polychaeta: Aphroditoidea) occurring in the seas surrounding the Arabian Peninsula. Part I: Polynoidae. Fauna Arab. 2006, 22, 23–197. [Google Scholar]
- Hanley, J.R.; Burke, M. Scaleworms (Polychaeta: Polynoidae) of Albany, Western Australia. In Proceedings of the Third International Marine Biological Workshop: The Marine Fauna of Albany, Western Australia; Wells, F.E., Walker, D.I., Kirkman, H., Lethbridge, R., Eds.; Western Australian Museum: Perth, Australia, 1990; Volume I, pp. 203–236. [Google Scholar]
- Aguado, M.T.; Capa, M.; Lago-Barcia, D.; Gil, J.; Pleijel, F.; Nygren, A. Species delimitation in Amblyosyllis (Annelida, Syllidae). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, A. Sur les divers types de stolons chez les syllidiens, specialement sur une nouvelle espèce (Syllis cirropunctata n.sp.) à stolons acephales et sur la reobservation du stolon tetracère de Syllis amica Qfg. C. R. L’acad. Sci. Paris 1909, 148, 318–320. [Google Scholar]
- Gravier, C. Contribution à l’étude des Annélides Polychètes de la Mer Rouge. Première partie. Nouv. Arch. Mus. D’hist. Nat. Paris 1900, 2, 137–282. [Google Scholar]
- Aguado, M.T.; San Martín, G. Syllidae (Polychaeta) from Lebanon with two new reports for the Mediterranean Sea. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2007, 48, 207–224. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Campos, P.; Giribet, G.; Riesgo, A. The Syllis gracilis species complex: A molecular approach to a difficult taxonomic problem (Annelida, Syllidae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 109, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, B.; Vieira, P.; Teixeira, M.; Lobo-Arteaga, J.; Hollatz, C.; Borges, L.; Duarte, S.; Troncoso, J.; Costa, F. Gap-analysis and annotated reference library for supporting macroinvertebrate metabarcoding in Atlantic Iberia. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 101307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, S.; Vieira, P.E.; Costa, F.O. Assessment of species gaps in DNA barcode libraries of non-indigenous species (NIS) occurring in European coastal regions. Metabarc. Metagen. 2020, 4, e55162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamungkas, J.; Glasby, C.J.; Read, G.B.; Wilson, S.P.; Costello, M.J. Progress and perspectives in the discovery of polychaete worms (Annelida) of the world. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2019, 73, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnaeus, C. Systema Naturae per Regna Tria Naturae, Secundum Classes, Ordines, Genera, Species, cum Characteribus, Differentiis, Synonymis, Locis. Tomus I. Editio Decima, Reformata; Laurentii Salvii: Stockholm, Sweden, 1758; p. 824. [Google Scholar]
- Barrelier, J. Icones Plantarum per Galliam, Hispaniam et Italiam Observatur ad Vivum Exivitarum; Opus Posthumum Editum Cura et Studio Antonii de Jussieu: Paris, France, 1714; p. 148. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers, E. Die Borstenwürmer (Annelida Chaetopoda) nach Systematischen und Anatomischen Untersuchungen Dargestellt; Wilhelm Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1864; Volume I, pp. 1–268. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers, E. Die Borstenwürmer (Annelida Chaetopoda) nach Systematischen und Anatomischen Untersuchungen Dargestellt; Wilhelm Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1868; Volume II, pp. 269–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claparède, É. Les Annélides Chétopodes du Golfe de Naples. Mém. Soc. Phys. Hist. Nat. Genève 1868, 19, 313–584. [Google Scholar]
- Claparède, É. Les annélides chétopodes du Golfe de Naples. Supplément. Mém. Soc. Phys. Hist. Nat. Genève 1870, 20, 365–542. [Google Scholar]
- Lamarck, J.B. Histoire Naturelle des Animaux sans Vertèbres, Présentant les Caractères Généraux et Particuliers de ces Animaux, Leur Distribution, Leurs Classes, Leurs Familles, Leurs Genres, et la Citation des Principales Espèces qui s’y Rapportent; Précédée d’une Introduction Offrant la Détermination des Caractères Essentiels de l’Animal, sa Distinction du Végétal et des Autres Corps Naturels, Enfin, L’exposition des Principes Fondamentaux de la Zoologie. Vol. 5; Déterville & Verdière: Paris, France, 1818; Volume 5, p. 612. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, O.F. Zoologicae Danicae Prodromus, seu Animalium Daniae et Norvegiae Indigenarum Characteres, Nomina et Synonyma Imprimis Popularium; Hallageriis: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1776; p. 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabricius, O. Fauna Groenlandica, Systematice Sistens, Animalia Groenlandiae Occidentalis Hactenus Indagata, Quoad Nomen Specificum, Triviale, Vernaculumque Synonyma Auctorum Plurium, Descriptionem, Locum, Victum, Generationem, Mores, Usum, Capturamque Singuli Prout Detegendi Occasio Fuit, Maximaque Parte Secundum Proprias Observationes; Impensis Ioannis Gottlob Rothe: Copenhagen, Denmark; Leipzig, Germany, 1780; p. 452. [Google Scholar]
- Örsted, A.S. Annulatorum Danicorum Conspectus. Fasc. 1 Maricolae; Librariae Wahlianae: Hafniae, Denmark, 1843; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Greeff, R. Über pelagische Anneliden von der Küste der canarischen Inseln. Z. Wiss. Zool. 1879, 32, 237–284. [Google Scholar]
- Steenstrup, J.S. Af Slaegten Tomopteris. Vidensk. Medd. Dan. Nat. Foren. I Köbenhavn 1850, 1850, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Busch, W. Beobachtungen ueber Anatomie und Entwicklung Einiger Wirbellosen Seethiere; Aug. Hirschwald: Berlin, Germany, 1851; p. 143. [Google Scholar]
- Linnaeus, C. Systema Naturae per Regna Tria Naturae, Editio Duodecima, Reformata, Tomus I, Pars II. Regnum Animale; Laurentii Salvii: Stockholm, Sweden, 1767. [Google Scholar]
- Arfianti, T.; Costello, M.J. Global biogeography of marine amphipod crustaceans: Latitude, regionalization, and beta diversity. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 638, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, C.; Saeedi, H.; Costello, M.J. Marine species richness is bimodal with latitude: A reply to Fernandez and Marques. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillebrand, H. Strength, slope and variability of marine latitudinal gradients. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 273, 251–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pamungkas, J.; Glasby, C.J.; Costello, M.J. Biogeography of polychaete worms (Annelida) of the world. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 657, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, C.; Saeedi, H.; Costello, M.J. Bimodality of latitudinal gradients in marine species richness. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, T.J.; Berghe, E.V.; O’Dor, R. Biodiversity’s big wet secret: The global distribution of marine biological records reveals chronic under-exploration of the deep pelagic ocean. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Izuka, A. The errantiate Polychaeta of Japan. J. Coll. Sci. Imp. Univ. Tokyo 1912, 30, 1–262. [Google Scholar]
- Pernet, B. Benthic egg masses and larval development of Amblyosyllis speciosa (Polychaeta: Syllidae). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1998, 78, 1369–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.K. Amblyosyllis nigrolineata, une nouvelle variété de l’A. speciosa Izuka. Annot. Zool. Jpn. 1934, 14, 317–320. [Google Scholar]
- Imajima, M.; Hartman, O. The Polychaetous Annelids from Japan. Pt. I. Allan Hancock Found. Spec. Publ. 1964, 26, 1–237. [Google Scholar]
- Malmgren, A.J. Annulata Polychaeta Spetsbergiae, Groelanlandiae, Islandiae et Scandinaviae Hactenus Cognita. Cum XIV. Tabulis; Ex Officina Frenckelliana: Helsinki, Finland, 1867; p. 127. [Google Scholar]
- Langerhans, P. Die Wurmfauna von Madeira. III. Z. Wiss. Zool. 1880, 34, 87–143. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, W.C. Report on the Annelida Polychaeta collected by the H.M.S. Challenger during the years 1873–1876. Rep. Sci. Res. Voy. H.M.S. Chall. 1872-76 1885, 12, 1–554. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, G. Miscellanea Zoologica. [Continued from vol. iv. p. 375.] Contributions towards a history of Irish Annelids (1). Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1840, 5, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.A.L.; Vieira, P.E.; Pleijel, F.; Sampieri, B.R.; Ravara, A.; Costa, F.O.; Nygren, A. Molecular and morphometric analyses identify new lineages within a large Eumida (Annelida) species complex. Zool. Scr. 2020, 49, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, P.E.; Desiderato, A.; Holdich, D.M.; Soares, P.; Creer, S.; Carvalho, G.R.; Costa, F.O.; Queiroga, H. Deep segregation in the open ocean: Macaronesia as an evolutionary hotspot for low dispersal marine invertebrates. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 1784–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, M.J.; Wiklund, H.; Neal, L.; Jeffreys, R.; Linse, K.; Ruhl, H.; Glover, A.G. DNA barcoding uncovers cryptic diversity in 50% of deep-sea Antarctic polychaetes. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 160432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nygren, A.; Parapar, J.; Pons, J.n.; Meißner, K.; Bakken, T.; Kongsrud, J.A.; Oug, E.; Gaeva, D.; Sikorski, A.; Johansen, R.A.; et al. A mega-cryptic species complex hidden among one of the most common annelids in the North East Atlantic. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, W. Descriptions of several new species of worms belonging to the Annelida Errantia and Sedentaria or Tubicola of Milne Edwards. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1863, 1863, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, C. Revision of the pantropical genus Treptopale (Annelida: Phyllodocida: Chrysopetalidae): Redescription of Treptopale rudolphi Perkins, 1985 and description of two new species including comparison of Treptopale populations in northern Australia. Beagle Rec. Mus. Art Gall. North. Territ. 2010, 26, 37–55. [Google Scholar]
- Gravier, C. Contribution à l’étude des Annélides Polychètes de la Mer Rouge (Suite). Bull. Mus. D’hist. Nat. Paris 1899, 6, 288–298. [Google Scholar]
- Grube, A.E. Actinien, Echinodermen und Wurmen des Adriatischen und Mittelmeers nach Eigenen Sammlungen Beschrieben; J. H. Bon: Königsberg, Russia, 1840; p. 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langeneck, J.; Scarpa, F.; Maltagliati, F.; Sanna, D.; Barbieri, M.; Cossu, P.; Mikac, B.; Curini Galletti, M.; Castelli, A.; Casu, M. A complex species complex: The controversial role of ecology and biogeography in the evolutionary history of Syllis gracilis Grube, 1840 (Annelida, Syllidae). J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2020, 58, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lobo, J.; Teixeira, M.A.L.; Borges, L.M.S.; Ferreira, M.S.G.; Hollatz, C.; Gomes, P.T.; Sousa, R.; Ravara, A.; Costa, M.H.; Costa, F.O. Starting a DNA barcode reference library for shallow water polychaetes from the southern European Atlantic coast. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Audzijonyte, A.; Ovcarenko, I.; Bastrop, R.; Vainola, R. Two cryptic species of the Hediste diversicolor group (Polychaeta, Nereididae) in the Baltic Sea, with mitochondrial signatures of different population histories. Mar. Biol. 2008, 155, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgilio, M.; Fauvelot, C.; Costantini, F.; Abbiati, M.; Backeljau, T. Phylogeography of the common ragworm Hediste diversicolor (Polychaeta: Nereididae) reveals cryptic diversity and multiple colonization events across its distribution. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 1980–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Nakashima, A. A review of Asian Hediste species complex (Nereididae, Polychaeta) with descriptiuons of two new species and a redescription of Hediste japonica (Izuka,1908). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. 2003, 137, 203–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosuji, H.; Bastrop, R.; Götting, M.; Park, T.; Hong, J.-S.; Sato, M. Worldwide molecular phylogeny of common estuarine polychaetes of the genus Hediste (Annelida: Nereididae), with special reference to interspecific common haplotypes found in southern Japan. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 1385–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.K.; Leaché, A.D.; Burbrink, F.T.; McGuire, J.A.; Moritz, C. Coalescent-based species delimitation in an integrative taxonomy. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaneto, D.; Flot, J.-F.; Tang, C.Q. Guidelines for DNA taxonomy, with a focus on the meiofauna. Mar. Biodivers. 2015, 45, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, J.; Hatch, A.S.; Hourdez, S.; Seid, C.A.; Rouse, G.W. Phylogeny and biogeography of Branchipolynoe (Polynoidae, Phyllodocida, Aciculata, Annelida), with descriptions of five new species from methane seeps and hydrothermal vents. Diversity 2019, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gastaldi, A. Harmothoe Imbricata: Species Complex or Complex Species? University of Alaska Fairbanks: Fairbanks, AK, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Campos, P.; Giribet, G.; San Martín, G.; Rouse, G.W.; Riesgo, A. Straightening the striped chaos: Systematics and evolution of Trypanosyllis and the case of its pseudocryptic type species Trypanosyllis krohnii (Annelida, Syllidae). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2017, 179, 492–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, J.T.; Vieira, P.E.; Ekrem, T.; Soares, P.; Costa, F.O. BAGS: An automated Barcode, Audit & Grade System for DNA barcode reference libraries. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann-Schröder, G. Annelida, Borstenwürmer, Polychaeta. Tierwelt Dtschl. 1971, 58, 1–594. [Google Scholar]
- Kinberg, J.G.H. Nya slägten och arter af Annelider. Öfvers. Kongliga Vetensk. Akad. Förhandlingarstockholm 1856, 12, 381–388. [Google Scholar]
- Schmarda, L.K. Neue wirbellose Thiere Beobachtet und Gesammelt auf Einer Reise un Die Erdr 1853 bis 1857. Erster Band (Zweite Halfte) Turbellarian, Rotatorien un Anneliden; Wilhelm Engelmann: Leipzig, Germany, 1861; p. 164. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, H.E.; Benedict, J.E. The Annelida Chaetopoda, from Eastport, Maine. Annu. Rep. United States Comm. Fish Fish. 1887, 12, 707–758. [Google Scholar]
