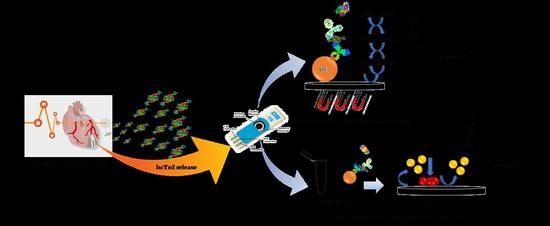
Studies towards hcTnI Immunodetection Using Electrochemical Approaches Based on Magnetic Microbeads
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Biochemicals
2.2. Materials and Instruments
2.3. Buffers and Solutions
2.4. Polyclonal Antibody Production against hcTnI
2.5. Preparation of Biotinylated Antibody Bioconjugates
2.6. Sandwich ELISA for cTnI
2.7. Specificity Studies
2.8. Preparation of the Magnetic Beads-Antibody Bioconjugates
2.9. Magneto-ELISA (mELISA) Protocol
2.10. Amperometric Magneto Immunosensor (AMIS) Protocol
2.11. Voltamperometric Magneto Immunosensor (VMIS) Protocol
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ELISA Sandwich for hcTnI
3.2. Specificity Studies
3.3. Assessment of the Bioactivity of Magnetic Beads-Antibody Bioconjugates
3.4. Development of Electrochemical Immunosensors for hcTnI Detection
3.4.1. Amperometric Magneto-Immunosensor (AMIS)
3.4.2. Voltamperommetric Magneto-Immunosensor (VMIS)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Cardiovascular diseases. Available online: http://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/en/ (accessed on 29 July 2018).
- Yang, Z.; Min Zhou, D. Cardiac markers and their point-of-care testing for diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Clin. Biochem. 2006, 39, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, J.L.; Adams, C.D.; Antman, E.M.; Bridges, C.R.; Califf, R.M.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Chavey, W.E., II; Fesmire, F.M.; Hochman, J.S.; Levin, T.N.; et al. ACC/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non-ST-Elevation myocardial infarction: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2002 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Unstable Angina/Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction) developed in collaboration with the American College of Emergency Physicians, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons endorsed by the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation and the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, e1–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savonitto, S.; Ardissino, D.; Granger, C.B.; Morando, G.; Prando, M.D.; Mafrici, A.; Cavallini, C.; Melandri, G.; Thompson, T.D.; Vahanian, A.; et al. Prognostic value of the admission electrocardiogram in acute coronary syndromes. JAMA 1999, 281, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, P.; Newby, L.K.; Fu, Y.; Hasselblad, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Christenson, R.H.; Harrington, R.A.; Ohman, E.M.; Topol, E.J.; Califf, R.M.; et al. Troponin T and quantitative ST-segment depression offer complementary prognostic information in the risk stratification of acute coronary syndrome patients. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamm, C.W.; Braunwald, E. A classification of unstable angina revisited. Circulation 2000, 102, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kost, G.J.; Tran, N.K. Point-of-care testing and cardiac biomarkers: The standard of care and vision for chest pain centers. Cardiol. Clin. 2005, 23, 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpert, J.; Thygesen, K.; Antman, E.; Bassand, J. Myocardial infarction redefined—A consensus document of the joint European society of cardiology/American college of cardiology committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Babuin, L.; Jaffe, A.S. Troponin: The biomarker of choice for the detection of cardiac injury. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2005, 173, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zethelius, B.; Johnston, N.; Venge, P. Troponin I as a predictor of coronary heart disease and mortality in 70-year-old men: A community-based cohort study. Circulation 2006, 113, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, D.A.; Antman, E.M.; Tanasijevic, M.; Rifai, N.; de Lemos, J.A.; McCabe, C.H.; Cannon, C.P.; Braunwald, E. Cardiac troponin I for stratification of early outcomes and the efficacy of enoxaparin in unstable angina: A TIMI-11B substudy. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 1812–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, C.W.; Heeschen, C.; Goldmann, B.; Vahanian, A.; Adgey, J.; Miguel, C.M.; Rutsch, W.; Berger, J.; Kootstra, J.; Simoons, M.L. Benefit of abciximab in patients with refractory unstable angina in relation to serum troponin T. levels. c7E3 fab antiplatelet therapy in unstable refractory angina (CAPTURE) study investigators. New Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggers, K.M.; Jaffe, A.S.; Lind, L.; Venge, P.; Lindahl, B. Value of cardiac troponin I cutoff concentrations below the 99th percentile for clinical decision-making. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, N.-Y.; Guo, H.-S.; Gu, C.-R.; Yang, D.; Zhang, J.-N. Chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay for cardiac troponin I detection—Optimization of experimental parameters. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. Chin. 2007, 28, 242–245. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, I.-H.; Paek, E.-H.; Kim, Y.-K.; Kim, J.-H.; Paek, S.