Wearable Enzymatic Alcohol Biosensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Detection and Catalysis
2.2. Laboratory Data Collection
2.3. Human Subject Data
3. Results
3.1. In Situ Laboratory Results
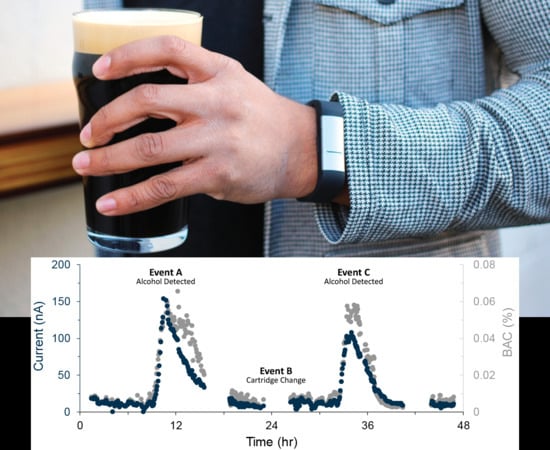
3.2. In Vivo Measurement Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Transdermal Alcohol
4.2. Membrane
4.3. Connection and Steady State
4.4. Sensor Response
4.5. Enzyme in Excess
4.6. Transdermal Measurements
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stahre, M.; Roeber, J.; Kanny, D.; Brewer, R.D.; Zhang, X. Peer reviewed: Contribution of excessive alcohol consumption to deaths and years of potential life lost in the United States. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2014, 11, E109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, J.J.; Gonzales, K.R.; Bouchery, E.E.; Tomedi, L.E.; Brewer, R.D. 2010 national and state costs of excessive alcohol consumption. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 49, e73–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moos, R.H.; Moos, B.S. Rates and predictors of relapse after natural and treated remission from alcohol use disorders. Addiction 2006, 101, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alessi, S.; Petry, N.; Barnett, N. Objective Continuous Monitoring of Alcohol Consumption for Three Months Among Alcohol Use Disorder Treatment Outpatients. Alcohol 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamella, M.; Campuzano, S.; Manso, J.; de Rivera, G.G.; López-Colino, F.; Reviejo, A.; Pingarrón, J. A novel non-invasive electrochemical biosensing device for in situ determination of the alcohol content in blood by monitoring ethanol in sweat. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 806, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeerapan, I.; Imani, S.; Cho, T.N.; Bandodkar, A.; Cinti, S.; Mercier, P.P.; Wang, J. Noninvasive alcohol monitoring using a wearable tattoo-based iontophoretic-biosensing system. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.V.; Windmiller, J.R.; Mishra, R.K.; Wang, J. Continuous minimally-invasive alcohol monitoring using microneedle sensor arrays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 574–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conroy, D.E.; Pincus, A.L.; Ram, N.; al’Absi, M. Thirsting to understand the temporal dynamics of physical activity and alcohol use. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 52, 1158–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, B.; Martini-Laithier, V.; Fiorido, T.; Annanouch, F.; Burtey, S.; Cassé-Perrot, C.; Audebert, C.; Bendahan, M.; Bouchakour, R.; Blin, O.; et al. Transdermal Alcohol Measurements Using MOX Sensors in Clinical Trials. Multidiscip. Dig. Publ. Inst. Proc. 2017, 1, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Sempionatto, J.R.; Imani, S.; Hartel, M.C.; Barfidokht, A.; Tang, G.; Campbell, A.S.; Mercier, P.P.; Wang, J. Simultaneous Monitoring of Sweat and Interstitial Fluid Using a Single Wearable Biosensor Platform. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, A.S.; Kim, J.; Wang, J. Wearable electrochemical alcohol biosensors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 10, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, B.; Aguir, K.; Fiorido, T.; Martini-Laithier, V.; Bouchakour, R.; Burtey, S.; Reynard-Carette, C.; Bendahan, M. Skin alcohol perspiration measurements using MOX sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 280, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Campbell, A.S.; de Ávila, B.E.F.; Wang, J. Wearable biosensors for healthcare monitoring. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.C.; Shukla, S.; Skoog, S.A.; Boehm, R.D.; Narayan, R.J. Current Advancements in Transdermal Biosensing and Targeted Drug Delivery. Sensors 2019, 19, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocchitta, G.; Spanu, A.; Babudieri, S.; Latte, G.; Madeddu, G.; Galleri, G.; Nuvoli, S.; Bagella, P.; Demartis, M.; Fiore, V.; et al. Enzyme Biosensors for Biomedical Applications: Strategies for Safeguarding Analytical Performances in Biological Fluids. Sensors 2016, 16, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fridberg, D.J.; Leeman, R.F.; Cook, R.L.; Porges, E.C. Wrist-Worn Alcohol Biosensors: Strengths, Limitations, and Future Directions. Alcohol 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, I.G.; Luczak, S.E.; Weiss, J. Blind deconvolution for distributed parameter systems with unbounded input and output and determining blood alcohol concentration from transdermal biosensor data. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 231, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, P.R.; McKnight, A.S. Evaluating Transdermal Alcohol Measuring Devices; Technical Report; National Highway Traffic Safety Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield, T.K.; Bond, J.; Kerr, W.C. Biomonitoring for improving alcohol consumption surveys: The new gold standard? Alcohol Res. Curr. Rev. 2014, 36, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Roushey, W.J., III; Hawthorne, J.S.; Wojcik, M.H.; Collins, D.C.; McGee, S.K. Moisture Control in a Transdermal Blood Alcohol Monitor. U.S. Patent US 2009/0182216 A1, 16 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, J.T.; Rahman, M.R.; Easton, E.B. The influence of relative humidity on the performance of fuel cell catalyst layers in ethanol sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, N.P.; Tidey, J.; Murphy, J.G.; Swift, R.; Colby, S.M. Contingency management for alcohol use reduction: A pilot study using a transdermal alcohol sensor. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011, 118, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alessi, S.M.; Barnett, N.P.; Petry, N.M. Experiences with SCRAMx alcohol monitoring technology in 100 alcohol treatment outpatients. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017, 178, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.M. Commentary on Patrick and Colleagues: High-Intensity Drinking Among Young Adults in the United States: Prevalence, Frequency, and Developmental Change. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couderc, R.; Baratti, J. Oxidation of methanol by the yeast, Pichia pastoris. Purification and properties of the alcohol oxidase. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1980, 44, 2279–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyakin, A.A.; Gitelmacher, O.V.; Karyakina, E.E. A high-sensitive glucose amperometric biosensor based on Prussian Blue modified electrodes. Anal. Lett. 1994, 27, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neff, V.D. Electrochemical oxidation and reduction of thin films of Prussian Blue. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1978, 125, 886–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itaya, K.; Shoji, N.; Uchida, I. Catalysis of the reduction of molecular oxygen to water at Prussian blue modified electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984, 106, 3423–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyakin, A.A.; Karyakina, E.E.; Gorton, L. Prussian-Blue-based amperometric biosensors in flow-injection analysis. Talanta 1996, 43, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, J.; Penrose, W.; Bobis, J. A potentiostat based on a voltage-controlled current source for use with amperometric gas sensors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1992, 41, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umasankar, Y.; Jalal, A.H.; Gonzalez, P.J.; Chowdhury, M.; Alfonso, A.; Bhansali, S. Wearable alcohol monitoring device with auto-calibration ability for high chemical specificity. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 13th International Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN), San Francisco, CA, USA, 14–17 June 2016; pp. 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posey, D.; Mozayani, A. The estimation of blood alcohol concentration. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2007, 3, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, R. Direct measurement of alcohol and its metabolites. Addiction 2003, 98, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.C.; Hlastala, M.P. The kinetics of transdermal ethanol exchange. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webster, G.D.; Gabler, H.C. Feasibility of transdermal ethanol sensing for the detection of intoxicated drivers. Annual Proceedings/Association for the Advancement of Automotive Medicine. Assoc. Adv. Automot. Med. 2007, 51, 449–464. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, J.G.; Wilkinson, P.K.; Sedman, A.J.; Kay, D.R.; Weidler, D.J. Elimination of alcohol from human blood. J. Pharm. Sci. 1976, 65, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.J. A method for determining the excretion of volatile substances through skin. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharm. 1985, 7, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, D. The pharmacokinetics of alcohol excretion in human perspiration. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharm. 1985, 7, 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Karns-Wright, T.E.; Roache, J.D.; Hill-Kapturczak, N.; Liang, Y.; Mullen, J.; Dougherty, D.M. Time delays in transdermal alcohol concentrations relative to breath alcohol concentrations. Alcohol Alcohol. 2016, 52, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, T.; Suzuki, T.; Tsujii, M.; Iitani, K.; Chien, P.J.; Ye, M.; Toma, K.; Iwasaki, Y.; Mitsubayashi, K. Real-time monitoring of skin ethanol gas by a high-sensitivity gas phase biosensor (bio-sniffer) for the non-invasive evaluation of volatile blood compounds. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 129, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, L.C.; Wolf, R.; Granger, D.; Taylor, Z. Continuous Recording of Blood Oxygen Tensions by Polarography. J. Appl. Physiol. 1953, 6, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, R.M.; Martin, C.S.; Swette, L.; Laconti, A.; Kackley, N. Studies on a wearable, electronic, transdermal alcohol sensor. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1992, 16, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swette, L.L.; Griffith, A.E.; LaConti, A.B. Potential and Diffusion Controlled Solid Electrolyte Sensor for Continuous Measurement of Very Low Levels of Transdermal Alcohol. U.S. Patent 5,944,661, 31 August 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Mitragotri, S. Modeling skin permeability to hydrophilic and hydrophobic solutes based on four permeation pathways. J. Controll. Release 2003, 86, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcıa-Jareno, J.; Sanmatıas, A.; Vicente, F.; Gabrielli, C.; Keddam, M.; Perrot, H. Study of Prussian Blue (PB) films by ac-electrogravimetry: Influence of PB morphology on ions movement. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 3765–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, C.; García-Jareño, J.J.; Keddam, M.; Perrot, H.; Vicente, F. Ac-electrogravimetry study of electroactive thin films. I. Application to Prussian Blue. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 3182–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeki, T.; Watanbe, I.; Ikeda, S. Study of the prussian blue/prussian white redox reaction by cyclic voltammothermometry. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1987, 236, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.C.; Chou, T.C. Electrodeposited nickel-boron thin-film ethanol sensor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, H127–H132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobos, R. Enzyme-based electrochemical biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1987, 6, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Gallego, F.; Betancor, L.; Hidalgo, A.; Dellamora-Ortiz, G.; Mateo, C.; Fernández-Lafuente, R.; Guisán, J.M. Stabilization of different alcohol oxidases via immobilization and post immobilization techniques. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecki, T.M. Assessment of Alcohol Use in the Natural Environment. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 43, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansdorp, B.; Strenk, E.; Arroyo, N.; Imberman, D. Transdermal Analyte Sensing Device. U.S. Patent 9,855,000, 2 January 2018. [Google Scholar]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lansdorp, B.; Ramsay, W.; Hamid, R.; Strenk, E. Wearable Enzymatic Alcohol Biosensor. Sensors 2019, 19, 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102380
Lansdorp B, Ramsay W, Hamid R, Strenk E. Wearable Enzymatic Alcohol Biosensor. Sensors. 2019; 19(10):2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102380
Chicago/Turabian StyleLansdorp, Bob, William Ramsay, Rashad Hamid, and Evan Strenk. 2019. "Wearable Enzymatic Alcohol Biosensor" Sensors 19, no. 10: 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102380
APA StyleLansdorp, B., Ramsay, W., Hamid, R., & Strenk, E. (2019). Wearable Enzymatic Alcohol Biosensor. Sensors, 19(10), 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19102380