Development of a Protein Microarray Chip with Enhanced Fluorescence for Identification of Semen and Vaginal Fluid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fabrication of the GLAD MEF Substrate
3. Development of the HSV-ID Chip
3.1. Fabrication and Analysis of the HSV-ID Chip
3.2. Effects of Chemical Modification of the MEF Substrate and Antibody
4. Evaluation of the HSV-ID Chip
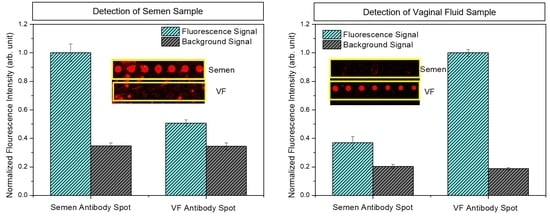
4.1. Identification of Semen and VF using the HSV-ID Chip
4.2. Effect of Incubation Time
4.3. Analysis of Detection Limit
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Ethics Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feine, I.; Gafny, R.; Pinkas, I. Combination of prostate-specific antigen detection and micro-Raman spectroscopy for confirmatory semen detection. Forensic Sci. Int. 2017, 270, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro, C.K.; Lednev, I.K. Race differentiation based on Raman spectroscopy of semen traces for forensic purposes. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4344–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giampaoli, S.; Berti, A.; Valeriani, F.; Gianfranceschi, G.; Piccolella, A.; Buggiotti, L.; Rapone, C.; Valentini, A.; Ripani, L.; Spica, V.R. Molecular identification of vaginal fluid by microbial signature. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2012, 6, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doi, M.; Gamo, S.; Okiura, T.; Nishimukai, H.; Asano, M. A simple identification method for vaginal secretions using relative quantification of Lactobacillus DNA. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2014, 12, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Jung, S.-E.; Lee, E.H.; Yang, W.I.; Shin, K.-J. DNA methylation profiling for a confirmatory test for blood, saliva, semen, vaginal fluid and menstrual blood. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 2016, 24, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.; Baird, A.; McAlister, C.; Siemieniuk, A.; Blackmore, L.; McCabe, B.; O’rourke, P.; Parekh, R.; Watson, E.; Wheelhouse, M. Improved detection of semen by use of direct acid phosphatase testing. Sci. Justice 2013, 53, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, I.; Kojima, K.; Yamasaki, T.; Yoshida, K.; Yoshiike, M.; Takano, S.; Mukai, T.; Iwamoto, T. Rapid detection of semenogelin by one-step immunochromatographic assay for semen identification. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 287, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, K.-J.; Seo, H.-K.; Hwang, H.; Pyo, D.-J.; Eom, I.-Y.; Hahn, J.-H.; Jung, Y.-M. Bioanalytical application of SERS immunoassay for detection of prostate-specific antigen. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Old, J.; Schweers, B.A.; Boonlayangoor, P.W.; Fischer, B.; Miller, K.W.; Reich, K. Developmental validation of RSID™-Semen: a lateral flow immunochromatographic strip test for the forensic detection of human semen. J. Forensic Sci. 2012, 57, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubisha, D.S.; Lipert, R.J.; Park, H.-Y.; Driskell, J.; Porter, M.D. Femtomolar detection of prostate-specific antigen: an immunoassay based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering and immunogold labels. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5936–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legg, K.M.; Powell, R.; Reisdorph, N.; Reisdorph, R.; Danielson, P.B. Discovery of highly specific protein markers for the identification of biological stains. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 3069–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draisci, R.; Volpe, G.; Compagnone, D.; Purificato, I.; Delli Quadri, F.; Palleschi, G. Development of an electrochemical ELISA for the screening of 17β-estradiol and application to bovine serum. Analyst 2000, 125, 1419–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igoh, A.; Doi, Y.; Sakurada, K. Identification and evaluation of potential forensic marker proteins in vaginal fluid by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 7135–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasari, S.; Pereira, L.; Reddy, A.P.; Michaels, J.-E.A.; Lu, X.; Jacob, T.; Thomas, A.; Rodland, M.; Roberts, C.T.; Gravett, M.G. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of human cervical-vaginal fluid. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, C.C. Detection of 17 β-estradiol in environmental samples and for health care using a single-use, cost-effective biosensor based on differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). Biosensors 2017, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boward, E.S.; Wilson, S.L. A comparison of ABAcard® p30 and RSID™-Semen test kits for forensic semen identification. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2013, 20, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, N.; Larson, D.N.; Stark, P.R.; Hainsworth, E.; LaBaer, J. Emerging tools for real-time label-free detection of interactions on functional protein microarrays. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 5412–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hall, D.A.; Ptacek, J.; Snyder, M. Protein microarray technology. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2007, 128, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, X.; Xiao, C.; Lau, W.-F.; Li, J.; Fu, J. Metal enhanced fluorescence improved protein and DNA detection by zigzag Ag nanorod arrays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 82, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, M.; Qiang, W.; Hu, H.; Li, W.; Xu, D. Metal-enhanced fluorescent detection for protein microarrays based on a silver plasmonic substrate. Analyst 2014, 139, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szmacinski, H.; Pugh, V.J.; Moore, W.E.; Corrigan, T.C.; Guo, S.-H.; Phaneuf, R. Enhanced fluorescence using silver nanoparticles patterned by e-beam lithography. In Proceedings of the SPIE 5703 Plasmonics in Biology and Medicine II, San Jose, CA, USA, 31 March 2005; pp. 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Aslan, K.; Leonenko, Z.; Lakowicz, J.R.; Geddes, C.D. Fast and slow deposition of silver nanorods on planar surfaces: application to metal-enhanced fluorescence. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 3157–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, K.; Badugu, R.; Lakowicz, J.R. Sulforhodamine adsorbed Langmuir-Blodgett layers on silver island films: effect of probe distance on the metal-enhanced fluorescence. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 7091–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geddes, C.D.; Parfenov, A.; Roll, D.; Fang, J.; Lakowicz, J.R. Electrochemical and laser deposition of silver for use in metal-enhanced fluorescence. Langmuir 2003, 19, 6236–6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, J.; Solla-Gullón, J.; Herrero, E.; Aldaz, A.; Feliu, J.M. Electrochemistry of shape-controlled catalysts: oxygen reduction reaction on cubic gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 14078–14083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Byeon, E.; Han, Y.-A.; Kim, S.-M. Fabrication of a substrate for Ag-nanorod metal-enhanced fluorescence using the oblique angle deposition process. Micro Nano Lett. 2013, 8, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.P.; Kumar, S.; Singh, J. Morphology dependent surface enhanced fluorescence study on silver nanorod arrays fabricated by glancing angle deposition. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 31341–31346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Chu, H.Y.; Zhao, Y.-P. Silver nanorod array substrates fabricated by oblique angle deposition: morphological, optical, and SERS characterizations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 8176–8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkeye, M.M.; Brett, M.J. Glancing angle deposition: fabrication, properties, and applications of micro- and nanostructured thin films. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2007, 25, 1317–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Kim, S.-M.; Seo, S.J. Fabrication of a large-area superhydrophobic SiO2 nanorod structured surface using glancing angle deposition. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 8305439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badshah, M.A.; Ju, J.; Lu, X.; Abbas, N.; Kim, S.-M. Enhancing the sensitivity of DNA microarrays by metal-enhanced fluorescence using vertical nanorod structures. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 274, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, C.K.; Vashist, S.K.; MacCraith, B.D.; Kennedy, R.O. Multisubstrate-compatible ELISA procedures for rapid and high-sensitivity immunoassays. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bart, J.; Tiggelaar, R.; Yang, M.; Schlautmann, S.; Zuilhof, H.; Gardeniers, H. Room-temperature intermediate layer bonding for microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3481–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abbas, N.; Lu, X.; Badshah, M.A.; In, J.B.; Heo, W.I.; Park, K.Y.; Lee, M.-K.; Kim, C.H.; Kang, P.; Chang, W.-J.; et al. Development of a Protein Microarray Chip with Enhanced Fluorescence for Identification of Semen and Vaginal Fluid. Sensors 2018, 18, 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113874
Abbas N, Lu X, Badshah MA, In JB, Heo WI, Park KY, Lee M-K, Kim CH, Kang P, Chang W-J, et al. Development of a Protein Microarray Chip with Enhanced Fluorescence for Identification of Semen and Vaginal Fluid. Sensors. 2018; 18(11):3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113874
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbbas, Naseem, Xun Lu, Mohsin Ali Badshah, Jung Bin In, Won Il Heo, Kui Young Park, Mi-Kyung Lee, Cho Hee Kim, Pilwon Kang, Woo-Jin Chang, and et al. 2018. "Development of a Protein Microarray Chip with Enhanced Fluorescence for Identification of Semen and Vaginal Fluid" Sensors 18, no. 11: 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113874
APA StyleAbbas, N., Lu, X., Badshah, M. A., In, J. B., Heo, W. I., Park, K. Y., Lee, M. -K., Kim, C. H., Kang, P., Chang, W. -J., Kim, S. -M., & Seo, S. J. (2018). Development of a Protein Microarray Chip with Enhanced Fluorescence for Identification of Semen and Vaginal Fluid. Sensors, 18(11), 3874. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18113874