IoT Wearable Sensors and Devices in Elderly Care: A Literature Review
Abstract
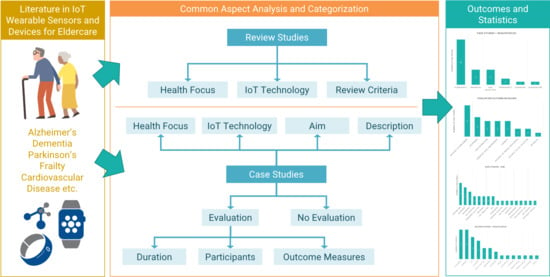
:1. Introduction
2. Related Review Studies in IoT Wearable Sensors and Devices for Eldercare
2.1. Health Focus
2.2. IoT Technology
2.3. Review Criteria
3. Review of Case Studies
3.1. Health Focus
3.2. IoT Technology
3.3. Aim
3.4. Description
3.5. Evaluation
3.5.1. Duration
3.5.2. Participants
3.5.3. Outcome Measures
4. Results and Statistics
5. Limitations and Challenges
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Department of Economic and Social Affairs PD. World Population Ageing 2019; Nations Department of Economic: Bangkok, Thailand, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Australia, D.; Baker, S.; Banerjee, S. Others Alzheimer’s Disease International. In World Alzheimer Report 2019: Attitudes to Dementia; Alzheimer’s Dis. Int.: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Alsheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures Includes a Special Report on Alzheimer’s Detection in the Primary Care Setting: Connecting Patients and Physicians; Alzheimer’s Dis. Int.: London, UK, 2019.
- Li, R.; Lu, B.; McDonald-Maier, K.D. Cognitive assisted living ambient system: A survey. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2015, 1, 229–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afilalo, J.; Karunananthan, S.; Eisenberg, M.J.; Alexander, K.P.; Bergman, H. Role of Frailty in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2009, 103, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghi, M.; Thurow, K.; Stoll, R. Wearable Devices in Medical Internet of Things: Scientific Research and Commercially Available Devices. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2017, 23, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavropoulos, T.G.; Meditskos, G.; Kompatsiaris, I. DemaWare2: Integrating sensors, multimedia and semantic analysis for the ambient care of dementia. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ienca, M.; Fabrice, J.; Elger, B.; Caon, M.; Scoccia Pappagallo, A.; Kressig, R.W.; Wangmo, T. Intelligent Assistive Technology for Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 56, 1301–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talboom, J.S.; Huentelman, M.J. Big data collision: The internet of things, wearable devices and genomics in the study of neurological traits and disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, R35–R39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Shaqi, R.; Mourshed, M.; Rezgui, Y. Progress in ambient assisted systems for independent living by the elderly. Springerplus 2016, 5, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.; Park, H.; Bonato, P.; Chan, L.; Rodgers, M. A review of wearable sensors and systems with application in rehabilitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banaee, H.; Ahmed, M.; Loutfi, A.; Banaee, H.; Ahmed, M.U.; Loutfi, A. Data Mining for Wearable Sensors in Health Monitoring Systems: A Review of Recent Trends and Challenges. Sensors 2013, 13, 17472–17500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salih, A.; Salih, M.; Abraham, A. A Review of Ambient Intelligence Assisted Healthcare Monitoring. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. Ind. Manag. Appl. 2013, 5, 741–750. [Google Scholar]
- Rashidi, P.; Mihailidis, A. A Survey on Ambient-Assisted Living Tools for Older Adults. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Inf. 2013, 17, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendran, D.; Janet, J.; Prabha, D.; Anisha, E. A Study on devices for assisting Alzheimer patients. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC)I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC) IEEE, Palladam, India, 30–31 August 2018; pp. 620–625. [Google Scholar]
