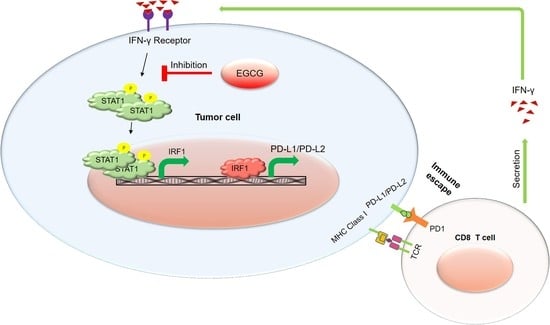
EGCG Inhibits Tumor Growth in Melanoma by Targeting JAK-STAT Signaling and Its Downstream PD-L1/PD-L2-PD1 Axis in Tumors and Enhancing Cytotoxic T-Cell Responses
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. EGCG Inhibits IFN-γ-Induced PD-L1/PD-L2 Expression at the Transcriptional Level in Human Metastatic Melanoma Cells
2.2. EGCG Inhibits IFN-γ-Induced JAK/STAT Signaling in Human Metastatic Melanoma Cells
2.3. EGCG Inhibits B16F10 Mouse Melanoma Growth In Vivo Comparable to Anti-PD-1 Antibody Treatment
2.4. EGCG Inhibits JAK/STAT Signaling in Tumors and Increases Granzyme Expression in CD8+ Cells in the B16F10 Tumor Microenvironment
2.5. CD8+ T Cells Are Required for EGCG-Mediated B16F10 Tumor Suppression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cells and Cell Culture
4.3. In Vitro Cell Treatment
4.4. Flow Cytometry
4.5. Animal Use
4.6. Mouse Tumor Experiment
4.7. Immunofluorescent and Immunohistochemical Staining of Tissues
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. RNA Extraction and Quantitative PCR Analysis
4.10. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamid, O.; Robert, C.; Daud, A.; Hodi, F.S.; Hwu, W.-J.; Kefford, R.; Wolchok, J.D.; Hersey, P.; Joseph, R.; Weber, J.; et al. Safety and Tumor Responses with Lambrolizumab (Anti–PD-1) in Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, Activity, and Immune Correlates of Anti–PD-1 Antibody in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powles, T.; Eder, J.P.; Fine, G.D.; Braiteh, F.S.; Loriot, Y.; Cruz, C.; Bellmunt, J.; Burris, H.A.; Petrylak, D.P.; Teng, S.-L.; et al. MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in metastatic bladder cancer. Nature 2014, 515, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarchoan, M.; Hopkins, A.; Jaffee, E.M. Tumor Mutational Burden and Response Rate to PD-1 Inhibition. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2500–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latchman, Y.E.; Wood, C.R.; Chernova, T.; Chaudhary, D.; Borde, M.; Chernova, I.; Iwai, Y.; Long, A.J.; Brown, J.A.; Nunes, R.; et al. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yearley, J.H.; Gibson, C.; Yu, N.; Moon, C.; Murphy, E.; Juco, J.; Lunceford, J.; Cheng, J.; Chow, L.Q.; Seiwert, T.Y.; et al. PD-L2 Expression in Human Tumors: Relevance to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3158–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miao, Y.R.; Thakkar, K.N.; Qian, J.; Kariolis, M.S.; Huang, W.; Nandagopal, S.; Yang, T.T.C.; Diep, A.N.; Cherf, G.M.; Xu, Y.; et al. Neutralization of PD-L2 is Essential for Overcoming Immune Checkpoint Blockade Resistance in Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4435–4448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanegashima, T.; Togashi, Y.; Azuma, K.; Kawahara, A.; Ideguchi, K.; Sugiyama, D.; Kinoshita, F.; Akiba, J.; Kashiwagi, E.; Takeuchi, A.; et al. Immune Suppression by PD-L2 against Spontaneous and Treatment-Related Antitumor Immunity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4808–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zerdes, I.; Matikas, A.; Bergh, J.; Rassidakis, G.Z.; Foukakis, T. Genetic, Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of the programmed death protein ligand 1 in cancer: Biology and clinical correlations. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4639–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozali, E.N.; Hato, S.V.; Robinson, B.W.; Lake, R.A.; Lesterhuis, W.J. Programmed Death Ligand 2 in Cancer-Induced Immune Suppression. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 656340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Diaz, A.; Shin, D.S.; Moreno, B.H.; Saco, J.; Escuin-Ordinas, H.; Rodriguez, G.A.; Zaretsky, J.M.; Sun, L.; Hugo, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Interferon Receptor Signaling Pathways Regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, F.; Cardoso, A.P.; Goncalves, R.M.; Serre, K.; Oliveira, M.J. Interferon-Gamma at the Crossroads of Tumor Immune Surveillance or Evasion. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valentinuzzi, D.; Simončič, U.; Uršič, K.; Vrankar, M.; Turk, M.; Jeraj, R. Predicting tumour response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy with computational modelling. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 64, 025017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carretero-González, A.; Lora, D.; Ghanem, I.