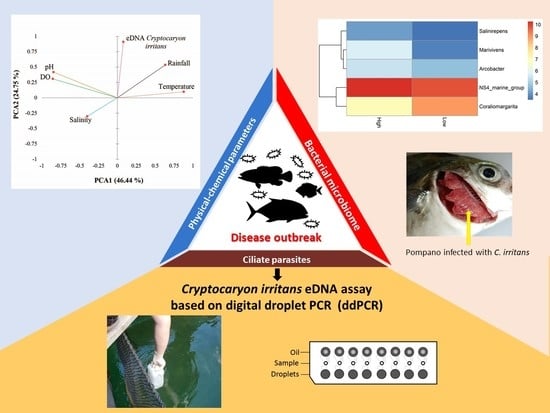
Digital Droplet PCR-Based Environmental DNA Tool for Monitoring Cryptocaryon irritans in a Marine Fish Farm from Hong Kong
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Farm Selection, Fish Species, and Parasite Identification
2.2. Water Sample Collection
2.3. Environmental and Physical-Chemical Parameters Measurement
2.4. Environmental DNA (eDNA) Filtration, Extraction, and Parasite Assay
2.5. Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) Assay
2.6. Library Preparation for Bacterial Microbiome Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis and Bioinformatics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blancheton, J.P.; Attramadal, K.J.K.; Michaud, L.; d’Orbcastel, E.R.; Vadstein, O. Insight into bacterial population in aquaculture systems and its implication. Aquac. Eng. 2013, 53, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salipante, S.J.; Sengupta, D.J.; Rosenthal, C.; Costa, G.; Spangler, J.; Sims, E.H.; Hoffman, N.G. Rapid 16S rRNA next-generation sequencing of polymicrobial clinical samples for diagnosis of complex bacterial infections. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bastos Gomes, G.; Hutson, K.S.; Domingos, J.A.; Infante Villamil, S.; Huerlimann, R.; Miller, T.L.; Jerry, D.R. Parasitic protozoan interactions with bacterial microbiome in a tropical fish farm. Aquaculture 2019, 502, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, L.; Shinn, A.P.; Pratoomyot, J.; Bastos Gomes, G. Unveiling associations between ciliate parasites and bacterial microbiomes under warm-water fish farm conditions—A review. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 13, 1097–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotob, M.H.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. The impact of co-infections on fish: A review. Vet. Res. 2016, 47, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Mao, Y.; Liu, M.; Chen, R.; Su, Y.; Zheng, W. Pathogenic bacterium Vibrio harveyi: An endosymbiont in the marine parasitic ciliate protozoan Cryptocaryon irritans. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentzon-Tilia, M.; Sonnenschein, E.C.; Gram, L. Monitoring and managing microbes in aquaculture-Towards a sustainable industry. Microb. Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Bruijn, I.; Liu, Y.; Wiegertjes, G.F.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Exploring fish microbial communities to mitigate emerging diseases in aquaculture. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Estrada, Á.M.; Gollas-Galván, T.; Martínez-Córdova, L.R.; Martínez-Porchas, M. Predictive functional profiles using metagenomic 16S rRNA data: A novel approach to understanding the microbial ecology of aquaculture systems. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colorni, A. Aspects of the biology of Cryptocaryon irritans, and hyposalinity as a control measure in cultured gilt-head sea bream Sparus aurata. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1985, 1, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, H.W.; Dawe, D. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis and Cryptocaryon irritans (phylum Ciliophora). Fish. Dis. Disord. 2016, 1, 116–153. [Google Scholar]
- Standing, D.; Brunner, T.; Aruety, T.; Ronen, Z.; Gross, A.; Zilberg, D. Mortality of Cryptocaryon irritans in sludge from a digester of a marine recirculating aquaculture system. Aquaculture 2017, 467, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, K.V.; Nhinh, D.T. The prevalence of Cryptocaryon irritans in wild marine ornamental fish from Vietnam. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 137, 012094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, X.M.; Li, A.X.; Lin, X.T.; Teng, N.; Zhu, X.Q. A standardized method to propagate Cryptocaryon irritans on a susceptible host pompano Trachinotus ovatus. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, C.K.; Abdul-Murad, A.M.; Kua, B.C.; Mohd-Adnan, A. Cryptocaryon irritans infection induces the acute phase response in Lates calcarifer: A transcriptomic perspective. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Thu Nguyen, T.T.; Tsai, M.A.; Ya-Zhen, E.; Wang, P.C.; Chen, S.C. A formalin-inactivated vaccine provides good protection against Vibrio harveyi infection in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 65, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diggles, B.K.; Lester, R.J.G. Influence of temperature and host species on the development of Cryptocaryon irritans. J. Parasitol. 1996, 82, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshinaga, T. Effects of high temperature and dissolved oxygen concentration on the development of Cryptocaryon irritans (Ciliophora) with a comment on the autumn outbreaks of cryptocaryoniasis. Fish Pathol. 