- Spasova, V.; Iliev, I. A survey on automatic fall detection in the context of ambient assisted living systems. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Res. 2014, 4, 94–109. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Dong, T.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Dong, T. A Review of Wearable Technologies for Elderly Care that Can Accurately Track Indoor Position, Recognize Physical Activities and Monitor Vital Signs in Real Time. Sensors 2017, 17, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piwek, L.; Ellis, D.A.; Andrews, S.; Joinson, A. The Rise of Consumer Health Wearables: Promises and Barriers. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, D.V. Medical Internet of Things and Big Data in Healthcare. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2016, 22, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpato, N.; Pieroni, A.; Di Nunzio, L.; Fallucchi, F. E-health-IoT universe: A review. Management 2017, 21, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Ryoo, H.-Y.; Shin, B.-S.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Ryoo, H.-Y.; Shin, B.-S. Sustainable Wearables: Wearable Technology for Enhancing the Quality of Human Life. Sustainability 2016, 8, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cedillo, P.; Sanchez, C.; Campos, K.; Bermeo, A. A Systematic Literature Review on Devices and Systems for Ambient Assisted Living: Solutions and Trends from Different User Perspectives. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on eDemocracy & eGovernment (ICEDEG) IEEE, Ambato, Ecuador, 4–6 April 2018; pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Baig, M.M.; Afifi, S.; GholamHosseini, H.; Mirza, F. A Systematic Review of Wearable Sensors and IoT-Based Monitoring Applications for Older Adults—A Focus on Ageing Population and Independent Living. J. Med. Syst. 2019, 43, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.; Hu, Y.; Nguyen, T.; Lan, G.; Khalifa, S.; Thilakarathna, K.; Hassan, M.; Seneviratne, A. A Survey of Wearable Devices and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2573–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, S.; Matlo, C.; Bobrovitskiy, C.; Waldoch, A.; Fang, M.L.; Jackson, P.; Mihailidis, A.; Nygård, L.; Astell, A.; Sixsmith, A. Ambient Assisted Living Technologies for Aging Well: A Scoping Review. J. Intell. Syst. 2016, 25, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peetoom, K.K.B.; Lexis, M.A.S.; Joore, M.; Dirksen, C.D.; De Witte, L.P. Literature review on monitoring technologies and their outcomes in independently living elderly people. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2015, 10, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisberg, B.; Prichep, L.; Mosconi, L.; John, E.R.; Glodzik-Sobanska, L.; Boksay, I.; Monteiro, I.; Torossian, C.; Vedvyas, A.; Ashraf, N.; et al. The pre-mild cognitive impairment, subjective cognitive impairment stage of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer Dement. 2008, 4, S98–S108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzawi, M.A.; Hassan, R.; Azmi, K.; Bakar, A. A Review on Internet of Things (IoT) in Healthcare IEEE 802.11aa Intra-AC Prioritization View project A Rule-Based Technique to Detect. Router Advertisement Flooding Attack Against Web Application View project. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2016, 11, 10216–10221. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Lee, H.; Chen, C.; Huang, H.; Luo, C. Wireless Body Sensor Network With Adaptive Low-Power Design for Biometrics and Healthcare Applications. IEEE Syst. J. 2009, 3, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Luis-Ferreira, F.; Sarraipa, J.; Goncalves, R. Behavioural Monitoring of Alzheimer Patients with Smartwatch Based System. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Intelligent Systems (IS) IEEE, Funchal-Madeira, Portugal, 25–27 September 2018; pp. 771–775. [Google Scholar]
