Polyimide-Based Capacitive Humidity Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Transducer Configuration
2.2. Sensing Material Preparation
2.3. Transducer and Sensing Material
2.4. Gas Mixing Apparatus
2.5. Capacitance Measurements Using an Impedance Analyzer
2.6. Capacitance Measurements Using Evaluation Kit
- Vth: threshold voltage (1.5 V)
- Vdd: positive supply voltage (3.3 V)
- CREF: reference capacitor
- N: number of charge transfer cycles needed to charge the Cs.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR Characterization
3.2. Effect of Frequency Using Impedance Analyzer
3.3. Dynamic Mode Using the Impedance Analyzer
3.4. Penetration Depth Using FEM Simulation
3.5. Nanograss Polyimide Film
3.6. Humidity Sensor Performance
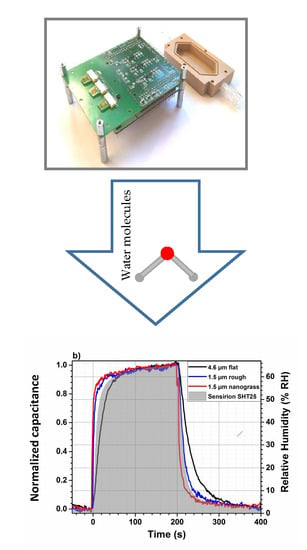
3.6.1. Dynamic Response Using Impedance Analyzer
3.6.2. Response and Recovery Times Using Evaluation Kit
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fraden, J. Handbook of Modern Sensors: Physics, Designs, and Applications, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Faia, P.M.; Jesus, E.L.; Louro, C.S. TiO2: WO3 composite humidity sensors doped with ZnO and CuO investigated by impedance spectroscopy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, A.; Pramanik, S.; Manna, A.; Shasmin, H.N.; Radzi, Z.; Abu Osman, N.A. Uniformly Porous Nanocrystalline CaMgFe1.33Ti3O12 Ceramic Derived Electro-Ceramic Nanocomposite for Impedance Type Humidity Sensor. Sensors 2016, 16, 2029. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathy, A.; Pramanik, S.; Manna, A.; Bhuyan, S.; Azrin Shah, N.F.; Radzi, Z.; Abu Osman, N.A. Design and Development for Capacitive Humidity Sensor Applications of Lead-Free Ca,Mg,Fe,Ti-Oxides-Based Electro-Ceramics with Improved Sensing Properties via Physisorption. Sensors 2016, 16, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinç Zor, Ş.; Cankurtaran, H. Impedimetric Humidity Sensor Based on Nanohybrid Composite of Conducting Poly(diphenylamine sulfonic acid). J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 5479092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Chan, C.C.; Chen, L.; Dong, X.; Huang, R.; Ma, Q. A chitosan-coated humidity sensor based on Mach-Zehnder interferometer with waist-enlarged fusion bitapers. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2017, 33, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, C. Humidity Sensors: A Review of Materials and Mechanisms. Sens. Lett. 2005, 3, 274–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiğil, A.B.; Cankurtaran, H.; Kahraman, M.V. Photo-crosslinked thiol-ene based hybrid polymeric sensor for humidity detection. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 114, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Majumdar, S. Polymers in sensor applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2004, 29, 699–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Shi, G. Gas Sensors Based on Conducting Polymers. Sensors 2007, 7, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCafferty, E.; Zettlemoyer, A.C. Adsorption of water vapour on alpha-Fe2O3. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1971, 52, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, T.; Nagao, M.; Tokuda, F. Relation between the amounts of chemisorbed and physisorbed water on metal oxides. J. Phys. Chem. 1969, 73, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grotthuss, C.J.T. Memoir on the decomposition of water and of the bodies that it holds in solution by means of galvanic electricity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1757, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahani, H.; Wagiran, R.; Hamidon, M.N. Humidity sensors principle, mechanism, and fabrication technologies: A comprehensive review. Sensors 2014, 14, 7881–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazoe, N.; Sakai, G.; Shimanoe, K. Oxide Semiconductor Gas Sensors. Catal. Surv. Asia 2003, 7, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Q.; Laib, P.T.; Zeng, S.H.; Huang, M.Q.; Cheng, Y.C. Photo-, thermal and humidity sensitivity characteristics of Sr1−xLaxTiO3 film on SiO2/Si substrate. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1997, 63, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, N.; Fuchigami, J.; Kishikawa, M.; Seiyama, T. Interactions of tin oxide surface with O2, H2O and H2. Surf. Sci. 1979, 86, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Sadaoka, Y.; Matsuguchi, M. Humidity sensors based on polymer thin films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1996, 35, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, Y.; Matsuguchi, M.; Hurukawa, T. Humidity sensor using cross-linked poly(chloromethyl styrene). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 66, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, S.; Jung, S.; Lee, J. Nano-grass polyimide-based humidity sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 154, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Huang, Q.