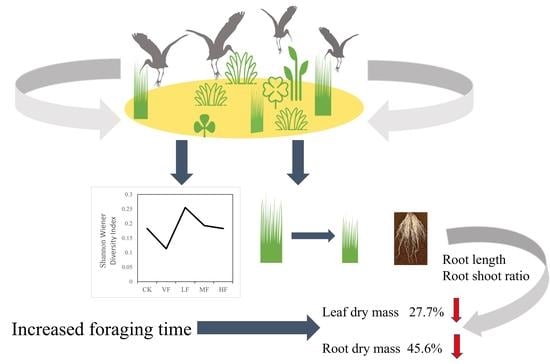
Effects of Waterbird Herbivory on Dominant Perennial Herb Carex thunbergii in Shengjin Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Community Structure
2.4. Morphological Trait of C. thunbergii
2.5. Chemical Traits of C. thunbergii
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Plant Community Diversity
3.2. Biomass of C. thunbergii
3.3. Plant Morphological Traits
3.4. Chemical Traits
3.5. PCA Analysis
3.6. Pathways That Directly or Indirectly Affect Dry Mass
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Different Foraging Intensity on the Diversity of Carex Community
4.2. Dry Mass and Elemental Allocation of C. thunbergii under Different Foraging Intensity
4.3. Functional Traits of C. thunbergii under Different Foraging Intensity
4.4. Mechanism of Bird’s Foraging-Induced Biomass Decrease
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brauns, M.; Garcia, X.F.; Walz, N.; Pusch, M.T. Effects of human shoreline development on littoral macroinvertebrates in lowland lakes. J. Appl. Ecol. 2007, 44, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, C.; Svedmark, M. Basic principles and ecological consequences of changing water regimes: Riparian plant communities. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beerens, J.M.; Gawlik, D.E.; Herring, G.; Cook, M.I. Dynamic habitat selection by two wading bird species with divergent foraging strategies in a seasonally fluctuating wetland. Auk 2011, 128, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.S.; Pagès, J.F.; Arthur, R.; Alcoverro, T. Assessing the role of large herbivores in the structuring and functioning of freshwater and marine angiosperm ecosystems. Ecography 2016, 39, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakker, E.S.; Sarneel, J.M.; Gulati, R.D.; Liu, Z.W.; van Donk, E. Restoring macrophyte diversity in shallow temperate lakes: Biotic versus abiotic constraints. Hydrobiologia 2012, 710, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakker, E.S.; Wood, K.A.; Pagès, J.F.; Veen, G.F.; Christianen, M.J.; Santamaría, L.; Nolet, B.A.; Hilt, S. Herbivory on freshwater and marine macrophytes: A review and perspective. Aquat. Bot. 2016, 135, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, K.A.; O’Hare, M.T.; McDonald, C.; Searle, K.R.; Daunt, F.; Stillman, R.A. Herbivore regulation of plant abundance in aquatic ecosystems. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1128–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.X.; Yang, G.; Lu, Z. Habitat use by waterbirds in coastal wetlands during migratory seasons in Shankou Nature Reserve, Guangxi, South China. Oceanol. Lim. Sin. 2014, 45, 513–521. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Fox, A.D. Birds and people both depend on China’s wetlands. Nature 2009, 460, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lei, G.; Liu, Y.; Lei, J.Y.; Yu, X.B.; Wen, L.; Zhou, Y.M. Restriction of herbivorous waterbird distributions in the middle and lower Yangtze River floodplain in view of hydrological isolation. Wetlands 2016, 37, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidding, B.; Nolet, B.A.; de Boer, T.; de Vries, P.P.; Klaassen, M. Compensatory growth in an aquatic plant mediates exploitative competition between seasonally tied herbivores. Ecology 2009, 90, 1891–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.H.; Xu, F.W.; Zheng, S.X.; Taube, F.; Bai, Y.F. Patterns and thresholds of grazing-induced changes in community structure and ecosystem functioning: Species-level responses and the critical role of species traits. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 54, 963–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Wang, Z.W.; Han, G.D.; Schellenberg, M.P.; Wu, Q.; Gu, C. Grazing induced changes in plant diversity is a critical factor controlling grassland productivity in the Desert Steppe, Northern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veen, G.F.; Sarneel, J.M.; Ravensbergen, L.; Huig, N.; van Paassen, J.; Rip, W.; Bakker, E.S. Aquatic grazers reduce the establishment and growth of riparian plants along an environmental gradient. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 1794–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, D.A.; Heithaus, M.R.; Fourqurean, J.W. Feeding preferences of herbivores in a relatively pristine subtropical seagrass ecosystem. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2012, 63, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škornik, S.; Vidrih, M.; Kaligarič, M. The effect of grazing pressure on species richness, composition and productivity in North Adriatic Karst pastures. Plant Biosyst. 