Ecofriendly Long Life Nanocomposite Sensors for Determination of Carbachol in Presence of Choline: Application in Ophthalmic Solutions and Biological Fluids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Stock Standard Solution
2.4. Procedures
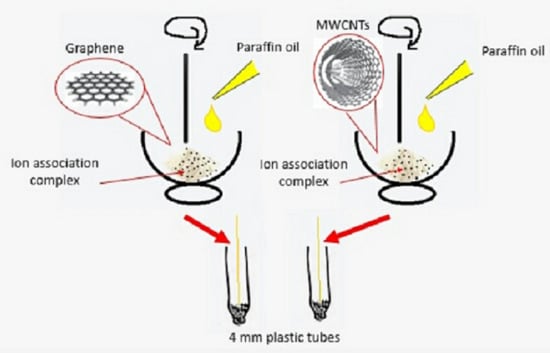
2.4.1. Preparation of the Ion-Association Complex
2.4.2. Sensor Fabrication
2.4.3. Sensor Calibration
2.4.4. Application in Ophthalmic Solutions
2.4.5. Application in Biological Fluids
2.4.6. Determination of Carbachol in Presence of Choline
3. Results
3.1. Sensor Mechanism and Fabrication


3.2. Sensor Calibration
3.3. Performance Characteristics of the Proposed Sensors
3.4. Effect of Nanoscale Carbon Materials
3.5. pH Study
3.6. Sensor Selectivity
3.7. Application in Ophthalmic Preparation and Spiked Biological Samples
3.8. Determination of Carbachol in Presence of Choline as a Stability Indicating Method
3.9. Statistical Comparison
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, S.H.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, J.Y. Comparison of the effective conductivity between composites reinforced by graphene nanosheets and carbon nanotubes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 243121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, E.P.; Daniel, A.M.A.; Aravind, V. An Introduction to Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes. MRS Bull. 2018, 43, 148–149. [Google Scholar]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsovvol, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.J.; Tung, V.C.; Kaner, R.B. Honeycomb carbon: A review of graphene. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, A.C.; Brownson, C.E.B. The Handbook of Graphene Electrochemistry; Springer: London, UK, 2014; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Sherif, A.; Liqun, Z.; Hsu-Chiang, K.; Jia-Bin, D.; Peter, M.; Jun, M. A novel approach to electrically and thermally conductive elastomers using graphene. Polymer 2013, 54, 3663–3670. [Google Scholar]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Fal, V.I.; Colombo, L.; Gellert, P.R.; Schwab, M.G.; Kim, K. A roadmap for graphene. Nature 2012, 490, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Ruoff, R.S. Chemical methods for the production of graphenes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radushkevich, L.V.; Lukyanovich, V.M. O strukture ugleroda, obrazujucegosja pri termiceskom razlozenii okisi ugleroda na zeleznom kontakte. Zurn. Fisic. Chim. 1952, 26, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Liliane, B. Multiwall carbon nanotube elastomeric composites: A review. Polymer 2007, 48, 4907–4920. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.; You, Y.; Sahajwalla, V.; Joshi, R.K. Transforming waste into carbon-based nanomaterials. Carbon 2016, 96, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volder, M.D.; Tawfick, S.H.; Baughman, R.H.; Hart, A.J. Carbon nanotubes: Present and future commercial applications. Science 2013, 339, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaccorso, F.; Colombo, L.; Yu, G.; Stoller, M.; Tozzini, V.; Ferrari, A.C.; Ruoff, R.S.; Pellegrini, V. Graphene related two-dimensional crystals and hybrid systems for energy conversion and storage. Science 2015, 347, 1246501–1246509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadipelli, S.; Guo, Z.X. Graphene-based materials: Synthesis and gas sorption, storage and separation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2015, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Huang, F. Electrochemical behavior and determination of fluphenazine at multi-walled carbon nanotubes/(3-mercaptopropyl)trimethoxysilane bilayer modified gold electrodes. Talanta 2004, 64, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Bol, A.A.; Jenkins, K.A.; Xia, F.; Farmer, D.B.; Zhu, Y.; Avouris, P. High-frequency scaled graphene transistors on diamond-like carbon. Nature 2011, 472, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M.S.; Mark, B.S.; Roger, A.H.; Jonathan, G.C. Glaucoma E-Book, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Health Sciences: London, UK, 2014; pp. 577–578. [Google Scholar]
