GSK5182, 4-Hydroxytamoxifen Analog, a New Potential Therapeutic Drug for Osteoarthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
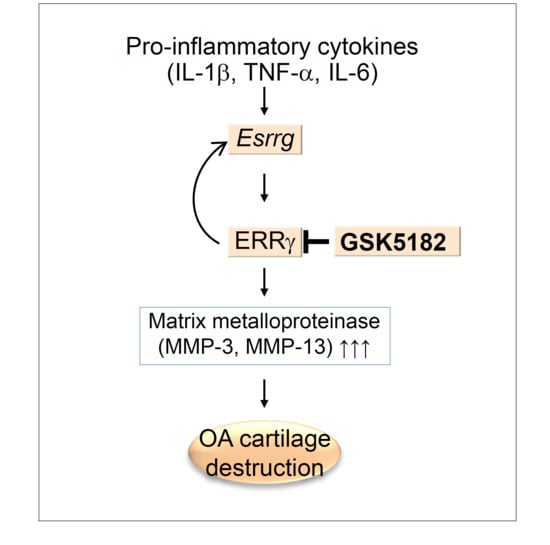
2.1. ERRγ Is Upregulated in Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Exposed Chondrocytes
2.2. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Increased ERRγ Protein, and ERRγ Overexpression Caused Upregulation of MMP Expression in Articular Chondrocytes
2.3. The Ectopic Expression or Genetic Ablation of ERRγ in the Mice
2.4. Inhibition of ERRγ by GSK5182 Attenuates Experimental OA Pathogenesis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Laboratory Ware
4.2. Experimental OA in Mice
4.3. Primary Culture of Articular Chondrocytes, Adenoviruses, Infection of Chondrocytes, and IA Injection
4.4. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Histology
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhen, G.; Wen, C.; Jia, X.; Li, Y.; Crane, J.L.; Mears, S.C.; Askin, F.B.; Frassica, F.J.; Chang, W.; Yao, J.; et al. Inhibition of TGF-β signaling in mesenchymal stem cells of subchondral bone attenuates osteoarthritis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latourte, A.; Cherifi, C.; Maillet, J.; Ea, H.K.; Bouaziz, W.; Funck-Brentano, T.; Cohen-Solal, M.; Hay, E.; Richette, P. Systemic inhibition of IL-6/Stat3 signalling protects against experimental osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, M.B.; Otero, M. Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belluzzi, E.; El Hadi, H.; Granzotto, M.; Rossato, M.; Ramonda, R.; Macchi, V.; De Caro, R.; Vettor, R.; Favero, M. Systemic and Local Adipose Tissue in Knee Osteoarthritis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 1971–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeser, R.F.; Goldring, S.R.; Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, W.S.; Lee, G.; Song, W.H.; Koh, J.T.; Yang, J.; Kwak, J.S.; Kim, H.E.; Kim, S.K.; Son, Y.O.; Nam, H.; et al. The CH25H-CYP7B1-RORalpha axis of cholesterol metabolism regulates osteoarthritis. Nature 2019, 566, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.O.; Park, S.; Kwak, J.S.; Won, Y.; Choi, W.S.; Rhee, J.; Chun, C.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, D.K.; Choi, H.S.; et al. Estrogen-related receptor gamma causes osteoarthritis by upregulating extracellular matrix-degrading enzymes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bian, Q.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, S.F.; Li, Y.P. Osteoarthritis: Genetic factors, animal models, mechanisms, and therapies. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 74–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felson, D.T.; Lawrence, R.C.; Dieppe, P.A.; Hirsch, R.; Helmick, C.G.; Jordan, J.M.; Kington, R.S.; Lane, N.E.; Nevitt, M.C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Osteoarthritis: New insights. Part 1: The disease and its risk factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 133, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagojevic, M.; Jinks, C.; Jeffery, A.; Jordan, K.P. Risk factors for onset of osteoarthritis of the knee in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troeberg, L.; Nagase, H. Proteases involved in cartilage matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1824, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blom, A.B.; van Lent, P.L.; Libregts, S.; Holthuysen, A.E.; van der Kraan, P.M.; van Rooijen, N.; van den Berg, W.B. Crucial role of macrophages in matrix metalloproteinase-mediated cartilage destruction during experimental osteoarthritis: Involvement of matrix metalloproteinase 3. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, C.B.; Barai, A.; Burkhardt, D.; Smith, S.M.; Fosang, A.J.; Werb, Z.; Shah, M.; Thompson, E.W. Matrix metalloproteinase 13-deficient mice are resistant to osteoarthritic cartilage erosion but not chondrocyte hypertrophy or osteophyte development. