Lipid Membrane Nanosensors for Environmental Monitoring: The Art, the Opportunities, and the Challenges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods for Preparing Biosensors Based on Lipid Films
2.1. Metal Supported Lipid Layers
2.2. BLMs Formed on Glassy Carbon Electrodes
2.3. Stabilized Lipid Films Formed on a Glass Fiber Filter
2.4. Polymer Supported BLMs
2.5. Lipid Films Supported on Nanomaterials
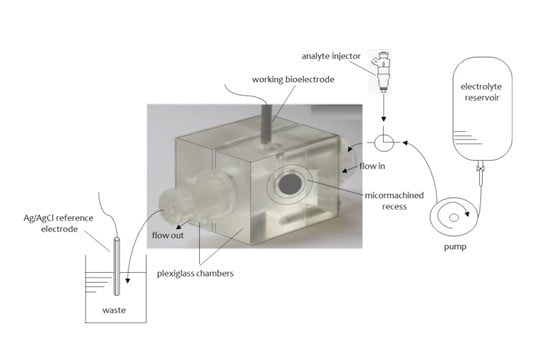
2.6. Micro- and Nano-Fabricated Lipid Bilayers
3. Applications of Lipid Membrane Nanosensors for Environmental Monitoring
4. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reshetilov, A.; Arlyapov, V.; Alferov, V.; Reshetilova, T. BOD Biosensors: Application of novel technologies and prospects for the development. In State of the Art in Biosensors—Environmental and Medical Applications; Rinken, T., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2013; pp. 57–77. [Google Scholar]
- Bahadir, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. Applications of commercial biosensors in clinical, food, environmental, and biothreat/biowarfare analyses. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 478, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashaghi, S.; Jadidi, T.; Koenderink, G.; Mashghi, A. Lipid nanotechnology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 4242–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.K.; Lee, H.; Nam, I.-M. Lipid-nanostructure hybrids and their applications in nanobiotechnology. NPG Asia Mater. 2013, 5, e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, D.; Sun, Q.; Su, K.; Wan, H.; Li, H.; Xu, N.; Sun, F.; Zhuang, L.; Hu, N.; Wang, P. Recent achievements in electronic tongue and bioelectronic tongue as taste sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Park, J.; Oh, E.H.; Ko, H.J.; Hong, S.; Park, T.H. Nanovesicle-based bioelectronic nose for the diagnosis of lung cancer from human blood. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, P.K.; Jaiswal, M.; Lim, C.H.; Wang, Y.; Sankaran, J.; Li, A.; Lim, C.T.; Wohland, T.; Barbaros, O.; Loh, K.P. A bioelectronic platform using a graphene-lipid bilayer interface. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 7387–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, P.; Rudin, D.O.; Tien, H.T.; Wescott, W.C. Reconstitution of cell membrane structure in vitro and its transformation into an excitable system. Nature 1962, 194, 979–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siontorou, C.G.; Batzias, F.A. Innovation in biotechnology: Moving from academic research to product development—The case of biosensors. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2010, 30, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, F.; Bally, M.; Städler, B.; Chandrawati, R. Liposomes and lipid bilayers in biosensors. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 249, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siontorou, C.G.; Nikoleli, G.-P.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Karapetis, S.K. Artificial lipid membranes: Past, present, and future. Membranes 2017, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siontorou, C.G. Bilayer lipid membrane constructs: A strategic technology evaluation approach. In Advanced Bioelectronic Materials; Tiwari, A., Patra, H.K., Turner, A.P.F., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 311–354. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, F.; Higson, S.P.J. Structured thin films as functional components within biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 21, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heider, S.; Reimhult, E.; Metzner, C. Real-time analysis of protein and protein mixture interaction with lipid bilayers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2018, 1860, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glazier, R.; Salaita, K. Supported lipid bilayer platforms to probe cell mechanobiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1859, 1465–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tien, H.T.; Salamon, Z. Formation of self-assembled lipid bilayers on solid substrates. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1989, 22, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolelis, D.P.; Siontorou, C.G.; Krull, U.J.; Katrivanos, P.L. Ammonium ion minisensors from self-assembled bilayer lipid membranes using gramicidin as an ionophore. Modulation of ammonium selectivity by platelet-activating factor. Anal. Chem. 1996, 15, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siontorou, C.G.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Krull, U.J.; Chiang, K.L. A triazine herbicide minisensor based on surface-stabilized bilayer lipid membranes. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hianik, T.; Dlugopolsky, J.; Gyepessova, M. Electrostriction of lipid bilayers on a solid support. Influence of hydrocarbon solvent and d.c. voltage. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1993, 31, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hianik, T.; Passechnik, V.I.; Sargent, D.F.; Dlugopolsky, J.; Sokolikova, L. Surface potentials and solvent redistribution may explain the dependence of electrical and mechanical properties of supported lipid bilayers on applied potential and bilayer history. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1995, 37, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passechnik, V.I.; Hianik, T.; Ivanov, S.A.; Sivak, B. Specific capacitance of metal supported lipid membranes. Electroanalysis 1998, 10, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomutov, G.B.; Kim, V.P.; Potapenkov, K.V.; Parshintsev, A.A.; Soldatov, E.S.; Usmanov, N.N.; Saletsky, A.M.; Sybachin, A.V.; Yaroslavov, A.A.; Migulin, V.A.; et al. Langmuir monolayers and Langmuir-Blodgett films of pH-sensitive lipid. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 532, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, R.P.; Berat, R.; Brisson, A.R. Formation of solid-supported lipid bilayers: An integrated view. Langmuir 2006, 22, 3497–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siontorou, C.G.; Brett, A.M.O.; Nikolelis, D.P. Evaluation of a glassy carbon electrode modified by a bilayer lipid membrane with incorporated DNA. Talanta 1996, 43, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, B.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Amperometric glucose biosensor based on lipid film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2000, 15, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Han, X.; Wang, J.; Tang, J.; Dong, S.; Wang, E. Concentration-dependent behavior of nisin interaction with supported bilayer lipid membrane. Biophys. Chem. 2002, 99, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Huang, W. Study of the ion-channel behavior on glassy carbon electrode supported bilayer lipid membranes stimulated by perchlorate anion. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 55, 431–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolelis, D.P.; Siontorou, C.G.; Andreou, V.G.; Krull, U.J. Stabilized bilayer-lipid membranes for flow-through experiments. Electroanalysis 1995, 7, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreou, V.G.; Nikolelis, D.P. Flow injection monitoring of aflatoxin M1 in milk and milk preparations using filter-supported bilayer lipid membranes. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 2366–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, A.M.; Koeppe, R.E.; Andersen, O.S. Kinetics of gramicidin channel formation in lipid bilayers: Transmembrane monomer association. Science 1990, 250, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelkar, D.A.; Chattopadhyay, A. The gramicidin ion channel: A model membrane protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 2011–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolelis, D.P.; Mitrokotsa, M. Stabilized lipid film based biosensor for atenolol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2002, 17, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolelis, D.P.; Simantiraki, M.; Siontorou, C.G.; Toth, K. Flow injection analysis of carbofuran in foods using air stable lipid film based acetylcholinesterase biosensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 537, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolelis, D.P.; Raftopoulou, G.; Nikoleli, G.-P.; Simantiraki, M. Stabilized lipid membrane based biosensors with incorporated enzyme for repetitive uses. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolelis, D.P.; Raftopoulou, G.; Chatzigeorgiou, P.; Nikoleli, G.-P.; Viras, K. Optical portable biosensors based on stabilized lipid membrane for the rapid detection of doping materials in human urine. Sens. Actuators B 2008, 130, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoleli, G.-P.; Israr, M.Q.; Tzamtzis, N.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Willander, M.; Psaroudakis, N. Structural characterization of graphene nanosheets for miniaturization of potentiometric urea lipid film based biosensors. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratakou, S.; Nikoleli, G.-P.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Psaroudakis, N. Development of a potentiometric chemical sensor for the rapid detection of carbofuran based on air stable lipid films with incorporated calix[4]arene phosphoryl receptor using graphene electrodes. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 2608–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psychoyios, V.N.; Nikoleli, G.-P.; Tzamtzis, N.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Psaroudakis, N.; Danielsson, B.; Israr, M.Q.; Willander, M. Potentiometric cholesterol biosensor based on ZnO nanowalls and stabilized polymerized lipid film. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratakou, S.; Nikoleli, G.-P.; Siontorou, C.G.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Tzamtzis, N. Electrochemical biosensor for naphthalene acetic acid in fruits and vegetables based on lipid films with incorporated auxin-binding protein receptor using graphene electrodes. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 2171–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karapetis, S.; Nikoleli, G.-P.; Siontorou, C.G.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Tzamtzis, N.; Psaroudakis, N. Development of an electrochemical biosensor for the rapid detection of cholera toxin based on air stable lipid films with incorporated ganglioside GM1 using graphene electrodes. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1584–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratakou, S.; Nikoleli, G.-P.; Siontorou, G.C.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Karapetis, S.; Tzamtzis, N. Development of an electrochemical biosensor for the rapid detection of saxitoxin based on air stable lipid films with incorporated Anti-STX using graphene electrodes. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, J.; Petrossian, L.; Goryll, M.; Thornton, T.J.; Goodnick, S.M.; Tang, J.M.; Eisenberg, R.S. Integrated electrodes on a silicon based ion channel measurement platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmstadt, N.; Nash, M.A.; Purnell, R.F.; Schmidt, J.J. Automated formation of lipid-bilayer membranes in a microfluidic device. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1961–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Pioufle, B.; Suzuki, H.K.; Tabata, V.; Noji, H.; Takeuchi, S. Lipid bilayer microarray for parallel recording of transmembrane ion currents. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.P.; Craighead, H.G. Surface engineering and patterning using parylene for biological applications. Materials 2010, 3, 1803–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Le Pioufle, B.; Takeuchi, S. Ninety-six-well planar lipid bilayer chip for ion channel recording fabricated by hybrid stereolithography. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, R.; Osaki, T.; Takeuchi, S. A parylene nanopore for stable planar lipid bilayer membranes. In Proceedings of the IEEE 23rd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Hong Kong, China, 24–28 January 2010; pp. 923–926. [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte, A.; Degache, A.; Descamps, E.; Dahan, L.; Bergaud, C. Biostability assessment of flexible parylene c-based implantable sensor in wireless chronic neural recording. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolelis, D.P.; Andreou, V.G. Electrochemical transduction of interactions of atrazine with bilayer lipid membranes. Electroanalysis 2005, 8, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolelis, D.P.; Siontorou, C.G. Flow injection monitoring and analysis of mixtures of simazine, atrazine, and propazine using filter-supported bilayer lipid membranes (BLMs). Electroanalysis 1996, 8, 907–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siontorou, C.G.; Nikolelis, D.P.; Tarus, B.; Dumbrava, J.; Krull, U.J. DNA biosensor based on self-assembled bilayer lipid membranes for the detection of hydrazines. Electroanalysis 1998, 10, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaloliakos, A.I.; Nikoleli, G.-P.; Siontorou, C.G.; Nikolelis, D.P. Rapid flow injection electrochemical detection of arochlor 1242 using stabilized lipid membranes with incorporated sheep anti-PCB antibody. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori, S.S.; Kohno, K.; Yamada, M. High performance smell sensor using spatially controlled LB films with polymer backbone. Sens. Actuators B 2000, 64, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimori, Y.; Kawano, K.; Tamura, H.; Aoyama, N.; Mouri, M.; Kase, T.; Tamiya, E.; Ishizuka, M. Advanced environmental monitoring system using ecosensor based on bilayer lipid membrane. In Proceedings of the SPIE 2001, Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring, GIS Applications, and Geology, Toulouse, France, 23 January 2002; Volume 4545. [Google Scholar]
