Biodiversity of Russian Local Sheep Breeds Based on Pattern of Runs of Homozygosity †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples and Genotyping
2.2. Quality Control
2.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
2.4. Runs of Homozygosity Estimation
2.5. Estimation of Genomic Inbreeding (FROH)
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Genetic Links between Sheep Breeds within the Wool-Type Groups
3.2. Pattern of Distribution of Runs of Homozygosity in Populations of Russian Local Sheep Breeds
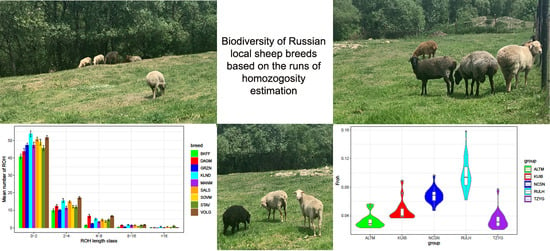
3.3. Ranging the Runs of Homozygosity by the Length Classes in Russian Local Sheep Breeds
3.4. Estimation of Genomic Inbreeding Coefficient Based on Runs of Homozygosity in Russian Local Sheep Breeds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McQuillan, R.; Leutenegger, A.L.; Abdel-Rahman, R.; Franklin, C.S.; Pericic, M.; Barac-Lauc, L. Runs of homozygosity in European populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 83, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curik, I.; Ferencčakovicć, M.; Soölkner, J. Inbreeding and runs of homozygosity: A possible solution to an old problem. Livest. Sci. 2014, 166, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirin, M.; McQuillan, R.; Franklin, C.S.; Campbell, H.; McKeigue, P.M.; Wilson, J.F. Genomic runs of homozygosity record population history and consanguinity. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceballos, F.C.; Joshi, P.K.; Clark, D.W.; Ramsay, M.; Wilson, J.F. Runs of homozygosity: Windows into population history and trait architecture. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sölkner, J.; Ferencčakovicć, M.; Gredler, B.; Curik, I. Genomic metrics of individual autozygosity, applied to a cattle population. In Book of Abstracts of the 61st Annual Meeting of the European Association of Animal Production; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2010; p. 306. [Google Scholar]
- Purfield, D.C.; Berry, D.P.; McParland, S.; Bradley, D.G. Runs of homozygosity and population history in cattle. BMC Genet. 2012, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zinovieva, N.A.; Dotsev, A.V.; Sermyagin, A.A.; Deniskova, T.E.; Abdelmanova, A.S.; Kharzinova, V.R.; Sölkner, J.; Reyer, H.; Wimmers, K.; Brem, G. Selection signatures in two oldest Russian native cattle breeds revealed using high-density single nucleotide polymorphism analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addo, S.; Klingel, S.; Thaller, G.; Hinrichs, D. Genetic diversity and the application of runs of homozygosity-based methods for inbreeding estimation in German White-headed Mutton sheep. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandolo, W.; Mészáros, G.; Banda, L.J.; Gondwe, T.N.; Lamuno, D.; Mulindwa, H.A.; Nakimbugwe, H.N.; Wurzinger, M.; Utsunomiya, Y.T.; Woodward-Greene, M.J.; et al. Timing and Extent of Inbreeding in African Goats. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mamun, H.A.; Clark, S.A.; Kwan, P.; Gondro, C. Genome-wide linkage disequilibrium and genetic diversity in five populations of Australian domestic sheep. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2015, 47, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purfield, D.C.; McParland, S.; Wall, E.; Berry, D.P. The distribution of runs of homozygosity and selection signatures in six commercial meat sheep breeds. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, S.; Di, J.; Han, B.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Li, W. Genome-wide scan for runs of homozygosity identifies candidate genes related to economically important traits in Chinese Merino. Animals 2020, 10, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mastrangelo, S.; Ciani, E.; Sardina, M.T.; Sottile, G.; Pilla, F.; Portolano, B.; the Bi.Ov. Ita Consortium. Runs of homozygosity reveal genome-wide autozygosity in Italian sheep breeds. Anim. Genet. 2018, 49, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Signer-Hasler, H.; Burren, A.; Ammann, P.; Drögemüller, C.; Flury, C. Runs of homozygosity and signatures of selection: A comparison among eight local Swiss sheep breeds. Anim. Genet. 2019, 50, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniskova, T.; Dotsev, A.; Lushihina, E.; Shakhin, A.; Kunz, E.; Medugorac, I.; Reyer, H.; Wimmers, K.; Khayatzadeh, N.; Sölkner, J.; et al. Population structure and genetic diversity of sheep breeds in the Kyrgyzstan. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abied, A.; Xu, L.; Sahlu, B.W.; Xing, F.; Ahbara, A.; Pu, Y.; Lin, J.; Berihulay, H.; Islam, R.; He, X.; et al. Genome-wide analysis revealed homozygosity and demographic history of five chinese sheep breeds adapted to different environments. Genes 2020, 11, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzomba, E.F.; Chimonyo, M.; Pierneef, R.; Muchadeyi, F.C. Runs of homozygosity analysis of South African sheep breeds from various production systems investigated using OvineSNP50k data. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovenko, A.M.; Aboneev, V.V.; Gorkovenko, L.G.; Marchenko, V.V. An effective method to improve the competitiveness of sheep breeding. Ovcy Kozy Sherstyanoe Delo 2016, 2, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Novopashina, S.I.; Sannikov, M.Y.; Khatataev, S.A.; Kuzmina, T.N.; Khmelevskaya, G.N.; Stepanova, N.G.; Tikhomirov, A.I.; Marinchenko, T.E. Status and Perspective Areas for Improving the Genetic Potential of Small Cattle: Scientific and Analytic Overview; Rosinformagrotekh: Moscow, Russia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vojtyuk, M.M.; Machneva, O.P. The current state of sheep breeding in Russia. Effektivnoe Zhivotnovodstvo 2021, 4, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboneev, V.V.; Gorkovenko, L.G. Some problems of the breed-forming process in domestic sheep breeding. Ovcy Kozy Sherstyanoe Delo 2018, 3, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Semyonov, S.I.; Selkin, I.I. Sheep. In Animal Genetics Resources of the USSR; Dmitriev, N.G., Ernst, L.K., Eds.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Dunin, I.M.; Dankvert, A.G. Spravochnik Porod i Tipov Sel’Skokhozyastvennykh Zhivotnykh, Razvodimykh v Rossiiskoi Federatsii; VNIIPLEM: Moskva, Russia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Deniskova, T.E.; Dotsev, A.V.; Selionova, M.I.; Kunz, E.; Medugorac, I.; Reyer, H.; Wimmers, K.; Barbato, M.; Traspov, A.A.; Brem, G.; et al. Population structure and genetic diversity of 25 Russian sheep breeds based on whole-genome genotyping. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kijas, J.W.; Lenstra, J.A.; Hayes, B.; Boitard, S.; Porto Neto, L.R.; San Cristobal, M.; Servin, B.; McCulloch, R.; Whan, V.; Gietzen, K.; et al. International Sheep Genomics Consortium Members. Genome-wide analysis of the world’s sheep breeds reveals high levels of historic mixture and strong recent selection. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. GigaScience 2015, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.B.; Oliphant, A.; Shen, R.; Kermani, B.G.; Garcia, F.; Gunderson, K.L.; Hansen, M.; Steemers, F.; Butler, S.L.; Deloukas, P.; et al. Highly parallel SNP genotyping. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2003, 68, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Marras, G.; Gaspa, G.; Sorbolini, S.; Dimauro, C.; Ajmone-Marsam, P.; Valentini, A.; Williams, J.L.; Macciotta, N.P. Analysis of runs of homozygosity and their relationship with inbreeding in five cattle breeds farmed in Italy. Anim. Genet. 2014, 46, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cran, R. Project.org: detectRUNS: Detect Runs of Homozygosity and Runs of Heterozygosity in Diploid Genomes. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/detectRUNS/index.html (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Tayshin, V.A.; Lkhasaranov, B.B. Ecological Adaptive Qualities of the Buryat Sheep: Aboriginal Buryat Sheep; Izd-vo BNTs SO RAN: Ulan-Ude, Russia, 1997; p. 123. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Deniskova, T.E.; Abdelmanova, A.; Dotsev, A.V.; Reyer, H.; Selionova, M.I.; Fornara, M.S.; Wimmers, K.; Brem, G.; Zinovieva, N.A. PSX-25 The distribution of runs of homozygosity in nine native Russian sheep breeds. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, 456–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunin, I.M.; Amerhanov, H.A.; Safina, G.F.; Grigoryan, L.N.; Hatataev, S.A.; Hmelevskaya, G.N.; Pavlov, M.B.; Stepanova, N.G. Ezhegodnik po Plemennoj Rabote v Ovcevodstve i Kozovodstve v Hozyajstvah Rossijskoj Federacii (2019 god); FGBNU Vserossiiskii nauchno-issledovatelskii institut plemennogo dela Lesnye Poliany: Moskva, Russia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- FarmIQ. Available online: https://farmiq.co.nz/ (accessed on 4 August 2021).