- Ehrler, F.; Lovis, C. Supporting elderly homecare with smartwatches: Advantages and drawbacks. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2014, 205, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.; Kaur, S. Gerontechnology—The study of alzheimer disease using cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Energy, Communication, Data Analytics and Soft Computing (ICECDS) IEEE, Chennai, India, 1–2 August 2017; pp. 3726–3733. [Google Scholar]
- Aljehani, S.S.; Alhazmi, R.A.; Aloufi, S.S.; Aljehani, B.D.; Abdulrahman, R. iCare: Applying IoT Technology for Monitoring Alzheimer’s Patients. In Proceedings of the 2018 1st International Conference on Computer Applications & Information Security (ICCAIS) IEEE, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 4–6 April 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Creation of an Assisted Living Environment for Elderly People using Ubiquitous Networking Technologies. Available online: https://www.iimcal.ac.in/sites/all/files/sirg/1-1-ageing-creation-assisted-living.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Karakaya, M.; Şengül, G.; Bostan, A. Remotely Monitoring Activities of the Elders Using Smart Watches. Int. J. Sci. Res. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2017, 3, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Barri Khojasteh, S.; Villar, J.R.; de la Cal, E.; González, V.M.; Sedano, J.; Yazgan, H.R. Evaluation of a Wrist-Based Wearable Fall Detection Method; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 377–386. [Google Scholar]
- Algase, D.L.; Beattie, E.R.A.; Leitsch, S.A.; Beel-Bates, C.A. Biomechanical activity devices to index wandering behaviour in dementia. Am. J. Alzheimer Dis. 2003, 18, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.H.K.; Tee, Y.X.; Toh, L.J.; Phang, S.J.; Liew, J.Y.; Queck, B.; Gottipati, S. Predicting Potential Alzheimer Medical Condition in Elderly Using IOT Sensors—Case Study; Singapore Management Universitity: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, J.R.; Rønn-Andersen, K.V.H.; Bień, P.; Özkil, A.G.; Forchhammer, B.H.; Maier, A.M. Pervasive assistive technology for people with dementia: A UCD case. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, R.J.; Ng, Y.S.; Zhu, S.; Tan, D.M.; Anderson, B.; Schlaug, G.; Wang, Y. A Validated Smartphone-Based Assessment of Gait and Gait Variability in Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiss, A.; Herman, T.; Mirelman, A.; Shiratzky, S.S.; Giladi, N.; Barnes, L.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Buchman, A.S.; Hausdorff, J.M. The transition between turning and sitting in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A wearable device detects an unexpected sequence of events. Gait Posture 2019, 67, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Ardle, R.; Morris, R.; Hickey, A.; Del Din, S.; Koychev, I.; Gunn, R.N.; Lawson, J.; Zamboni, G.; Ridha, B.; Sahakian, B.J.; et al. Gait in Mild Alzheimer’s Disease: Feasibility of Multi-Center Measurement in the Clinic and Home with Body-Worn Sensors: A Pilot Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 63, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.R.; Pinho, M.S.; Macedo, L.; Moulin, C.; Caldeira, S.; Firmino, H. It is not only memory: Effects of sensecam on improving well-being in patients with mild alzheimer disease. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.; Gago, M.F.; Yelshyna, D.; Ferreira, J.; Silva, H.D.; Rocha, L.; Sousa, N.; Bicho, E. Application of Machine Learning in Postural Control Kinematics for the Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Sabbagh, M.; Wyman, R.; Liebsack, C.; Kunik, M.E.; Najafi, B. Instrumented Trail-Making Task (iTMT) to Differentiate Persons with No Cognitive Impairment, Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment, Alzheimer’s Disease-Proof of Concept Study. Gerontology 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, Y.