2001, 36, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imajoh, M.; Morimitu, K.; Sukeda, M.; Umezaki, T.; Monno, S.; Goda, H.; Oshima, S.-I. TaqMan real-Time PCR detection and phylogenetic analysis of Cryptocaryon irritans in Nomi Bay, Kochi, Japan. Fish Pathol. 2016, 51, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, P.J.; Nigrelli, R.F.; Ruggieri, G.D. Studies on cryptocaryoniasis in marine fish: Effect of temperature and salinity on the reproductive cycle of Cryptocaryon irritans Brown, 1951. J. Fish Dis. 1979, 2, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, P.; Matthews, R. Cryptocaryon irrttans (Ciliophora): Photoperiod and transmission in marine fish. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1994, 74, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, L.; Spatharis, S.; Dario, M.A.; Dwyer, T.; Roca, I.J.T.; Kintner, A.; Praebel, K. Environmental DNA: A new low-cost monitoring tool for pathogens in salmonid aquaculture. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elberri, A.I.; Galal-Khallaf, A.; Gibreel, S.E.; El-Sakhawy, S.F.; El-Garawani, I.; El-Sayed Hassab ElNabi, S.; Mohammed-Geba, K. DNA and eDNA-based tracking of the North African sharptooth catfish Clarias gariepinus. Mol. Cell. Probes 2020, 51, 101535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, H.L.; Noble, T.H.; Saunders, R.J.; Robson, S.K.; Burrows, D.W.; Jerry, D.R. Fine-tuning for the tropics: Application of eDNA technology for invasive fish detection in tropical freshwater ecosystems. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capo, E.; Spong, G.; Koizumi, S.; Puts, I.; Olajos, F.; Königsson, H.; Byström, P. Droplet digital PCR applied to environmental DNA, a promising method to estimate fish population abundance from humic-rich aquatic ecosystems. Environ. DNA 2020, 3, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.; Santos, R. Nanofluidic digital PCR for the quantification of Norovirus for water quality assessment. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haramoto, E.; Malla, B.; Thakali, O.; Kitajima, M. First environmental surveillance for the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater and river water in Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 140405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos Gomes, G.; Hutson, K.S.; Domingos, J.A.; Chung, C.; Hayward, S.; Miller, T.L.; Jerry, D.R. Use of environmental DNA (eDNA) and water quality data to predict protozoan parasites outbreaks in fish farms. Aquaculture 2017, 479, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Takahara, T.; Minamoto, T.; Matsuhashi, S.; Uchii, K.; Yamanaka, H. Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (PCR) outperforms real-time PCR in the detection of environmental DNA from an invasive fish species. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 5601–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.E.; Dorazio, R.M.; Butterfield, J.S.; Meigs-Friend, G.; Nico, L.G.; Ferrante, J.A. Detection limits of quantitative and digital PCR assays and their influence in presence-absence surveys of environmental DNA. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2017, 17, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, H.; Uchii, K.; Takahara, T.; Matsuhashi, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Minamoto, T. Use of droplet digital PCR for estimation of fish abundance and biomass in environmental DNA surveys. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, S.C.; Laperriere, G.; Germain, H. Droplet Digital PCR versus qPCR for gene expression analysis with low abundant targets: From variable nonsense to publication quality data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yanong, R.P.E. Cryptocaryon irritans infections (marine white spot disease) in fish. In Program in Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, SFRC, Florida Cooperative Extension Service; Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Li, Y.W.; Abdullahi, A.Y.; Dan, X.M.; Gong, H.; Ke, Q.Z.; Li, G.Q. Placemat and rotational culturing: A novel method to control Cryptocaryon irritans infection by removing tomonts. Aquaculture 2016, 459, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos Gomes, G.; Jerry, D.R.; Miller, T.L.; Hutson, K.S. Current status of parasitic ciliates Chilodonella spp. (Phyllopharyngea: Chilodonellidae) in freshwater fish aquaculture. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobert, G.; Cotillard, A.; Fourmestraux, C.; Pruvost, L.; Miguet, J.; Boyer, M. Droplet digital PCR improves absolute quantification of viable lactic acid bacteria in faecal samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 148, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R. RStudio; PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westaway, J. Aquaculture_Project. GitHub Repository 2021. Available online: https://JacobAFW/Aquaculture_Project-github.com/ (accessed on 11 June 2021).