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 3723–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasson, S.S.; Askew, R.; Sheppard, B.; Carito, B.; Blanchet, T.; Ma, H.L.; Flannery, C.R.; Peluso, D.; Kanki, K.; Yang, Z.; et al. Deletion of active ADAMTS5 prevents cartilage degradation in a murine model of osteoarthritis. Nature 2005, 434, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, M.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Lajeunesse, D.; Pelletier, J.P.; Fahmi, H. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nature reviews. Rheumatology 2011, 7, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Abu-Amer, Y.; O’Keefe, R.J.; McAlinden, A. Inflammation and epigenetic regulation in osteoarthritis. Connect. Tissue Res. 2017, 58, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.Y.; Ahmad, N.; Haqqi, T.M. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Kim, J.; Ryu, J.H.; Oh, H.; Chun, C.H.; Kim, B.J.; Min, B.H.; Chun, J.S. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha is a catabolic regulator of osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ryu, J.H.; Oh, H.; Jeon, J.; Kwak, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.A.; Chun, C.H.; Chun, J.S. NAMPT (visfatin), a direct target of hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha, is an essential catabolic regulator of osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeon, J.; Shin, M.; Won, Y.; Lee, M.; Kwak, J.S.; Lee, G.; Rhee, J.; Ryu, J.H.; Chun, C.H.; et al. Regulation of the catabolic cascade in osteoarthritis by the zinc-ZIP8-MTF1 axis. Cell 2014, 156, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giguère, V. To ERR in the estrogen pathway. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 13, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, A.M.; Giguère, V. The NR3B subgroup: An ovERRview. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 2007, 5, e009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deblois, G.; Giguère, V. Functional and physiological genomics of estrogen-related receptors (ERRs) in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Misra, J.; Kim, D.K.; Choi, H.S. ERRγ: A Junior Orphan with a Senior Role in Metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggins, R.B.; Lan, J.P.; Zhu, Y.; Klimach, U.; Zwart, A.; Cavalli, L.R.; Haddad, B.R.; Chen, L.; Gong, T.; Xuan, J.; et al. ERRgamma mediates tamoxifen resistance in novel models of invasive lobular breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8908–8917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.B.; Park, J.H.; Kim, D.K.; Hwang, J.H.; Oh, S.; Park, S.B.; Shong, M.; Lee, I.K.; Choi, H.S. Transcriptional corepressor SMILE recruits SIRT1 to inhibit nuclear receptor estrogen receptor-related receptor gamma transactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 28762–28774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chow, Y.Y.; Chin, K.Y. The Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 8293921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryu, J.H.; Yang, S.; Shin, Y.; Rhee, J.; Chun, C.H.; Chun, J.S. Interleukin-6 plays an essential role in hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha-induced experimental osteoarthritic cartilage destruction in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2732–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, J.E.; Santos, M.J.; Canhão, H.; Choy, E. Interleukin-6 as a key player in systemic inflammation and joint destruction. Autoimmun. Rev. 2009, 8, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Lee, E.J.; Park, W.D.; Kim, J.B.; Kim, E.O.; Choi, S.W. Anti-inflammatory and anti-osteoarthritis effects of fermented Achyranthes japonica Nakai. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawyer, T.; Wingerter, S.; Tucci, M.; Benghuzzi, H. Cellular effects of catabolic inflammatory cytokines on chondrocytes—Biomed 2011. Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 47, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.O.; Kim, H.E.; Choi, W.S.; Chun, C.H.; Chun, J.S. RNA-binding protein ZFP36L1 regulates osteoarthritis by modulating members of the heat shock protein 70 family. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardelli, M.; Aubin, J.E. ERRgamma is not required for skeletal development but is a RUNX2-dependent negative regulator of postnatal bone formation in male mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.K.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, K.S.; Park, S.H.; Kim, Y.D.; Koh, M.; Shin, M.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Inverse agonist of estrogen-related receptor gamma controls Salmonella typhimurium infection by modulating host iron homeostasis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, C.B.; Hunter, D.J. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis: From mouse models to clinical trials. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2013, 9, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklatvala, J. Tumour necrosis factor alpha stimulates resorption and inhibits synthesis of proteoglycan in cartilage. Nature 1986, 322, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadjichristos, C.; Ghayor, C.; Kypriotou, M.; Martin, G.; Renard, E.; Ala-Kokko, L.; Suske, G.; de Crombrugghe, B.; Pujol, J.P.; Galéra, P. Sp1 and Sp3 transcription factors mediate interleukin-1 beta down-regulation of human type II collagen gene expression in articular chondrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 39762–39772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stöve, J.; Huch, K.; Günther, K.P.; Scharf, H.P. Interleukin-1beta induces different gene expression of stromelysin, aggrecan and tumor-necrosis-factor-stimulated gene 6 in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes In Vitro. Pathobiology 2000, 68, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, V.; Peeters-Joris, C.; Vaes, G. Modulation by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha of production of collagenase, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases and collagen types in differentiated and dedifferentiated articular chondrocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1990, 1052, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboul, P.; Pelletier, J.P.; Tardif, G.; Cloutier, J.M.; Martel-Pelletier, J. The new collagenase, collagenase-3, is expressed and synthesized by human chondrocytes but not by synoviocytes. A role in osteoarthritis. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 2011–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, S.; Satoh, T.; Chiba, J.; Ju, C.; Inoue, K.; Kagawa, J. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 levels in serum and synovial fluid of patients with osteoarthritis. Cytokines Cell. Mol. Ther. 2000, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, S.; Ma, C.; Ma, S.; Chen, G.; Yuan, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, H. Estrogen-Related Receptor γ Induces Angiogenesis and Extracellular Matrix Degradation of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis in Rats. Front. Pharmacother. 2019, 10, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, Y.Y.; Bae, I.H.; Kim, D.K.; Koo, S.H.; Choi, H.R.; Kim, S.H.; Franceschi, R.T.; Koh, J.T.; et al. The orphan nuclear receptor estrogen receptor-related receptor gamma negatively regulates BMP2-induced osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 14211–14218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonnelye, E.; Reboul, P.; Duval, N.; Cardelli, M.; Aubin, J.E. Estrogen receptor-related receptor alpha regulation by interleukin-1beta in prostaglandin E(2)- and cAMP-dependent pathways in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2374–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coward, P.; Lee, D.; Hull, M.V.; Lehmann, J.M. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen binds to and deactivates the estrogen-related receptor gamma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8880–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chao, E.Y.; Collins, J.L.; Gaillard, S.; Miller, A.B.; Wang, L.; Orband-Miller, L.A.; Nolte, R.T.; McDonnell, D.P.; Willson, T.M.; Zuercher, W.J. Structure-guided synthesis of tamoxifen analogs with improved selectivity for the orphan ERRgamma. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, Y.K.; Do, J.Y.; Choi, Y.K.; Ha, C.M.; Lee, S.J.; Jeon, J.H.; Lee, W.K.; Choi, H.S.; Park, K.G.; et al. Estrogen-Related Receptor γ Plays a Key Role in Vascular Calcification Through the Upregulation of BMP2 Expression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 2384–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.K.; Ryu, D.; Koh, M.; Lee, M.W.; Lim, D.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Cho, W.J.; Lee, C.H.; Park, S.B.; et al. Orphan nuclear receptor estrogen-related receptor γ (ERRγ) is key regulator of hepatic gluconeogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 21628–21639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, Y.K.; Byun, J.K.; Kim, M.K.; Kang, Y.N.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.; Jang, B.K.; Park, K.G. Estrogen-related receptor γ is upregulated in liver cancer and its inhibition suppresses liver cancer cell proliferation via induction of p21 and p27. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, M.J.; Gujra, S.; Whitworth, T.; Tobias, J.H. Tamoxifen stimulates cancellous bone formation in long bones of female mice. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryu, J.H.; Shin, Y.; Huh, Y.H.; Yang, S.; Chun, C.H.; Chun, J.S. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha regulates Fas-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis during osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, H.; Chun, C.H.; Chun, J.S. Dkk-1 expression in chondrocytes inhibits experimental osteoarthritic cartilage destruction in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2568–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosset, M.; Berenbaum, F.; Thirion, S.; Jacques, C. Primary culture and phenotyping of murine chondrocytes. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasson, S.S.; Chambers, M.G.; Van Den Berg, W.B.; Little, C.B. The OARSI histopathology initiative—Recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the mouse. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18 (Suppl. 3), S17–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Genes | Strand | Primer Sequences | Size (bp) | AT (°C) | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADAMTS5 | S AS | 5′-GCCATTGTAATAACCCTGCACC-3′ 5′-TCAGTCCCATCCGTAACCTTTG-3′ | 292 | 58 | Mouse |
| Esrrg | S AS | 5′-AAGATCGACACATTGATTCCAGC-3′ 5′-GCTTCACATGATGCAACCCC-3′ | 350 | 64 | Mouse |
| GAPDH | S AS | 5′-TCACTGCCACCCAGAAGAC-3′ 5′-TGTAGGCCATGAGGTCCAC-3′ | 450 | 58 | Mouse |
| MMP-3 | S AS | 5′-AGGGATGATGATGCTGGTATGG-3′ 5′-CCATGTTCTCCAACTGCAAAGG-3′ | 434 | 58 | Mouse |
| MMP-12 | S AS | 5′-CCCAGAGGTCAAGATGGATG-3′ 5′-GGCTCCATAGAGGGACTGAA-3′ | 482 | 60 | Mouse |
| MMP-13 | S AS | 5′-TGATGGACCTTCTGGTCTTCTGG-3′ 5′-CATCCACATGGTTGGGAAGTTCT-3′ | 473 | 58 | Mouse |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, Y.; Kim, D.; Suminda, G.G.D.; Zhao, X.; Kim, M.; Zhao, Y.; Son, Y.-O. GSK5182, 4-Hydroxytamoxifen Analog, a New Potential Therapeutic Drug for Osteoarthritis. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13120429
Min Y, Kim D, Suminda GGD, Zhao X, Kim M, Zhao Y, Son Y-O. GSK5182, 4-Hydroxytamoxifen Analog, a New Potential Therapeutic Drug for Osteoarthritis. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(12):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13120429
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Yunhui, Dahye Kim, Godagama Gamaarachchige Dinesh Suminda, Xiangyu Zhao, Mangeun Kim, Yaping Zhao, and Young-Ok Son. 2020. "GSK5182, 4-Hydroxytamoxifen Analog, a New Potential Therapeutic Drug for Osteoarthritis" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 12: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13120429
APA StyleMin, Y., Kim, D., Suminda, G. G. D., Zhao, X., Kim, M., Zhao, Y., & Son, Y. -O. (2020). GSK5182, 4-Hydroxytamoxifen Analog, a New Potential Therapeutic Drug for Osteoarthritis. Pharmaceuticals, 13(12), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13120429