-L.; Chung, P.-C.; Wang, W.-H.; Pai, M.-C.; Wang, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-W.; Wu, H.-L.; Wang, J.-S. Gait and Balance Analysis for Patients With Alzheimer’s Disease Using an Inertial-Sensor-Based Wearable Instrument. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 2014, 18, 1822–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbate, S.; Avvenuti, M.; Light, J. Usability Study of a Wireless Monitoring System among Alzheimer’s Disease Elderly Population. Int. J. Telemed. Appl. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodberry, E.; Browne, G.; Hodges, S.; Watson, P.; Kapur, N.; Woodberry, K. The use of a wearable camera improves autobiographical memory in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Memory 2015, 23, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuty, V.; Boger Masc, J.; Phd, L.Y.; Hoey, J.; Mihailidis, A.; Boger, J.; Young, L. Engaging Older Adults with Dementia in Creative Occupations Using Artificially Intelligent Assistive Technology. Assist. Technol. 2013, 25, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancioni, G.E.; Singh, N.N.; O’reilly, M.F.; Sigafoos, J.; Renna, C.; Ventrella, M.; Pinto, K.; Minervini, M.G.; Oliva, D.; Groeneweg, J. Supporting daily activities and indoor travel of persons with moderate Alzheimer’s disease through standard technology resources. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloulou, H.; Mokhtari, M.; Tiberghien, T.; Biswas, J.; Phua, C.; Kenneth Lin, J.H.; Yap, P. Deployment of assistive living technology in a nursing home environment: Methods and lessons learned. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2013, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pot, A.M.; Willemse, B.M.; Horjus, S. A pilot study on the use of tracking technology: Feasibility, acceptability, and benefits for people in early stages of dementia and their informal caregivers. Aging Ment. Health 2012, 16, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagnin, A.; Jelcic, N.; Agostini, M.; Meneghello, F.; Parise, S.; Galano, A.; Tonin, P.; Dam, M.; Busse, C. Feasibility and efficacy of cognitive telerehabilitation in early Alzheimer’s disease: A pilot study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]











| Review Study | Year | Health Focus | IoT Technology | Review Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Talboom & Huentelman [9] | 2018 | Alzheimer’s, | Wearables | Ease of Use, |
| Parkinson’s | Biometric Sensors | Efficacy, | ||
| Invasiveness, | ||||
| Esthetics | ||||
| Ienca et al. [8] | 2017 | Dementia, | Wearables, Smartphones, | Efficacy, |
| Alzheimer’s | Applications, | Performance, | ||
| Robotics | Clinical Value | |||
| Li et al. [4] | 2015 | Dementia, | Smart Home | Networking |
| Chronic Disease | Social Inclusion, | |||
| Ontologies | ||||
| Al-Shaqi et al. [10] | 2016 | Dementia, | Biometric Sensors, Environmental Sensors, | Networking, |
| Alzheimer’s | Indoor Positioning, Smart Home | Ease of Use, | ||
| Cost, | ||||
| Efficacy | ||||
| Patel et al. [11] | 2012 | Dementia, | Wearables, | Cost, |
| Alzheimer’s, | Biometric Sensors, | Energy Consumption | ||
| Parkinson’s, | Indoor Positioning, | |||
| CVD | Microphone | |||
| Banaee et al. [12] | 2013 | Dementia, | Wearables | Sensor Types, |
| Alzheimer’s, | Networking | |||
| Parkinson’s, | ||||
| CVD | ||||
| Salih et al. [13] | 2013 | Dementia, | Microphone, | Networking, |
| Alzheimer’s, | Environmental Sensors, | Security | ||
| CVD | Biometric Sensors, | |||
| Smart Home | ||||
| Rashidi & Mihailidis [14] | 2013 | Dementia | Wearables, | Sensor Types, |
| Wearable Cameras, | Data Format | |||
| Biometric Sensors, | ||||
| Environmental Sensors, | ||||
| Indoor Positioning | ||||
| Surendran et al. [15] | 2018 | Alzheimer’s | Wearables, | Networking, |
| Wearable Cameras | Accuracy | |||
| Spasova & I. Iliev [16] | 2014 | Frailty and Falls, | Wearables, | Networking, |