- Teuvo, T. Prevention of Prolonged Voiding Problems after unexpected Postoperative Urinary Retention: Comparison of Phenoxybenzamine and Carbachol. J. Urol. 1986, 6, 1254–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Van Boxtel, C.J.; Budiono, S.; Ralph, E. Drug Benefits and Risks: International Textbook of Clinical Pharmacology; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2001; pp. 255–257. [Google Scholar]
- Sangster, B.; Savelkoul, T.J.F.; Nieuwenhuis, M.G.; van der Sluys Veer, J. Two cases of carbachol intoxication. Neth. J. Med. 1979, 22, 27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lowden, B.A. Error in glaucoma therapy. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1980, 123, 176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mönig, H.; Bruhn, H.D.; Meissner, A.; Hausmann, B. Kreislaufkollaps durch Carbachol-haltige Augentropfen. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 1989, 114, 1860. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cochrane, O. Spontaneous oesophageal rupture after carbachol therapy. Br. Med. J. 1973, 1, 463–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Thomas, G.; Klaus, S.; Hilke, A.; Nikolai, K.; Achim, S. Case report: Acute unintentional carbachol intoxication. Crit. Care 2006, 10, R84. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.Q.; Guo, L.; Du, L.M.; Fu, Y.L. Competitive supramolecular interaction of carbachol and berberine with cucurbit [7] uril and its analytical application. Microchem. J. 2013, 110, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, A.J.; Dickinson, N.A.; Waigh, R.D. 1H NMR as an analytical tool for the investigation of hydrolysis rates: A method for the rapid evaluation of the shelf-life of aqueous solutions of drugs with ester groups. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1991, 43, 860–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffrey, G.B.; Maral, P.S.M.; Mohamed, K.A. Electrochemical Sensing of Carbachol in Ophthalmic Solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, 835–839. [Google Scholar]
- Ramona, P.; Richard, D.P. Determination of Carbachol in Aqueous Solution. J. Pharm. Sci. 1969, 58, 602–604. [Google Scholar]
- Perati, P.; Rohrer, J. Determination of Cholinergic Compounds in Ophthalmic Solutions Using a Reagent-FreeTM Ion Chromatography System. LC GC N. Am. 2008, 26, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, J.; Chafetz, L. IR spectrophotometric assay of carbachol solutions. J. Pharm. Sci. 1977, 66, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Pharmacopeia. NF 29, The United State Pharmacopoeial Convention; US Pharmacopeia: Rockvill, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Fundamentals and applications. In Electrochemical Methods, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- Feiner, A.S.; McEvoythe, A.J. The Nernst Equation. J. Chem. Educ. 1994, 71, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, C.A.; Philip, N.B.; Jacek, L. Electrochemistry of Carbon Electrodes; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 106–108. [Google Scholar]
- Agnieszka, G.; Piotr, K.; Zdzislaw, M.M.; Jacek, N. Analytical Eco-Scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Buck, R.P.; Lindner, E. Recommendations for Nomenclature of ion selective electrodes. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soledad, G.M.; Joaquín, A.O.; María, C.; Mustafa, S.A. Use of a New Ziprasidone-Selective Electrode in Mixed Solvents and Its Application in the Analysis of Pharmaceuticals and Biological Fluids. Sensors 2011, 11, 8813–8825. [Google Scholar]
- Amira, M.E.; Mostafa, A.S.; Nagiba, Y.H.; Ahmad, S.F.; Badr, A.E. Membrane electrodes for the determination of glutathione. Talanta 2005, 66, 746–754. [Google Scholar]
- Francesca, M.K.; Ray, M. Alternative Solvents for Green Chemistry, 2nd ed.; RSC: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa, Y.; Bühlmann, P.; Umezawa, K.; Tohda, K.; Amemiya, S. Potentiometric selectivity coefficients of ion-selective electrodes. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1851–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengguo, H.; Shengshui, H. Carbon Nanotube-Based Electrochemical Sensors: Principles and Applications in Biomedical Systems. J. Sens. 2009, 2009, 187615. [Google Scholar]
- Endo, M.; Iijima, S.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Carbon Nanotubes, 1st ed.; BPC Wheatons Ltd.: Exeter, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]






| Parameter | Graphene Sensor 1 | MWCNTs Sensor 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Slope (mV/decade) | 50.80 | 58.14 |