-H. Chemiluminometric enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA)-on-a-chip biosensor based on cross-flow chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 632, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyytiä, H.; Järvenpää, M.-L.; Ristiniemi, N.; Lövgren, T.; Pettersson, K. A comparison of capture antibody fragments in cardiac troponin I immunoassay. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katrukha, A.G.; Bereznikova, A.V.; Filatov, V.L.; Esakova, T.V.; Kolosova, O.V.; Pettersson, K.; Lövgren, T.; Bulargina, T.V.; Trifonov, I.R.; Gratsiansky, N.A.; et al. Degradation of cardiac troponin I: Implication for reliable immunodetection. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 2433–2440. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.E.; Bodor, G.S.; Dávila-Román, V.G.; Delmez, J.A.; Apple, F.S.; Ladenson, J.H.; Jaffe, A.S. Cardiac troponin I: A marker with high specificity for cardiac injury. Circulation 1993, 88, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, S.; Junikka, M.; Laitinen, P.; Majamaa-Voltti, K.; Alfthan, H.; Pettersson, K. Negative Interference in cardiac troponin i immunoassays from a frequently occurring serum and plasma component. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, S.; Halenius, H.; Pulkki, K.; Hellman, J.; Pettersson, K. Negative interference in cardiac troponin i immunoassays by circulating troponin autoantibodies. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vdovenko, M.M.; Byzova, N.A.; Zherdev, A.V.; Dzantiev, B.B.; Sakharov, I.Y. Ternary covalent conjugate (antibody-gold nanoparticle-peroxidase) for signal enhancement in enzyme immunoassay. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 48827–48833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodor, G.S.; Porter, S.; Landt, Y.; Ladenson, J.H. Development of monoclonal antibodies for an assay of cardiac troponin-I and preliminary results in suspected cases of myocardial infarction. Clin. Chem. 1992, 38, 2203–2214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Penttilä, K.; Penttilä, I.; Bonnell, R.; Kerth, P.; Koukkunen, H.; Rantanen, T.; Svanas, G. Comparison of the troponin T and troponin, I. ELISA tests, as measured by microplate immunoassay techniques, in diagnosing acute myocardial infarction. Eur. J. Clin. Chem. Clin. Biochem. 1997, 35, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Moal, E.; Giuliani, I.; Bertinchant, J.-P.; Polge, A.; Larue, C.; Villard-Saussine, S. Earlier detection of myocardial infarction by an improved cardiac TnI assay. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 40, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdorahim, M.; Rabiee, M.; Alhosseini, S.N.; Tahriri, M.; Yazdanpanah, S.; Alavi, S.H.; Tayebi, L. Nanomaterials-based electrochemical immunosensors for cardiac troponin recognition: An illustrated review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, V.; Carrara, S.; Sharma, P.; Nangia, Y.; Suri, C.R. Gold nanoparticles mediated label-free capacitance detection of cardiac troponin I. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, M.M.; Hays, H.C.W.; Hodges, C.S.; Ponnambalam, S.; Vohra, R.; Millner, P.A. Mixed self-assembled monolayer (mSAM) based impedimetric immunosensors for cardiac troponin I (cTnI) and soluble lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (sLOX-1). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 173, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, S.K.; Chen, R.; Kukkar, M.; Song, C.K.; Mutreja, R.; Singh, S.; Paul, A.K.; Lee, H.; Kim, K.-H.; Deep, A.; et al. A label-free electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of cardiac marker using graphene quantum dots (GQDs). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venge, P.; Johnston, N.; Lindahl, B.; James, S. Normal plasma levels of cardiac troponin i measured by the high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I access prototype assay and the impact on the diagnosis of myocardial ischemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 54, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conzuelo, F.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas, M.V.; Campuzano, S.; Gamella, M.; Torrente-Rodriguez, R.M.; Reviejo, A.J.; Pingarrón, J.M. Rapid screening of multiple antibiotic residues in milk using disposable amperometric magnetosensors. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 820, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban-Fernández de Ávila, B.; Escamilla-Gómez, V.; Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; Salvador, J.P.; Marco, M.P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Ultrasensitive amperometric magnetoimmunosensor for human C-reactive protein quantification in serum. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinacho, D.; Sánchez-Baeza, F.; Pividori, M.-I.; Marco, M.-P. Electrochemical detection of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in milk using a magneto immunosensor. Sensors 2014, 14, 15965–15980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruls, D.M.; Evers, T.H.; Kahlman, J.A.; van Lankvelt, P.J.; Ovsyanko, M.; Pelssers, E.G.; Schleipen, J.J.; de Theije, F.K.; Verschuren, C.A.; van der Wijk, T.; et al. Rapid integrated biosensor for multiplexed immunoassays based on actuated magnetic nanoparticles. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 3504–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmer, W.U.; Evers, T.H.; Hardeman, W.M.; Huijnen, W.; Kamps, R.; de Kievit, P.; Neijzen, J.H.; Nieuwenhuis, J.H.; Sijbers, M.J.; Dekkers, D.W.; et al. Rapid, high sensitivity, point-of-care test for cardiac troponin based on optomagnetic biosensor. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, A.; Qi, D.; Yi, W.; Hu, C. A novel microfluidic immunoassay system based on electrochemical immunosensors: An application for the detection of NT-proBNP in whole blood. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 31, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Hou, L.; Niessner, R.; Xu, M.; Gao, Z.; Knopp, D. Multiplexed electrochemical immunoassay of biomarkers using metal sulfide quantum dot nanolabels and trifunctionalized magnetic beads. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 46, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Guo, P.; Ding, Y.; Lei, C.; Luo, Y. A multi-region magnetoimpedance-based bio-analytical system for ultrasensitive simultaneous determination of cardiac biomarkers myoglobin and C-reactive protein. Sensors 2018, 18, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballesteros, B.; Barceló, D.; Camps, F.; Marco, M.-P. Preparation of antisera and development of a direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of the antifouling agent Irgarol 1051. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 347, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines, M.G.; Thorpe, R. Purification of immunoglobulin G (IgG). In Immunochemical Protocols; Manson, M.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 1992; pp. 79–104. [Google Scholar]
- Filatov, V.L. Troponin: Structure, properties, and mechanism of functioning. Biochemistry 1999, 64, 969–985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Hwang, M.P.; Lee, K.H. Immunomagnetic nanoparticle-based assays for detection of biomarkers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4543–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Tannoudji, L.; Bertrand, E.; Baudry, J.; Robic, C.; Goubault, C.; Pellissier, M.; Johner, A.; Thalmann, F.; Lee, N.K.; Marques, C.M.; et al. Measuring the kinetics of biomolecular recognition with magnetic colloids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y. Quantum-dots based electrochemical immunoassay of interleukin-1α. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 1573–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, E.; García-Febrero, R.; Pividori, I.; Sánchez-Baeza, F.; Marco, M.P. Coulombimetric immunosensor for paraquat based on electrochemical nanoprobes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 194, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valera, E.; Muriano, A.; Pividori, I.; Sánchez-Baeza, F.; Marco, M.P. Development of a Coulombimetric immunosensor based on specific antibodies labeled with CdS nanoparticles for sulfonamide antibiotic residues analysis and its application to honey samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.A.; Wang, J.; Kawde, A.-N.; Xiang, Y.; Gothelf, K.V.; Collins, G. Quantum-dot/aptamer-based ultrasensitive multi-analyte electrochemical biosensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2228–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zethelius, B.; Berglund, L.; Sundström, J.; Ingelsson, E.; Basu, S.; Larsson, A.; Venge, P.; Arnlöv, J. Use of multiple biomarkers to improve the prediction of death from cardiovascular causes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| ELISA a | mELISA b | AMIS c | VMI d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beads (mg) | - | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.1 |
| [MBs] (mg mL−1) | - | 0.05 | 0.025 | 0.5 |
| Total Assay Time (min) | >120 | 120 | 30 | 120 |
| Slope | 5.34 ± 0.17 | 7.68 ± 0.311 | 3.71 ± 0.29 | 57.26 ± 3.93 |
| Ordinate | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.207 ± 0.04 | 52.03 ± 17.19 | −0.91 ± 0.51 |
| LOD (µg mL−1) | 0.010 ± 0.002 | 0.023 ± 0.001 | 0.005 ± 0.002 | 0.023 ± 0.014 |
| LOQ (µg mL−1) | 0.031 ± 0.007 | 0.075 ± 0.044 | 0.020 ± 0.006 | 0.068 ± 0.045 |
| R2 | 0.990 ± 0.003 | 0.988 ± 0.01 | 0.989 ± 0.004 | 0.977 ± 0.058 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Albors, A.; Colom, G.; Salvador, J.-P.; Marco, M.-P. Studies towards hcTnI Immunodetection Using Electrochemical Approaches Based on Magnetic Microbeads. Sensors 2018, 18, 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082457
Hernández-Albors A, Colom G, Salvador J-P, Marco M-P. Studies towards hcTnI Immunodetection Using Electrochemical Approaches Based on Magnetic Microbeads. Sensors. 2018; 18(8):2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082457
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Albors, Alejandro, Gloria Colom, J.-Pablo Salvador, and M.-Pilar Marco. 2018. "Studies towards hcTnI Immunodetection Using Electrochemical Approaches Based on Magnetic Microbeads" Sensors 18, no. 8: 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082457
APA StyleHernández-Albors, A., Colom, G., Salvador, J. -P., & Marco, M. -P. (2018). Studies towards hcTnI Immunodetection Using Electrochemical Approaches Based on Magnetic Microbeads. Sensors, 18(8), 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18082457