- Callahan, B.J.; Sankaran, K.; Fukuyama, J.A.; McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.P. Bioconductor workflow for microbiome data analysis: From raw reads to community analyses. F1000Research 2016, 5, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKnight, D.T.; Huerlimann, R.; Bower, D.S.; Schwarzkopf, L.; Alford, R.A.; Zenger, K.R. microDecon: A highly accurate read-subtraction tool for the post-sequencing removal of contamination in metabarcoding studies. Environ. DNA 2019, 1, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.5823. [Google Scholar]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 4th ed.; Sage Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Saksis, R.; Silamikelis, I.; Laksa, P.; Megnis, K.; Peculis, R.; Mandrika, I.; Konrade, I. Medication for acromegaly reduces expression of MUC16, MACC1 and GRHL2 in pituitary neuroendocrine tumour tissue. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 593760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, R. Pathology of Cultured Fish in Hong Kong, 1st ed.; Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department: Hong Kong, China, 2015; pp. 145–146.
- Jiang, C.; Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Gu, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Miao, W. Diversity and seasonality dynamics of ciliate communities in four estuaries of Shenzhen, China (South China Sea). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, D.; Stentiford, G.D.; Littlewood, D.T.J.; Hartikainen, H. Diverse Applications of Environmental DNA Methods in Parasitology. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stentiford, G.D.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Flegel, T.W.; Williams, B.A.; Withyachumnarnkul, B.; Itsathitphaisarn, O.; Bass, D. New paradigms to help solve the global aquaculture disease crisis. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, D.; Bateman, A.; Li, S.; Tabata, A.; Schulze, A.; Mordecai, G.; Krkosek, M. Environmental DNA from multiple pathogens is elevated near active Atlantic salmon farms. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20202010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonga, S.W. The Stress Response in Fish. Physiol. Rev. 1997, 77, 91–625. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Biological Hazards on a request from European Commission on Food Safety considerations of animal welfare aspects and husbandry systems for farmed fish. EFSA J. 2008, 867, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bergqvist, J.; Gunnarsson, S. Finfish Aquaculture: Animal Welfare, the Environment, and Ethical Implications. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2011, 26, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.; Medhat, S.; Hanan, G.; Khallaf, M.; Sherif, S.; Amira, O. Seasonal parasitic infestations and their close relationship to immune suppression in cultured sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) and sea bream (Sparus auratus). Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2018, 6, 5371–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-L.; Lao, G.-F.; Li, Y.-W.; Yang, M.; Mo, Z.-Q.; Dan, X.-M. Effects of temperature and host species on the life cycle of Cryptocaryon irritans. Aquaculture 2018, 485, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.C.; Xie, M.Q.; Zhu, X.Q.; Li, A.X. Some characteristics of host-parasite relationship for Cryptocaryon irritans isolated from South China. Parasitol. Res. 2008, 102, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parris, D.J.; Brooker, R.M.; Morgan, M.A.; Dixson, D.L.; Stewart, F.J. Whole gut microbiome composition of damselfish and cardinalfish before and after reef settlement. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yukgehnaish, K.; Kumar, P.; Sivachandran, P.; Marimuthu, K.; Arshad, A.; Paray, B.A.; Arockiaraj, J. Gut microbiota metagenomics in aquaculture: Factors influencing gut microbiome and its physiological role in fish. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1903–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Jankowiak, J.; Koch, F.; Gobler, C.J. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbiomes associated with blooms of the ichthyotoxic dinoflagellate Cochlodinium (Margalefidinium) polykrikoides in New York, USA, estuaries. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolda, A.; Gavrilović, A.; Jug-Dujaković, J.; Ljubešić, Z.; El-Matbouli, M.; Lillehaug, A.; Kapetanović, D. Profiling of bacterial assemblages in the marine cage farm environment, with implications on fish, human and ecosystem health. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopprio, G.A.; Cuong, L.H.; Luyen, N.D.; Duc, T.M.; Ha, T.H.; Huong, L.M.; Gärdes, A. Carrageenophyte-attached and planktonic bacterial communities in two distinct bays of Vietnam: Eutrophication indicators and insights on ice-ice disease. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathlavath, S.; Kumar, S.; Nayak, B.B. Comparative isolation and genetic diversity of Arcobacter sp. from fish and the coastal environment. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 65, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, H.; Aydin, S. Pathological effects of Arcobacter cryaerophilus infection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum). Acta Vet. Hung. 2006, 54, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overstreet, R.M.; Hawkins, W.E. Diseases and mortalities of fishes and other animals in the Gulf of Mexico. In Habitats and Biota of the Gulf of Mexico: Before the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill, 1st ed.; Ward, C.H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 1589–1738. [Google Scholar]
- Legrand, T.P.R.A.; Wynne, J.W.; Weyrich, L.S.; Oxley, A.P.A. A microbial sea of possibilities: Current knowledge and prospects for an improved understanding of the fish microbiome. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 12, 1101–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuypers, J.; Jerome, K.R. Applications of digital PCR for clinical microbiology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1621–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dingle, T.C.; Sedlak, R.H.; Cook, L.; Jerome, K.R. Tolerance of droplet-digital PCR vs. real-time quantitative PCR to inhibitory substances. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1670–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rusch, J.C.; Hansen, H.; Strand, D.A.; Markussen, T.; Hytterod, S.; Vralstad, T. Catching the fish with the worm: A case study on eDNA detection of the monogenean parasite Gyrodactylus salaris and two of its hosts, Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, A.S.; Haugen, T.; Netzer, R.; Tondervik, A.; Dahle, S.W.; Hageskal, G. Multiplex droplet digital PCR assay for detection of Flavobacterium psychrophilum and Yersinia ruckeri in Norwegian aquaculture. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 177, 106044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Primer/Probe | Primer/Probe Sequence 5′ → 3′ | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| FCrypto Primer | TACGTCCCTGCCCTTTGTACA | 84 |
| RCrypto Primer | CAGTGTTAGCGCAGTCCAGAAG | |
| Crypto Probe | CCGTCGCTCCTACCGA-FAM |
| Cryptocaryon irritans eDNA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Predictors | Odd Ratios | Standard Error | p |
| Dissolved oxygen | 0.07 | 1.56 | 0.090 |
| Rainfall | 0.08 | 1.22 | 0.034 |
| NS4 marine group | 0.10 | 1.30 | 0.081 |
| Coraliomargarita | 2053.29 | 3.51 | 0.030 |
| Salinity | 0.31 | 0.94 | 0.208 |
| Arcobacter | 0.33 | 0.97 | 0.253 |
| Observations | 125 | ||
| Marginal R2/Conditional R2 | 0.737/0.839 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsang, H.H.; Domingos, J.A.; Westaway, J.A.F.; Kam, M.H.Y.; Huerlimann, R.; Bastos Gomes, G. Digital Droplet PCR-Based Environmental DNA Tool for Monitoring Cryptocaryon irritans in a Marine Fish Farm from Hong Kong. Diversity 2021, 13, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080350
Tsang HH, Domingos JA, Westaway JAF, Kam MHY, Huerlimann R, Bastos Gomes G. Digital Droplet PCR-Based Environmental DNA Tool for Monitoring Cryptocaryon irritans in a Marine Fish Farm from Hong Kong. Diversity. 2021; 13(8):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080350
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsang, Hin Hung, Jose A. Domingos, Jacob A. F. Westaway, Maximilian H. Y. Kam, Roger Huerlimann, and Giana Bastos Gomes. 2021. "Digital Droplet PCR-Based Environmental DNA Tool for Monitoring Cryptocaryon irritans in a Marine Fish Farm from Hong Kong" Diversity 13, no. 8: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080350
APA StyleTsang, H. H., Domingos, J. A., Westaway, J. A. F., Kam, M. H. Y., Huerlimann, R., & Bastos Gomes, G. (2021). Digital Droplet PCR-Based Environmental DNA Tool for Monitoring Cryptocaryon irritans in a Marine Fish Farm from Hong Kong. Diversity, 13(8), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080350