2010, 144, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulungan, M.A.; Suzuki, S.; Gavina, M.K.A. Grazing enhances species diversity in grassland communities. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Violle, C.; Navas, M.L.; Vile, D.; Kazakou, E.; Fortunel, C.; Hummel, I.; Garnier, E. Let the concept of trait be functional! Oikos 2007, 116, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.F.; Liu, T.J.; Han, X.F.; Lu, Y.J.; Xu, X.M.; Wang, L.X.; Liao, Z.L.; Dong, Z.; Jiao, R.; Liang, W.T.; et al. Adaptive traits of three dominant desert-steppe species under grazing-related degradation: Morphology, structure, and function. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 28, e01647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.H.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, H.M.; Wang, L.X.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Liang, C.Z. Single grazing is more detrimental to grasslands than mixed grazing: Evidence from the response of functional traits of dominant plants to grazing systems. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 682289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, D.; Xing, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, L. Combined effects of resource heterogeneity and simulated herbivory on plasticity of clonal integration in a rhizomatous perennial herb. Plant Biol. 2014, 16, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Kattge, J.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Wright, I.J.; Lavorel, S.; Dray, S.; Reu, B.; Kleyer, M.; Wirth, C.; Prentice, I.C.; et al. The global spectrum of plant form and function. Nature 2016, 529, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovett-Doust, J. Plant strategies, vegetation processes, and ecosystem properties. J. Veg. Sci. 2002, 13, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freschet, G.T.; Violle, C.; Bourget, M.Y.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; Fort, F. Allocation, morphology, physiology, architecture: The multiple facets of plant above- and below-ground responses to resource stress. New Phytol. 2018, 219, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsberry, L.; Baker, M.A.; Ewanchuk, P.J.; Bertness, M.D. Clonal integration and the expansion of Phragmites australis. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.T.; Zhong, M.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Wu, R.X.; Shao, X.Q. Covariation in root traits of Leymus chinensis in response to grazing in steppe rangeland. Rangel. J. 2019, 41, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, Q.S.; Solovyeva, D.; Lameris, T.; Batbayar, N.; Bysykatova-Harmey, I.; Li, H.; Emelyanov, V.; Rozenfeld, S.B. Population trends and migration routes of the East Asian Bean Goose Anser fabalis middendorffii and A. f. serrirostris. Wildfowl 2020, 70, 124–156. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.Q.; Zhao, Q.S.; Solovyeva, D.; Lee, H.; Bysykatova-Harmey, I.; Xu, Z.G.; Ushiyama, K.; Shimada, T.; Koyama, K.; Park, J.; et al. Contrasting trends in two East Asian populations of the Greater White-fronted Goose Anser albifrons. Wildfowl 2020, 6, 181–205. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.Y.; Hui, D.F.; Huangfu, C.H. Site conditions interact with litter quality to affect home-field advantage and rhizosphere effect of litter decomposition in a subtropical wetland ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.J.; Cong, P.H.; Barter, M.; Fox, A.D.; Cao, L. The changing abundance and distribution of Greater White-fronted Geese Anser albifrons in the Yangtze River floodplain: Impacts of recent hydrological changes. Bird Conserv. Int. 2012, 22, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wass, R.T.; Mitchell, S.F. What do Herbivore Exclusion Experiments Tell Us? An Investigation Using Black Swans (Cygnus atratus) and Filamentous Algae in a Shallow Lake. In The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, K.P.; Liu, Y.M. Measurement method I for biological community diversity: Alpha diversity measurement method (the second half). Chin. Biodivers. 1994, 2, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.P.; Minggagud, H.; Baoyin, T.; Li, F.Y. Plant production decreases whereas nutrients concentration increases in response to the decrease of mowing stubble height. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.Y.; Pan, Y.; Gong, J.R.; Li, X.B.; Liu, M.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.H.; Baoyin, T. Physiology of Leymus chinensis under seasonal grazing: Implications for the development of sustainable grazing in a temperate grassland of Inner Mongolia. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 271, 110984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Pan, F.J.; Li, D.J.; Chen, H.S.; Wang, K.L. Changes in nitrogen and phosphorus limitation during secondary succession in a karst region in southwest China. Plant Soil 2015, 391, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Grace, J.B.; Johnson, D.J.; Lefcheck, J.S.; Byrnes, J.E.K. Quantifying relative importance: Computing standardized effects in models with binary outcomes. Ecosphere 2018, 9, e02283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.J.; Cao, L.; Fox, A.D. The benefits of being big: Effects of body size on energy budgets of three wintering goose species grazing Carex beds in the Yangtze River floodplain, China. J. Ornithol. 2013, 154, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.A.; Stillman, R.A.; Clarke, R.T.; Daunt, F.; O’Hare, M.T. The impact of waterfowl herbivory on plant standing crop: A meta-analysis. Hydrobiologia 2012, 686, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angassa, A. Effects of grazing intensity and bush encroachment on herbaceous species and rangeland condition in Southern Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 25, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.X.; Wu, J.X.; Wu, J.J.; Guo, Y.J.; Lha, D.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.Z. Heavy grazing altered the biodiversity–productivity relationship of alpine grasslands in Lhasa River Valley, Tibet. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 698707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Prins, H.H.; Versluijs, M. Experimental evidence shows the importance of behavioural plasticity and body size under Competition in Waterfowl. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prop, J.; Vulink, T. Digestion by Barnacle Geese in the annual cycle: The interplay between retention time and food quality. Funct. Ecol. 1992, 6, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, G.T.; Gawlik, D.E.; Rutchey, K. Distribution of wading birds relative to vegetation and water depths in the northern everglades of florida, USA. Waterbirds 2002, 25, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, D. The digestion of fibre in herbivorous Anatidae—A review. Wildfowl 2003, 54, 7–24. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, I.J.; Prins, H.H.T.; Mallon, J.; Puk, L.D.; Miranda, E.B.P.; Starling-Manne, C.; van der Wal, R.; Moore, B.; Foley, W.; Lush, L.; et al. The Ecology of Browsing and Grazing in Other Vertebrate Taxa. In The Ecology of Browsing and Grazing II; Gordon, I.J., Prins, H.H.T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 339–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Y.; Zou, Y.A.; Xie, Y.H.; Zhang, S.Q.; Chen, X.S.; Li, F.; Deng, Z.M.; Zhang, H.; Tu, W. Hydrology-driven responses of herbivorous geese in relation to changes in food quantity and quality. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 10, 5281–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van der Graaf, A.J.; Coehoorn, P.; Stahl, J. Sward height and bite size affect the functional response of barnacle geese Branta leucopsis. J. Ornithol. 2006, 147, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jckmans, K.; Clarys, P.; Nijs, J.; Meeus, M.; Aerenhouts, D. Association between cognitive performance, physical fitness, and physical activity level in women with chronic fatigue syndrome. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2013, 50, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.J.; Wei, C.; Adamowski, J.F.; Biswas, A.; Li, Y.M.; Zhu, G.F.; Liu, C.F.; Feng, Q. On China’s Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, duration of grazing exclosure alters R:S ratio, root morphology and attending root biomass. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.J.; Cieraad, E.; Clarkson, B.R.; Colmer, T.D.; Pedersen, O.; Visser, E.J.W.; Voesenek, L.A.C.J.; van Bodegom, P.M. Drivers of plant traits that allow survival in wetlands. Funct. Ecol. 2020, 34, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briske, D.D.; Richards, J.H. Plant responses to defoliation: A physiological, morphological, and demographic evolution. dividual plants to grazing: Current status and ecological significance. In Wildland Plants: Physiological Ecology and Developmental Biology; Bedunah, D.J., Sosebee, R.E., Eds.; Society for Range Management: Denver, CO, USA, 1995; pp. 635–710. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.D.; Wang, J.Z.; Wu, H.D.; Yan, Z.Q.; Zhang, K.R.; Kang, X.M. Grazing significantly increases root shoot ratio but decreases soil organic carbon in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau grasslands: A hierarchical meta-analysis. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2369–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Wardle, D.A.; Yeates, G.W. Linking above-ground and below-ground interactions: How plant responses to foliar herbivory influence soil organisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.W.; Gornish, E.S.; Mariotte, P.; Chen, J.Q.; Liang, C.Z. Foliar nutrient content mediates grazing effects on species dominance and plant community biomass. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 72, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.P.; Zhang, W.P.; Fornara, D.A.; Li, L. Contrasting responses of nitrogen: Phosphorus stoichiometry in plants and soils under grazing: A global meta-analysis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 58, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, A.M.; Posse, G.; Collantes, M.B. Plant functional traits, herbivore selectivity and response to sheep grazing in Patagonian steppe grasslands. J. Appl. Ecol. 2005, 42, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gong, J.R.; Yang, B.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, B.; Zhu, C.C.; Hou, X.Y. Differences in the photosynthetic and physiological responses of Leymus chinensis to different levels of grazing intensity. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heberling, J.M.; Brouwer, N.L.; Kalisz, S. Effects of deer on the photosynthetic performance of invasive and native forest herbs. AoB Plants 2017, 9, plx011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Harguindeguy, N.; Díaz, S.; Garnier, E.; Lavorel, S.; Poorter, H.; Jaureguiberry, P.; Bret-Harte, M.S.; Cornwell, W.K.; Craine, J.M.; Gurvich, D.E.; et al. New handbook for standardized measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust. J. Bot. 2013, 61, 167–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chen, S.P.; Han, X.G.; Lin, G.X. Effects of long term grazing on the morphological and functional traits of Leymus chinensis in the semiarid grassland of Inner Mongolia, China. Ecol. Res. 2008, 24, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.L.; Zhang, T.H.; Yue, P.; Lv, P.; Hu, Y.; Medina-Roldán, E.; Zuo, X.A. Increased grazing intensities induce differentiation of the relationships between functional traits and aboveground plant biomass in shrub and grass dominated community in desert steppe. Ecol. Res. 2021, 36, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Terms | Explanation | Terms | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | no foraging | SLA | specific leaf area |
| VF | very little foraging | RL | root length |
| LF | light foraging | RD | root diameter |
| MF | moderate foraging | RSA | root surface area |
| HF | heavy foraging | RV | root volume |
| C | carbon | NL | number of links |
| N | nitrogen | NT | number of tips |
| P | phosphorus | RSR | root: shoot ratio |
| LC | leaf carbon | RC | root carbon |
| LN | leaf nitrogen | RN | root nitrogen |
| LP | leaf phosphorus | RP | root phosphorus |
| Parameters | Foraging Intensity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | VF | LF | MF | HF | ||
| C (%) | Leaf | 43.35 ± 1.06 a | 44.38 ± 0.64 a | 42.69 ± 1.22 a | 42.97 ± 0.98 a | 41.95 ± 1.39 a |
| Root | 45.86 ± 0.64 a | 43.80 ± 1.01 ab | 41.70 ± 0.79 b | 45.21 ± 0.83 a | 44.35 ± 1.01 ab | |
| N (%) | Leaf | 2.14 ± 0.11 a | 2.20 ± 0.18 a | 2.18 ± 0.25 a | 2.16 ± 0.13 a | 2.23 ± 0.15 a |
| Root | 0.97 ± 0.04 abc | 1.06 ± 0.05 ab | 0.93 ± 0.07 bc | 1.12 ± 0.03 a | 0.81 ± 0.04 c | |
| P (%) | Leaf | 0.27 ± 0.06 a | 0.22 ± 0.04 a | 0.20 ± 0.03 a | 0.19 ± 0.03 a | 0.22 ± 0.06 a |
| Root | 0.13 ± 0.01 ab | 0.12 ± 0.03 b | 0.18 ± 0.01 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 b | 0.13 ± 0.02 ab | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Xu, W.; Ye, X. Effects of Waterbird Herbivory on Dominant Perennial Herb Carex thunbergii in Shengjin Lake. Diversity 2022, 14, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050331
Wang X, Zhao J, Xu W, Ye X. Effects of Waterbird Herbivory on Dominant Perennial Herb Carex thunbergii in Shengjin Lake. Diversity. 2022; 14(5):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050331
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xin, Jinming Zhao, Wenjing Xu, and Xiaoxin Ye. 2022. "Effects of Waterbird Herbivory on Dominant Perennial Herb Carex thunbergii in Shengjin Lake" Diversity 14, no. 5: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050331
APA StyleWang, X., Zhao, J., Xu, W., & Ye, X. (2022). Effects of Waterbird Herbivory on Dominant Perennial Herb Carex thunbergii in Shengjin Lake. Diversity, 14(5), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050331