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Castellano, D.; Sepúlveda, J.M.; Lopez-Martin, J.A.; De Velasco, G.; Paz-Ares, L.G. Analysis of response rate with anti-PD1/PDL1 antibodies in advanced solid tumors: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCT). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, e14576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, M.K.; Postow, M.A.; Wolchok, J.D. CTLA-4 and PD-1 Pathway Blockade: Combinations in the Clinic. Front. Oncol. 2015, 4, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamid, O.; Robert, C.; Daud, A.; Hodi, F.S.; Hwu, W.J.; Kefford, R.; Wolchok, J.D.; Hersey, P.; Joseph, R.; Weber, J.S.; et al. Five-year survival outcomes for patients with advanced melanoma treated with pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-001. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, R.N.; Behera, M.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Pakkala, S.; Belani, C.P.; Khuri, F.R.; Ahmed, R.; Ramalingam, S.S. Comparison of the toxicity profile of PD-1 versus PD-L1 inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic analysis of the literature. Cancer 2018, 124, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forester, S.C.; Lambert, J.D. The role of antioxidant versus pro-oxidant effects of green tea polyphenols in cancer prevention. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, K.-J.; Kwon, T.K. Anticancer effects and molecular mechanisms of epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Integr. Med. Res. 2014, 3, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohishi, T.; Goto, S.; Monira, P.; Isemura, M.; Nakamura, Y. Anti-inflammatory Action of Green Tea. Anti-Inflamm. Anti-Allergy Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 15, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, L.Z.; Liu, W.; Luo, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Qu, D.; Dunn, J.H.; Fujita, M. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses melanoma growth by inhibiting inflammasome and IL-1beta secretion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 414, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senggunprai, L.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Prawan, A.; Kukongviriyapan, U. Quercetin and EGCG Exhibit Chemopreventive Effects in Cholangiocarcinoma Cells via Suppression of JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Phyther. Res. 2014, 28, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-G.; Jenabi, J.M.; Liu, X.F.; Reynolds, C.P.; Triche, T.J.; Sorensen, P.H. Inhibition of the Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Receptor by Epigallocatechin Gallate Blocks Proliferation and Induces the Death of Ewing Tumor Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rawangkan, A.; Wongsirisin, P.; Namiki, K.; Iida, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Fujiki, H.; Suganuma, M. Green Tea Catechin Is an Alternative Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor that Inhibits PD-L1 Expression and Lung Tumor Growth. Molecules 2018, 23, 2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, G.Y.; Liao, J.; Kim, K.; Yurkow, E.J.; Yang, C.S. Inhibition of growth and induction of apoptosis in human cancer cell lines by tea polyphenols. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, S.; Hastak, K.; Afaq, F.; Ahmad, N.; Mukhtar, H. Essential role of caspases in epigallocatechin-3-gallate-mediated inhibition of nuclear factor kappaB and induction of apoptosis. Oncogene 2003, 23, 2507–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.J.; Maliakal, P.; Chen, L.; Meng, X.; Bondoc, F.Y.; Prabhu, S.; Lambert, G.; Mohr, S.; Yang, C.S. Pharmacokinetics of tea catechins after ingestion of green tea and (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate by humans. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2002, 11, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.; Wei, S.; Hurt, E.M.; Green, M.D.; Zhao, L.; Vatan, L.; Szeliga, W.; Herbst, R.; Harms, P.W.; Fecher, L.A.; et al. Host expression of PD-L1 determines efficacy of PD-L1 pathway blockade-mediated tumor regression. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basu, A.; Sanchez, K.; Leyva, M.J.; Wu, M.; Betts, N.M.; Aston, C.E.; Lyons, T.J. Green Tea Supplementation Affects Body Weight, Lipids, and Lipid Peroxidation in Obese Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2010, 29, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowko, E. Green Tea Catechins and Sport Performance. In Antioxidants in Sport Nutrition; Lamprecht, M., Ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Webster, D.; Cao, J.; Shao, A. The safety of green tea and green tea extract consumption in adults—Results of a systematic review. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 95, 412–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, P.C.; Ramot, Y.; Malarkey, D.E.; Blackshear, P.; Kissling, G.E.; Travlos, G.; Nyska, A. Fourteen-Week Toxicity Study of Green Tea Extract in Rats and Mice. Toxicol. Pathol. 2010, 38, 1070–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfram, S.; Raederstorff, D.; Preller, M.; Wang, Y.; Teixeira, S.R.; Riegger, C.; Weber, P. Epigallocatechin Gallate Supplementation Alleviates Diabetes in Rodents. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2512–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Lostao, L.; Anel, A.; Pardo, J. How Do Cytotoxic Lymphocytes Kill Cancer Cells? Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 5047–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mellor-Heineke, S.; Villanueva, J.; Jordan, M.B.; Marsh, R.; Zhang, K.; Bleesing, J.J.; Filipovich, A.L.H.; Risma, K.A. Elevated Granzyme B in Cytotoxic Lymphocytes is a Signature of Immune Activation in Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowacki, T.M.; Kuerten, S.; Zhang, W.; Shive, C.L.; Kreher, C.R.; Boehm, B.O.; Lehmann, P.V.; Tary-Lehmann, M. Granzyme B production distinguishes recently activated CD8+ memory cells from resting memory cells. Cell. Immunol. 2007, 247, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larimer, B.M.; Wehrenberg-Klee, E.; Dubois, F.; Mehta, A.; Kalomeris, T.; Flaherty, K.; Boland, G.; Mahmood, U. Granzyme B PET Imaging as a Predictive Biomarker of Immunotherapy Response. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2318–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prizment, A.E.; Vierkant, R.; Smyrk, T.C.; Tillmans, L.S.; Nelson, H.; Lynch, C.F.; Pengo, T.; Thibodeau, S.N.; Church, T.R.; Cerhan, J.R.; et al. Cytotoxic T Cells and Granzyme B Associated with Improved Colorectal Cancer Survival in a Prospective Cohort of Older Women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2017, 26, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goggi, J.L.; Hartimath, S.V.; Xuan, T.Y.; Khanapur, S.; Jieu, B.; Chin, H.X.; Ramasamy, B.; Cheng, P.; Rong, T.J.; Fong, Y.F.; et al. Granzyme B PET Imaging of Combined Chemotherapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Colon Cancer. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2021, 23, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.; Ramesh, A.; Kumar, S.; Nandi, D.; Brouillard, A.; Wells, A.; Pobezinsky, L.; Osborne, B.; Kulkarni, A.A. Granzyme B nanoreporter for early monitoring of tumor response to immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, C.; Levy, D.; Decker, T. JAK-STAT Signaling: From Interferons to Cytokines. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20059–20063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darnell, J.E.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharpe, A.H.; Wherry, E.J.; Ahmed, R.; Freeman, G.J. The function of programmed cell death 1 and its ligands in regulating autoimmunity and infection. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohaegbulam, K.C.; Assal, A.; Lazar-Molnar, E.; Yao, Y.; Zang, X. Human cancer immunotherapy with antibodies to the PD-1 and PD-L1 pathway. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abiko, K.; Matsumura, N.; Hamanishi, J.; Horikawa, N.; Murakami, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Baba, T.; Konishi, I.; Mandai, M. IFN-gamma from lymphocytes induces PD-L1 expression and promotes progression of ovarian cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayers, M.; Lunceford, J.; Nebozhyn, M.; Murphy, E.; Loboda, A.; Kaufman, D.R.; Albright, A.; Cheng, J.D.; Kang, S.P.; Shankaran, V.; et al. IFN-gamma-related mRNA profile predicts clinical response to PD-1 blockade. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2930–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibahara, D.; Tanaka, K.; Iwama, E.; Kubo, N.; Ota, K.; Azuma, K.; Harada, T.; Fujita, J.; Nakanishi, Y.; Okamoto, I. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Regulation of PD-L2 Expression in Oncogene-Driven Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 926–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loke, P.; Allison, J.P. PD-L1 and PD-L2 are differentially regulated by Th1 and Th2 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5336–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Q. Regulation of PD-L1 expression in cancer and clinical implications in immunotherapy. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Pezzani, R.; Redaelli, M.; Zorzan, M.; Imran, M.; Khalil, A.A.; Salehi, B.; Sharopov, F.; Cho, W.C.; Sharifi-Rad, F.; et al. Preclinical Pharmacological Activities of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate in Signaling Pathways: An Update on Cancer. Molecules 2020, 25, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, X.; Deng, C.; Yang, L.; Yan, E.; Guo, T.; Li, Y.; Xu, M.X. Mechanism of the inhibition of the STAT3 signaling pathway by EGCG. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2691–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pae, M.; Ren, Z.; Meydani, M.; Shang, F.; Meydani, S.N.; Wu, D. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Directly Suppresses T Cell Proliferation through Impaired IL-2 Utilization and Cell Cycle Progression. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, J.-Y.; Lee, J.-K.; Jeon, Y.-K.; Kim, C.-W. Exosome derived from epigallocatechin gallate treated breast cancer cells suppresses tumor growth by inhibiting tumor-associated macrophage infiltration and M2 polarization. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Man, G.C.W.; Chan, T.H.; Kwong, J.; Wang, C.C. A prodrug of green tea polyphenol (–)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (Pro-EGCG) serves as a novel angiogenesis inhibitor in endometrial cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 412, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Yan, F.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Ying, L. Green Tea Polyphenol EGCG Attenuates MDSCs-mediated Immunosuppression through Canonical and Non-Canonical Pathways in a 4T1 Murine Breast Cancer Model. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santilli, G.; Piotrowska, I.; Cantilena, S.; Chayka, O.; D’Alicarnasso, M.; Morgenstern, D.A.; Himoudi, N.; Pearson, K.; Anderson, J.; Thrasher, A.J.; et al. Polyphenon E enhances the antitumor immune response in neuroblastoma by inactivating myeloid suppressor cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Cao, R. Angiogenesis inhibited by drinking tea. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 398, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, K.B.; Makey, K.L.; Chinchar, E.; Huang, M.; Sheehan, N.; Vijayakumar, S.; Gu, J.W. EGCG Suppresses Melanoma Tumor Angiogenesis and Growth without Affecting Angiogenesis and VEGF Expression in the Heart and Skeletal Muscles in Mice. J. Cancer Res. Updates 2014, 3, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Uphoff, C.C.; Drexler, H.G. Detecting Mycoplasma Contamination in Cell Cultures by Polymerase Chain Reaction. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 731, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ravindran Menon, D.; Li, Y.; Yamauchi, T.; Osborne, D.G.; Vaddi, P.K.; Wempe, M.F.; Zhai, Z.; Fujita, M. EGCG Inhibits Tumor Growth in Melanoma by Targeting JAK-STAT Signaling and Its Downstream PD-L1/PD-L2-PD1 Axis in Tumors and Enhancing Cytotoxic T-Cell Responses. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111081
Ravindran Menon D, Li Y, Yamauchi T, Osborne DG, Vaddi PK, Wempe MF, Zhai Z, Fujita M. EGCG Inhibits Tumor Growth in Melanoma by Targeting JAK-STAT Signaling and Its Downstream PD-L1/PD-L2-PD1 Axis in Tumors and Enhancing Cytotoxic T-Cell Responses. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(11):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111081
Chicago/Turabian StyleRavindran Menon, Dinoop, Yang Li, Takeshi Yamauchi, Douglas Grant Osborne, Prasanna Kumar Vaddi, Michael F Wempe, Zili Zhai, and Mayumi Fujita. 2021. "EGCG Inhibits Tumor Growth in Melanoma by Targeting JAK-STAT Signaling and Its Downstream PD-L1/PD-L2-PD1 Axis in Tumors and Enhancing Cytotoxic T-Cell Responses" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 11: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111081
APA StyleRavindran Menon, D., Li, Y., Yamauchi, T., Osborne, D. G., Vaddi, P. K., Wempe, M. F., Zhai, Z., & Fujita, M. (2021). EGCG Inhibits Tumor Growth in Melanoma by Targeting JAK-STAT Signaling and Its Downstream PD-L1/PD-L2-PD1 Axis in Tumors and Enhancing Cytotoxic T-Cell Responses. Pharmaceuticals, 14(11), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111081