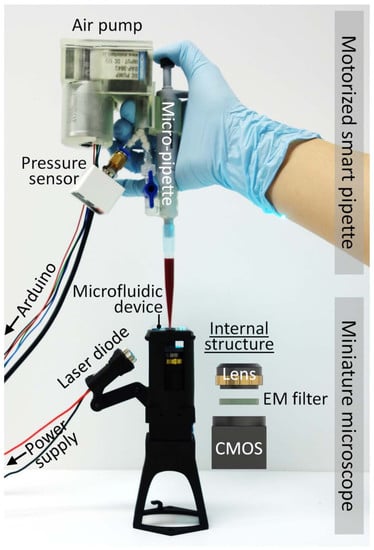
Handheld Microflow Cytometer Based on a Motorized Smart Pipette, a Microfluidic Cell Concentrator, and a Miniaturized Fluorescence Microscope
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Device Design and Fabrication
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Volume Metering and Flow Rate Control Using the Motorized Smart Pipette
3.2. Microfluidic Cell Concentrator
3.3. Microscopic WBC Imaging Using the Miniaturized Fluorescence Microscope
3.4. Handheld rWBC Counting Using Integrated Microflow Cytometry
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steinkamp, J.A. Flow cytometry. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1984, 55, 1375–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakis, S.; Holzner, G.; Choo, J.; deMello, A. High-throughput microfluidic imaging flow cytometry. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 55, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laerum, O.D.; Farsund, T. Clinical application of flow cytometry: A review. Cytometry 1981, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, F.E.; Foon, K.A. Flow cytometric immunophenotyping for hematologic neoplasms. Blood 2008, 111, 3941–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finak, G.; Langweiler, M.; Jaimes, M.; Malek, M.; Taghiyar, J.; Korin, Y.; Raddassi, K.; Devine, L.; Obermoser, G.; Pekalski, M.L.; et al. Standardizing Flow Cytometry Immunophenotyping Analysis from the Human ImmunoPhenotyping Consortium. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.; Stewart, M.P.; Sharei, A.; Weaver, J.C.; Langer, R.S.; Jensen, K.F. High-throughput Nuclear Delivery and Rapid Expression of DNA via Mechanical and Electrical Cell-Membrane Disruption. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 0039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharei, A.; Zoldan, J.; Adamo, A.; Sim, W.Y.; Cho, N.; Jackson, E.; Mao, S.; Schneider, S.; Han, M.-J.; Lytton-Jean, A.; et al. A vector-free microfluidic platform for intracellular delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2082–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wlodkowic, D.; Skommer, J.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Flow cytometry-based apoptosis detection. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 559, 19–32. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.; Choi, S. A continuous-flow microfluidic syringe filter for size-based cell sorting. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1250–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Song, S.; Choi, C.; Park, J.-K. Microfluidic self-sorting of mammalian cells to achieve cell cycle synchrony by hydrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 1964–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateya, D.A.; Erickson, J.S.; Howell, P.B., Jr.; Hilliard, L.R.; Golden, J.P.; Ligler, F.S. The good, the bad, and the tiny: A review of microflow cytometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 391, 1485–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piyasena, M.E.; Graves, S.W. The intersection of flow cytometry with microfluidics and microfabrication. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1044–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tahara, M.; Inoue, T.; Miyakura, Y.; Horie, H.; Yasuda, Y.; Fujii, H.; Kotake, K.; Sugano, K. Cell diameter measurements obtained with a handheld cell counter could be used as a surrogate marker of G2/M arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer cell lines exposed to SN-38. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 434, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, G. Automated handheld instrument improves counting precision across multiple cell lines. BioTechniques 2010, 48, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennuru, S.; Pion, S.D.; Kamgno, J.; Wanji, S.; Nutman, T.B. Repurposed automated handheld counter as a point-of-care tool to identify individuals ‘at risk’ of serious post-ivermectin encephalopathy. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Mavandadi, S.; Coskun, A.F.; Yaglidere, O.; Ozcan, A. Optofluidic fluorescent imaging cytometry on a cell phone. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6641–6647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.; Keles, H.O.; Ozcan, A.; Khademhosseini, A.; Hæggström, E.; Kuritzkes, D.; Demirci, U. Integrating microfluidics and lensless imaging for point-of-care testing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3208–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Shin, S.; Lee, Y.; Um, C.; You, D.; Yun, H.; Choi, S. High-throughput residual white blood cell counter enabled by microfluidic cell enrichment and reagent-containing patch integration. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 283, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsam, J.; Bruck, H.A.; Rasooly, A. Webcam-based flow cytometer using wide-field imaging for low cell number detection at high throughput. Analyst 2014, 139, 4322–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zandi, M.; Ho, C.-C.; Kaval, N.; Papautsky, I. Single stream inertial focusing in a straight microchannel. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.J.; Gossett, D.R.; Di Carlo, D. Three dimensional, sheathless, and high-throughput microparticle inertial focusing through geometry-induced secondary flows. Small 2013, 9, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yan, S.; Yuan, D.; Du, H.; Alici, G.; Li, W. High-throughput sheathless and three-dimensional microparticle focusing using a microchannel with arc-shaped groove arrays. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Asghari, M.; Serhatlioglu, M.; Ortaç, B.; Solmaz, M.E.; Elbuken, C. Sheathless Microflow Cytometry Using Viscoelastic Fluids. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Avino, G.; Romeo, G.; Villone, M.M.; Greco, F.; Netti, P.A.; Maffettone, P.L. Single line particle focusing induced by viscoelasticity of the suspending liquid: Theory, experiments and simulations to design a micropipe flow-focuser. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Park, J.-K. Sheathless hydrophoretic particle focusing in a microchannel with exponentially increasing obstacle arrays. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3035–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Choi, S. Field-free, sheathless cell focusing in exponentially expanding hydrophoretic channels for microflow cytometry. Cytom. Part A 2013, 83, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, Y.-C.; Huang, K.-W.; Chong, W.; Chiou, P.-Y. Tunnel Dielectrophoresis for Tunable, Single-Stream Cell Focusing in Physiological Buffers in High-Speed Microfluidic Flows. Small 2016, 12, 4343–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalb, D.M.; Fencl, F.A.; Woods, T.A.; Swanson, A.; Maestas, G.C.; Juárez, J.J.; Edwards, B.S.; Shreve, A.P.; Graves, S.W. Line-Focused Optical Excitation of Parallel Acoustic Focused Sample Streams for High Volumetric and Analytical Rate Flow Cytometry. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9967–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, X.; Li, D. Focused electrophoretic motion and selected electrokinetic dispensing of particles and cells in cross-microchannels. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 3552–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, A.Y.; Spence, C.; Scherer, A.; Arnold, F.H.; Quake, S.R. A microfabricated fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 1109–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonnet, C.; Groisman, A. High-throughput and high-resolution flow cytometry in molded microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5653–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; You, D.; Kim, Y.-J.; Oh, I.; Choi, S. Motorized smart pipette for handheld operation of a microfluidic blood plasma separator. Sens. Actuators B 2018, 267, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Choi, Y.J.; Seo, H.; Shin, E.-C.; Choi, S. Deterministic Migration-Based Separation of White Blood Cells. Small 2016, 12, 5159–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Oh, S.; Kim, B.; Hahn, Y.K.; Choi, S. Rapid preparation and single-cell analysis of concentrated blood smears using a high-throughput blood cell separator and a microfabricated grid film. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1507, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, B.M.; Furrer-Burger, M. Enumeration of residual cells in leucodepleted blood products: Techniques and pitfalls. In Universal Leucodepletion: The European Experience; SIMTI Servizi: Milano, Italy, 2003; pp. 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Cervia, J.S.; Wenz, B.; Ortolano, G.A. Leukocyte reduction’s role in the attenuation of infection risks among transfusion recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szuflad, P.; Dzik, W.H. A general method for concentrating blood samples in preparation for counting very low numbers of white cells. Transfusion 1997, 37, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, D.S.; Birch, P.; O’Toole, J.; Henderson, D.; Scalia, V. Flow cytometric determination of residual white blood cell levels in preserved samples from leukoreduced blood products. Transfusion 2008, 48, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, B.; Choi, S. On-Chip Cell Staining and Counting Platform for the Rapid Detection of Blood Cells in Cerebrospinal Fluid. Sensors 2018, 18, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, J.G.; Yoo, D.; Hahn, Y.K.; Choi, S. A portable somatic cell counter based on a multi-functional counting chamber and a miniaturized fluorescence microscope. Talanta 2017, 170, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, B.; Kang, D.; Choi, S. Handheld Microflow Cytometer Based on a Motorized Smart Pipette, a Microfluidic Cell Concentrator, and a Miniaturized Fluorescence Microscope. Sensors 2019, 19, 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122761
Kim B, Kang D, Choi S. Handheld Microflow Cytometer Based on a Motorized Smart Pipette, a Microfluidic Cell Concentrator, and a Miniaturized Fluorescence Microscope. Sensors. 2019; 19(12):2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122761
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Byeongyeon, Dayoung Kang, and Sungyoung Choi. 2019. "Handheld Microflow Cytometer Based on a Motorized Smart Pipette, a Microfluidic Cell Concentrator, and a Miniaturized Fluorescence Microscope" Sensors 19, no. 12: 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122761
APA StyleKim, B., Kang, D., & Choi, S. (2019). Handheld Microflow Cytometer Based on a Motorized Smart Pipette, a Microfluidic Cell Concentrator, and a Miniaturized Fluorescence Microscope. Sensors, 19(12), 2761. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19122761