Field-Based Optimal Placement of Antennas for Body-Worn Wireless Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
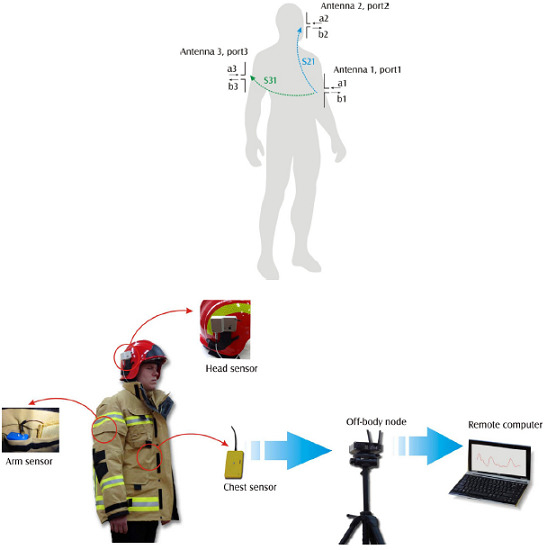
S31 = b3/a1 while a2 = 0 and a3 = 0
2. Methods
2.1. The Numerical Human Body Model
2.2. Statement of the Optimal Design Problem
Having fixed the position of both a head sensor (antenna 2) and an arm sensor (antenna 3), find the position of the chest sensor (antenna 1) minimizing both S21 and S31 scattering parameters in the frequency band B between fL and fH (for 2.4 GHz ISM band we assumed that fL = 2.4 GHz and fH = 2.5 GHz while for 5GHz ISM band fL = 5.7 GHz and fH = 5.9 GHz).
2.3. Optimization Algorithm
- Setting m = m0 and d = d0 at the initial iteration, the generation of the design vector x = m + du takes place, resorting to a stochastic sample ; generally, u is a normally distributed sample. Vector x is accepted if it fulfils bounds and constraints; otherwise, a new design vector is generated until the corresponding design point falls inside the feasible region.
- The associated objective function f(x) is then evaluated, and the test f(x) < f(m) is performed; if the test is successful, m is replaced by x (mutation operator), otherwise m is conserved.
- The last step rules the size of the search region that will be used for the successive iteration: when a design point that is better than the current one is found, the radius of the search region is increased around the new point to search for further improvements; if no improvement is found, the radius of the search region is gradually decreased, up to convergence.
3. Simulations and Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alam, M.M.; Hamida, E.B. Surveying Wearable Human Assistive Technology for Life and Safety Critical Applications: Standards, Challenges and Opportunities. Sensors 2014, 14, 9153–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movassaghi, S.; Abolhasan, M.; Lipman, J.; Smith, D.; Jamalipour, A. Wireless Body Area Network: A Survey. IEEE Commun. 2014, 16, 1658–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Liu, Q.; Wei, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, G.; Han, G. A Survey of Body Sensor Networks. Sensors 2013, 13, 5406–5447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- FLORA—Wearable Electronic Platform. Available online: https://www.adafruit.com/products/659 (accessed on 20 January 2016).
- Cheng, J.; Lukowicz, P.; Henze, N.; Schmidt, A.; Amft, O.; Salvatore, G.A.; Troster, G. Smart Textiles: From Niche to Mainstream Publication. IEEE Pervasive Comput. Mag. 2013, 12, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, J.P.; Huang, J. Pulse Oximetry in the External Auditory Canal—A New Method of Mobile Vital Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andreagiovanni, F.; Nardin, A. Towards the fast and robust optimal design of wireless body area networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 37, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andreagiovanni, F.; Krolikowski, J.; Pulaj, J. A fast hybrid primal heuristic for multiband robust capacitated network design with multiple time periods. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 26, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, J. Optimal design of energy-efficient and cost-efficient wireless body area networks. Ad Hoc Netw. Arch. 2014, 13, 560–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringuier, J.N.; Mittra, R. Electromagnetic Wave Propagation in Body Area Networks Using the Finite-Difference-Time-Domain Method. Sensors 2012, 12, 9862–9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- XFDTD 7.3 Reference Manual; Remcom Inc.: State College, PA, USA, 2012.
- Xu, X.G.; Eckerman, K.F. Handbook of Anatomical Models for Radiation Dosimetry; Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Robin, A. Electromagnetic Modelling of Human Tissues and its Application on the Interaction between Antenna and Human Body in the BAN Context. PhD Thesis, Université Paris-Est, Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Panagamuwa, C.J.; Whittow, W.G.; Edwards, R.M.; Vardaxoglou, J.C. Experimental Verification of a Modified Specific Anthropomorphic Mannequin (SAM) Head used for SAR Measurements. In Proceedings of the Antennas and Propagation Conference, Loughborough, UK, 2–3 April 2007; pp. 261–264.
- Arkko, A. Properties of numerical SAM phantom used in mobile phone antenna simulations. In Proceedings of the Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 3–8 July 2005; pp. 450–453.
- Uno, Y.; Saito, K.; Takahashi, M.; Ito, K. Structure of cylindrical tissue-equivalent phantom for medical applications. In Proceedings of the Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA), Sydney, Australia, 20–24 September 2010; pp. 406–409.
