T-Patterns Revisited: Mining for Temporal Patterns in Sensor Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Description of the Problem and Related Work
3. T-patterns
4. The Modified T-Pattern Algorithm
4.1. Testing Independence between Two Temporal Point Processes
4.2. Modelling Inter-Event Times
5. Experiments
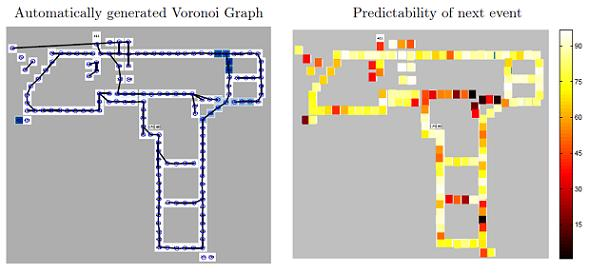
5.1. An Experimental Testbed
5.2. The MERL Motion Detector Dataset
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Magnusson, MS. Discovering hidden time patterns in behavior: T-patterns and their detection. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput 2000, 32, 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Tavenard, R; Salah, AA; Pauwels, EJ. Searching for Temporal Patterns in AmI Sensor Data. In Constructing Ambient Intelligence: Proceedings of AmI-07 Workshops; Mühlhäuser, M, Ferscha, A, Aitenbichler, E, Eds.; Springer Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2007; Volume CCIS 11, pp. 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wren, C; Ivanov, Y; Leigh, D; Westhues, J. The MERL Motion Dataset: 2007 Workshop on Massive Datasets. Technical report TR2007-069 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, P; Steinbach, M; Kumar, V; Potter, C; Klooster, S; Torregrosa, A. Finding spatio-temporal patterns in earth science data. Proceedings of the KDD Workshop on Temporal Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, August 2001.
- Klemettinen, M; Mannila, H; Toivonen, H. Rule Discovery in Telecommunication Alarm Data. J. Netw. Syst. Manag 1999, 7, 395–423. [Google Scholar]
- Kordic, S; Lam, P; Xiao, J; Li, H; Australia, W. Analysis of Alarm Sequences in a Chemical Plant. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Advanced Data Mining and Applications; LNCS 5139,. Springer: Chengdu, China, October 2008; pp. 135–146. [Google Scholar]
- Casari, P; Castellani, A; Cenedese, A; Lora, C; Rossi, M; Schenato, L; Zorzi, M. The Wireless Sensor Networks for City-Wide Ambient Intelligence (WISE-WAI) Project. Sensors 2009, 9, 4056–4082. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, V; Lin, K. Energy efficient strategies for object tracking in sensor networks: A data mining approach. J. Syst. Softw 2007, 80, 1678–1698. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, V; Lu, E. Energy-efficient real-time object tracking in multi-level sensor networks by mining and predicting movement patterns. J. Syst. Softw 2009, 82, 697–706. [Google Scholar]
- Caris-Verhallen, W; Timmermans, L; van Dulmen, S. Observation of nurse–patient interaction in oncology: Review of assessment instruments. Patient Educ. Couns 2004, 54, 307–320. [Google Scholar]
- Ermes, M; Parkka, J; Mantyjarvi, J; Korhonen, I. Detection of daily activities and sports with wearable sensors in controlled and uncontrolled conditions. IEEE Tran. Inf. Technol. Biomed 2008, 12, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, S; Fukui, K; Moriyama, K; Kurihara, S; Numao, M. Extracting human behaviors with infrared sensor network. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Networked Sensing Systems, Braunschweig, Germany, June 2007; pp. 122–125.
- Ivanov, Y; Bobick, A. Recognition of visual activities and interactions by stochastic parsing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell 2000, 22, 852–872. [Google Scholar]
- Micheloni, C; Snidaro, L; Foresti, G. Exploiting temporal statistics for events analysis and understanding. Im. Vis. Comp 2009, 27, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar]
- van Kasteren, T; Noulas, A; Englebienne, G; Kröse, B. Accurate activity recognition in a home setting. Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Seoul, South Korea, September 2008; pp. 1–9.
- Wilson, D; Atkeson, C. Simultaneous tracking and activity recognition (STAR) using many anonymous, binary sensors. Proceedings of the International Conference on Pervasive Computing; Springer: Kauai Island, HI, USA, March 2005; pp. 62–79. [Google Scholar]
- Artikis, A; Paliouras, G. Behaviour Recognition using the Event Calculus. Proceedings of the 5th IFIP Conference on Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations; Springer: Thessaloniki, Greece, April 2009; pp. 469–478. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, D; Hightower, J; Liao, L; Schulz, D; Borriello, G. Bayesian filtering for location estimation. IEEE Pervasive Comput 2003, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Dietterich, T; Michalski, R. Discovering patterns in sequences of events. Artif. Intell 1985, 25, 117–246. [Google Scholar]
- Elman, J. Finding structure in time. Cogn. Sci 1990, 14, 179–211. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S; Cook, D. Predicting inhabitant action using action and task models with application to smart homes. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Tools 2004, 13, 81–99. [Google Scholar]
- Bobick, A; Wilson, A. A State-based approach to the representation and recognition of gesture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell 1997, 19, 1325–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, T; Matsuyama, T. Multi-object behavior recognition by event driven selective attention method. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell 2000, 22, 873–887. [Google Scholar]
- Guralnik, V; Srivastava, J. Event detection from time series data. Proceedings of the 5th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Diego, CA, USA, August 1999; pp. 33–42.