- Tanfani, F.; Ambrosini, A.; Albertini, G.; Bertoli, E.; Curatola, G.; Zolese, G. Interaction of the herbicide atrazine with model membranes. I: Physico-chemical studies on dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1990, 55, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, T.; Zhang, Y.; Dunlop, J.; Dalziel, J. Bilayer lipid membranes supported on Teflon filters: A functional environment for ion channels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3127–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, R.; Tsuji, Y.; Kamiya, K.; Kodama, T.; Osaki, T.; Miki, N.; Takeuchi, S. A portable lipid bilayer system for environmental sensing with a transmembrane protein. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anrather, D.; Smetazko, M.; Saba, M.; Alguel, Y.; Schalkhammer, T. Supported membrane nanodevices. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2004, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, T.W.; Prommapan, P.; Rainer, Q.; Van Winkle, D.; Lenhert, S. Lipid multilayer grating arrays integrated by nanointaglio for vapor sensing by an optical nose. Sensors 2015, 15, 20863–20872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taitt, C.R.; Anderson, G.P.; Ligler, F.S. Evanescent wave fluorescence biosensors: Advances of the last decade. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silin, V.; Kasianowicz, J.J.; Michelman-Ribeiro, A.; Panchal, R.G.; Bavari, S.; Robertson, J.W.F. Biochip for the detection of bacillus anthracis lethal factor and therapeutic agents against anthrax toxins. Membranes 2016, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siontorou, C.G.; Georgopoulos, K.N.; Nalantzi, M.-M. Designing biosensor networks for the environmental risk assessment of aquatic systems. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 40–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Pollutant Class | Bioelement | Membrane System/Detection Method | Analytical Performance | Real Sample Analysis | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| carbamate pesticides: Carbofuran | calix[4]arene phosphoryl receptor | graphene nanosheets with incorporated lipid films/potentiometric | RT: 20 s | fruits and vegetables | [37] |
| DL: 100 nM | |||||
| triazine herbicides: Atrazine | N/A | solventless BLMs doped with dipalmitoyl phosphatidic acid and platelet activating factor/electrochemical | RT: 55.6 ± 5.4 s | N/A | [49] |
| DL: 0.1 ppm | |||||
| triazine herbicides: Simazine; Atrazine; Propazine | N/A | Filter supported BLMs doped with dipalmitoyl phosphatidic acid/electrochemical | RT: 34–50 s (simazine); 62–78 s (atrazine); 96–144 s (propazine) | N/A | [50] |
| DL: 18 ppb (simazine); 0.05 ppm (atrazine); 30 ppb (propazine) | |||||
| triazine herbicides: Simazine; Atrazine; Propazine | N/A | Metal supported BLMs doped with dipalmitoyl phosphatidic acid/electrochemical | RT: 10 s | N/A | [18] |
| DL: 1 ppb (simazine); 15 ppb (atrazine); 30 ppb (propazine) | |||||
| hydrazines: Hydrazine; Methylhydrazine; Dimethylhydrazine; Phenylhydrazine | N/A | Metal supported BLMs doped with ssDNA/electrochemical | RT: 18–20 s | N/A | [51] |
| DL: 51.5 ppb (hydrazine); 0.005 ppb (methyl hydrazine); 0.02 ppb (dimethylhydrazine); 0.11 ppb (phenylhydrazine) | |||||
| plant growth regulators: Naphthalene Acetic Acid | auxin-binding protein 1 receptor | graphene nanosheets with incorporated lipid films/potentiometric | RT: 5 min | fruits and vegetables | [39] |
| DL: 10 nM | |||||
| toxins: Cholera toxin | ganglioside GM1 | graphene nanosheets with incorporated lipid films/potentiometric | RT: 5 min | lake water samples | [40] |
| DL: 1 nM | |||||
| polychlorinated biphenyls: Arochlor 1242 | sheep anti-PCB antibody | Filter supported polymerized lipid films doped with dipalmitoyl phosphatidic acid/electrochemical | RT: 45–55 s | N/A | [52] |
| DL: 10 nM | |||||
| toxins: Saxitoxin | anti-STX receptor | graphene nanosheets with incorporated lipid films/potentiomeric | RT: 5–20 min | shellfish samples and lake water samples | [41] |
| DL: 1 nM | |||||
| polyaromatic hydrocarbons | N/A | Fullurene spatially controlled LB fims/quartz crystal microbalance | Not reported | indoor air | [53] |
| volatile organic chlorides | N/A | Inkjet printed BLM from lipid droplets/electrochemical | RT: 1 min | underground water samples | [54] |
| DL: 10 ppb |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikoleli, G.-P.; Nikolelis, D.; Siontorou, C.G.; Karapetis, S. Lipid Membrane Nanosensors for Environmental Monitoring: The Art, the Opportunities, and the Challenges. Sensors 2018, 18, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010284
Nikoleli G-P, Nikolelis D, Siontorou CG, Karapetis S. Lipid Membrane Nanosensors for Environmental Monitoring: The Art, the Opportunities, and the Challenges. Sensors. 2018; 18(1):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010284
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikoleli, Georgia-Paraskevi, Dimitrios Nikolelis, Christina G. Siontorou, and Stephanos Karapetis. 2018. "Lipid Membrane Nanosensors for Environmental Monitoring: The Art, the Opportunities, and the Challenges" Sensors 18, no. 1: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010284
APA StyleNikoleli, G. -P., Nikolelis, D., Siontorou, C. G., & Karapetis, S. (2018). Lipid Membrane Nanosensors for Environmental Monitoring: The Art, the Opportunities, and the Challenges. Sensors, 18(1), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18010284