- Bergsten, J.; Bilton, D.T.; Fujisawa, T.; Elliott, M.; Monaghan, M.T.; Balke, M.; Hendrich, L.; Geijer, J.; Herrmann, J.; Foster, G.N.; et al. The effect of geographical scale of sampling on DNA barcoding. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 851–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cariani, A.; Messinetti, S.; Ferrari, A.; Arculeo, M.; Bonello, J.J.; Bonnici, L.; Cannas, R.; Carbonara, P.; Cau, A.; Charilaou, C.; et al. Improving the Conservation of Mediterranean Chondrichthyans: The ELASMOMED DNA Barcode Reference Library. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.M.; Knebelsberger, T.; Landi, M.; Soares, P.; Raupach, M.J.; Costa, F.O. Assembling and auditing a comprehensive DNA barcode reference library for European marine fishes. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 89, 2741–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, F.O.; Landi, M.; Martins, R.; Costa, M.H.; Costa, M.E.; Carneiro, M.; Alves, M.J.; Steinke, D.; Carvalho, G.R. A ranking system for reference libraries of DNA barcodes: Application to marine fish species from Portugal. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fauchald, K. The polychaete worms. Definitions and keys to the orders, families and genera. Nat. Hist. Mus. Los Angel. County. Sci. Ser. 1977, 28, 1–188. [Google Scholar]
- Grube, A.E. Die Familien der Anneliden. Arch. Nat. Berl. 1850, 16, 249–364. [Google Scholar]
- Kinberg, J.G.H. Annulata nova. Öfvers. Kongliga Vetensk. Akad. Förhandlingarstockholm 1865, 21, 559–574. [Google Scholar]
- Böggemann, M. Revision of the Glyceridae Grübe 1850 (Annelida: Polychaeta). Abh. Senckenbergischen Nat. Ges. 2002, 555, 1–249. [Google Scholar]
- Böggemann, M. Revision of the Goniadidae (Annelida, Polychaeta). Abh. Nat. Ver. Hambg. (Neue Folgen) 2005, 39, 1–354. [Google Scholar]
- Böggemann, M. Worms that might be 300 million years old. Mar. Biol. Res. 2006, 2, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böggemann, M. Polychaetes (Annelida) of the abyssal SE Atlantic. Org. Divers. Evol. 2009, 9, 251–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.; Schwarz, F.; Hering, L.; Böggemann, M.; Bleidorn, C. The utility of genome skimming for phylogenomic analyses as demonstrated for glycerid relationships (Annelida, Glyceridae). Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 3443–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, V.; Pleijel, F.; Rouse, G.W.; Erseus, C.; Siddall, M.E. A molecular phylogeny of annelids. Cladistics 2007, 23, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böggemann, M. Chapter 7.11.8 Glyceridae Grube, 1850. In Handbook of Zoology Online; Westheide, W., Purschke, G., Böggemann, M., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Böggemann, M. Chapter 7.11.9 Goniadidae Kinberg, 1865. In Handbook of Zoology Online; Westheide, W., Purschke, G., Böggemann, M., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Imajima, M. Polychaetous Annelids from Sagami Bay and Sagami Sea Collected by the Emperor Showa of Japan and Deposited at the Showa Memorial Institute, National Science Museum, Tokyo (II): Orders included within the Phyllodocida, Amphinomida, Spintherida and Eunicida. Natl. Sci. Mus. Monogr. 2003, 23, 1–221. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, B.M.; Bailey-Brock, J.H. Progoniada oahuensis, a new species from Oahu, Hawaii (Annelida: Polychaeta: Goniadidae). Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 2005, 118, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böggemann, M.; Orensanz, J.M. Glyceriformia Fauchald, 1977 (Annelida:“Polychaeta”) from the SW Atlantic Shelf, between 30º and 45º S. Mitt. Aus Dem Hambg. Zool. Mus. Und Inst. 2007, 104, 11–59. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, A.E.; Steiner, T.M.; Amaral, A.C.Z. Glyceridae Grube 1850 (Annelida: Polychaeta) from southern and southeastern brazil, including a new species of Glycera. Biota Neotrop. 2007, 7, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imajima, M. Deep-sea benthic polychaetes off Pacific coast of the northern Honshu, Japan. Natl. Mus. Nat. Sci. Monogr. 2009, 39, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Böggemann, M.; Bienhold, C.; Gaudron, S.M. A new species of Glyceridae (Annelida:“Polychaeta”) recovered from organic substrate experiments at cold seeps in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Biodivers. 2012, 42, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhaes, W.F.; Rizzo, A.E. Glyceridae (Annelida: Polychaeta) from Guam, Mariana Islands with description of a new species of Glycera Savigny in Lamarck, 1818. Zootaxa 2012, 3338, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Hutchings, P.A. Glycera sheikhmujibi n. sp.(Annelida: Polychaeta: Glyceridae): A new species of Glyceridae from the saltmarsh of Bangladesh. Diversity 2020, 12, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arwidsson, I. Studien über die Familien Glyceridae und Goniadidae. Bergen. Mus. Årb. 1899, 2, 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Fauchald, K. Benthic polychaetous annelids from deep water off western Mexico and adjacent areas in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. Allan Hancock Monogr. Mar. Biol. 1972, 7, 1–575. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, F. Einiges über die Annelidenfauna der Insel Santa Catharina an der brasilianischen Küste. Arch. Für Nat. 1858, 24, 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Audouin, J.V.; Milne Edwards, H. Classification des Annélides, et description de celles qui habitent les côtes de la France. Ann. Sci. Nat. Paris 1833, 30, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, O. Goniadidae, Glyceridae and Nephtyidae. Allan Hancock Pac. Exped. 1950, 15, 1–181. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann-Schröder, G. Polychaeten aus dem Roten Meer. Kiel. Meeresforsch. 1960, 16, 69–125. [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel, P. Annélides polychètes nouvelles de l’Inde. I. Bull. Mus. D’hist. Nat. Paris 1928, 34, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, O. Deep-water benthic polychaetous annelids off New England to Bermuda and other North Atlantic areas. Occas. Pap. Allan Hancock Found. 1965, 28, 1–378. [Google Scholar]
- Böggemann, M. Polychaeten der Deutschen Küstengewässer (Auswertung einer “Senckenberg”-Fahrt im Sommer 1990). Ph.D. Thesis, Westfälischen Wilhelms-Universität Münster, Münster, Germany, 1995; pp. 1–281. [Google Scholar]
- Böggemann, M.; Fiege, D. Proboscidial papillae of the Glyceridae (Annelida, Polychaeta)—A useful taxonomic character. Verh. Dtsch. Zool. Ges. Kurzpublikationen 1996, 89, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.E.; Trabanino, S.; Baerwald, R.J. Scanning electron microscopical observations of the proboscideal papillae of Glycinde armigera (Annelida: Polychaeta). Invertebr. Biol. 1995, 14, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiege, D.; Böggemann, M. Scanning electron microscopy of the proboscidal papillae of some European Glyceridae. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1997, 60, 559–563. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, G. Kieferorgane von Glyceriden (Polychaeta) ihre Funktion und ihr taxonomischer Wert. Senckenbergiana Marit. 1977, 9, 261–283. [Google Scholar]
- Ockelmann, K.W.; Vahl, O. On the biology of the polychaete Glycera alba, especially its burrowing and feeding. Ophelia 1970, 8, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauchald, K.; Jumars, P.A. The diet of worms: A study of polychaete feeding guilds. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 1979, 17, 193–284. [Google Scholar]
- Klawe, W.L.; Dickie, L.M. Biology of the bloodworm, Glycera dibranchiata Ehlers, and its relation to the bloodworm of the Maritime Provinces. Bull. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1957, 115, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Mattson, S. Burrowing and feeding of Goniada maculata Ørsted (Polychaeta). Sarsia 1981, 66, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B. Maine’s baitworm fisheries: Resources at risk? Am. Zool. 1993, 33, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, W.C. A monograph of the British annelids. Polychaeta. Syllidae to Ariciidae. Ray Soc. Lond. 1910, 2, 233–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, W.C. Notes from the Gatty Marine Laboratory, St. Andrews. No. 26. 1. On the Pacific, Atlantic and Japanese Palolo. 2. On the British Goniadidae and Ariciidae. 3. On the same groups found in the ‘Porcupine’ Expeditions of1869 and 1870. 4. On the same groups dredged by Dr. Whiteaves of Canadain 1872 and 1873. 5. On the same groups procured by Canon Norman inNorway and Finmark. 6. On some Japanese Glyceridae. 7. On the form described as Hemipodus magellanicus in the Challenger. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1905, 715, 33–57. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Eliahu, M.N.; Golani, D. Polychaetes (Annelida) in the gut contents of goatfishes (Muliidae), with new polychaete records for the Mediterranean coast of Israel and the Gulf of Elat (Red Sea). Mar. Ecol. 1990, 11, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Eliahu, M.N.; Golani, D.; Ben-Tuvia, A. On predation of polychaetes (Annelides) by the squirrel- fish Adioryx ruber (Holocentridae), with a new polychaete record for the Mediterranean coast of Israel. Téthys 1983, 11, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Benham, W.B. Notes on Polychaeta: Two new species of the genus Goniada. Bull. Soc. Linn. Normandie 1932, 9, 553–566. [Google Scholar]
- Creaser, E.P., Jr. Reproduction of the bloodworm Glycera dibranchiata in the Sheepscot Estuary, Maine. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1973, 30, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettibone, M.H. Marine polychaete worms of the New England region. Part 1. Families Aphroditidae through Trochochaetidae. Bull. United States Natl. Mus. 1963, 227, 1–356. [Google Scholar]
- Treadwell, A.L. Polychaetous annelids collected by Captain Robert A. Bartlett in Greenland, Fox Basin, and Labrador. J. Wash. Acad. Sci. 1937, 27, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, B. The worms crawl in, the worms crawl out, what’s the bait worm fishery all about. Am. Zool. 1992, 32, 174A. [Google Scholar]
- Creaser, E.P.; Clifford, D.A.; Hogan, M.J.; Sampson, D.B. A commercial sampling program for sandworms, Nereis virens Sars, and bloodworms, Glycera dibranchiata Ehlers, harvested along the Maine coast. Noaa Tech. Rep. 1983, NMFS SSRF-767, 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Dow, R.L. Chances in abundance of the marine worm, Glycera dibranchiata, associated with seawater temperature fluctuations. Commer. Fish. Rev. 1964, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Dow, R.L. Fluctuations in marine species abundance during climatic cycles. Mar. Tech. Soc. J. 1973, 7, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Olive, P.J.W. Polychaeta as a world resource: A review of exploitation as a sea angling baits, and the potential for aquaculture based production. Mém. Mus. Natl. D’hist. Nat. Paris 1994, 162, 603–610. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, P.M.; Saloman, C.H. Some effects of dredging and coastal development in Boca Ciega Bay, Florida. United States Fish Wild Life Serv. Fish. Bull. 1968, 67, 213–241. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, G.J.; Murray, J.M.; Schaefer, M.; Bonner, A. Bait worms: A valuable and important fishery with implications for fisheries and conservation management. Fish Fish. 2017, 18, 374–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, W.H., Jr.; Ruff, R.E. Species profiles: Life histories and environmental requirements of coastal fishes and invertebrates (North Atlantic)—Sandworm and bloodworm. United States Fish Wildl. Serv. Biol. Rep. 1988, 82, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Böggemann, M. Annelida, Polychaeta, Phyllodocida, Glyceridae, Glycera branchiopoda Moore, 1911. In Handbook of Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Fauna. Denisia 18; Desbruyères, D., Segonzac, M., Bright, M., Eds.; IFREMER: Brest, France, 2006; p. 195. [Google Scholar]
- Desbruyères, D. Annelida, Polychaeta, Phyllodocida, Glyceridae, Glycera tesselata Grube, 1863. In Handbook of Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vent Fauna. Denisia 18; Desbruyères, D., Segonzac, M., Bright, M., Eds.; IFREMER: Brest, France, 2006; pp. 196–197. [Google Scholar]
- Schüller, M. Evidence for a role of bathymetry and emergence in speciation in the genus Glycera (Glyceridae, Polychaeta) from the deep Eastern Weddell Sea. Polar Biol. 2011, 34, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böggemann, M.; Dietz, A. Glyceriformia (Annelida) from the deep sea of the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean. Polar Biol. 2016, 39, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, M.J.; Harle, J.; Wiklund, H.; Jeffreys, R.M.; Linse, K.; Ruhl, H.A.; Glover, A.G. Distributional patterns of polychaetes across the West Antarctic based on DNA barcoding and particle tracking analyses. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutchings, P.A.; Kupriyanova, E. Cosmopolitan polychaetes—Fact or fiction? Personal and historical perspectives. Invertebr. Syst. 2018, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, L.; George, K.H.; Arbizu, P.M. Submarine ridges do not prevent large-scale dispersal of abyssal fauna: A case study of Mesocletodes (Crustacea, Copepoda, Harpacticoida). Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2011, 58, 839–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böggemann, M. Glyceriformia (Annelida) of the abyssal SW Atlantic and additional material from the SE Atlantic. Mar. Biodivers. 2016, 46, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, G.W. Bias? What bias? The evolution of downstream larval-feeding in animals. Zool. Scr. 2000, 29, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stramma, L.; England, M. On the water masses and mean circulation of the South Atlantic Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1999, 104, 20863–20883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckel, B.; Baumann, K.-H.; Henrich, R.; Kinkel, H. Coccolith distribution patterns in South Atlantic and Southern Ocean surface sediments in relation to environmental gradients. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2006, 53, 1073–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A. Chapter 8. The Polar Deep Sea. In Ecosystems of the Deep Oceans. Ecosystems of the World 28; Tyler, P.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 239–260. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez Arbizu, P.; Brix, S. Bringing light into deep-sea biodiversity. Zootaxa 1866, 5, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Arbizu, P.; Schminke, H.K. DIVA-1 expedition to the deep sea of the Angola Basin in 2000 and DIVA-1 workshop in 2003. Org. Divers. Evol. 2005, 5, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebbesmeyer, C.C.; Ingraham, W.J., Jr. Pacific toy spill fuels ocean current pathways research. Eostrans. Am. Geophys. Union 1994, 75, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohn, D. Moby-Duck. The True Story of 28,800 Bath Toys Lost at Sea and of the Beachcombers, Oceanographers, Environmentalists, and Fools, Including the Author, Who Went in Search of Them; Viking: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pettibone, M.H. Annelida. Polychaeta. In Synopsis and Classifiction of Living Organisms; Parker, S.P., Ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 2, pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Støp-Bowitz, C. Polychaeta from the Michael Sars North Atlantic deep-sea expedition 1910. Rep. Sci. Results Michael Sars North Atl. Deep-Sea Exped. 1948, 5, 1–91. [Google Scholar]