| Intercept (mV) | 487.27 | 605.48 |
| LOD (M) | 1.2 × 10−8 | 1.1 × 10−8 |
| Response time (seconds) | 5 | 5 |
| Working pH range | 4–8 | 4–8 |
| Concentration range (M) | 10−7–10−2 | 10−7–10−2 |
| Stability (days) | 45 | 60 |
| Average recovery 1 | 98.68 | 100.41 |
| Correlation coefficient | 0.9992 | 0.9998 |
| Intraday precision 2 (%RSD) | 1.2 | 0.50 |
| Interday precision 2 (%RSD) | 2.1 | 0.11 |
| Parameter | Proposed Nanoscale Sensors | Ordinary Scale Sensors [28] |
|---|---|---|
| LOD (M) | 1.2 × 10−8–1.1 × 10−8 | 2.6 ×10−6–1.2 × 10−7 |
| Response time (seconds) | 5 | 6–8 |
| Sensitivity (M) | 1 × 10−7 | 10−5–10−6 |
| Stability (days) | 45–60 | 28–30 |
| Average recovery 1 | 98.68–100.41 | - |
| Intraday precision 2 (%RSD) | 0.5–1.2 | - |
| Interday precision 2 (%RSD) | 0.11–2.10 | - |
| Impact on environment | No VOC used | THF used |
| Applications | Plasma Urine Ophthalmic solutions | Ophthalmic solutions |
| Interferent | Log K for Sensor 1 | Log K for Sensor 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Choline | 0.7 × 10−3 | 0.2 × 10−4 |
| Benzalkonium chloride | 0.3 × 10−3 | 0.3 × 10−3 |
| NaCl | 0.4 × 10−3 | 0.8 × 10−4 |
| KCl | 0.4 × 10−3 | 0.3 × 10−4 |
| CaCl2 hydrate | 0.4 × 10−3 | 0.3 × 10−4 |
| 2-chloroethanol | 0.5 × 10−3 | 0.2 × 10−3 |
| Urea | 0.3 × 10−3 | 0.2 × 10−4 |
| K carbamate | 0.7 × 10−3 | 0.3 × 10−3 |
| Triethylamine | 0.4 × 10−3 | 0.8 × 10−3 |
| Pharmaceutical Preparation | Sensor 1 Recovery% ± SD | Sensor 2 Recovery% ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Miostat 0.01% | 99.74 ± 2.11 | 100.98 ± 0.314 |
| Jestryl 0.00025/mL | 100.33 ± 1.815 | 100.07 ± 0.487 |
| Plasma Samples (Sensor 1) | Plasma Samples (Sensor 2) | |||
| Claimed (M) | Found (M) | Recovery 1% | Found (M) | Recovery 1% |
| 1 × 10−7 | 1.04 × 10−7 | 104.00 | 9.94 × 10−8 | 99.40 |
| 1 × 10−5 | 9.87 × 10−6 | 98.70 | 9.98 × 10−5 | 99.80 |
| 1 × 10−3 | 1.02 × 10−3 | 102.00 | 9.98 × 10−2 | 99.80 |
| Mean ± SD | 101.60 ± 2.68 | 99.70 ± 0.23 | ||
| Urine Samples (Sensor 1) | Urine Samples (Sensor 1) | |||
| Claimed (M) | Found (M) | Recovery 1% | Found (M) | Recovery 1% |
| 1 × 10−7 | 1.08 × 10−7 | 108.00 | 9.97 × 10−8 | 99.70 |
| 1 × 10−6 | 9.93 × 10−7 | 99.30 | 9.94 × 10−7 | 99.40 |
| 1 × 10−5 | 1.07 × 10−5 | 107.00 | 9.99 × 10−6 | 99.90 |
| Mean ± SD | 104.80 ± 4.76 | 99.70 ± 0.25 | ||
| Choline Concentration | Sensor 1 Recovery % | Sensor 2 Recovery % |
|---|---|---|
| 10.0% | 99.59 | 100.11 |
| 20.0% | 101.50 | 100.60 |
| 30.0% | 100.23 | 101.62 |
| 40.0% | 101.82 | 100.81 |
| 50.0% | 101.21 | 100.03 |
| 60.0% | 102.17 | 100.75 |
| 70.0% | 102.73 | 101.46 |
| 80.0% | 103.11 | 102.33 |
| 90.0% | 102.92 | 102.34 |
| Mean ± SD | 101.70 ± 1.21 | 101.12 ± 0.87 |
| Parameter | Sensor 1 | Sensor 2 | The Official Method [32] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean % | 98.68 | 100.41 | 99.72 |
| SD | 1.21 | 0.86 | 1.19 |
| Variance | 1.46 | 0.74 | 1.42 |
| n | 6 | 6 | 4 |
| Students t-test | 1.33 (2.36) * | −1.0 (2.57) * | -- |
| F-test | 1.03 (9.01) * | 1.92 (5.40) * | -- |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Harbi, E.A.; Abdelrahman, M.H.; El-Kosasy, A.M. Ecofriendly Long Life Nanocomposite Sensors for Determination of Carbachol in Presence of Choline: Application in Ophthalmic Solutions and Biological Fluids. Sensors 2019, 19, 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102357
Al-Harbi EA, Abdelrahman MH, El-Kosasy AM. Ecofriendly Long Life Nanocomposite Sensors for Determination of Carbachol in Presence of Choline: Application in Ophthalmic Solutions and Biological Fluids. Sensors. 2019; 19(10):2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102357
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Harbi, Eman A., Mona H. Abdelrahman, and Amira M. El-Kosasy. 2019. "Ecofriendly Long Life Nanocomposite Sensors for Determination of Carbachol in Presence of Choline: Application in Ophthalmic Solutions and Biological Fluids" Sensors 19, no. 10: 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102357
APA StyleAl-Harbi, E. A., Abdelrahman, M. H., & El-Kosasy, A. M. (2019). Ecofriendly Long Life Nanocomposite Sensors for Determination of Carbachol in Presence of Choline: Application in Ophthalmic Solutions and Biological Fluids. Sensors, 19(10), 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102357