-A.; Qin, M. A novel capacitive-type humidity sensor using CMOS fabrication technology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2004, 99, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laconte, J.; Wilmart, V.; Flandre, D.; Raskin, J.-P. High-sensitivity capacitive humidity sensor using 3-layer patterned polyimide sensing film. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors 2003, Toronto, ON, Canada, 22–24 October 2003; pp. 372–377, IEEE Cat. No.03CH37498. [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen, J.; Ukkonen, L.; Björninen, T.; Sydänheimo, L. Printed humidity sensor for UHF RFID systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium (SAS), Limerick, Ireland, 23–25 February 2010; pp. 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Rivadeneyra, A.; Fernández-Salmerón, J.; Agudo-Acemel, M.; López-Villanueva, J.A.; Capitan-Vallvey, L.F.; Palma, A.J. Printed electrodes structures as capacitive humidity sensors: A comparison. Sens. Actuators A 2016, 244, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrey, P.M.; Ramsey, B.J.; Evans, P.S.A.; Harrison, D.J. Capacitive-type humidity sensors fabricated using the offset lithographic printing process. Sens. Actuators B 2002, 87, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Kim, D.S.; Yang, H.J.; Ryu, M.S.; Chang, S.P. A highly sensitive humidity sensor with a novel hole array structure using a polyimide sensing layer. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 32075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Hong, S.-M.; Moon, B.-M.; Kim, K. High-performance capacitive humidity sensor with novel electrode and polyimide layer based on MEMS technology. Microsyst. Technol. 2010, 16, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, H.-E.; Jander, H.D.; Göttler, W. A test system for gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1995, 23, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, H.-E.; Drost, S.; Hutter, F. Impedance spectroscopy on dielectric gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 22, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastasi, G.; Scuderi, A.; Endres, H.-E.; Hell, W.; Bock, K. Simple Cost Effective and Network Compatible Readout for Capacitive and Resistive (Chemical) Sensors. Procedia Eng. 2014, 87, 1234–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, N.; Ponoth, S.; Plawsky, J.; Persans, P.D. Roughness evolution in polyimide films during plasma etching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 2294–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonck, P. Plasma Etching. Oficina de Microfabrição: Projeto e Construção de CI’s MOS; UNICAMP, Campinas: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2006; Chapter 10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Diao, Y.; Lee, H.; Mirabito, T.J.; Johnson, R.W.; Puodziukynaite, E.; John, J.; Carter, K.R.; Emrick, T.; Mannsfeld, S.C.B.; et al. Intrinsic and extrinsic parameters for controlling the growth of organic single-crystalline nanopillars in photovoltaics. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 5547–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.-C.; Huang, S.-Y.; Shieh, J.; Chen, S.-H. Enhanced Piezoelectricity of Nanoimprinted Sub-20 nm Poly(vinylidene fluoride–trifluoroethylene) Copolymer Nanograss. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanowicz, B.F.; Laudon, M. 2005 NSTI Nanotechnology Conference and Trade Show: NSTI Nanotech 2005, Anaheim, CA, USA, 8–12 May 2005; NSTI: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]









| 4.6 µm Flat | 1.5 µm Flat | 1.5 µm Rough | 1.5 µm Nanograss | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity (fF/% RH) | 15.2 | 9.48 | 7.47 | 4.75 |
| linearity | 0.999 | 0.995 | 0.998 | 0.998 |
| RH Sensor (SHT 25) | 4.6 µm Flat | 1.5 µm Rough | 1.5 µm Nanograss | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Response time τ90res (s) | 42 | 54 | 26 | 18 |
| Recovery time τ90rec (s) | 40 | 80 | 45 | 31 |
| Increase in τ90rec compared to τ90res | −5 | 48 | 73 | 72 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boudaden, J.; Steinmaßl, M.; Endres, H.-E.; Drost, A.; Eisele, I.; Kutter, C.; Müller-Buschbaum, P. Polyimide-Based Capacitive Humidity Sensor. Sensors 2018, 18, 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051516
Boudaden J, Steinmaßl M, Endres H-E, Drost A, Eisele I, Kutter C, Müller-Buschbaum P. Polyimide-Based Capacitive Humidity Sensor. Sensors. 2018; 18(5):1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051516
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoudaden, Jamila, Matthias Steinmaßl, Hanns-Erik Endres, Andreas Drost, Ignaz Eisele, Christoph Kutter, and Peter Müller-Buschbaum. 2018. "Polyimide-Based Capacitive Humidity Sensor" Sensors 18, no. 5: 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051516
APA StyleBoudaden, J., Steinmaßl, M., Endres, H. -E., Drost, A., Eisele, I., Kutter, C., & Müller-Buschbaum, P. (2018). Polyimide-Based Capacitive Humidity Sensor. Sensors, 18(5), 1516. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051516