- Uschakov, P.V. Fauna of the USSR. Polychaetes. Vol. I. Polychaetes of the suborder Phyllodociformia of the Polar Basin and the North-Western part of the Pacific. (Family Phyllodocidae, Alciopidae, Tomopteridae, Typhloscolecidae and Lacydoniidae). Akad. Nauk Sssr 1972, 102, 1–272. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bergström, E. Zur Systematik der Polychætenfamilie der Phyllodociden. Zool. Bidr. Upps. 1914, 3, 37–224. [Google Scholar]
- Dales, R.P. The evolution of the pelagic alciopid and phyllodocid polychaetes. Proc. Zool. Soc. Lond. 1955, 125, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern, R. Polychaeta of the coasts of Ireland. Pelagic Phyllodocidae. Fish. Irel. Sci. Investig. 1909, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Støp-Bowitz, C. A new genus and species (Yndolacia lopadorrhynchoides) of pelagic polychaetes representative of a new family, Yndolaciidae. Bull. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1987, 7, 128–130. [Google Scholar]
- Rouse, G.W.; Pleijel, F. Problems in polychaete systematics. Hydrobiologia 2003, 496, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, G.W.; Pleijel, F. Reproductive Biology and Phylogeny of Annelida; Science Publishers Inc.: Enfield, NH, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Southern, R. Polychaeta of the coasts of Ireland. 3. The Alciopidae, Tomopteridae and Typhloscolecidae. Fish. Irel. Sci. Investig. 1911, 3, 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Apstein, C. Vorbericht ueber Die Alciopiden und Tomopteriden der Plankton-Expedition 1; Lipsius & Tischer: Kiel, Germany, 1899; pp. 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Apstein, C. Die Alciopiden und Tomopteriden der Plankton-Expedition 2; Lipsius: Kiel, Germany; Tischer: Leipzig, Germany, 1900; p. 62. [Google Scholar]
- Dales, R.P. The pelagic Polychaetes of Monterey Bay, California. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1955, 12, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dales, R.P. Pelagic polychaetes of the Pacific Ocean. Bull. Scripss Inst. Oceanogr. Univ. Calif. 1957, 7, 99–167. [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel, P. Faune de France. Polychètes Errantes. Faune Fr. 1923, 5, 1–488. [Google Scholar]
- Heath, H. A connecting link between the Annelida and the Echiuroidea Gephyrea armata. J. Morphol. 1930, 49, 223–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, O. Polychaetous annelids collected by the USNS Eltanin and Staten Island cruises, chiefly from Antarctic Seas. Allan Hancock Monogr. Mar. Biol. 1967, 2, 1–387. [Google Scholar]
- Osborn, K.J.; Rouse, G.W. Multiple origins of pelagicism within Flabelligeridae (Annelida). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 49, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halanych, K.M.; Cox, L.N.; Struck, T.H. A brief review of holopelagic annelids. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2007, 47, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struck, T.H.; Schult, N.; Kusen, T.; Hickman, E.; Bleidorn, C.; McHugh, D.; Halanych, K.M. Annelid phylogeny and the status of Sipuncula and Echiura. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uljanin, B. Sur le Genre Sagitella N. Wagner. Arch. Zool. Exp. Gén. 1878, 7, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Brigss, D.E.G.; Clarkson, E.N.K. The first tomopterid, a polychaete from the Carboniferous of Scotland. Lethaia 1987, 20, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, N. Shrimping at Granton-the Muirhouse’shrimp-bed’revisited. Edinb. Geol. 2014, 55, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, S.A. Reproductive biology, systematics, and evolution in the polychaete family Alciopidae. Bull. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1987, 7, 114–127. [Google Scholar]
- Støp-Bowitz, C. Some new or rare species of pelagic polychaetes from the Gulf of Guinea. Ophelia 1991, (Suppl. 5), 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Støp-Bowitz, C. Polychètes pélagiques des campagnes de l’Ombango dans les eaux équatoriales et tropicales Ouest-Africanes. Ed. L’orstrom Collect. Études Thèses 1992, 1992, 1–115. [Google Scholar]
- Dales, R.P. An annotated list of the pelagic Polychaeta. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. Ser. 12 1956, 9, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dales, R.P.; Peter, G. A synopsis of the Pelagic Polychaeta. J. Nat. Hist. 1972, 6, 55–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A. Illustrazione Iconografica degli Anellidi rari o poco conosciuti del Golfo di Napoli. Annu. Dell’instituto Mus. Zool. Dell’univ. Napoli 1864, 2, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Viguier, C. Etudes sur les Animaux inferieurs de la Baie d’Alger. Recherches sur les Annelides pelagiques. Arch. Zool. Exp. Gén. 1886, 4, 347–442. [Google Scholar]
- Viguier, C. Nouvelles etudes sur le plankton de la baie d’Alger. Ann. Sci. Nat. Paris 1911, 13, 187–267. [Google Scholar]
- Kolbasova, G.; Kosobokova, K.; Neretina, T. Bathy-and mesopelagic annelida from the Arctic Ocean: Description of new, redescription of known and notes on some “cosmopolitan” species. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2020, 165, 103327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, J.; Hernández, F.; Ocaña, O.; Jiménez, S. Poliquetos pélagicos de Canarias: Familias Iospilidae y Lopadorrhynchidae. Vieraea 1992, 21, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Grube, A.E. Beschreibungen neuer oder wenig bekannter Anneliden. Arch. Nat. Berl. 1855, 21, 81–136. [Google Scholar]
- Treadwell, A.L. Scientific Results of Cruise VII of the Carnegie during 1928–1929 under Command of Captain J.P. Ault. Biology—IV. Biological results of the last cruise of the Carnegie. III. Polychaetous annelids. Carnegie Inst. Wash. Publ. 1943, 55, 30–59. [Google Scholar]
- Eschscholtz, F. Berich ueber zoologische Ausbeute waehrend der Reise von Kronstadt bis St. Peter und Paul. Isis Von Oken 1825, 16, 733–747. [Google Scholar]
- Quoy, J.R.; Gaimard, P. Observations zoologiques faites a bord de l’Astrolabe en mai 1826, dans le detroit de Gibraltar. Ann. Sci. Nat. Paris 1827, 10, 5–239. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, D. Nouve specie di Tomopteridi. Diagnosi preliminari. Boll. Mus. Zool. Anat. Comp. Torino 1908, 23, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Day, J.H. A monograph on the Polychaetes of Southern Africa. Part 1. Errantia. Trustees Br. Mus. (Nat. Hist.) 1967, 656, 1–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Alamo, M.A. Tomopterids (Annelida: Polychaeta) from the Eastern Tropical Pacific Ocean. In: Proceedings of the VI International Polychaete Conference. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2000, 67, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, N. Nouveau groupe d’Annelides. Tr. Obsch. Estest St. Petersburg 1872, 3, 344–347. [Google Scholar]
- Levinsen, G.M.R. Spolia atlantica. Om nogle pelagiske Annulata. Skr. Fra Vidensk. I Kjoebenhavnmath.-Nat. Rekke 1885, 3, 321–344. [Google Scholar]
- Krohn, A. Zoologische und anatomische Bemerkungen über die Alciopen. Arch. Nat. Berl. 1845, 11, 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Fauchald, K.; Rouse, G.W. Polychaete systematics: Past and present. Zool. Scr. 1997, 26, 71–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Álamo, M.A. Los poliquetos pelágicos (Annelida-Polychaeta) del Pacífico Tropical Oriental: Sistemática y Zoogeografía. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de Mexico, Ciudad de México, Mexico, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Orensanz, J.M.; Ramirez, F.C. Taxonomía y distribución de los poliquetos pelágicos del Atlántico Sudoccidental. Bol. Inst. Biol. Mar. Mar Plata 1973, 21, 1–122. [Google Scholar]
- Costello, M.J.; Bouchet, P.; Boxshall, G.; Arvanitidis, C.; Appeltans, W. European Register of Marine Species. Alciopini Ehlers. 1864. Available online: http://www.marbef.org/data/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=932 (accessed on 8 December 2020).
- Chamberlin, R.V. The annelida polychaeta (In: Reps. Sci. Res. Expeds. U. S. Fish. Steamer “Albatross”, 1891, 1899–1900 and 1904–1905). Mem. Mus. Comp. Zool. Harv. Coll. 1919, 48, 1–514. [Google Scholar]
- Uschakov, P.V. Polychaeta of the Far Eastern seas of the Soviet Union. Akad. Nauk Sssr 1955, 56, 1–445. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Pleijel, F.; Dales, R.P. Polychaetes: British Phyllodocoideans, Typhloscolecoideans and Tomopteroideans; Universal Book Services/Dr. W. Backhuys: Avon, OH, USA, 1991; p. 202. [Google Scholar]
- Hering, E. Zur Kenntnis der Alciopiden von Messina. Sber. Akad. Wiss. Wien 1892, 101, 713–768. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.L.; Hua, L. Phylogeny of Alciopidae (pelagic polychaetes): A cladistic analysis. Mém. Mus. Natl. D’hist. Nat. Paris 1994, 162, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Cueto, S.; Suárez-Morales, E. An account of Alciopina, Torrea, and Rhynconereella (Polychaeta: Alciopidae) of the western Caribbean Sea. Belg. J. Zool. 2008, 138, 70. [Google Scholar]
- San Martín, G.; Álvarez-Campos, P.; Kondo, Y.; Núñez, J.; Fernández-Álamo, M.A.; Pleijel, F.; Goetz, F.E.; Nygren, A.; Osborn, K.J. New symbiotic association in marine annelids: Ectoparasites of comb jellies. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 191, 672–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Støp-Bowitz, C. Polychaeta. In Atlas del zooplancton del Atlántico Sudoccidental y Métodos de Trabajo con el Zooplancton Marino; Boltovskoy, D., Ed.; Instituto Nacional de Investigacion y Desarrollo Pesquero: Mar del Plato, Argentina, 1981; pp. 471–492. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, D.; Reish, D.J. Pelagic polychaetes from ice stations (Arlis I and II) in the Arctic Basin. J. Nat. Hist. 1984, 18, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, L. Annelidi, Alciopidi e Fillidocidi. Raccolte planctoniche fatte dalla R. Nave Liguria nel viaggio di circonnavigazione del 1903-05 sotto il commando di S.A.R. Luigi di Savioa, Duca degli Abruzzi. Pub. R. Inst. Stud. Sup. Prat. Perfez. Firenze Sez. Sci. Fis. Nat. 1911, 2, 245–327. [Google Scholar]
- Reibisch, J.G.F. Die Pelagischen Phyllodociden und Typhloscoleciden der Plankton-Expedition; Lipsius & Tischer: Kiel, Germany, 1895. [Google Scholar]
- Tebble, N. The distribution of pelagic polychaetes in the South Atlantic Ocean. Dis. Rep. 1960, 30, 161–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebble, N. The distribution of pelagic polychaetes across the North Pacific Ocean. Bull. Br. Mus. (Nat. Hist.) 1962, 7, 371–492. [Google Scholar]
- Dales, R.P. Pelagic polychaetes from the Bay of Biscay. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1957, 9, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, O. Catalogue of the polychaetous Annelids of the World, parts 1-2. Allan Hancock Found. Publ. Occas. Pap. 1959, 23, 1–628. [Google Scholar]
- Eklöf, J.; Pleijel, F.; Sundberg, P. Phylogeny of benthic Phyllodocidae (Polychaeta) based on morphological and molecular data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 45, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Álamo, M.A. Iospilidae Bergström, 1914. In Poliquetos (Annelida: Polychaeta) de México y América Tropical; León-González, J.A.B.-Z., Bastida Zavala, J.R., Carrera-Parra, L.F., García-Garza, M.E., Peña-Rivera, A., Salazar-Vallejo, S.I., Solís-Weiss, V., Eds.; Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León: Monterrey, Mexico, 2009; pp. 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Tovar-Faro, B.; Leocádio, M.; de Paiva, P.C. Distribution of Iospilidae (Annelida) along the eastern Brazilian coast (from Bahia to Rio de Janeiro). Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2013, 41, 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Benham, W.B. The pelagic Polychaeta. Br. Antarct. Terra Nova Exped. Nat. Hist. Rep. Zool. 1929, 7, 183–201. [Google Scholar]
- Berkeley, C. A checklist of Polychaeta recorded from British Columbia since 1923, with references to name changes, descriptions, and synonymies. I. Errantia. Can. J. Zool. 1967, 45, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkeley, E.; Berkeley, C. Some further records of pelagic Polychaeta from the northeast Pacific north of latitude 40º N and east of longitude 175º W, together with records of Siphonophora, Mollusca and Tunicata from the same region. Can. J. Zool. 1960, 38, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savigny, J.-C. Système des annelides, principalement de celles des côtes de l’Égypte et de la Syrie, offrant les caractères tant distinctifs que naturels des Ordres, Familles et Genres, avec la description des espèces. Des 1822, 1, 1–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yingst, D.R. The vertical distribution and reproductive biology of Pelagobia longicirrata (Annelida) in the central Arctic Ocean. Biol. Bull. 1974, 147, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Álamo, M.A. Lopadorrhynchidae Claparède, 1868. In Poliquetos (Annelida: Polychaeta) de México y América Tropical; León-González, J.A.B.-Z., Bastida Zavala, J.R., Carrera-Parra, L.F., García-Garza, M.E., Peña-Rivera, A., Salazar-Vallejo, S.I., Solís-Weiss, V., Eds.; Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León: Monterrey, Mexico, 2009; pp. 255–261. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmo, R.; Gambi, M.C.; Granata, A.; Guglielmo, L.; Minutoli, R. Composition, abundance and distribution of holoplanktonic polychaetes within the Strait of Magellan (southern America) in austral summer. Polar Biol. 2014, 37, 999–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lana, P.C.; Blankensteyn, A. Poliquetas pelágicos coletados pelo N. Ap. Oc. “Barão de Teffé”, durante a I Expedição Antártica Brasileira. Ann. Acad. Ciênc. 1986, 58, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lana, P.C.; Blankensteyn, A. Distribution patterns of pelagic polychaetes in the Southern Drake Passage and Bransfield Strait (January-February 1984). Nerítica 1987, 2, 37–64. [Google Scholar]