| Dementia, | Cameras, | Sensor Types, | ||
| Alzheimer’s | Smart Home, | Efficacy | ||
| Environmental Sensors, | ||||
| Indoor Positioning | ||||
| Wang et al. [17] | 2017 | Frailty and Falls, | Indoor Positioning | Accuracy, |
| CVD | Security, | |||
| Networking, | ||||
| Range, | ||||
| Cost, | ||||
| Ease of Use | ||||
| Piwek et al. [18] | 2016 | Anxiety, | Wearables, Smartphones, Applications | Robustness, |
| Obesity, | Security | |||
| Sleep Disorders | ||||
| Dimitrov [19] | 2016 | Orthopedics, | Wearables | Ease of Usage, |
| Robotic Surgery, | Networking | |||
| CVD | ||||
| Scarpato et al. [20] | 2017 | Pulmonary, | Wearables, | Energy Consumption, |
| CVD | Biometric Sensors | Size | ||
| Haghi et al. [6] | 2017 | Healthcare | Wearables, | Cost, |
| Biometric Sensors | Size, | |||
| Energy Consumption | ||||
| Lee et al. [21] | 2016 | Healthcare | Wearables | Robustness, |
| Cost, | ||||
| Size, | ||||
| Energy Consumption | ||||
| Cedillo et al. [22] | 2018 | Eldercare | Wearables, | Sensor Types, |
| Applications | Networking | |||
| Baig et al. [23] | 2019 | Eldercare | Wearables | Ease of Use, |
| Energy | ||||
| Seneviratne et al. [24] | 2017 | Eldercare | Wearables | Energy Consumption |
| Blackman et al. [25] | 2016 | Eldercare | Wearables, Environmental Sensors, | Safety, |
| Indoor Positioning | Ease of Use | |||
| Peetoom et al. [26] | 2015 | Eldercare, | Wearables, | Sensor Types, |
| Frailty and Falls | Smart Home, | Efficacy | ||
| Cameras, | ||||
| Microphone |
| Case Study | Year | Health Focus | IoT Technology | Aim | Description | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rodrigues et al. [30] | 2018 | Alzheimer’s, Fall Detection | Wearables, Smartphones | Fall Detection, Wandering Detection, Emergency | Fall and wandering detection for emergency alerts | - |
| Ehrler & Lovis [31] | 2014 | Eldercare | Wearables | Comparison | Smartwatches for elderly support | - |
| Sharma & Kaur [32] | 2017 | Alzheimer’s, Telemedicine | Smartphones, Applications | Monitoring, Symptom Detection | Android app to monitor AD symptoms and contact doctors | - |
| Aljehani et al. [33] | 2018 | Alzheimer’s | Wearables, Applications | GPS Tracking, Biometric Sensors | GPS and heart rate logging | - |
| Bose [34] | 2013 | Dementia, Alzheimer’s | Biometric Sensors | Emergency | Detect emergency and send alerts | - |
| Karakaya et al. [35] | 2017 | Fall Detection | Wearables, Applications | Fall Prediction | Predictive model for falls | - |
| Khojasteh et al. [36] | 2018 | Fall Detection | Wearables | Development | Fall detection from wrist-worn sensors | - |
| Algase et al. [37] | 2018 | Dementia | Wearables | Wandering Detection | Four devices for wandering detection | ✓ |
| Hao et al. [38] | 2017 | Alzheimer’s | Indoor Positioning Sensors | Pattern Detection | Detect indoor movement patterns of AD | ✓ |
| Thorpe et al. [39] | 2016 | Dementia | Wearables, Applications | User-centered AAL | User-centered approach to develop AAL | ✓ |
| Ellis et al. [40] | 2015 | Fall Detection, Parkinson’s | Wearables, Applications | GAIT Analysis | GAIT analysis from two devices | ✓ |
| Weiss et al. [41] | 2019 | Parkinson’s | Wearables | Movement Analysis | Movement analysis (turn and sit) for PD | ✓ |
| Mc Ardle et al. [42] | 2018 | Alzheimer’s | Wearables | GAIT Analysis | GAIT analysis, acceptability, and feasibility | ✓ |
| Silva et al. [43] | 2017 | Alzheimer’s | Wearable Cameras | Intervention | Camera intervention for improvement | ✓ |
| Costa et al. [44] | 2016 | Alzheimer’s | Wearables | Fall Prediction, Assessment | Fall prediction and AD assessment | ✓ |
| Zhou et al. [45] | 2016 | Alzheimer’s | Wearables | Assessment | Motor-cognitive assessment | ✓ |
| Hsu et al. [46] | 2014 | Alzheimer’s | Wearables | Assessment | Indicators for AD assessment | ✓ |