- Lim, H.B.; Baumann, D.; Li, E.P. A Human Body Model for Efficient Numerical Characterization of UWB Signal Propagation in Wireless Body Area Networks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iswandi; Aoyagi, T.; Kim, M.; Takada, J. The utilization of body skeleton model for modeling the dynamic BAN channels. In Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), Prague, Czech Republic, 26–30 March 2012; pp. 540–543.
- Januszkiewicz, Ł.; Hausman, S. Simplified human phantoms for narrowband and ultra-wideband body area network modelling. COMPEL Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2015, 34, 439–447. [Google Scholar]
- Januszkiewicz, Ł. Simplified human body models for interference analysis in the cognitive radio for medical body area networks. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Medical Information and Communication Technology (ISMICT), Firenze, Italy, 2–4 April 2014; pp. 1–5.
- Hausman, S.; Januszkiewicz, Ł. Impact of Indoor Environment on Path Loss in Body Area Networks. Sensors 2014, 14, 19551–19560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Chong, J.K.; Park, K.Y.; Lowther, D.A. Differential evolution strategy for constrained global optimization and application to practical engineering problems. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2007, 43, 1565–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, E.F.; Guimarães, F.G.; Takahashi, R.H.C.; Lowther, D.A.; Ramírez, J.A. Multiobjective memetic algorithms with quadratic approximation-based local search for expensive optimization in electromagnetics. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 1126–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crevecoeur, G.; Sergeant, P.; Dupré, L.; van de Walle, V. A two-level genetic algorithm for electromagnetic optimization. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 2585–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Campelo, F.; Iijima, Y.; Kawano, K.; Matsuo, T.; Mifune, T.; Igarashi, H. Optimization of inductors using evolutionary algorithms and its experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 3393–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Barba, P.; Mognaschi, M.E.; Palka, R.; Savini, A. Optimization of the MIT Field Exciter by a Multiobjective Design. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 1530–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, L.S.; Alotto, P. Electromagnetic optimization using a cultural self-organizing migrating algorithm approach based on normative knowledge. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 1446–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D. Biogeography-based optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2008, 12, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, U.; Kumar, H.; Kamal, T.S. Design of Yagi-Uda Antenna Using Biogeography Based Optimization. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2010, 58, 3375–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Mittal, E.; Sachdeva, G. NSBBO for Gain-Impedance Optimization of Yagi-Uda Antenna Design. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Information and Communication Technologies, Trivandrum, India, 30 October–2 November 2012; pp. 856–860.
- Robinson, J.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Particle Swarm Optimization in Electromagnetics. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2004, 52, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Advances in Particle Swarm Optimization for Antenna Designs: Real-Number, Binary, Single-Objective and Multiobjective Implementations. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 2745–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, Z.; Komurcu, M.; Bossard, J.A.; Werner, D.H. The Wind Driven Optimization Technique and its Application in Electromagnetics. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2013, 61, 2745–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queipo, N.E.; Haftka, R.T.; Shyy, W.; Goel, T.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Tucker, P.K. Surrogate-based analysis and optimization. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2005, 41, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Rotaru, M.; Sykulski, J.K. Exploration versus exploitation using kriging surrogate modelling in electromagnetic design. COMPEL Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2012, 31, 1541–1551. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Gonzalez, S.; Vasilakos, A.; Cao, H.; Leung, V.C. Body Area Networks: A Survey. ACM/Springer Mob. Netw. Appl. 2011, 16, 171–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, J.W.; Bateman, D.; Hauberg, S.; Wehbring, R. GNU Octave: Free Your Numbers. Available online: https://www.gnu.org/software/octave/octave.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2013).











| Optimization Scenario | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Antennas, 2.4 GHz Fixed Distance | 2 Antennas, 2.4 GHz Variable Distance | 3 Antennas, 2.4 GHz Variable Distance | 3 Antennas, 5 GHz Variable Distance | |
| Final Value of Angle [rad] | 0.63 | 0.5 | 0.22 | 0.35 |
| Final Value of Vertical Coordinate [m] | 0.567 | 0.379 | 0.18 | 0.335 |
| Final Value of Antenna Distance [m] | 0.001 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.0045 |
| Initial Value of Objective Function [dB] | −81 | −81 | −109 | −124 |
| Final Value of Objective Function [dB] | −69 | −64 | −80 | −96 |
| Improvement of Objective Function [dB] | 12 | 17 | 29 | 28 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Januszkiewicz, Ł.; Di Barba, P.; Hausman, S. Field-Based Optimal Placement of Antennas for Body-Worn Wireless Sensors. Sensors 2016, 16, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050713
Januszkiewicz Ł, Di Barba P, Hausman S. Field-Based Optimal Placement of Antennas for Body-Worn Wireless Sensors. Sensors. 2016; 16(5):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050713
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanuszkiewicz, Łukasz, Paolo Di Barba, and Sławomir Hausman. 2016. "Field-Based Optimal Placement of Antennas for Body-Worn Wireless Sensors" Sensors 16, no. 5: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050713
APA StyleJanuszkiewicz, Ł., Di Barba, P., & Hausman, S. (2016). Field-Based Optimal Placement of Antennas for Body-Worn Wireless Sensors. Sensors, 16(5), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16050713