- Sicinski, J. Pelagic Polychaeta in the Scotia Front west of Elephant Island (BIOMASS III, October-November 1986). Pol. Polar Res. 1988, 9, 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Bellan, G. Polychaeta. In European Register of Marine Species: A Check-List of the Marine Species in Europe and a Bibliography of Guides to Their Identification; Costello, M.J., Emblow, C., White, R.J., Eds.; Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 214–231. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.S. Family Pontodoridae. In Polychaetes & Allies: The Southern Synthesis. Fauna of Australia. Vol. 4A. Polychaeta, Myzostomida, Pogonophora, Echiura, Sipuncula; Beesley, P.L.G., Ross, J.B., Glasby, C.J., Eds.; CSIRO Publishing: Melbourne, Australia, 2000; pp. 156–157. [Google Scholar]
- Berkeley, E.; Berkeley, C. Notes on some pelagic and some swarming polychaeta taken off the coast of Perú. Can. J. Zool. 1964, 42, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Álamo, M.A. Pontodoridae Bergström, 1914. In Poliquetos (Annelida: Polychaeta) de México y América Tropical; León-González, J.A.B.-Z., Bastida Zavala, J.R., Carrera-Parra, L.F., García-Garza, M.E., Peña-Rivera, A., Salazar-Vallejo, S.I., Solís-Weiss, V., Eds.; Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León: Monterrey, Mexico, 2009; pp. 473–476. [Google Scholar]
- Day, J.H. Zooplancton de la région de Nosy-Bé. X. The Biology of planktonic Polychaeta near Nosy-Bé, Madagascar. Cah. Orstom (Off. Rech. Sci. Tech. Outre-Mer) Ser. Océanogr. 1975, 13, 197–216. [Google Scholar]
- Malaquin, A.; Carin, F. Note preliminaire sur les annelides pelagiques provenant des Campganes de l’Hirondelle et de la Princesse-Alice. Bull. L’inst. Océanogr. 1911, 205, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Malaquin, A.; Carin, F. Tomopterides provenant des campagnes de l’Hirondelle et de la Princesse-Alice (1888–1910). Result. Camp. Sci. Monaco 1922, 61, 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Mileikovsky, S.A. On the systematic interrelationships within the Polychaeta and Annelida. An attempt to create an integrated system based on their larval morphology. In Essays on Polychaetous Annelids in Memory of Dr. Olga Hartman; Reish, D.J., Fauchald, K., Eds.; The Allan Hancock Foundation, University of Southern California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1977; pp. 503–524. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Álamo, M.A. Tomopteridae Grube, 1850. In Poliquetos (Annelida: Polychaeta) de México y América Tropical; León-González, J.A.B.-Z., Bastida Zavala, J.R., Carrera-Parra, L.F., García-Garza, M.E., Peña-Rivera, A., Salazar-Vallejo, S.I., Solís-Weiss, V., Eds.; Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León: Monterrey, Mexico, 2009; pp. 657–663. [Google Scholar]
- Rakusa-Suszczewski, S. Predation of chaetognatha by Tomopteris helgolandica Greff. Ices J. Mar. Sci. 1968, 32, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Álamo, M.A.; Thuese, A.B. Polychaeta. In South Atlantic Zooplankton; Boltovskoy, D., Ed.; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Álamo, M.A. Composition, abundance and distribution of holoplanktonic polychaetes from the expedition “El Golfo 6311-12” of Scripps Institution of Oceanography. Sci. Mar. 2006, 70, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, S. Zoogeography of the Sea; Sidgwick & Jackson, Ltd.: London, UK, 1953; p. 417. [Google Scholar]
- Izuka, A. On the pelagic annelids of Japan. J. Coll. Sci. Imp. Univ. Tokyo 1914, 36, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Álamo, M.A. Composición, densidad y distribución de los poliquetos planctónicos (Phyllodocida: Tomopteridae) en el Domo Térmico de Costa Rica, Pacífico Tropical Oriental. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2020, 68, S238–S247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmo, R.; Bergamasco, A.; Minutoli, R.; Patti, F.P.; Belmonte, G.; Spanò, N.; Zagami, G.; Bonanzinga, V.; Guglielmo, L.; Granata, A. The Otranto Channel (South Adriatic Sea), a hot-spot area of plankton biodiversity: Pelagic polychaetes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, C. Die pelagische Thierwelt in groesseren Meerestiefen. Bibl. Zool. Cassel 1887, 1, 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, R.S. Family Tomopteridae. In Polychaetes & Allies: The Southern Synthesis. Fauna of Australia. Vol. 4A. Polychaeta, Myzostomida, Pogonophora, Echiura, Sipuncula; Beesley, P.L.G., Ross, J.B., Glasby, C.J., Eds.; CSIRO Publishing: Melbourne, Australia, 2000; pp. 167–168. [Google Scholar]
- Glasby, C.J.; Hutchings, P.A.; Fauchald, K.; Paxton, H.; Rouse, G.W.; Watson Russell, C.; Wilson, R.S. Class Polychaeta. In Polychaetes & Allies: The Southern Synthesis. Fauna of Australia. Vol. 4A. Polychaeta, Myzostomida, Pogonophora, Echiura, Sipuncula; Beesley, P.L.G., Ross, J.B., Glasby, C.J., Eds.; CSIRO Publishing: Melbourne, Australia, 2000; pp. 1–296. [Google Scholar]
- Struck, T.H.; Halanych, K.M. Origins of holopelagic Typhloscolecidae and Lopadorhynchidae within Phyllodocidae (Phyllodocida, Annelida). Zool. Scr. 2010, 39, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, A.; Pleijel, F. Chimaeras and the origins of the holopelagic annelids Typhloscolecidae and Lopadorhynchidae: A reply to Struck & Halanych (2010). Zool. Scr. 2011, 40, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigenbaum, D. Predation on chaetoganths by typhloscolecid polychaetes, one explanation for headless specimens. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 1979, 59, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øresland, V.; Pleijel, F. An ectoparasitic typhloscolecid polychaete on the chaetognath Eukronia hamata from the Antarctic Peninsula. Mar. Biol. 1991, 108, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øresland, V.; Bray, R.A. Parasites and headless chaetognaths in the Indian Ocean. Mar. Biol. 2005, 147, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Álamo, M.A. Typhloscolecidae Uljanin, 1878. In Poliquetos (Annelida: Polychaeta) de México y América Tropical; León-González, J.A.B.-Z., Bastida Zavala, J.R., Carrera-Parra, L.F., García-Garza, M.E., Peña-Rivera, A., Salazar-Vallejo, S.I., Solís-Weiss, V., Eds.; Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León: Monterrey, Mexico, 2009; pp. 671–675. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, S.J. Polychaetes: British Chrysopetaloidea, Pisionoidea, and Aphroditoidea. Synop. Br. Fauna 1997, 54, 1–202. [Google Scholar]
- Buzhinskaja, G. Two new genera of the pelagic family Yndolaciidae (Polychaeta) from the Arctic Ocean with an addition to the description of Yndolacia lopadorrhynchoides Stöp-Bowitz. Sarsia 2004, 89, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Álamo, M.A.; Tejera, E.; León, M.E. Poliquetos pelágicos de las Islas de Cabo Verde: Resultados de la campaña TFMCBM/98, Proyecto Macaronesia 2000. Rev. Acad. Canar. Cienc. Folia Canar. Acad. Sci. 2003, 15, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhadan, A.E.; Tzetlin, A.B. Polychaetes from deep pelagic zone of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Invertebr. Zool. 2008, 5, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrzavý, J.; Ríha, P.; Piálek, L.; Janouskovec, J. Phylogeny of Annelida (Lophotrochozoa): Total-evidence analysis of morphology and six genes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pleijel, F.; Dahlgren, T.G. Position and delineation of Chrysopetalidae and Hesionidae (Annelida, Polychaeta, Phyllodocida). Cladistics 1998, 14, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinsen, G.M.R. Systematisk geografisk Oversigt over do Nordiske Annulata, Gephyrea, Choetognathi, og Balanoglossi; II. Vidensk. Medd. Fra Dan. Nat. Foren. I Kjφbenhavn 1883, 4, 92–350. [Google Scholar]
- Hatschek, B. System der Anneliden, ein vorläufiger Bericht. Lotos 1893, 13, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Grube, A.E. Annulata Örstediana. Enumeratio Annulatorum, quae in itinere per Indiam occidentalem et Americam centralem annis 1845–1848 suscepto legit cl. A. S. Örsted, adjectis speciebus nonnullis a cl. H. Kröyero in itinere ad Americam meridionalem collectis. (Fortsaettelse). [Part 2]. Vidensk. Medd. Fra Dan. Nat. Foren. I Köbenhavn 1857, 1857, 158–186. [Google Scholar]
- Kinberg, J.G.H. Annulata nova. Continuatio. [various errantia & sedentaria]. Ofvers. Afk. Vetensk. Forh. Stockh. 1867, 22, 239–258. [Google Scholar]
- Cuvier, G.L. Le Règne Animal Distribué D’après Son Organisation, pour Servir de Base à L’histoire Naturelle des Animaux et D’introduction à L’anatomie Comparée. Vol. 4 Les Zoophytes, les Tables, et les Planches; Deterville: Paris, France, 1817. [Google Scholar]
- Fauchald, K. Nephtyidae (Polychaeta) from the Bay of Nha Trang, South Vietnam. Sci. Res. Mar. Invert. S. China Sea G. Thailand, 1959–61. NAGA Rep. 1968, 4, 5–33. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, H. Polychaetenstudien. IV- Zur polychaetenfauna der Barents-See. Kiel. Meeresforsch. 1939, 3, 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- Grube, A.E. Anneliden-Ausbeute S.M.S. Gazelle. Mon. K. Preuss. Akad. Wiss. Zu Berl. 1877, 509–554. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers, E. Report on the annelids of the dredging expedition of the U.S. coast survey steamer Blake. Mem. Mus. Comp. Zool. Harv. Coll. 1887, 15, 1–335. [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel, P. Annélides polychètes non-pélagiques provenant des campagnes de l’Hirondelle et de la Princesse-Alice (1885–1910). Résultats Des. Camp. Sci. Accompl. Sur Son Yatch Par Albert Ier Prince Souver. Monaco 1914, 46, 1–432. [Google Scholar]
- Benham, W.B. Report on the Polychaeta obtained by the F.I.S. ‘Endeavour’ on the coasts of New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania and South Australia. Part 2. In Fisheries. Zoological (and Biological) results of the Fishing Experiments carried out by F.I.S. "Endeavour", 1909–1914; H.C. Dannevig: Sydney, Australia, 1916; Volume 4, pp. 127–169. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, O. Polychaetous annelids. Part II. Chrysopetalidae to Goniadidae. Allan Hancock Pac. Exped. 1940, 7, 173–287. [Google Scholar]
- Petterson, H.; Jerlov, N.G.; Kullenberg, B. Reports of the Swedish Deep-Sea Expedition 1947–1948; Swedish National Scientific Research Council: Stockholm, Sweden, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Dnestrovskaya, N.Y.; Jirkov, I.A. Nephtyidae Grube, 1850. In Polikhety Severnogo Ledovitogo Okeana [Polychaeta of the Arctic Ocean]; Jirkov, I.A., Ed.; Yanus-K Press: Moscow, Russia, 2001; pp. 181–212. [Google Scholar]
- Dnestrovskaya, N.Y.; Jirkov, I.A. Micronephthys (Polychaeta: Nephtyidae) of Northern Europe and Arctic. Invertebr. Zool. 2010, 7, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dnestrovskaya, N.Y.; Jirkov, I.A. Identification key for Nephtyidae (Polychaeta) of the eastern Atlantic and the North Polar Basin. Invertebr. Zool. 2012, 9, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauchald, K. Nephtyidae (Polychaeta) from Norwegian waters. Sarsia 1963, 13, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foret-Montardo, P. Étude systématique et écologique des Nephtyidae (Polychètes Errantes) des parages de Marseille. Téthys 1969, 1, 807–832. [Google Scholar]
- Jirkov, I.A.; Paraketsova, N. Review of the species of the genus Micronephthys (Polychaeta: Nephthyidae) from the white sea. Zool. Zhurnal 1996, 75, 831–840. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Laborda, A.J. Annelida, Polychaeta I. In Fauna Iberica, 25th ed.; Viéitez, J.M., Alós, C., Parapar, J., Besteiro, C., Moreira, J., Nuñez, J., Laborda, A.J., San Martin, G., Eds.; Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales (MNCN–CSIC): Madrid, Spain, 2004; pp. 390–419. [Google Scholar]
- Rainer, S.F. Nephtys pente sp. nov. (Polychaeta: Nephtyidae) and a Key to Nephtys from Northern Europe. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1984, 64, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainer, S.F. Redescription of Nephtys assimilis and N. kersivalensis (Polychaeta: Phyllodocida) and a key to Nephtys from Northern Europe. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1989, 69, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainer, S.F. The genus Nephtys (Polychaeta: Phyllodocida) in Northern Europe: Redescription of N. hystricis and N. incisa. J. Nat. Hist. 1990, 24, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainer, S.F. The genus Nephtys (Polychaeta: Phyllodocida) of northern Europe: A review of species, including the description of N. pulchra sp. n. and a key to the Nephtydae. Helgoländer Meeresunters. 1991, 45, 65–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rainer, S.F. Nephtyid Polychaetes from the Faroe Islands. Northurlandahsth Arsrit 1992, 1991–1992, 80–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ravara, A.; Cunha, M.R.; Pleijel, F. Nephtyidae (Annelida, Polychaeta) from southern Europe. Zootaxa 2010, 2682, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, O. Review of the annelid worms of the family Nephtyidae from the Northeast Pacific, with descriptions of five new species. Proc. United States Natl. Mus. 1938, 85, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, O. Polychaeta Errantia of the Antarctica. Antarct. Res. Ser. 1964, 3, 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, O. Polychaeta from the Weddel Sea quadrant, Antarctica. Antarct. Res. Ser. 1978, 26, 125–223. [Google Scholar]