- Han, J; Pei, J; Yin, Y; Mao, R. Mining frequent patterns without candidate generation: A frequent-pattern tree approach. Data Min. Knowl. Discov 2004, 8, 53–87. [Google Scholar]
- Last, M; Klein, Y; Kandel, A. Knowledge discovery in time series databases. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 2001, 31, 160–169. [Google Scholar]
- Mannila, H; Toivonen, H; Inkeri Verkamo, A. Discovery of frequent episodes in event sequences. Data Min. Knowl. Discov 1997, 1, 259–289. [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy, S; Zaki, M; Ogihara, M; Dwarkadas, S. Incremental and Interactive Sequence Mining. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Kansas City, MO, USA, November 1999; pp. 251–258.
- Pei, J; Han, J; Mortazavi-Asl, B; Pinto, H; Chen, Q; Dayal, U; Hsu, M. PrefixSpan: Mining Sequential Patterns Efficiently by Prefix-Projected Pattern Growth. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany, April 2001; pp. 215–224.
- Pinto, H; Han, J; Pei, J; Wang, K; Chen, Q; Dayal, U. Multi-dimensional Sequential Pattern Mining. Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Atlanta, GA, USA, November 2001; pp. 81–88.
- Casas-Garriga, G. Discovering unbounded episodes in sequential data. Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Principles and Practice of Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Cavtat-Dubrovnik, Croatia, September 2003; pp. 83–94.
- Cule, B; Goethals, B; Robardet, C. A New Constraint for Mining Sets in Sequences. Proceedings of the SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, Sparks, NV, USA, April 2009; pp. 317–328.
- Eagle, N; Pentland, A. Eigenbehaviors: Identifying structure in routine. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol 2009, 63, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, DJ. Prediction Algorithms for Smart Environments. In Smart Environments: Technologies, Protocols, and Applications; Cook, DJ, Das, SK, Eds.; Wiley Series on Parallel and Distributed Computing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 175–192. [Google Scholar]
- Borrie, A; Jonsson, G; Magnusson, M. Temporal pattern analysis and its applicability in sport: An explanation and exemplar data. J. Sports Sci 2002, 20, 845–852. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, S, Jr; Collier, N. C-quence: A tool for analyzing qualitative sequential data. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput 2002, 34, 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, C; Burns, J; Bui, H. Recovering social networks from massive track datasets. SRI International Technical Note 564 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Choset, H; Burdick, J. Sensor-based exploration: The hierarchical generalized Voronoi graph. Int. J. Rob. Res 2000, 19, 96–122. [Google Scholar]
- Beeson, P; Jong, N; Kuipers, B. Towards autonomous topological place detection using the extended Voronoi graph. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Barcelona, Spain, April 2005; 4, pp. 4373–4379.





| Layout 1 | Layout 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 person | 2 persons | 1 person | 2 persons | |
| LZ | 29.8 | 17.7 | 56.5 | 13.2 |
| ALZ | 21.1 | 18.8 | 66.4 | 19.6 |
| LZW | 28.9 | 22.0 | 60.5 | 15.1 |
| T-patterns | 28.8 | 17.1 | 61.5 | 24.2 |
| GMM T-patterns | 34.8 | 29.3 | 61.9 | 48.3 |
| Without Bonferroni | With Bonferroni | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SITPat | TTPat | GMMTPat | SITPat | TTPat | GMMTPat | |
| Spurious | 111.6 | 86.6 | 1.4 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 |
| Correct | 85.8 | 94.2 | 47.6 | 61.2 | 74.8 | 37.6 |
| Missed | 29.2 | 20.8 | 67.4 | 53.8 | 40.2 | 77.4 |
| Gray | 30.2 | 31.8 | 6.6 | 17.2 | 20.4 | 3.4 |
| α | 462.910 | 17.180 | 690 | 363.740 | 12.790 | 635 |
| E[α] | 405.000 | 14.812 | 900 | 405.000 | 14.812 | 900 |
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Salah, A.A.; Pauwels, E.; Tavenard, R.; Gevers, T. T-Patterns Revisited: Mining for Temporal Patterns in Sensor Data. Sensors 2010, 10, 7496-7513. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100807496
Salah AA, Pauwels E, Tavenard R, Gevers T. T-Patterns Revisited: Mining for Temporal Patterns in Sensor Data. Sensors. 2010; 10(8):7496-7513. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100807496
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalah, Albert Ali, Eric Pauwels, Romain Tavenard, and Theo Gevers. 2010. "T-Patterns Revisited: Mining for Temporal Patterns in Sensor Data" Sensors 10, no. 8: 7496-7513. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100807496
APA StyleSalah, A. A., Pauwels, E., Tavenard, R., & Gevers, T. (2010). T-Patterns Revisited: Mining for Temporal Patterns in Sensor Data. Sensors, 10(8), 7496-7513. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100807496