Essential Limitations of the Standard THz TDS Method for Substance Detection and Identification and a Way of Overcoming Them
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Description of the Setup and Measurements
3. Spectral Analysis
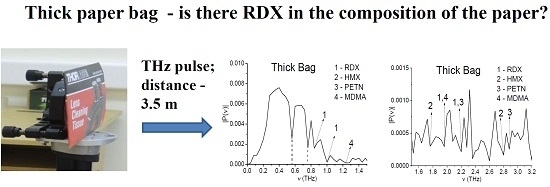
3.1. Spectral Properties of the Thick Bag Sample
3.2. Spectral Properties of Si-Based Semiconductors
4. SDA-Method and Modified Integral Correlation Criteria
4.1. Advantages of the Spectral Dynamics Analysis Method (SDA-Method)
4.2. SDA-Method
4.3. Integral Correlation Criteria
5. Identification Based on Integral Correlation Criteria
5.1. Detecting the Absence of RDX in the Thick Bag Sample
5.2. Detecting Paper in the Sample
5.3. Detecting RDX Absence in the Si-Based Semiconductors
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| THz TDS | Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy |
| SDA-method | Spectral Dynamics Analysis method |
| FDR | Frequency detection range |
References
- Federici, J.F.; Schulkin, B.; Huang, F.; Gary, D.; Barat, R.; Oliveira, F.; Zimdars, D. THz imaging and sensing for security applications—Explosives, weapons and drugs. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2005, 20, S266–S280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.; Lo, T.; Tribe, W.R.; Cole, B.E.; Hogbin, M.R.; Kemp, M.C. Detection of concealed explosives at a distance using terahertz technology. IEEE Proc. 2007, 95, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, M.C. Screening mail for powders using terahertz technology. Proc. SPIE 2011, 8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigang, R.; Biedron, S.G.; Dyjak, S.; Ellrich, F.; Magnus, W.; Haakestad, M.W.; Hübsch, D.; Kartaloglu, T.; Ozbay, E.; Ospald, F.; et al. Comparison of terahertz technologies for detection and identification of explosives. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, G.; Zybin, S.; Goddard, W.A.; Zeiri, Y.; Kosloff, R. Direct MD simulations of terahertz absorption and 2D spectroscopy applied to explosive crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leahy-Hoppa, M.R.; Fitch, M.J.; Zheng, X.; Hayden, L.M.; Osiander, R. Wideband terahertz spectroscopy of explosives. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 434, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.G.; Burnett, A.D.; Fan, W.; Linfield, E.H.; Cunningham, J.E. Terahertz spectroscopy of explosives and drugs. Mater. Today 2008, 11, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Hong, T.; Sim, K.I.; Ha, T.; Park, B.C.; Chung, J.H.; Cho, S.G.; Kim, J.H. Reflection terahertz time-domain spectroscopy of RDX and HMX explosives. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 023105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, H.; Bastiaans, G.J.; Zhang, X.C. Absorption coefficients of selected explosives and related compounds in the range of 0.1–2.8 THz. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 12060–12067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, M.C. Explosives detection by terahertz spectroscopy—A bridge too far? IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Shen, J. Fingerprint extraction from interference destruction terahertz spectrum. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 21798–21803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palka, N. Identification of concealed materials, including explosives, by terahertz reflection spectroscopy. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortolani, M.; Lee, J.S.; Schade, U.; Hübers, H.W. Surface roughness effects on the terahertz reflectance of pure explosive materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withayachumnankul, W.; Fischer, B.M.; Abbott, D. Numerical removal of water vapor effects from terahertz time-domain spectroscopy measurements. Proc. R. Soc. A 2008, 464, 2435–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.-C. Identification of explosive media using their spectrum dynamics under the action of THz pulse. Proc. SPIE 2009, 7486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. 2D THz signature for substance identification. Pros. SPIE 2010, 7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Shen, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Shi, Y. 2D signature for identification of drugs. Proc. SPIE 2011, 8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Palka, N.; Szustakowski, M.; Trzcinski, T. The method of the spectral dynamics analysis of reflected signal for problem of identification of substance. Proc. SPIE 2011, 8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Peskov, N.V.; Kirillov, D.A. Efficiency of using correlation function for estimation of probability of substance detection on the base of THz spectral dynamics. Proc. SPIE 2012, 8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Szustakowski, M.; Palka, N. Influence of surface of explosive on its detection and identification using the SDA method for analysis of the reflected THz signal. Proc. SPIE 2013, 8734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Trofimov, V.V.; Tikhomirov, V.V. Peculiarities of the detection and identification of substance at long distance. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Trofimov, V.V. Transmission of THz pulse with a few circles through opaque samples placed at long distance (4–6 m). Proc. SPIE 2014, 9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. Real-time criteria based on spectral dynamics of medium response for the detection and identification of substance using THz signal. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A.; Trofimov, V.V. Possibility of the detection and identification of substance at long distance at using broad THz pulse. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. Efficiency of using the spectral dynamics for pulsed THz spectroscopy of both explosives and other materials. Proc. SPIE 2015, 9454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. An effective method for substance detection using the broad spectrum THz signal: A “terahertz nose”. Sensors 2015, 15, 12103–12132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S. Sensors—An effective approach for the detection of explosives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buryakov, I.A.; Buryakov, T.I.; Matsaev, V.T. Optical chemical sensors for the detection of explosives and associated substances. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 69, 616–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, T.; Toko, K. Towards an electronic dog nose: Surface plasmon resonance immunosensor for security and safety. Sensors 2014, 14, 16586–16616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Patz, A.; Mouchliadis, L.; Yan, J.; Lograsso, T.A.; Perakis, I.E.; Wang, J. Femtosecond switching of magnetism via strongly correlated spin-charge quantum excitations. Nature 2013, 496, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Chatzakis, I.; Patz, A.; Wang, J. Ultrafast terahertz probes of interacting dark excitons in chirality-specific semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A-level Applied Science/Colour Chemistry/Fibres/Cellulose. Available online: https://www.en.wikibooks.org/wiki/A-level_Applied_Science/Colour_Chemistry/Fibres/Cellulose) (accessed on 31 March 2016).
- Vieira, F.S.; Pasquini, C. Determination of cellulose crystallinity by terahertz-time domain spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 3780–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RDX. Available online: https://www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RDX (accessed on 31 March 2016).
- Kemp, M.C.; Baker, C.; Gregory, I. NATO Security through Science Series; IOS Press Books Online: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, A.; Jin, Y.; Ma, X.F.; Zhang, X.-C.; Bliss, D.; Larkin, J.; Alexander, M. Terahertz optical rectification from <110> zinc-blende crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1994, 64, 1324–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Litz, M.; Zhang, X.-C. Broadband detection capability of ZnTe electro-optic field detectors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 68, 2924–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- THz Database 2.0. Available online: http://www.riken.jp/THzdatabase/ (accessed on 31 March 2016).
- Dai, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Grischkowsky, D. Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy characterization of the far-infrared absorption and index of refraction of high-resistivity, float-zone silicon. JOSA B 2004, 21, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Dai, Q.F.; Wu, L.J.; Lan, S.; Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. Effects of p-type doping on the optical properties of InAs/GaAs quantum dots. Solid State Commun. 2012, 152, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trofimov, V.A.; Varentsova, S.A. Essential Limitations of the Standard THz TDS Method for Substance Detection and Identification and a Way of Overcoming Them. Sensors 2016, 16, 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040502
Trofimov VA, Varentsova SA. Essential Limitations of the Standard THz TDS Method for Substance Detection and Identification and a Way of Overcoming Them. Sensors. 2016; 16(4):502. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040502
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrofimov, Vyacheslav A., and Svetlana A. Varentsova. 2016. "Essential Limitations of the Standard THz TDS Method for Substance Detection and Identification and a Way of Overcoming Them" Sensors 16, no. 4: 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040502
APA StyleTrofimov, V. A., & Varentsova, S. A. (2016). Essential Limitations of the Standard THz TDS Method for Substance Detection and Identification and a Way of Overcoming Them. Sensors, 16(4), 502. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16040502