- Alalykina, I.L.; Dnestrovskaya, N.Y.; Jirkov, I.A. Identification key to Nephtyidae (Annelida) of the Sea of Okhotsk. ZooKeys 2017, 684, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon-Bridges, K.; Gladstone, W.; Hutchings, P. One new species of Micronephthys Fredrich, 1939 and one new species of Nephtys Cuvier, 1817 (Polychaeta: Phylllodocidae: Nephtyidae) from eastern Australia with notes on Aglaophamus australiensis (Fauchald, 1965) and a key to all Australian species. Zootaxa 2014, 3872, 513–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dnestrovskaya, N.Y. Identification key to Nephtyidae (Annelida) of the Black Sea. ZooKeys 2020, 908, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauchald, K. Some Nephtyidae (Polychaeta) from Australian waters. Rec. Aust. Mus. 1965, 26, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franco, N.B.; Rizzo, A.E. Nephtyidae (Annelida: Polychaeta) from the Campos Basin, including two new species and a new record. Zootaxa 2016, 4114, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, O.; Fauchald, K. Deep-water benthic polychaetous annelids off New England to Bermuda and other North Atlantic Areas. Part II. Allan Hancock Monogr. Mar. Biol. 1971, 6, 1–327. [Google Scholar]
- Hilbig, B. The annelida. Part 1. Oligochaeta: Phyllodocida (Phyllodocidae to Paralacydoniidae). In Taxonomic Atlas of the Benthic Fauna of the Santa Maria Basin and the Western Santa Barbara Channel; Blake, J.A., Hilbig, B., Scott, P.H., Eds.; US Department of the Interior, Minerals Management Service, Pacific OCS Region: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 1997; Volume 42, pp. 317–349. [Google Scholar]
- Imajima, M.; Takeda, Y. Nephtyidae (Polychaeta) from Japan. I. The genera Inermonephtys, Micronephtys and Aglaophamus. Bull. Natl. Sci. Mus. Tokyo 1985, 11, 57–90. [Google Scholar]
- Imajima, M.; Takeda, Y. Nephtyidae (Polychaeta) from Japan. II. The genera Dentinephtys and Nephtys. Bull. Natl. Sci. Mus. Tokyo 1987, 13, 41–77. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, R.H.; Hong, J.S. Nephtyidae (Annelida: Polychaeta) from the Yellow Sea. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1997, 60, 371–384. [Google Scholar]
- Lana, P.C. Nephtyidae (Annelida: Polychaeta) do litoral do estado do Paraná (Brasil). Nerítica 1986, 1, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, A.; Wong, E.; Hutchings, P.A. Nephtyidae (Annelida: Phyllodocida) of Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Zootaxa 2015, 4019, 414–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nateewathana, A.; Hylleberg, J. Nephtyid polychaetes from the west coast of Phuket Island, Andaman Sea, Thailand with description of five new species. Proc. Linn. Soc. New South. Wales 1986, 108, 195–215. [Google Scholar]
- Paxton, H. Contribution to the study of Australian Nephtyidae (Polychaeta). Rec. Aust. Mus. 1974, 29, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Torrijos, J.; Hernández-Alcántara, P.; Solís-Weiss, V. Nephtyidae (Polychaeta) from the Gulf of California (Mexican Pacific) with the description of two new species of Aglaophamus. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2009, 89, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainer, S.F.; Hutchings, P. Nephtyidae (Polychaeta: Errantia) from Australia. Rec. Aust. Mus. 1977, 31, 307–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rainer, S.F.; Kaly, U.L. Nephtyidae (Polychaeta: Phyllodocida) of Australia: New species from the North West Shelf, and a key to Australian species. J. Nat. Hist. 1988, 22, 685–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.E.; Amaral, A.C.Z. Nephtyidae (Annelida: Polychaeta) from São Paulo state, Brazil, including a new record for the Brazilian coast. Biota Neotrop. 2007, 7, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rozbaczylo, N.; Castilla, J.C. La familia Nephtyidae en Chile (Annelida, polychaeta). Stud. Neotrop. Fauna 1974, 9, 179–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.L. Chapter 35. Family Nephtyidae Grube, 1850. In Taxonomic Guide to the Polychaetes of the Northern of Gulf of Mexico; Uebelacker, J.M., Johnson, P.G., Eds.; Barry A. Vittor & Associates, Inc.: Mobile, AL, USA, 1984; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Pattaratumrong, M.S.; Wongkhamhaeng, K. The molecular Identification of Nephtys species (Polychaeta: Phyllodocida) from Songkhla Lake, Southern Thailand. Naresuan Univ. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravara, A.; Wiklund, H.; Cunha, M.R.; Pleijel, F. Phylogenetic relationships within Nephtyidae (Polychaeta, Annelida). Zool. Scr. 2010, 39, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.B. Observations on the food of Nephtys. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1962, 7, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, A.; Reise, K. Predatory effects of Nephtys hombergii on other polychaetes in tidal flat sediments. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1986, 34, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würzberg, L.; Peters, J.; Schüller, M.; Brandt, A. Diet insights of deep-sea polychaetes derived from fatty acid analyses. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2011, 58, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benham, W.B. Report on the Polychaeta obtained by the F.I.S. ’Endeavour’ on the coasts of New South. Wales, Victoria, Tasmania and South. Australia, Part. 1; H.C. Dannevig: Sydney, Australia, 1915; pp. 171–237. [Google Scholar]
- Eliason, A. Polychaeta. In Reports of the Swedish Deep-Sea Expedition 1947–1948; Petterson, H., Jerlov, N.G., Kullenberg, B., Eds.; Swedish National Scientific Research Council: Stockholm, Sweden, 1951; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Demopoulos, A.W.J.; Bourque, J.R.; Durkin, A.; Cordes, E.E. The influence of seep habitats on sediment macrofaunal biodiversity and functional traits. Deep Sea Res. Part. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2018, 142, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grupe, B.M.; Krach, M.L.; Pasulka, A.L.; Maloney, J.M.; Levin, L.A.; Frieder, C.A. Methane seep ecosystem functions and services from a recently discovered southern California seep. Mar. Ecol. 2015, 36, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levin, L.A.; Ziebis, W.; Mendoza, G.F.; Growney, V.A.; Tryon, M.D.; Brown, K.M.; Mahn, C.; Gieskes, J.M.; Rathaburn, A.E. Spatial heterogeneity of macrofauna at northern California methane seeps: Influence of sulfide concentration and fluid flow. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 265, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.; Velasco, F.; Olaso, I. Polychaete annelids in the diet of demersal fish from the southern shelf of the Bay of Biscay. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2003, 83, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadharajan, D.; Soundarapandian, P. Contribution of polychaetes in feeding capability of commercially important crabs, South East coast of India. Mar. Sci. Res. Dev. 2013, 3, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Day, J.H. The Polychaete fauna of South Africa. Part 2. Errant species from Cape shores and estuaries. Ann. Natal Mus. 1953, 12, 397–441. [Google Scholar]
- Meißner, K.; Darr, A.; Rachor, E. Development of habitat models for Nephtys species (Polychaeta: Nephtyidae) in the German Bight (North Sea). J. Sea Res. 2008, 60, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olive, P.J.W.; Garwood, P.R.; Bentley, M.G. Reproductive failure and oosorption in Polychaeta in relation to their reproductive strategies. Bull. Soc. Zool. Fr. 1981, 106, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Olive, P.J.W.; Morgan, P.J. The reproductive cycles of four British intertidal Nephtys species in relation to their geographical distribution (Polychaeta: Nephtyidae). In: Systematics, biology and morphology of world polychaeta. Proceedings of the Second International Polychaeta Conference. Ophelia 1991, 5, 351–361. [Google Scholar]
- Rainer, S.F. Distribution, growth and production of Nephtys hombergii and N. assimilis (Polychaeta: Nephtyidae) in benthic communities of the North Sea. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1991, 48, 330–345. [Google Scholar]
- Olive, P.J.W.; Garwood, P.R.; Bentley, M.G.; Wright, N.H. Reproductive success, relative abundance and population structure of two species of Nephtys in an estuarine beach. Mar. Biol. 1981, 63, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desroy, N.; Retière, C. The influence of structure and dynamics of infaunal predator populations on predatory activity: The example of Nephtys hombergii. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2003, 58, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern, R. Fauna of the Chilka Lake and also of fresh and brackish waters in other parts of India. Mem. Indian Mus. Calcutta 1921, 5, 563–659. [Google Scholar]
- Monro, C.A.A. On some freshwater polychaetes from Uruguay. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. Mus. Lond. 1937, 10, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.S. Polychaetes & Allies: The southern synthesis. Fauna of Australia. Vol. 4a Polychaeta, Myzostomida, Pogonophora, Echiura, Sipuncula. In Family Nephtyidae; Beesley, P.L., Ross, G.J.B., Glasby, C.J., Eds.; CSIRO Publishing: Melbourne, Australia, 2000; pp. 136–137. [Google Scholar]
- Perejaslavzeva, S.M. Supplementations to the fauna of the Black Sea. Proc. Soc. Nat. Kharkov Univ. 1891, 25, 235–274. [Google Scholar]
- Wesenberg-Lund, E. Polychaetes of the Iranian Gulf. Dan. Sci. Investig. Iran. 1949, 4, 247–400. [Google Scholar]
- Savigny, J.C. Troisième partie. Systèmes de diverses classes d’animaux sans vertèbres. Système des annélides, principalement de celles des côtes de l’Égypte et de la Syrie, offrant les charactères tant distinctifs que naturels des Ordres, Familles et Genres, avec la description des espèces. Descr. L’egyptehist. Nat. 1822, 3, 1–128. [Google Scholar]
- Böggemann, M. Polychaeten aus der Deutschen Bucht. Taxonomische Beabeitung und Dokumentation der vom Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg hauptsachlich in der Deutschen Bucht gesammelten Polychaeten. C. Forschung. Senckenb. 1997, 202, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Malm, A.W. Annulata i hafvet utmed Sveriges westkust och omkring Göteborg. Göteborgs K. Vetensk. Och Vitterh. Handl. 1874, 14, 67–105. [Google Scholar]
- Gravier, C. Contribution à l’étude des Annélides Polychètes de la Mer Rouge. Familles des Nereidiens, Aphroditiens, tribus des Polynoina, Sigalionina, familles des Amphinomiens, Palmyriens. Nouv. Arch. Mus. Paris Sér. 4 1902, 3, 147–268. [Google Scholar]
- Lamarck, J.B. Ordre Second. Radiaires Échinodermes. Hist. Nat. Des. Animaux Sans Vertèbres 1816, 2, 522–568. [Google Scholar]
- Marenzeller, E. Südjapanische Anneliden.III. Denkschr. Akad. Wiss. Wien. 1902, 72, 563–582. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, J.X.; Troschel, F.H. System der Asteriden; F. Papier, Druck und Verlag von Friedrich Vieweg und Son: Brünswick, Germany, 1842. [Google Scholar]
- Seidler, H.J. Beitrage zur kenntnis der Polynoiden, I. Arch. Nat. Berl. 1923, 89, 1–217. [Google Scholar]
- Uschakov, P.V.; Reish, D.J.; Fauchald, K. Phylogenetic relationships in the family Polynoidae (Polychaeta). In Essays on Polychaetous Annelids in Memory of Dr. Olga Hartman; University of Southern California, Allan Hancock Press: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1977; pp. 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Struck, T.H.; Purschke, G.; Halanych, K.M. A scaleless scale worm: Molecular evidence for the phylogenetic placement of Pisione remota (Pisionidae, Annelida). Mar. Biol. Res. 2005, 1, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, H.; Nygren, A.; Pleijel, F.; Sundberg, P. Phylogeny of Aphroditiformia (Polychaeta) based on molecular and morphological data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 37, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norlinder, E.; Nygren, A.; Wiklund, H.; Pleijel, F. Phylogeny of scale-worms (Aphroditiformia, Annelida), assessed from 18SrRNA, 28SrRNA, 16SrRNA, mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI), and morphology. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 65, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Rouse, G.W.; Wiklund, H.; Pleijel, F.; Watanabe, H.K.; Chen, C.; Qian, P.-Y.; Qiu, J.-W. Phylogeny, evolution and mitochondrial gene order rearrangement in scale worms (Aphroditiformia, Annelida). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 125, 200–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifácio, P.; Menot, L. New genera and species from the Equatorial Pacific provide phylogenetic insights into deep-sea Polynoidae (Annelida). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2018, 185, 555–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettibone, M.H. Revision of the genus Macellicephala McIntosh and the subfamily Macellicephalinae Hartmann-Schröder (Polychaeta: Polynoidae). Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 1976, 229, 1–71. [Google Scholar]
- Uschakov, P.V. Polychaetes of the Suborder Aphroditiformia of the Arctic Ocean and the Northwestern Part of the Pacific, Families Aphroditidae and Polynoidae. Fauna Sssrmnogoshchetinkovyye Chervi 1982, 2, 1–272. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tebble, N.; Chambers, S. Polychaetes from Scottish Waters, Part. 1. Family Polynoidae; Royal Scottish Museum: Edinburgh, UK, 1982; p. 73. [Google Scholar]
- Britayev, T.A.; Fauchald, K. New species of symbiotic scaleworms Asterophilia (Polychaeta, Polynoidae) from Vietnam. Invertebr. Zool. 2005, 2, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, G. Diagnoses préliminaires de vingt-huit espèces nouvelles de stomatopodes et décapodes macroures de la Mer Rouge. Bull. Mus. D’hist. Nat. Paris 1904, 10, 228–238. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, J.E. XXXII. A synopsis of the genera and species of the class Hypostoma (Asterias, Linnaeus). Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 1840, 6, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, W.E. Annulosa. In Encyclopedia Britannica, Supplement to the Fourth, Fifth and Sixth Editions; Encyclopedia Britannica, Inc.: London, UK, 1816; Volume 1, pp. 401–453. [Google Scholar]
- Malmgren, A.J. Nordiska Hafs-Annulater. [part one of three]. Öfvers. Königlich Vetensk. Förhandlingarstockholm 1865, 22, 51–110. [Google Scholar]
