Preparation and Characterization of Developed CuxSn1−xO2 Nanocomposite and Its Promising Methane Gas Sensing Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
3. Results and Discussions
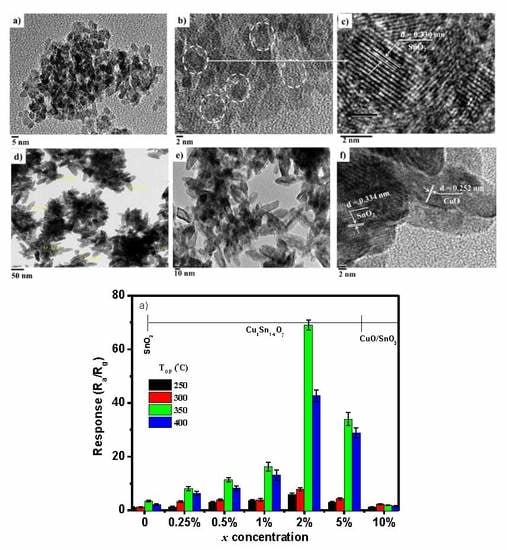
3.1. Effect of Concentration Ratio on Crystal Structure and Morphology
3.2. Effect of Concentration Ratio on Fluorescence Spectra
3.3. Sensing Mechanism of the Composites
3.4. Effect of Concentration Ratio on Sensor Response
3.5. The Correlation of Sensing Properties and Surface Area
3.6. Calibration Curve and Sensor Stability
3.7. Response and Recovery Time Constants
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Lei, M.; Tang, W.; Guo, X.; Wang, X. Facile route to straight SnO2 nanowires and their optical properties. J. Alloys Comp. 2009, 477, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, S.; Liu, H.; Hu, S.; Zhang, D.; Ning, H. A survey on gas sensing technology. Sensors 2012, 12, 9635–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harraz, F.A.; Ismail, A.A.; Al-Sayari, S.A.; Al-Assiri, M.S. Highly sensitive ethanol chemical sensor based on nanostructured SnO2 doped ZnO modified glassy carbon electrode. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2015, 639, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, F.; Rella, R.; Siciliano, P.; Capone, S.; Epifani, M.; Vasanelli, L.; Licciulli, A.; Zocco, A. A novel gas sensor based on SnO2\Os thin film for the detection of methane at low temperature. Sens. Actuators B 1999, 58, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horastani, Z.K.; Sayedi, S.M.; Sheikhi, M.H.; Rahimi, E. Effect of silver additive on electrical conductivity and methane sensitivity of SnO2. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2015, 35, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Ghosh, B.; Das, D.; Sen, A.; Maiti, H.S. Methane sensitivity of Fe-doped SnO2 thick films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 105, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z. Hydrothermally prepared porous 3D SnO2 microstructures for methane sensing at lower operating temperature. Mater. Lett. 2019, 237, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Ding, D.; Xue, Q.; Du, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Pan, X.; Xing, W. Great enhancement of CH4 sensitivity of SnO2 based nanofibers by heterogeneous sensitization and catalytic effect. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 254, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.-K.; Choi, S.-D. Undoped and 0.1 wt.% Ca-doped Pt-catalyzed SnO2 sensors for CH4 detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.; Bauer, M.; Sauerwald, T.; Kohl, C.-D.; Tiemann, M. X-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy investigation of the oxidation state of Pd species in nanoporous SnO2 gas sensors for methane detection. Thin Solid Films 2011, 520, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabot, A.; Vila, A.; Morante, J. Analysis of the catalytic activity and electrical characteristics of different modified SnO2 layers for gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 84, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fateminia, F.S.; Mortazavi, Y.; Khodadadi, A.A. Au-promoted Ce-Zr catalytic filter for Pt/SnO2 sensor to selectively detect methane and ethanol in the presence of interfering indoor gases. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 90, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kootia, M.; Keshtkara, S.; Askariehb, M.; Rashidi, A. Progress toward a novel methane gas sensor based on SnO2 nanorods nanoporous graphene hybrid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navazani, S.; Shokuhfar, A.; Hassanisadi, M.; Carlo, A.D.; Nia, N.Y.; Agresti, A. A PdPt decorated SnO2 -rGO nanohybrid for high-performance resistive sensing of ethane. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2019, 95, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somacescu, S.; Osiceanu, P.; Calderon-Moreno, J.M.; Sackmann, A.; Simion, C.E.; Stănoiu, A. Mesoporous Sn0.9−xIn0.1Cux (I)O2−δ gas sensors with selectivity to H2S working under humid air conditions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014, 197, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Qiu, F.; Quan, B. Investigation of a new catalytic combustion-type CH4 gas sensor with low power consumption. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 66, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Dai, Y.; Huang, B. Role of Cu Doping in SnO2 Sensing Properties Toward H2S. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 18597–18602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhong, J.; Sun, X. Facile Fabrication of a Well-Ordered Porous Cu-Doped SnO2 Thin Film for H2S Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14975–14980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, J.; Qiu, Z.; Lv, S.; Zhang, K.; Tang, D. Cu2+-Doped SnO2 Nanograin/Polypyrrole Nanospheres with Synergic Enhanced Properties for Ultrasensitive Room-Temperature H2S Gas Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 11135–11142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johari, A.; Johari, A.; Bhatnagar, M.C.; Sharma, M. Structural, Optical and Sensing Properties of Pure and Cu-Doped SnO2 Nanowires. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 5288–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaalan, N.M.; Rashad, M.; Abdel-Rahim, M.A. CuO nanoparticles synthesized by a microwave-assisted method for methane sensing. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2016, 48, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaalan, N.; Rashad, M.; Moharram, A.; Abdel-Rahim, M. Promising methane gas sensor synthesized by microwave-assisted Co3O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 46, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaalan, N.M.; Rashad, M.; Abdel-Rahim, M.A. Repeatability of indium oxide gas sensors for detecting methane at low temperature. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 56, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, N. New Approaches for Improving Semiconductor Gas Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1991, 5, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, A.R.; Wilson, A.C.J. The diffraction of X rays by distorted crystal aggregates—I. Proc. Phys. Soc. 1944, 56, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riad, A.; Mahmoud, S.; Ibrahim, A. Structural and DC electrical investigations of ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis technique. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2001, 296, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.W.; Condon, N.G.; Thornton, G. Effect of stoichiometry on the structure of TiO2(110). Phys. Rev. B 1995, 51, 10989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinnert, H.; Miska, P.; Vergnat, M.; Schmerber, G.; Colis, S.; Dinia, A.; Muller, D.; Ferblantier, G.; Slaoui, A. Photoluminescence of Nd-doped SnO2 thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 101908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, N.; Sakai, G.; Shimanoe, K. Oxide semiconductor gas sensors. Catal. Surv. Asia 2003, 7, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qin, Z.; Zeng, D.; Xie, C. Metal-oxide-semiconductor based gas sensors: Screening, preparation, and integration. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 6313–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Xiong, H.; Dai, J. Controlled synthesis of ZnO hollow microspheres via precursor-template method and its gas sensing property. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 8431–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zhou, M.; Du, W. Improved acetone sensing properties of ZnO hollow nanofibers by single capillary electrospinning. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-D.; Chung, W.-Y.; Sohn, B.-K. High sensitivity and selectivity methane gas sensors doped with Rh as catalyst. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1993, 13–14, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haridas, D.; Gupta, V. Enhanced response characteristics of SnO2 thin film based sensors loaded with Pd clusters for methane detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166–167, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sensing Material | Operating Temperature (°C) | CH4 Concentration % | Response | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SnO2 | 350 | 0.200 | 1.35 | [4] |
| Ag–SnO2 | 430 | 0.200 | 1.75 | [5] |
| Fe–SnO2 | 350 | 0.025 | 1.30 | [6] |
| porous 3D SnO2 | 120 | 0.050 | 1.80 | [7] |
| Pt–SnO2 | 350 | 0.100 | 4.50 | [8] |
| Pt–SnO2 | 400 | 0.100 | 1.55 | [9] |
| Pd–SnO2 | 400 | 0.660 | 20.00 | [10] |
| Pd–SnO2 | 350 | 0.100 | 1.35 | [11] |
| Pt/SnO2 | 400 | 0.500 | 30.00 | [12] |
| SnO2 NR–NP–Gr hybrids | 150 | 1.000 | 50.00 | [13] |
| PdPt–SnO2–rGO | 150 | 0.100 | 69.50 | [14] |
| Sn0.9-xIn0.1CuxO2 | 400 | 0.250 | 9.00 | [15] |
| SnO2–In2O3–TiO2/MgO | 300 | 0.500 | 2.40 | [16] |
| CuO NCs | 200 | 1.000 | 2.22 | [21] |
| Co3O4 NPs | 200 | 1.000 | 1.28 | [22] |
| Cu0.02Sn0.98O2 nanocomposite | 350 | 0.250 | 3.50 | Present |
| 0.375 | 4.50 | |||
| 0.500 | 5.50 | |||
| 0.675 | 10.00 | |||
| 0.750 | 50.50 | |||
| 1.000 | 69.60 |
| Intended Molar Fraction (x %) | X-ray Florescence Molar Fraction% | EDX Measurements | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu% | Sn% | OK | SnL | CuK | Cu/Sn | O/(Cu + Sn) at. | ||||
| wt.% | at.% | wt.% | at.% | wt.% | at.% | at. | ||||
| 0.00 | 0.000 | 100.000 | ||||||||
| 0.25 | 0.188 | 99.811 | ||||||||
| 0.50 | 0.472 | 99.527 | 16.320 | 58.1600 | 79.760 | 38.320 | 3.920 | 3.520 | 0.092 | 1.386 |
| 1.00 | 0.941 | 99.058 | ||||||||
| 2.00 | 2.342 | 97.657 | 7.950 | 36.510 | 79.900 | 49.450 | 12.140 | 14.040 | 0.283 | 0.575 |
| 5.00 | 4.500 | 95.499 | ||||||||
| 10.00 | 11.087 | 88.912 | 20.440 | 54.870 | 52.050 | 35.180 | 27.510 | 9.950 | 0.282 | 1.219 |
| XRD Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample x% | Average Crystallite Size (nm) | Lattice Parameter a, c (Å) | Unit Cell Volume (Å3) |
| 0.00 | 5.90 | 4.7406, 3.1676 | 72.19 |
| 0.25 | 5.82 | 4.7533, 3.1956 | 72.20 |
| 0. 50 | 4.80 | 4.7529, 3.1965 | 72.21 |
| 1.00 | 4.74 | 4.7566, 3.1919 | 72.22 |
| 2.00 | 4.70 | 4.7566, 3.1927 | 72.24 |
| 5.00 | 4.69 | 4.7643, 3.1894 | 72.39 |
| 10.00 | 15.28 | 4.7616, 3.1896 | 72.32 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaalan, N.M.; Hamad, D.; Aljaafari, A.; Abdel-Latief, A.Y.; Abdel-Rahim, M.A. Preparation and Characterization of Developed CuxSn1−xO2 Nanocomposite and Its Promising Methane Gas Sensing Properties. Sensors 2019, 19, 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102257
Shaalan NM, Hamad D, Aljaafari A, Abdel-Latief AY, Abdel-Rahim MA. Preparation and Characterization of Developed CuxSn1−xO2 Nanocomposite and Its Promising Methane Gas Sensing Properties. Sensors. 2019; 19(10):2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102257
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaalan, Nagih M., Dalia Hamad, Abdullah Aljaafari, Atta Y. Abdel-Latief, and Mostafa A. Abdel-Rahim. 2019. "Preparation and Characterization of Developed CuxSn1−xO2 Nanocomposite and Its Promising Methane Gas Sensing Properties" Sensors 19, no. 10: 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102257
APA StyleShaalan, N. M., Hamad, D., Aljaafari, A., Abdel-Latief, A. Y., & Abdel-Rahim, M. A. (2019). Preparation and Characterization of Developed CuxSn1−xO2 Nanocomposite and Its Promising Methane Gas Sensing Properties. Sensors, 19(10), 2257. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102257