| Breed | Code | n 1 | n50k2 | n600k3 | Region of Sampling 4 | Main Products |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deniskova et al. (2018) [24] | This Study | |||||
| Coarse wool breeds | ||||||
| Andean | ANDB | 17 | 17 | - | Dagestan/North Caucasus | Meat, wool, milk |
| Buubei | BUUB | 39 | 17 | 22 | Yakutia/Far Eastern | Meat, wool |
| Edilbai | EDLB | 44 | 17 | 27 | Volgograd region/South | Meat, fat |
| Kalmyk | KALM | 20 | 18 | 2 | Kalmykia/South | Meat, fat |
| Karakul | KARA | 41 | 16 | 25 | Astrakhan region/South | Pelts, fur |
| Karachaev | KRCH | 43 | 22 | 21 | Karachay-Cherkessia/North Caucasus | Meat, wool, milk |
| Kuchugur | KUCH | 16 | 16 | - | Voronezh region/Central | Meat, wool |
| Lezgin | LEZG | 41 | 15 | 26 | Dagestan/South | Meat, wool, milk |
| Mongolian | MONG | 27 | - | 27 | Buryatia/Far Eastern | Meat |
| Ossetin | OSET | 30 | - | 30 | Ossetia/North Caucasus | Meat, wool, milk |
| Romanov | RMNV | 36 | 26 | 10 | Yaroslavl, Kaluga, and Tula regions/Central | Meat, skins |
| Tushin | TUSH | 17 | 9 | 8 | Dagestan/North Caucasus | Meat, wool, milk |
| Tuva | TUVA | 41 | 16 | 25 | Tyva/Siberian | Meat, wool, |
| Semi-fine wool breeds | ||||||
| Altai Mountain | ALTM | 14 | 12 | 2 | Altai region/Siberian | Wool, meat |
| Kuibyshev | KUIB | 15 | 15 | - | Samara region/Volga | Meat, wool |
| North Caucasian | NCSN | 16 | 16 | - | Stavropol region/North Caucasus | Meat, wool |
| Russian longhaired | RULH | 32 | 16 | 16 | Voronezh region/Central | Meat, wool |
| Tsigai | TZYG | 16 | 16 | 2 | Saratov region/Volga | Meat, wool |
| Fine wool breeds | ||||||
| Baikal fine-fleeced | BKFF | 15 | 7 | 8 | Yakutia/Far Eastern | Wool, meat |
| Dagestan Mountain | DAGM | 16 | 16 | - | Dagestan/North Caucasus | Meat, wool |
| Groznensk | GRZN | 35 | 13 | 22 | Stavropol region/North Caucasus | Wool |
| Kulundin | KLND | 16 | 16 | - | Altai region/Siberian | Wool, meat |
| Manych Merino | MANM | 16 | 16 | - | Stavropol region/North Caucasus | Wool |
| Salsk | SALS | 35 | 16 | 19 | Rostov region/South | Wool |
| Soviet Merino | SOVM | 15 | 14 | 1 | Stavropol region/North Caucasus | Wool |
| Stavropol | STAV | 16 | 14 | 2 | Stavropol region/North Caucasus | Wool, meat |
| Volgograd | VOLG | 37 | 15 | 22 | Volgograd region/South | Meat, wool |
| Breed | Code | n 1 | ROH Length | ROH Number | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Min 2 | Max 3 | Mean | Min 2 | Max 3 | |||
| Coarse wool breeds | ||||||||
| Andean | ANDB | 17 | 190.64 ± 19.55 | 76.11 | 383.4 | 78.88 ± 3.82 | 56 | 116 |
| Buubei (1) | BUUB_1 | 20 | 120.5 ± 17 | 60.64 | 379.4 | 58.55 ± 2.16 | 43 | 79 |
| Buubei (2) | BUUB_2 | 19 | 105.82 ± 21.28 | 54.11 | 483.11 | 56.58 ± 1.67 | 41 | 76 |
| Edilbai | EDLB | 44 | 111.6 ± 5.06 | 76.69 | 268.69 | 67.25 ± 1.25 | 47 | 83 |
| Kalmyk | KALM | 20 | 104.83 ± 8.95 | 71.6 | 257.81 | 62.7 ± 1.91 | 44 | 80 |
| Karakul | KARA | 41 | 128.17 ± 3.39 | 81.06 | 180.04 | 79.34 ± 1.64 | 47 | 94 |