- Nygren, A.; Norlinder, E.; Panova, M.; Pleijel, F. Colour polymorphism in the polychaete Harmothoe imbricata (Linnaeus, 1767). Mar. Biol. Res. 2011, 7, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettibone, M.H. A new scale-worm commensal with deep-sea mussels on the Galapagos hydrotermal vent (Polychaeta: Polynoidae). Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1984, 97, 226–239. [Google Scholar]
- Delle Chiaje, S. Descrizione et Notomia Degli Animali Invertebrati de la Sicilia Cateriore Oservati Vivi Negli Anni 1822–1830; Batelli & Co.: Naples, Italy, 1841; Volume 5, pp. 1–137. [Google Scholar]
- Pettibone, M.H.; Reish, D.J.; Fauchald, K. Review of Halosydnopsis and related genera (Polychaeta: Polynoidae: Lepidonotinae). In Essays on Polychaetous Annelids in Memory of Dr. Olga Hartman; The Allan Hancock Foundation, University of Southern California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1977; pp. 39–62. [Google Scholar]
- Pettibone, M.H. Scaled polychaetes (Polynoidae) associated with ophiuroids and other invertebrates and review of species referred to Malmgrenia McIntosh and replaced by Malmgeniella Hartman, with descriptions of new taxa. Smithson. Contrib. Zool. 1993, 538, 1–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemésio, A. A replacement name for Wilsoniella Pettibone, 1993 (Annelida: Polynoidae), junior homonym of Wilsoniella Khalfin, 1939 (Brachiopoda: Rhynchonellida), and revalidation of Pessoaiella Guimarães, 1940 over Wilsoniella Eichler, 1940 (Phthiraptera: Ischnocera: Philopteridae) also a junior homonym of Wilsoniella Khalfin, 1939. Zootaxa 2006, 1260, 67–68. [Google Scholar]
- Serpetti, N.; Taylor, M.L.; Brennan, D.; Green, D.H.; Rogers, A.D.; Paterson, G.L.J.; Narayanaswamy, B.E. Ecological adaptations and commensal evolution of the Polynoidae (Polychaeta) in the Southwest Indian Ocean Ridge: A phylogenetic approach. Deep Sea Res. Part. II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2017, 137, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, M.A.; Glover, A.G.; Wiklund, H. Polynoid polychaetes of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and a new holothurian association. Mar. Biol. Res. 2013, 9, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditlevsen, H. Annelids. I; H. Hagerup: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1917; Volume VI, p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Hanley, J.R.; Burke, M. A new genus and species of commensal scaleworm (Polychaeta, Polynoidae) from Broome, Western Australia. Beagle Rec. Mus. Art Gall. North. Territ. 1989, 6, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Pettibone, M.H. Review of some species referred to Scalisetosus McIntosh (Polychaeta, Polynoidae). Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1969, 82, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, O. A review of the types of polychaetous annelids at the Peabody Museum of Natural History, Yale University. Bull. Bingham Oceanogr. Coll. 1942, 8, 1–98. [Google Scholar]
- Michaelsen, W. Polychaeten von Ceylon. Jb. Hamb. Wiss. Anst. 1892, 9, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings, P.A.; Murray, A. Taxonomy of Polychaetes from the Hawkesbury River and the Southern Estuaries of New South Wales, Australia. Rec. Aust. Mus. 1984, 36, 1–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, B.C.; Martínez, A.; Borda, E.; Iliffe, T.M.; Fontaneto, D.; Worsaae, K. Genetic spatial structure of an anchialine cave annelid indicates connectivity within—But not between—Islands of the Great Bahama Bank. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2017, 109, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarvala, J. Ecology of Harmothoe sarsi (Malmgren) (Polychaeta, Polynoidae) in the northern Baltic area. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 1971, 8, 231–309. [Google Scholar]
- Plyuscheva, M.; Martin, D.; Britayev, T.A. Diet analyses of the scale-worms Lepidonotus squamatus and Harmothoe imbricata (Polychaeta, Polynoidae) in the White Sea. Mar. Biol. Res. 2010, 6, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbruyères, D.; Laubier, L. Exploitation d’une source de matière organique concentrée dans l’océan profond: Intervention d’une annélide polychète nouvelle [Exploitation of a concentrated organic matter source in the deep sea: Role of a new polychaetous annelid]. C. R. Hebdomaidaire Des. Séances L’acad. Des. Sci. 1988, 307, 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Hatch, A.S.; Liew, H.; Hourdez, S.; Rouse, G.W. Hungry scale worms: Phylogenetics of Peinaleopolynoe (Polynoidae, Annelida), with four new species. ZooKeys 2020, 932, 27–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, M.; Piroddi, C.; Steenbeek, J.; Kaschner, K.; Ben Rais Lasram, F.; Aguzzi, J.; Ballesteros, E.; Bianchi, C.N.; Corbera, J.; Dailianis, T.; et al. The biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Estimates, patterns and treats. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiseleva, M.I. Mnogoshchetinkovye Chervi (Polychaeta) Chernogo i Azovskogo Morei [Polychaeta from the Black and Azov Seas]; Russian Academy of Sciences, Kola Scientific Center, Murmansk Marine Biological Institute: Murmansk, Russian; National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, A.O. Kovalevsky Institute of Biology of the South Seas, Apatity, KSCRAN Publications: Kiev, Ukraine, 2004.
- Horst, R. On new and little-known species of Polynoinae from the Netherland’s East Indies. Zool. Meded. Leiden 1915, 1, 2–20. [Google Scholar]
- Potts, F.A. Polychaeta of the Indian ocean. Pt. 2. The Palmyridae, Aphroditidae, Polynoidae, Acoetidae and Sigalionidae. Trans. Linn. Soc. Zool. 1910, 16, 325–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnich, R.; Fiege, D.; Sun, R. Polychaeta (Annelida) of Hainan Island, South China Sea Part III. Aphroditoidea. Species Divers. 2004, 9, 285–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Britayev, T.A.; Antokhina, T.I. Chapter 1. Symbiotic polychaetes of from the Bay of Nhatrang Bay, Vietnam. In Benthic fauna of the Bay of Nhatrang, Southern Vietnam. Volume 2; Britayev, T.A., Pavlov, D.S., Eds.; KMK Scientific Press Ltd.: Moscow, Russia, 2012; Volume 2, pp. 11–54. [Google Scholar]
- Salazar-Vallejo, S.I.; Carrera-Parra, L.F.; Muir, A.I.; León-González, J.A.d.; Piotrowsky, C.; Sato, M. Polychaete species (Annelida) described from the Philippine and China Seas. Zootaxa 2014, 3842, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasby, C.J.; Lee, Y.-L.; Hsueh, P.-W. Marine Annelida (excluding clitellates and siboglinids) from the South China Sea. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2016, (Suppl. 34), 178–234. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Pan-Wen-Hsueh-2/publication/306216590_Marine_Annelida_excluding_clitellates_and_siboglinids_from_the_South_China_Sea/links/57f3505908ae280dd0b56b0c/Marine-Annelida-excluding-clitellates-and-siboglinids-from-the-South-China-Sea.pdf (accessed on 4 February 2021).
- Ravara, A.; Cunha, M.R. Two new species of scale worms (Polychaeta: Aphroditiformia) from deep-sea habitats in the Gulf of Cadiz (NE Atlantic). Zootaxa 2016, 4097, 422–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taboada, S.; Silva, A.S.; Neal, L.; Cristobo, J.; Ríos, P.; Álvarez-Campos, P.; Hestetun, J.T.; Koutsouveli, V.i.; Sherlock, E.; Riesgo, A. Insights into the symbiotic relationship between scale worms and carnivorous sponges (Cladorhizidae, Chondrocladia). Deep Sea Res. Part. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2020, 156, 103191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada, S.; Serra Silva, A.; Díez-Vives, C.; Neal, L.; Cristobo, J.; Ríos, P.; Hestetun, J.T.; Clark, B.; Rossi, M.E.; Junoy, J.; et al. Sleeping with the enemy: Unravelling the symbiotic relationships between the scale worm Neopolynoe chondrocladiae (Annelida: Polynoidae) and its carnivorous sponge hosts. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, zlaa146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Assis, J.E.; de Souza, J.R.B.; de Lima, M.M.; de Lima, G.V.; Cordeiro, R.T.S.; Pérez, C.D. Association between deep-water scale-worms (Annelida: Polynoidae) and black corals (Cnidaria: Antipatharia) in the Southwestern Atlantic. Zoologia 2019, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barnich, R.; Beuck, L.; Freiwald, A. Scale worms (Polychaeta: Aphroditiformia) associated with cold-water corals in the eastern Gulf of Mexico. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2013, 93, 2129–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, V.d.R.; Brasil, A.C.S. Two new species and a new record of Scale-worms (Polychaeta) from Southwest Atlantic deep-sea coral mounds. Zootaxa 2014, 3856, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaparelli, S.; Alvaro, M.C.; Bohn, J.; Albertelli, G. ‘Hitchhiker’ polynoid polychaetes in cold deep waters and their potential influence on benthic soft bottom food webs. Antarct. Sci. 2010, 22, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettibone, M.H. A new scale worm commensal with deep-sea mussels in the seep-sites at the Florida Escarpment in the Eastern Gulf of Mexico (Polychaeta: Polynoidae: Branchipolynoidae). Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1986, 99, 444–451. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, M.E.; Britayev, T.A. A new genus and species of polynoid scaleworm commensal with Chaetopterus appendiculatus Grube from the Banda Sea (Annelida: Polychaeta), with a review of commensals of Chaetopteridae. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1997, 60, 261–276. [Google Scholar]
- Britayev, T.A.; Mekhova, E.; Deart, Y.; Martin, D. Do syntopic host species harbour similar symbiotic communities? The case of Chaetopterus spp. (Annelida: Chaetopteridae). PeerJ 2017, 5, e2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, W.C.H. Über die Gattung Bdella, Savigny, (Limnatis, Moquin-Tandon) und die in Mossambique beobachteten Anneliden, wovon hier eine Mittheilung folgt [informal title in meeting report]. Ber. Über Die Zur Bekanntm. Geeigneten Verh. Königlichen Preuss. Akad. Wiss. Zu Berl. 1854, 21, 607–614. [Google Scholar]
- Britayev, T.A.; Zamyshliak, E.A. Association of the commensal scaleworm Gastrolepidia clavigera (Polychaeta: Polynoidae) with holothurians near the coast of South Vietnam. Ophelia 1996, 45, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dales, R.P. Interrelations of organisms. A. Commensalism. In Treatise on marine ecology and palaeecology (Ed. J.W. Hedgpeth). Mem. Geol. Soc. Am. 1957, 67, 391–412. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, R.H.; Phillips, D.W.; Standing, J.D.; Hand, C. Commensalism or mutualism: Atraction of a sea star towards a symbiotic polychaete. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1979, 39, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Camillo, C.G.; Martin, D.; Britayev, T.A. Symbiotic association between Solanderia secunda (Cnidaria, Hydrozoa, Solanderiidae) and Medioantenna variopinta sp. nov. (Annelida, Polychaeta, Polynoidae) from North Sulawesi (Indonesia). Helgol. Mar. Res. 2011, 65, 495–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inaba, M. Soshu, Miura, Misaki ni oide edaru Hydroidea. [The hydroids collected at Miura and Misaki in Soshu.]. Zool. Mag. 1892, 4, 124–131. [Google Scholar]
- Sars, G.O. Bidrag til Kundskaben om Dyrelivet paa vore Havbanker. Forh. Vidensk. Selsk. I Christiania 1873, 1872, 73–119. [Google Scholar]
- Britayev, T.A.; Mekhova, E.S. Assessment of hidden diversity of crinoids and their symbionts in the Bay of Nhatrang, Vietnam. Org. Divers. Evol. 2011, 11, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marudhupandi, T.; Kumar, T.T.A.; Prakash, S.; Gopi, M.; Balasubramanian, T. A first report of symbiotic polychaete scale worm Gastrolepidia clavigera Schmarda, 1861 (Phyllodocida: Polynoidae) from Lakshadweep Archipelago, India. J. Treatened Taxa 2014, 6, 3685–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Britayev, T.A.; Lyskin, S.A. Feeding of the symbiotic polychaete Gastrolepidia clavigera (Polynoidae) and its interactions with its hosts. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2002, 385, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.R. A new host and locality records of the commensal Adyte crinoidicola (Polychaeta, Polynoidae). Beagle Rec. Mus. Art Gall. North. Territ. 1984, 1, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Hanley, J.R. Revision of the scaleworm genera Arctonoe Chamberlin and Gastrolepidia Schmarda (Polychaeta, Polynoidae) with the erection of a new subfamily, Arctonoinae. Beagle Rec. Mus. Art Gall. North. Territ. 1989, 6, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama, T.; Jimi, N.; Goto, R. Widening the host range of the ectosymbiotic scale-worm Asterophilia culcitae (Annelida: Polynoidae) to three echinoderm classes, with data on its body color variation. Plankton Benthos Res. 2020, 15, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willey, A. Report on the Polychaeta collected by Professor Herdman, at Ceylon, in 1902. Rep. Gov. Ceylon Pearl Oys 1905, 30, 212–324. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, H.P. A preliminary account of the marine annelids of the Pacific coast, with descriptions of new species. Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 1897, 1, 153–199. [Google Scholar]
- Britayev, T.A.; Ivashchenko, N.I.; Litvinov, E.G. Peculiarities of the commensal complex in the polychaete Arctonoe vittata. Biol. Morya 1977, 1978, 76–78. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.; Lee, S.; Kim, W. New record of commensal scale worms, Arctonoe vittata (Grube, 1855) and Hyperhalosydna striata (Kinberg, 1856)(Polychaeta: Polynoidae) from Korean waters. J. Species Res. 2016, 5, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokaji, H.i.; Nakahara, K.; Goshima, S. Host switching improves survival rate of the symbiotic polychaete Arctonoe vittata. Plankton Benthos Res. 2014, 9, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davenport, D. Studies in the physiology of commensalism. I. The polynoid genus Arctonoë. Biol. Bull. 1950, 98, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagu, G., II. Description of several Marine Animals found on the South Coast of Devonshire. Trans. Linn. Soc. Lond. 1808, 9, 81–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conradi, M.; Bandera, M.E.; Marin, I.; Martin, D. Polychaete-parasitizing copepods from the deep-sea Kuril-Kamchatka Trench (Pacific Ocean), with the description of a new species of Ophelicola. Deep Sea Res. Part. II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2015, 111, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capa, M.; Aguado, M.T.; Bakken, T. Phylogenetic hypothesis of Sphaerodoridae Malmgren, 1867 (Annelida) and its position within Phyllodocida. Cladistics 2016, 32, 335–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capa, M.; Bakken, T. Revision of the Australian Sphaerodoridae (Annelida) including the description of four new species. Zootaxa 2015, 4000, 227–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruderman, L. Recherches sur Ephesia gracilis Rathke, Annélide polychète de la famille des sphaerodorides; morphologie, anatomie, histologie. Mém. Soc. Zool. Fr. 1911, 24, 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, H. Morphologie der Polychaetengattung Sphaerodorum. Monographie. Zool. Jahrbücherabteilung Syst. Ökologie Und Geogr. Tiere 1933, 64, 41–110. [Google Scholar]
