High-Precision Hysteresis Sensing of the Quartz Crystal Inductance-to-Frequency Converter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Switching Mode Inductance-to-Frequency Converter
2.1. Switching Converter Principle
2.2. Converter Hysteresis Measurement Principle
2.3. Temperature Compensation
2.4. The Shortcoming of the Temperature Compensation
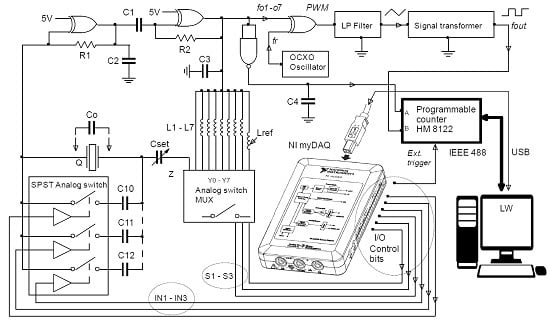
2.5. Experimental Setup
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Inductance-Frequency Characteristics of the Converter
3.2. Temperature/Frequency Stability of the Switching Converter
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kenton, B.J.; Leang, K.K. Design and control of a three-axis serial-kinematic high-bandwidth nanopositioner. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 17, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noth, K.T.; Ryu, U.C.; Lee, Y.W. Compact and wide range polarimetric strain sensor based on polarization-maintaining photonic crystal fiber. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 213, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.C.; Le, D.K.; Nguyen, V.S. Inductive displacement sensors with a notch filter for an active magnetic bearing system. Sensors 2014, 14, 12640–12657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.X.; Shao, Z.B.; Li, T. An analog-digital mixed measurement method of inductive proximity sensor. Sensors 2016, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.; Li, C.; Jia, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Xue, C.; Tan, Q. An Insertable passive lc pressure sensor based on an alumina ceramic for in situ pressure sensing in high-temperature environments. Sensors 2015, 15, 21844–21856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Tan, Q.; Jia, P.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Xue, C.; Xiong, J. Review of research status and development trends of wireless passive LC resonators for harsh environments. Sensors 2015, 15, 13097–13109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, J.A.; Chen, S. Thermal hysteresis and voltage shift analysis for differential pressure sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 135, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Morón, C.; Tremp, E. Magnetic sensor for building structural vibration. Sensors 2014, 14, 2468–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeranče, N.; Bednar, N.; Stojanović, G. An Ink-Jet Printed Eddy Current Position Sensor. Sensors 2013, 13, 5205–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.H.; Barrera, D.; Amat, R.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V.; Sales, S. Magnetic actuator based on giant magnetostrictive material Terfenol-D with strain and temperature monitoring using FBG optical sensor. Measurement 2016, 80, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matko, V.; Jezernik, K. New quartz oscillator switching method for nano-henry range inductance measurements. Sensors 2012, 12, 3105–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnau, A. A review of interface electronic systems for AT-cut quartz crystal microbalance applications in liquids. Sensors 2008, 8, 370–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Ferrari, V.; Marioli, D.; Taroni, A.; Suman, M.; Dalcanale, E. In-liquid sensing of chemical compounds by QCM sensors coupled with high-accuracy ACC oscillator. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2006, 55, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnepain, J.J. Sensitivity of quartz oscillator to the environment: Characterization methods and pitfalls. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelect. Freq. Cont. 1990, 37, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrüfer, E. Quartz as a frequency reference. In Electrical Measurement; Carl Hanser Verlag: Munich, Germany, 1992; pp. 405–412. [Google Scholar]
- Brice, J.C. Crystals for quartz resonators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1985, 57, 105–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeker, T.R. Theory and Properties of Piezoelectric Resonators and Waves. In Precision Frequency Control; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 47–119. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, C.A.; Lai, Y.S. Digital pulsewidth modulation technique for a synchronous buck converter to reduce switching frequency. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Lai, J.S.; Cho, Y. Dual-mode double-carrier-based sinusoidal pulse width modulation inverter with adaptive smooth transition control between modes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiatsookkanatorn, P.; Sangwongwanich, S. A unified PWM method for matrix converters and its carrier-based realization using dipolar modulation technique. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, M.M. Oscillator AM-to-FM Noise conversion due to the dynamic frequency-drive sensitivity of the crystal resonator. IEEE FCS 2008, 672–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filler, R.L.; Vig, J.R. Long-term aging of the oscillators. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Cont. 1992, 39, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Matko, V.; Jezernik, K. Greatly improved small inductance measurement using quartz crystal parasitic capacitance compensation. Sensor 2010, 10, 3954–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, I.C.; Lo, C.W.; Fong, K.L. Method and Apparatus for a Crystal Oscillator to Achieve Fast Start-Up Time, Low Power and Frequency Calibration. US Patent 7348861 B1, 25 March 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ruslan, R.I.; Satoh, T.; Akitsu, T. Short-term Stability in the Intermediate Region between Quartz Crystal Oscillation and LC Oscillation. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2012, 7, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutman, J. Characterization of phase and frequency instabilities in precision frequency sources. Proc. IEEE 1978, 66, 1048–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, G.; Caspani, A.; Tocchio, A. Design criteria of low-power oscillators for consumer-grade MEMS resonant sensors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lee, F. Analysis and applications of parasitic capacitance cancellation techniques for EMI suppression. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, P.; Allara, D.; Tadigadapa, S. Fabrication and performance characteristics of high-frequency micromachined bulk acoustic wave quartz resonator arrays. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matko, V.; Milanović, M. High-Precision Hysteresis Sensing of the Quartz Crystal Inductance-to-Frequency Converter. Sensors 2016, 16, 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16070995
Matko V, Milanović M. High-Precision Hysteresis Sensing of the Quartz Crystal Inductance-to-Frequency Converter. Sensors. 2016; 16(7):995. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16070995
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatko, Vojko, and Miro Milanović. 2016. "High-Precision Hysteresis Sensing of the Quartz Crystal Inductance-to-Frequency Converter" Sensors 16, no. 7: 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16070995
APA StyleMatko, V., & Milanović, M. (2016). High-Precision Hysteresis Sensing of the Quartz Crystal Inductance-to-Frequency Converter. Sensors, 16(7), 995. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16070995