Catalytic Gold Deposition for Ultrasensitive Optical Immunosensing of Prostate Specific Antigen
Abstract
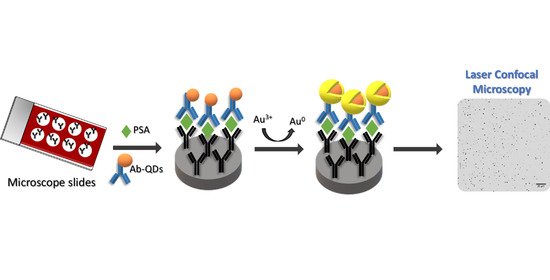
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.1.1. Reagents
2.1.2. Instrumentation
2.2. Procedures
2.2.1. Synthesis of Cysteine-Capped Mn-ZnS QDs and Ligand Exchange Process
2.2.2. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles
2.2.3. Bioconjugation Reactions
2.2.4. Sandwich Type Immunoassay Format
2.2.5. Quantitative Image Processing of Confocal Microscopy Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Gold Deposition on the Surface of the Mn-ZnS QDs and AuNPS Acting as Catalytic Seeds
3.2. Optimization of the QD-Size Amplification Procedure
3.3. Confocal Microscopy Measurement of the Gold Amplification for Development of a PSA Immunoassay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, R.; Wu, P.; Yang, L.; Hou, X.; Lv, Y. Inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry-based immunoassay: A review. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2013, 33, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Jin, M.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, P.; She, Y.; Jin, F.; Shao, H.; et al. A competitive bio-barcode amplification immunoassay for small molecules based on nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, L.; Turemis, M.; Marini, B.; Ippodrino, R.; Giardi, M.T. Better together: Strategies based on magnetic particles and quantum dots for improved biosensing. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Cui, Y.; Chen, G. Nanoparticle-based immunoassays in the biomedical field. Analyst 2013, 138, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y.; Wu, L.; Hou, X.; Lv, Y. Highly Sensitive Immunoassay Based on Immunogold−Silver Amplification and Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometric Detection. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2330–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Jiang, B.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, T. Semiconductor quantum dots in tumor research. J. Lumin. 2019, 209, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfézou, M.; Turner, A.P.; Merkoçi, A. Cancer detection using nanoparticle-based sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2606–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zheng, J.; Yang, R.; Cai, H.; Qi, P.; Qing, Z.; Yan, Q.; Qiu, L.; Tan, W.; Yang, R. Human serum albumin as an intrinsic signal amplification amplifier for ultrasensitive assays of the prostate-specific antigen in human plasma. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 1843–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirkin, C.A.; Elghanian, R.; Thomas, A.D.; Stoeva, S.I.; Lee, J.-S.; Smith, N.D.; Schaeffer, A.J.; Klocker, H.; Horninger, W.; Bartsch, G.; et al. Nanoparticle-based bio-barcode assay redefines "undetectable" PSA and biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18437–18442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.-F.; Hung, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Chen, R.-C.; Su, L.-C.; Lai, C.-S.; Chou, C. Discrimination of breast cancer by measuring prostate-specific antigen levels in women’s serum. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5324–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, W.; Gao, Y. silver enhancement of gold nanoparticles for biosensing: From qualitative to quantitative. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2013, 49, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenzl, C.; Hirsch, T.; Baeumner, A.J. Nanomaterials as versatile tools for signal amplification in (bio)analytical applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Huda, S.; Kilpatrick, P.K.; Velev, O.D. Characterization and optimization of gold immunoassays. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 3810–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, L.Y.T.; Fischer, H.C.; Perrault, S.D.; Chan, W.C.W. Visualizing quantum dots in biological samples using silver staining. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4560–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, A.M.; Sindhwani, S.; Wilhelm, S.; Kingston, B.R.; Lee, D.S.W.; Gommerman, J.; Chan, W.C.W. Three-dimensional imaging of transparent tissues via metal nanoparticle labeling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9961–9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cortes, M.; Encinar, J.R.; Costa-Fernandez, J.M.; Sanz-Medel, A. Highly sensitive nanoparticle-based immunoassays with elemental detection: Application to prostate-specific antigen quantification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 85, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Deng, D.; Liu, R.; Lv, Y. Single nanoparticle analysis by ICP-MS: A potential tool for bioassay. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhwani, S.; Syed, A.M.; Wilhelm, S.; Chan, W.C.W. Exploring passive clearing for 3D optical imaging of nanoparticles in intact tissues. Bioconjugate Chem. 2016, 28, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Z. Rapid intracellular growth of gold nanostructures assisted by functionalized graphene oxide and its application for surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10338–10344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cortes, M.; Sotelo-Gonzalez, E.; Fernández-Argüelles, M.T.; Encinar, J.R.; Costa-Fernandez, J.M.; Sanz-Medel, A. Capping of Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots with DHLA for their stabilization in aqueous media: Determination of the nanoparticle number concentration and surface ligand density. Langmuir 2017, 33, 6333–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, A.R.; Goldman, E.R.; Mattoussi, H. Capping of CdSe—ZnS quantum dots with DHLA and subsequent conjugation with proteins. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frens, G.; Turkevic, J.; Hillier, J. Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in monodisperse gols suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.; Metwalli, E.; Yao, Y.; Schwartzkopf, M.; Yu, S.; Roth, S.V.; Müller-Buschbaum, P.; Paul, A. Templating growth of gold nanostructures with a CdSe quantum dot array. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9703–9714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danscher, G.; Stoltenberg, M. Silver enhancement of quantum dots resulting from (1) metabolism of toxic metals in animals and humans, (2) In Vivo, In Vitro and immersion created zinc–sulphur/zinc–selenium nanocrystals, (3) metal ions liberated from metal implants and particles. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 2006, 41, 57–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Daniel, W.L.; Mirkin, C.A. Microarray-based multiplexed scanometric immunoassay for protein cancer markers using gold nanoparticle probes. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9183–9187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weizmann, Y.; Patolsky, F.; Willner, I. Amplified detection of DNA and analysis of single-base mismatches by the catalyzed deposition of gold on Au-nanoparticles. Analyst 2001, 126, 1502–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cortés, M.; Fernández-Argüelles, M.T.; Costa-Fernandez, J.M.; Sanz-Medel, A. Sensitive prostate specific antigen quantification using dihydrolipoic acid surface-functionalized phosphorescent quantum dots. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 987, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Yin, H.; Xu, L.; Wu, X.; Kuang, H.; Wang, L.; Xu, C. Ultrasensitive aptamer-based SERS detection of PSAs by heterogeneous satellite nanoassemblie. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9737–9740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, W. Cascade signal amplification based on copper nanoparticle-reported rolling circle amplification for ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of the prostate cancer biomarker. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stowell, L.I.; Sharman, L.E.; Hamel, K. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for prostate-specific antigen. Forensic Sci. Int. 1991, 50, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, J.; Lv, Z.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, B. Simultaneous determination of free and total prostate-specific antigen by a magnetic particle-based time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2017, 31, e22137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, P.; Khoshsafar, H.; Ahar, M.J.; Arduini, F.; Afkhami, A.; Bagheri, H. Colorimetric immunosensor for determination of prostate specific antigen using surface plasmon resonance band of colloidal triangular shape gold nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 222, 117218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Javadi, A.; Li, H.; Gong, S. Ultrasensitive immunosensor for the detection of cancer biomarker based on graphene sheet. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, M.; Kong, R.-M.; Zheng, Y.; Qu, F. Graphene oxide quantum dots@silver core–shell nanocrystals as turn-on fluorescent nanoprobe for ultrasensitive detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 74, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, Q. Biosensors and bioelectronics on smartphone for portable biochemical detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 75, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Analytical Label | Amplification Step | Detection Technique | Biosensor Format | LOD pg·mL−1 | Dynamic Range | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRP | Enzymatic | Absorbance | Sandwich immunosensor | 400 | 1–50 ng·mL−1 | [30] |
| Eu, Sm, and magnetic beads | - | Time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay | Homogeneous sandwich immunosensor | 50 | 0.5–100 ng·mL−1 | [31] |
| Mn-ZnS QDs | Nanoparticle-enhanced sensitivity | Phosphorescence | Sandwich immunosensor | 17 | 0.05–240 ng·mL−1 | [27] |
| AuNPs | Nanoparticle-enhanced sensitivity | Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) | Colorimetric immunosensor | 9 | 0.01–20 ng·mL−1 | [32] |
| HRP | Enzyme | Amperometric | Sandwich immunosensor | 1 | 0.002–10 ng·mL−1 | [33] |
| Graphene oxide QD-Ag core-shell and magnetic beads | Nanoparticle-enhanced sensitivity | Fluorescence | Sandwich immunosensor | 0.3 | 0.001–20 ng·mL−1 | [34] |
| Au@AgNPs | Nanoparticle enhanced sensitivity | Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) | Aptasensor | 2 × 10−4 | 0.3–16 pg·mL−1 | [28] |
| AuNPs and CuNPs | Rolling circle amplification and cascade signal amplification | Voltamperometric | Aptasensor | 2 × 10−5 | 0.05–500 pg·mL−1 | [29] |
| Gold-amplified Mn-ZnS QDs | Catalytic gold deposition | ICP-MS (Au) | Sandwich immunosensor | 26 × 10−6 | 1 pg–10 ng·mL−1 | [16] |
| Gold-amplified Mn-ZnS QDs | Catalytic gold deposition | Reflection confocal microscopy | Sandwich immunosensor | 3.5 × 10−3 | 0.01–100 pg·mL−1 | This work |
| Theoretical PSA Concentration | Experimental PSA Concentration | % Recovery |
|---|---|---|
| 5 pg·mL−1 | 5.3 ± 0.4 pg·mL−1 | 105% |
| 10 pg·mL−1 | 10.3 ± 0.2 pg·mL−1 | 103% |
| 20 pg·mL−1 | 18.6 ± 0.8 pg·mL−1 | 93% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cid-Barrio, L.; Ruiz Encinar, J.; Costa-Fernández, J.M. Catalytic Gold Deposition for Ultrasensitive Optical Immunosensing of Prostate Specific Antigen. Sensors 2020, 20, 5287. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185287
Cid-Barrio L, Ruiz Encinar J, Costa-Fernández JM. Catalytic Gold Deposition for Ultrasensitive Optical Immunosensing of Prostate Specific Antigen. Sensors. 2020; 20(18):5287. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185287
Chicago/Turabian StyleCid-Barrio, Laura, Jorge Ruiz Encinar, and José Manuel Costa-Fernández. 2020. "Catalytic Gold Deposition for Ultrasensitive Optical Immunosensing of Prostate Specific Antigen" Sensors 20, no. 18: 5287. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185287
APA StyleCid-Barrio, L., Ruiz Encinar, J., & Costa-Fernández, J. M. (2020). Catalytic Gold Deposition for Ultrasensitive Optical Immunosensing of Prostate Specific Antigen. Sensors, 20(18), 5287. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20185287