- Capa, M.; Bakken, T.; Meißner, K.; Nygren, A. Three, two, one! Revision of the long-bodied sphaerodorids (Sphaerodoridae, Annelida) and synonymization of Ephesiella, Ephesiopsis and Sphaerodorum. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capa, M.; Osborn, K.J.; Bakken, T. Sphaerodoridae (Annelida) of the deep Northwestern Atlantic, including remarkable new species of Euritmia and Sphaerephesia. ZooKeys 2016, 615, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capa, M.; Rouse, G.W. Sphaerodoridae (Annelida) from Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef, Australia, including the description of two new species and reproductive notes. Zootaxa 2015, 4019, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Capa, M.; Nygren, A.; Parapar, J.; Bakken, T.; Meißner, K.; Moreira, J. Systematic re-structure and new species of Sphaerodoridae (Annelida) after morphological revision and molecular phylogenetic analyses of the North East Atlantic fauna. ZooKeys 2019, 845, 1–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lützen, J. Sur une nouvelle espèce de Polychète, Sphaerodoridium commensalis n. gen., n. spec. (Polychaeta Errantia, famille des Sphaerodoridae) vivant en commensal de Terebellides stroemi Sars. Cah. Biol. Mar. 1961, 2, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Fauchald, K. Sphaerodoridae (Polychaeta: Errantia) from world-wide areas. J. Nat. Hist. 1974, 8, 257–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbruyères, D. Sphaerodoridae (Annélides Polychètes) profonds du Nord-Est Atlantique. Bull. Mus. D’hist. Nat. Paris 1980, 4, 109–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kudenov, J.D. Five new species of Sphaeroridae (Annelida: Polychaeta) from the Gulf of Mexico. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1987, 100, 927–935. [Google Scholar]
- Sardá-Borroy, R. Sphaerodoridae (Annelida, Polychaeta) from the region of the Gibraltar strait with description of Euritmia hamulisetosa gen. et sp. n. Zool. Scr. 1987, 16, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.E. A new species of Ephesiopsis (Polychaeta: Sphaerodoridae) from off southeastern Brazil. Zootaxa 2009, 2307, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, C.; Capa, M. Comparative analyses of morphological characters in Sphaerodoridae and allies (Annelida) revealed by an integrative microscopical approach. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 1, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, D.; Alvà, V. Sphaerodorum ophiurophoretos n. sp., une nouvelle éspece de Sphaerodoridae (Annelida, Polychaeta) commensal sur Amphipholis squamata (Echinodermata, Ophiuridae). Bull. L’inst. R. Des. Sci. Nat. Belg. Biol. 1988, 58, 45–49. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.P. Polychaetous annelids from Monterey Bay and San Diego, California. Proc. Acad. Nat. Sci. Phila. 1909, 61, 235–295. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, J.; Parapar, J. Sphaerodoridae (Annelida: Polychaeta) from the Bellingshausen Sea (Antarctica) with the description of two new species. Polar Biol. 2011, 34, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fauvel, P. Annélides Polychètes. Duc d’Orleans’ Campagne Arctique de 1907; Charles Bulens: Brussels, Belgium, 1911; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Kudenov, J.D. Four species of Sphaerodoridae (Anellida: Polychaeta) including one new genus and three new species from Alaska. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1987, 100, 917–926. [Google Scholar]
- Borowski, C. Three new deep-sea species of Sphaerodoridae (Annelida, Polychaeta) from the eastern tropical South Pacific. Zool. Scr. 1994, 23, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleijel, F. Sphaerodoridae Malmgren, 1867. In Polychaetes; Rouse, G.W., Pleijel, F., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 136–138. [Google Scholar]
- Capa, M.; Bakken, T.; Purschke, G. Sphaerodoridae Malmgren, 1867; De Gruyter: Ösnabruck, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann-Schröder, G. Zur kenntnis des eulitorals der Australischen küsten unter besonderer berücksichigung de Polychaeten und Ostracoden. Teil 6. Die Polychaeten der tropisch-subtropischen westküste Australiens (zwischen Exmouth im Norden und Cervantes im Süden). Mitt. Hambg. Zool. Mus. Inst. 1981, 78, 19–96. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, J.; Parapar, J. Two new species of Sphaerodoropsis Hartman & Fauchald, 1971 (Polychaeta: Sphaerodoridae) from Iceland (BIOICE programme). Mar. Biol. Res. 2012, 8, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villora-Moreno, S. Environmental heterogeneity and the biodiversity of interstitial Polychaeta. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1997, 60, 494–501. [Google Scholar]
- Worsaae, K.; Kristensen, R.M. Evolution of interstitial Polychaeta (Annelida). In Morphology, Molecules, Evolution and Phylogeny in Polychaeta and Related Taxa; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 319–340. [Google Scholar]
- Spalding, M.D.; Fox, H.E.; Allen, G.R.; Davidson, N.; Ferdaña, Z.A.; Max, F.; Halpern, B.S.; Jorge, M.A.; Lombana, A.; Lourie, S.A.; et al. Marine ecoregions of the world: A bioregionalization of coastal and shelf areas. Bioscience 2007, 57, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agassiz, A. On alternate generation of annelids and the embryology of Autolytus cornutus. J. Boston Soc. Nat. Hist. 1862, 7, 384–409. [Google Scholar]
- Langerhans, P. Die Wurmfauna von Madeira [part I]. Z. Wiss. Zool. 1879, 32, 513–592. [Google Scholar]
- Malaquin, A. Recherches sur les syllidiens: Morphologie, anatomie, reproduction, développement. Mém. Soc. Des. Sci. L’agric. Des. Arts Lille4e Sér. 1893, 18, 1–477. [Google Scholar]
- Rioja, E. Anélidos poliquetos de San Vicente de la Barquera (Cantábrico). Trab. Mus. Nac. Cienc. Nat. Ser. Zool. 1925, 53, 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Aguado, M.T.; San Martín, G. Phylogeny of Syllidae (Polychaeta) based on morphological data. Zool. Scr. 2009, 38, 379–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Martín, G. Annelida, Polychaeta II: Syllidade. In Fauna Iberica., vol. 21; Ramos, M.A., Alba, J., Bellés, X., Gosálbez, J., Guerra, A., Macpherson, E., Serrano, J., Templado, J., Eds.; CSIC: Madrid, Spain, 2003; Volume 21, p. 554. [Google Scholar]
- San Martín, G.; Aguado, M.T. Family Syllidae. In Handbook of Zoology Online, Annelida; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, O.F. Von Würmern des Süssen und Salzigen Wassers; H. Mumme and Faber: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1771; p. 200. [Google Scholar]
- Audouin, J.V.; Milne-Edwards, H. Recherches pour Servir a L’histoire Naturelle du Littoral de la France, ou, Recueil de Mémoires sur L’anatomie, la Physiologie, la Classification et les Moeurs des Animaux des nos Côtes: Ouvrage Accompagné de Planches Faites D’après Nature; Crochard: Paris, France, 1834. [Google Scholar]
- Licher, F. Revision der Gattung Typosyllis Langerhans, 1879 (Polychaeta: Syllidae). Morphologie, Taxonomie und Phylogenie. Abh. Senckenbergischen Nat. Ges. 1999, 551, 1–336. [Google Scholar]
- Nygren, A. Phylogeny and reproduction in Syllidae (Polychaeta). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. 1999, 126, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, A.; Sundberg, P. Phylogeny and evolution of reproductive modes in Autolytinae (Syllidae, Annelida). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 29, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, M.T.; Martin, S.; Siddall, G. Systematics and evolution of syllids. Annelidasyllidae. Cladistics 2012, 28, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, M.T.; Nygren, A.; Siddall, M.E. Phylogeny of Syllidae (Polychaeta) based on combined molecular analysis of nuclear and mitochondrial genes. Cladistics 2007, 23, 552–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, A. Revision of Autolytinae (Syllidae: Polychaeta). Zootaxa 2004, 680, 1–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Martín, G.; López, E.; Aguado, M.T. Revision of the genus Pionosyllis (Polychaeta: Syllidae: Eusyllinae), with a cladistic analysis, and the description of five new genera and two new species. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2009, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, M.T.; Bleidorn, C. Conflicting signal within a single gene confounds syllid phylogeny (Syllidae, Annelida). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 55, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, J.H. The polychaete fauna of South Africa Part 8: New species and records from grab samples and dredgings. Bull. Br. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1963, 10, 381–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, M.T.; Glasby, C.J.; Schroeder, P.l.C.; Weigert, A.; Bleidorn, C. The making of a branching annelid: An analysis of complete mitochondrial genome and ribosomal data of Ramisyllis multicaudata. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Augener, H. Polychaeta I. Errantia. In Die Fauna Südwest-Australiens. Ergebnisse der Hamburger Südwest-Australischen Forschungsreise l905; Michaelsen, W., Hartmeyer, R., Eds.; Gustav Fischer: Jena, Germany, 1913; Volume IV, pp. 65–304. [Google Scholar]
- San Martín, G.; Hutchings, P. Eusyllinae (Polychaeta: Syllidae) from Australia with the description of a new genus and fifteen new species. Rec. Aust. Mus. 2006, 58, 257–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguado, M.T.; Murray, A.; Hutchings, P.A. Syllidae (Annelida: Phyllodocida) from Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Zootaxa 2015, 4019, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, M.J.; San Martin, G. Syllidae (Annelida) from East Timor and the Philippines (Pacific Ocean), with the description of three new species of Syllis Savigny in Lamarck, 1818. Zootaxa 2020, 4834, 231–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann-Schröder, G. Die Polychaeten der tropischen Nordwestküste Australiens (Zwischen Port Samson in Norden und Port Hedland in Süden). Teil 2. In: Hartmann-Schröder, G. and Hartmann, G. (eds.), Zur Kenntnis des Eulitorals der australischen Küsten unter besonder Berücksichtigung der Polychaeten und Ostracoden. Mitt. Hambg. Zool. Mus. Inst. 1979, 76, 75–218. [Google Scholar]
- Glasby, C.J.; Watson, C. A new genus and species of Syllidae (Annelida: Polychaeta) commensal with octocorals. Beagle Rec. Mus. Art Gall. North. Territ. 2001, 17, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Glasby, C.J.; Schroeder, P.C.; Aguado, M.T. Branching out: A remarkable new branching syllid (Annelida) living in a Petrosia sponge (Porifera: Demospongiae). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2012, 164, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.P.; Ponz-Segrelles, G.; Helm, C.; Egger, B.; Aguado, M.T. A new species of Syllis Grube, 1850 including transcriptomic data and an updated phylogeny of Syllinae (Annelida: Syllidae). Mar. Biodivers. 2020, 50, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, M.T.; Richter, S.; Sontowski, R.; Golombek, A.; Struck, T.H.; Bleidorn, C. Syllidae mitochondrial gene order is unusually variable for Annelida. Gene 2016, 594, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Campos, P.; Riesgo, A.; Hutchings, P.; San Martin, G. The genus Syllis Savigny in Lamarck, 1818 (Annelida, Syllidae) from Australia. Molecular analysis and re-description of some poorly-known species. Zootaxa 2015, 4052, 297–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponz-Segrelles, G.; Ribeiro, R.P.; Bleidorn, C.; Aguado, M.T. Sex-specific gene expression differences in reproducing Syllis prolifera and Nudisyllis pulligera (Annelida, Syllidae). Mar. Genom. 2020, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponz-Segrelles, G.; Bleidorn, C.; Aguado, M.T. Expression of vasa, piwi, and nanos during gametogenesis in Typosyllis antoni (Annelida, Syllidae). Evol. Dev. 2018, 20, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.P.; Ponz-Segrelles, G.; Bleidorn, C.; Aguado, M.T. Comparative transcriptomics in Syllidae (Annelida) indicates that posterior regeneration and regular growth are comparable, while anterior regeneration is a distinct process. Bmc Genom. 2019, 20, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Martín, G.; Álvarez-Campos, P.; Hutchings, P. The genus Syllis Savigny in Lamarck, 1818 (Annelida: Syllidae: Syllinae) from Australia (second part): Four new species and re-description of twelve previously described species. Zootaxa 2017, 4237, 201–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguado, M.T.; San Martín, G. Re-description of some enigmatic genera of Syllidae (Phyllodocida: Polychaeta). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. United Kingd. 2008, 88, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, M.V.; San Martin, G.; Carrerette, O.; Paresque, K. On a new species of the rare syllid genus Exogonoides (Annelida, Phyllodocida, Syllidae). Zootaxa 2016, 4144, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claparède, É. Glanures zootomiques parmi les annélides de Port-Vendres (Pyrénées Orientales). Mém. Soc. Phys. D’hist. Nat. Gen. 1864, 17, 463–600. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, W.C. On a remarkably branched Syllis dredged by H.M.S. Challenger. J. Linn. Soc. 1879, 14, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleijel, F. Syllidae Grube, 1850. In Polychaetes; Rouse, G.W., Pleijel, F., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001; pp. 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- San Martín, G.; Aguado, M.T. Contribution of Scanning Electron Microscope to the study of morphology, biology, reproduction, and phylogeny of the family Syllidae (Polychaeta). In Scanning Electron Microscopy; Kazmiruk, V., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; Volume 8, pp. 129–145. [Google Scholar]