| Karachaev | KRCH | 43 | 116.8 ± 6.92 | 70.6 | 374.81 | 69.12 ± 1.36 | 48 | 91 |
| Kuchugur | KUCH | 16 | 223.81 ± 52.81 | 50.34 | 872.75 | 80.38 ± 5.87 | 37 | 105 |
| Lezgin | LEZG | 41 | 89.8 ± 5.6 | 48.78 | 282.82 | 59.68 ± 1.75 | 38 | 94 |
| Mongolian | MONG | 27 | 86.44 ± 3.19 | 60.62 | 140.96 | 60.11 ± 1.42 | 43 | 73 |
| Ossetin | OSET | 30 | 114.57 ± 13.75 | 64.33 | 463.41 | 64.43 ± 1.83 | 44 | 88 |
| Romanov | RMNV | 36 | 282.15 ± 10.46 | 182.03 | 457.36 | 123,14 ± 1,84 | 103 | 146 |
| Tushin | TUSH | 17 | 115.93 ± 11.04 | 72.3 | 208.29 | 63.29 ± 3.54 | 41 | 104 |
| Tuva | TUVA | 41 | 91.72 ± 3.33 | 58.03 | 148.89 | 60.85 ± 1.6 | 39 | 86 |
| Semi-fine wool breeds | ||||||||
| Altai Mountain | ALTM | 14 | 86.77 ± 7.2 | 61.49 | 149.39 | 37.64 ± 1.53 | 26 | 47 |
| Kuibyshev | KUIB | 15 | 126.09 ± 10.08 | 97.66 | 236.33 | 47.4 ± 1.67 | 38 | 66 |
| North Caucasian | NCSN | 16 | 181.81 ± 7.31 | 125 | 256.15 | 66.25 ± 1.51 | 48 | 74 |
| Russian longhaired | RULH | 32 | 257.15 ± 9.86 | 164.43 | 418.49 | 84.31 ± 1.89 | 62 | 104 |
| Tsigai | TZYG | 16 | 91.17 ± 8.9 | 54.92 | 204.21 | 39.19 ± 1.69 | 30 | 55 |
| Fine wool breeds | ||||||||
| Baikal fine-fleeced | BKFF | 15 | 92.82 ± 2.77 | 77.1 | 111.44 | 52.53 ± 1.67 | 42 | 65 |
| Dagestan Mountain | DAGM | 16 | 144.26 ± 7.06 | 105.12 | 194.71 | 64.31 ± 2.02 | 52 | 77 |
| Groznensk | GRZN | 35 | 109.93 ± 3.64 | 75,97 | 183.56 | 60.43 ± 1.39 | 44 | 80 |
| Kulundin | KLND | 16 | 171.31 ± 9.69 | 126.28 | 277.98 | 76.44 ± 1.81 | 63 | 93 |
| Manych Merino | MANM | 16 | 125.24 ± 6.19 | 84.18 | 181.25 | 63.38 ± 1.99 | 46 | 77 |
| Salsk | SALS | 35 | 162.7 ± 9.44 | 88.94 | 351.75 | 72.17 ± 1.37 | 52 | 90 |
| Soviet Merino | SOVM | 15 | 125.41 ± 5.05 | 98.45 | 168.69 | 65.33 ± 1.89 | 51 | 76 |
| Stavropol | STAV | 16 | 157.18 ± 20.46 | 89.41 | 419.32 | 64.5 ± 2.5 | 51 | 85 |
| Volgograd | VOLG | 37 | 174.53 ± 4.42 | 110.65 | 224.6 | 77.38 ± 1.63 | 53 | 98 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deniskova, T.; Dotsev, A.; Selionova, M.; Brem, G.; Zinovieva, N. Biodiversity of Russian Local Sheep Breeds Based on Pattern of Runs of Homozygosity. Diversity 2021, 13, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080360
Deniskova T, Dotsev A, Selionova M, Brem G, Zinovieva N. Biodiversity of Russian Local Sheep Breeds Based on Pattern of Runs of Homozygosity. Diversity. 2021; 13(8):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080360
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeniskova, Tatiana, Arsen Dotsev, Marina Selionova, Gottfried Brem, and Natalia Zinovieva. 2021. "Biodiversity of Russian Local Sheep Breeds Based on Pattern of Runs of Homozygosity" Diversity 13, no. 8: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080360
APA StyleDeniskova, T., Dotsev, A., Selionova, M., Brem, G., & Zinovieva, N. (2021). Biodiversity of Russian Local Sheep Breeds Based on Pattern of Runs of Homozygosity. Diversity, 13(8), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/d13080360