| Abbate et al. [47] | 2014 | Alzheimer’s, Fall Detection | Wearables, Indoor Positioning | Fall Detection, Monitoring | Long-term monitoring and fall detection in nursing homes | ✓ |
| Woodberry et al. [48] | 2015 | Alzheimer’s | Wearable Cameras | Intervention | External memory aid to promote recall of episodic memories | ✓ |
| Leuty et al. [49] | 2013 | Dementia | Wearables | Intervention | Promote engagement, art creation | ✓ |
| Lancioni et al. [50] | 2013 | Alzheimer’s | Indoor Positioning | AAL, Intervention | Indoor activity and travel support | ✓ |
| Aloulou et al. [51] | 2013 | Dementia | Indoor Positioning | AAL | AAL in nursing homes | ✓ |
| Pot et al. [52] | 2012 | Alzheimer’s | Indoor Positioning | Monitoring | GPS for indoor tracking | ✓ |
| Jelcic et al. [53] | 2014 | Alzheimer’s | Telemedicine | Assessment, Intervention | Lexical-semantic stimulation through Telecommunication | ✓ |
| Case Study | Year | Study Duration | Participants | Outcome Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algase et al. [37] | 2018 | 1 Week | 178 (mean age 85.3 y/o) | Acceptance, Accuracy of Wandering Detection |
| Hao et al. [38] | 2017 | 6 Months | 20 | Accuracy of Assessment by Pattern Detection |
| Thorpe et al. [39] | 2016 | 7 Days | 10 (61–73 y/o) | Acceptance, Feedback |
| Ellis et al. [40] | 2015 | 1–2 h | 24: 12 PD & 12 HC (40–85 y/o) | Accuracy of Assessment by GAIT Analysis |
| Weiss et al. [41] | 2019 | Less than 1 h | 96 PD | Accuracy of PD Assessment by Movement Analysis |
| Mc Ardle et al. [42] | 2018 | 7 Days | 20 (55–80 y/o) | Acceptance, Accuracy of Assessment by GAIT Analysis |
| Silva et al. [43] | 2017 | 6-Week Trial, 6-Month Follow-up | 51 AD (60–80 y/o) | Cognitive State Improvement through Intervention |
| Costa et al. [44] | 2016 | 2–3 h | 72: 36 AD (76 ± 7 y/o), 36 HC (70 ± 8 y/o) | Accuracy of Fall Detection and Assessment |
| Zhou et al. [45] | 2016 | 5 Min Session | 30: 11 HC, 10 aMCI, 9 AD (71–93 y/o) | Reliability, Accuracy of Motor-cognitive Assessment |
| Hsu et al. [46] | 2014 | A Few h | 71: 21 AD & 50 HC | Accuracy of Assessment |
| Abbate et al. [47] | 2014 | 2–4 Days | 4 AD (75–92 y/o). | Acceptance, User Satisfaction, Accuracy of Fall Detection |
| Woodberry et al. [48] | 2015 | 3.5 Months | 6 (64–84 y/o) | User Satisfaction, Cognitive State Improvement through Intervention |
| Leuty et al. [49] | 2013 | Five 1-Hour Trials | 6 (mean age 89.2 y/o) | User Satisfaction, Feedback |
| Lancioni et al. [50] | 2013 | Ten 1-Minute Trials | 6 (75–89 y/o) | Cognitive State Improvement through Intervention |
| Aloulou et al. [51] | 2013 | 14 Months | 10: 8 AD, 2 Carers | Feedback, Accuracy of Indoor Positioning |
| Pot et al. [52] | 2012 | 3 Months | 56 Patient-Carer pairs | User Satisfaction, Acceptance, Feedback, Accuracy of Indoor Positioning |
| Jelcic et al. [53] | 2014 | 3 Months | 27 | Cognitive State Improvement through Intervention, Accuracy of Assessment |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stavropoulos, T.G.; Papastergiou, A.; Mpaltadoros, L.; Nikolopoulos, S.; Kompatsiaris, I. IoT Wearable Sensors and Devices in Elderly Care: A Literature Review. Sensors 2020, 20, 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102826
Stavropoulos TG, Papastergiou A, Mpaltadoros L, Nikolopoulos S, Kompatsiaris I. IoT Wearable Sensors and Devices in Elderly Care: A Literature Review. Sensors. 2020; 20(10):2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102826
Chicago/Turabian StyleStavropoulos, Thanos G., Asterios Papastergiou, Lampros Mpaltadoros, Spiros Nikolopoulos, and Ioannis Kompatsiaris. 2020. "IoT Wearable Sensors and Devices in Elderly Care: A Literature Review" Sensors 20, no. 10: 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102826
APA StyleStavropoulos, T. G., Papastergiou, A., Mpaltadoros, L., Nikolopoulos, S., & Kompatsiaris, I. (2020). IoT Wearable Sensors and Devices in Elderly Care: A Literature Review. Sensors, 20(10), 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20102826