- Westheide, W.; Hass-Cordes, E. Molecular taxonomy: Description of a cryptic Petitia species (Polychaeta: Syllidae) from the island of Mahé (Seychelles, Indian Ocean) using RAPD markers and ITS2 sequences. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 2001, 39, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico, M.; da Cunha Lana, P.; Garraffoni, A.R.S. Distribution patterns of interstitial polychaetes in sandy beaches of southern Brazil. Mar. Ecol. 2009, 30, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, J.M.M.; San Martín, G.; Fukuda, M.V. On some exogonines (Polychaeta, Syllidae, Exogoninae) from the northern coast of the State of São Paulo, southeastern Brazil. Results of BIOTA/FAPESP/Bentos Marinho Project. Meiofauna Mar. 2004, 13, 45–77. [Google Scholar]
- Riera, R.; Núñez, J.; Brito, M.C. A new species of the interstitial genus Neopetitia (Polychaeta, Syllidae, Eusyllinae) from Tenerife, with modified acicular chaetae in males. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2007, 61, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barroso, R.; Paiva, P.C.D.; Nogueira, J.M.D.M.; Fukuda, M.V. Deep sea Syllidae (Annelida, Phyllodocida) from Southwestern Atlantic. Zootaxa 2017, 4221, 401–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böggemann, M.; Purschke, G. Abyssal benthic Syllidae (Annelida: Polychaeta) from the Angola Basin. Org. Divers. Evol. 2005, 5, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- San Martín, G. Deep sea Syllidae from the Pacific Ocean collected during cruises with the RV Sonne (Annelida, Polychaeta, Syllidae). Senckenbergiana Biol. 2004, 84, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hortal, J.; Jiménez-Valverde, A.; Gómez, J.F.; Lobo, J.M.; Baselga, A. Historical bias in biodiversity inventories affects the observed environmental niche of the species. Oikos 2008, 117, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomolino, M.V. Conservation Biogeography. Frontiers of Biogeography: New Directions in the Geography of Nature; Lomolino, M.V., Heaney, L.R., Eds.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- San Martín, G. Estudio Biogeográfico, Faunístico y Sistemático de los Poliquetos de la Familia Sílidos (Syllidae, Polychaeta) en Baleares. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Complutense, Madrid, Spain, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, T.H. Syllidae (Polychaeta), principlally from Florida, with descriptions of a new genus and twenty-one new species. Proc. Biol. Soc. Wash. 1980, 93, 1080–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Uebelacker, J.M. Chapter 30. Family Syllidae. In Taxonomic Guide to the Polychaetes of the Northern Gulf of Mexico; Uebelacker, J.M., Johnson, P.G., Eds.; Barry A. Vitor & Associated: Mobile, AL, USA, 1984; pp. 1–151. [Google Scholar]
- San Martín, G. Eusyllinae (Syllidae, polychaeta) from Cuba and Gulf of Mexico. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1990, 46, 590–619. [Google Scholar]
- San Martín, G. Grubeosyllis and Exogone (Exogoninae, Syllidae, Polychaeta) from Cuba, the Gulf of Mexico, Florida and Puerto Rico, with a revision of Exogone. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1991, 49, 715–740. [Google Scholar]
- San Martín, G. Syllis Savigny in Lamarck, 1818 (Polychaeta: Syllidae: Syllinae) from Cuba, The Gulf of Mexico, Florida and North Carolina, with a revision of several species described by Verrill. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1992, 51, 167–196. [Google Scholar]
- Capa, M.; San Martín, G.; López, E. Syllinae (Syllidae: Polychaeta) del Parque Nacional de Coiba, Panamá. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2001, 49, 103–115. [Google Scholar]
- Capa, M.; San Martín, G.; López. E. Autolytinae, Eusyllinae y Exogoninae (Syllidae: Polychaeta) del Parque Nacional de Coiba, Panamá. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2001, 49, 621–628. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann-Schröder, G. Zur kenntnis des eulitorals des Australischen küsten unter besonderer berücksichtigung der Polycheten und Ostracoden. Teil 2. Die Polychaeten der tropischen Nord westküste Australiens (zwischen Derby im Nordem und Port Hedland im Südem). Mitt. Hambg. Zool. Mus. Inst. 1979, 76, 75–218. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann-Schröder, G. Die Polychaeten der subtropisch-tropischen bis tropischen Ostkueste Australiens zwischen Maclean (New South Wales) und Gladstone (Queensland) sowie von Heron Island (Grosses Barrier Riff) IN: Hartmann-Schröder, Gesa and Gerd Hartmann. Zur Kenntnis des eulitorals der australischen Kuesten unter besounderer Beruecksichtigung des Polychaeten und Ostracoden. Teil 16. Mitt. Hambg. Zool. Mus. Inst. 1991, 88, 17–71. [Google Scholar]
- San Martin, G. Exogoninae (Polychaeta:Syllidae) from Australia with the description of a new genus and twenty-two new species. Rec. Aust. Mus. 2005, 57, 39–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- San Martín, G.; Hutchings, J.A.; Aguado, M.T. Syllinae (Polychaeta: Syllidae) from Australia. Part 1. Genera Branchiosyllis, Eurysyllis, Karroonsyllis, Parasphaerosyllis, Plakosyllis, Rhopalosyllis, Tetrapalpia n.gen., and Xenosyllis. Rec. Aust. Mus. 2008, 60, 119–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- San Martín, G.; Hutchings, P.; Aguado, M.T. Syllinae (Polychaeta: Syllidae) from Australia. Part 3. Genera Alcyonosyllis, Genus A, Parahaplosyllis, and Trypanosyllis (Trypanobia). Zootaxa 2010, 2493, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musco, L.; Giangrande, A. A new sponge-associated species, Syllis mayeri n. sp.(Polychaeta: Syllidae), with a discussion on the status of S. armillaris (Müller, 1776). Sci. Mar. 2005, 69, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musco, L.; Giangrande, A. Mediterranean Syllidae (Annelida: Polychaeta) revisited: Biogeography, diversity and species fidelity to environmental features. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 304, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, C.N. Biodiversity issues for the forthcoming tropical Mediterranean Sea. Hydrobiologia 2007, 580, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikac, B.; Musco, L. Faunal and biogeographic analysis of Syllidae (Polychaeta) from Rovinj (Croatia, northern Adriatic Sea). Sci. Mar. 2010, 74, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hutchings, P.A.; Lavesque, N. I know who you are, but do others know? Why correct scientific names are so important for the biological sciences. Zoosymposia 2020, 19, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattig, P.; San Martín, G.; Martin, D. Taxonomic and morphometric analyses of the Haplosyllis spongicola complex (Polychaeta: Syllidae: Syllinae) from Spanish seas, with re-description of the type species and descriptions of two new species. Sci. Mar. 2007, 71, 551–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lattig, P.; Martin, D. A taxonomic revision of the genus Haplosyllis Langerhans, 1887 (Polychaeta: Syllidae: Syllinae). Zootaxa 2009, 2220, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniz, P.; Pires, A.M.S. Trophic structure of polychaetes in the São Sebastião Channel (southeastern Brazil). Mar. Biol. 1999, 134, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliosa, P.R. Another diet of worms: The applicability of polychaete feeding guilds as a useful conceptual framework and biological variable. Mar. Ecol. 2005, 26, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangrande, A.; Licciano, M.; Pagliara, P. The diversity of diets in Syllidae (Annelida: Polychaeta). Cah. Biol. Mar. 2000, 41, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Campos, P.; Fernández-Leborans, G.; Verdes, A.; San Martín, G.; Martin, D.; Riesgo, R. The tag-along friendship: Epibiotic protozoans and syllid polychaetes. Implications for the taxonomy of Syllidae (Annelida), and description of three new species of Rhabdostyla and Cothurnia (Ciliophora, Peritrichia). Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2014, 17, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddall, M.E.; Aguado, M.T. Molecular phylogenetic evidence of a haplosporidian parasite infecting the polychaete Syllis nipponica (Imajima, 1966). Parasitol. Res. 2006, 99, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattig, P.; Martin, D. Sponge-associated Haplosyllis (Polychaeta: Syllidae: Syllinae) from the Caribbean Sea, with the description of four new species. Sci. Mar. 2011, 75, 733–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paresque, K.; Nogueira, J.M.M. The genus Haplosyllis Langerhans, 1879 (Polychaeta: Syllidae) from northeastern Brazil, with descriptions of two new species. Mar. Biol. Res. 2014, 10, 554–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasby, C.J.; Aguado, M.T. A new species and new records of the anthozoan commensal genus Alcyonosyllis (Polychaeta: Syllidae). Beagle Rec. Mus. Art Gall. North. Territ. 2009, 25, 55–63. [Google Scholar]


























| Family | Species | TL | AOI | BNN | BOA | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chrysopetalidae | Bhawania goodei | Bermuda | Mediterranean Sea | Florida Keys, USA (1 seq) | [39] | |
| Glyceridae | Glycera capitata | Greenland | Black Sea | Artic Russia (9 seq)—Kandalaksha Bay, Velikaya Salma Strait; NAmerica (10 seq)—Hudson Bay, Canada; Saglek Fiord, Canada; Devon Island, Canada; Alaska, USA; Ratnagiri coast, India (2 seq) | [40] | |
| Hesionidae | Podarkeopsis capensis | South Africa | E Mediterranean | N Spain (1 seq) | [39] | |
| Nephtyidae | Inermonephtys inermis(1) | Florida Keys, USA | Red Sea | China (3 seq)—Laizhou Bay | [40] | |
| Nereididae | Alitta succinea | Cuxhaven, Germany | Australian Exclusive Economic Zone; Argentina; Caribbean Sea; Hawaii; Japan; South Africa; USA Pacific | USA Atlantic (8 seq) | [39,40] | |
| Nereididae | Alitta virens(2) | Manger (N Bergen, Norway) | Baltic Sea, North Sea | Kandalaksha Bay, Velikaya Salma Strait, Russia Arctic (3 seq) St. Andrews, Blockhouse, USA Atlantic (50 seq) | [40] | |
| Nereididae | Leonnates decipiens | Gulf of Mannar, Indian Ocean | Mediterranean | India (1 seq)—Mumbai coast | [40] | |
| Nereididae | Namalycastis abiuma | Santa Catarina Island, Brazil | Hawaii | China (2 seq)—Yuandang Lake in Xiamen; India (5 seq)—Kadinamkulam estuary | [40] | |
| Nereididae | Neanthes acuminata(3) | Gulf of Naples, Italy | USA Pacific | S California, USA (54 seq) | Portugal (5 seq); Hawai (1 seq), USA Atlantic, Connecticut (5 seq); Baja California, Pacific Mexico (6 seq) | [40] |
| Nereididae | Perinereis aibuhitensis | Palau, Pacific Ocean | Japan, Portugal | No GPS data (7 seq); Zhoushan Zhujiajian, China (1 seq) | [40] | |
| Nereididae | Perinereis nuntia | Gulf of Suez | Mediterranean Sea | Pari Island, Indonesia (1 seq) | [40] | |
| Nereididae | Pseudonereis anomala | Gulf of Aden | Mediterranean Sea | Queensland, Australia (21 seq) | [39] | |
| Paralacydoniidae | Paralacydonia paradoxa(4) | Monaco, Mediterranean Sea | Red Sea | Bohai Sea, China (18 seq) | [39,40] | |
| Phyllodocidae | Eumida sanguinea(5) | Denmark (Kattegat) | Hawaii | NE Atlantic (29 seq)—Scilly islands, Great Britain; Finnmark, Norway; Bergen, Norway; Bohuslän, Sweden; Helsingör, Denmark | [40] | |
| Pilargidae | Sigambra parva | S South Africa | E Mediterranean | Ratnagiri coast, India (2 seq) | [39] | |
| Polynoidae | Paralepidonotus ampulliferus | Philippines | New Zealand | No GPS data (3 seq) | [40] | |
| Polynoidae | Subadyte pellucida(6) | Croatia, Adriatic Sea | Red Sea | Cádiz—Spain (2 seq) | [40] | |
| Sigalionidae | Pisione guanche | La Gomera, Spain | E Mediterranean | Lanzarote, Spain (1 seq) | [39] | |
| Syllidae | Amblyosyllis speciosa(7) | Misaki, Japan | USA Pacific | Port of Los Angeles, San Pedro Marina (3 seq) | [40] | |
| Syllidae | Branchiosyllis exilis(8) | Djibouti, Red Sea | Aegean Sea, USA Pacific | Shark Bay, Western Australia (1 seq) | ||
| Syllidae | Eusyllis kupfferi | Madeira island, Portugal | E Mediterranean | Kalbarry, Western Australia (1 seq) | [39] | |
| Syllidae | Syllis bella(9) | Laguna Beach, Pacific USA | E Mediterranean | Philipines (1 seq) | [39] | |
| Syllidae | Syllis gracilis(10) | Gulf of Naples, Mediterranean Sea | Argentina | Peru (5 seq); Australia (2 seq); Los Angeles, Pacific USA (12); Phillipines (8 seq); Italy (2 seq); Galicia, Spain (4 seq) | [40] | |
| Syllidae | Megasyllis nipponica | Sea of Japan | USA Pacific | Manazuru Peninsula, Pacific coast of Japan (1 seq) | [40] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martin, D.; Aguado, M.T.; Fernández Álamo, M.-A.; Britayev, T.A.; Böggemann, M.; Capa, M.; Faulwetter, S.; Fukuda, M.V.; Helm, C.; Petti, M.A.V.; et al. On the Diversity of Phyllodocida (Annelida: Errantia), with a Focus on Glyceridae, Goniadidae, Nephtyidae, Polynoidae, Sphaerodoridae, Syllidae, and the Holoplanktonic Families. Diversity 2021, 13, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030131
Martin D, Aguado MT, Fernández Álamo M-A, Britayev TA, Böggemann M, Capa M, Faulwetter S, Fukuda MV, Helm C, Petti MAV, et al. On the Diversity of Phyllodocida (Annelida: Errantia), with a Focus on Glyceridae, Goniadidae, Nephtyidae, Polynoidae, Sphaerodoridae, Syllidae, and the Holoplanktonic Families. Diversity. 2021; 13(3):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030131
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartin, Daniel, Maria Teresa Aguado, María-Ana Fernández Álamo, Temir Alanovich Britayev, Markus Böggemann, María Capa, Sarah Faulwetter, Marcelo Veronesi Fukuda, Conrad Helm, Monica Angelica Varella Petti, and et al. 2021. "On the Diversity of Phyllodocida (Annelida: Errantia), with a Focus on Glyceridae, Goniadidae, Nephtyidae, Polynoidae, Sphaerodoridae, Syllidae, and the Holoplanktonic Families" Diversity 13, no. 3: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030131
APA StyleMartin, D., Aguado, M. T., Fernández Álamo, M. -A., Britayev, T. A., Böggemann, M., Capa, M., Faulwetter, S., Fukuda, M. V., Helm, C., Petti, M. A. V., Ravara, A., & Teixeira, M. A. L. (2021). On the Diversity of Phyllodocida (Annelida: Errantia), with a Focus on Glyceridae, Goniadidae, Nephtyidae, Polynoidae, Sphaerodoridae, Syllidae, and the Holoplanktonic Families. Diversity, 13(3), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13030131