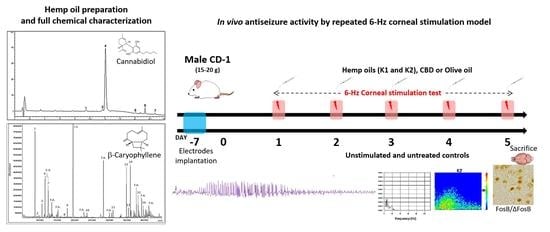
Antiseizure Effects of Fully Characterized Non-Psychoactive Cannabis sativa L. Extracts in the Repeated 6-Hz Corneal Stimulation Test
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Cannabinoids in Hemp Oils
2.2. GC-MS Analysis of Terpenes in Olive Oil Extracts
2.3. Characterization of the Seizures Induced by 6-Hz Corneal Stimulations
2.4. Different Responses to Treatment
2.5. Characterization of the Duration of Ictal ECoG Recordings and Time to Recover from Seizures
2.6. Analysis of the Power Band Spectrum
2.7. FosB/ΔFosB Immunoreactivity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical and Solvents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Preparation of the Olive Oil Extracts
4.4. UHPLC-HRMS Analysis
4.5. HPLC-UV Analysis
4.6. GC-MS Analysis
4.7. Experimental Design
4.8. Electrodes Implatation and v-ECoG Recordings
4.9. Corneal Stimulation Protocol
4.10. Behavioral and ECoG Analysis
4.11. Immunohistochemistry
4.12. Image Analysis
4.13. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (Ed.) Neurological Disorders: Public Health Challenges; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; ISBN 978-92-4-156336-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ngugi, A.K.; Bottomley, C.; Kleinschmidt, I.; Sander, J.W.; Newton, C.R. Estimation of the Burden of Active and Life-Time Epilepsy: A Meta-Analytic Approach: Estimation of the Burden of Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2010, 51, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdulle, A.M.; Abera, S.F.; Abyu, G.Y.; Ahmed, M.B.; Aichour, A.N.; Aichour, I.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Neurological Disorders during 1990–2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 877–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, A.-M.; Marchiò, M.; Bruni, G.; Bernabei, S.M.; Cavalieri, S.; Bondi, M.; Biagini, G. Evaluation of E-Health Applications for Paediatric Patients with Refractory Epilepsy and Maintained on Ketogenic Diet. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, D. WHO-CHOICE Cost-Effectiveness of First-Line Antiepileptic Drug Treatments in the Developing World: A Population-Level Analysis. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, V.; Bialer, M.; Perucca, E. Cannabidiol in the Treatment of Epilepsy: Current Evidence and Perspectives for Further Research. Neuropharmacology 2021, 185, 108442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, R.A.; Whalley, B.J. The Proposed Mechanisms of Action of CBD in Epilepsy. Epileptic Disord. 2020, 22, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senn, L.; Cannazza, G.; Biagini, G. Receptors and Channels Possibly Mediating the Effects of Phytocannabinoids on Seizures and Epilepsy. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.L.; Heblinski, M.; Absalom, N.L.; Hawkins, N.A.; Bowen, M.T.; Benson, M.J.; Zhang, F.; Bahceci, D.; Doohan, P.T.; Chebib, M.; et al. Cannabigerolic Acid, a Major Biosynthetic Precursor Molecule in Cannabis, Exhibits Divergent Effects on Seizures in Mouse Models of Epilepsy. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 4826–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goerl, B.; Watkins, S.; Metcalf, C.; Smith, M.; Beenhakker, M. Cannabidiolic Acid Exhibits Entourage-like Improvements of Anticonvulsant Activity in an Acute Rat Model of Seizures. Epilepsy Res. 2021, 169, 106525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamplona, F.A.; da Silva, L.R.; Coan, A.C. Potential Clinical Benefits of CBD-Rich Cannabis Extracts Over Purified CBD in Treatment-Resistant Epilepsy: Observational Data Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferber, S.G.; Namdar, D.; Hen-Shoval, D.; Eger, G.; Koltai, H.; Shoval, G.; Shbiro, L.; Weller, A. The “Entourage Effect”: Terpenes Coupled with Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Mood Disorders and Anxiety Disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaVigne, J.E.; Hecksel, R.; Keresztes, A.; Streicher, J.M. Cannabis Sativa Terpenes Are Cannabimimetic and Selectively Enhance Cannabinoid Activity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternelli, M.; Brighenti, V.; Anceschi, L.; Poto, M.; Bertelli, D.; Licata, M.; Pellati, F. Innovative Methods for the Preparation of Medical Cannabis Oils with a High Content of Both Cannabinoids and Terpenes. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 186, 113296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.E.; Klein, B.D.; Wolf, H.H.; White, H.S. Pharmacological Characterization of the 6 Hz Psychomotor Seizure Model of Partial Epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2001, 47, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.S. General Principles: Discovery and Preclinical Development of Antiepileptic Drugs. In Antiepileptic Drugs; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bialer, M.; White, H.S. Key Factors in the Discovery and Development of New Antiepileptic Drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, C.; Costa, A.M.; Lucchi, C.; Leo, G.; Brunel, L.; Fehrentz, J.-A.; Martinez, J.; Torsello, A.; Biagini, G. Progressive Seizure Aggravation in the Repeated 6-Hz Corneal Stimulation Model Is Accompanied by Marked Increase in Hippocampal p-ERK1/2 Immunoreactivity in Neurons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lucchi, C.; Costa, A.M.; Giordano, C.; Curia, G.; Piat, M.; Leo, G.; Vinet, J.; Brunel, L.; Fehrentz, J.-A.; Martinez, J.; et al. Involvement of PPARγ in the Anticonvulsant Activity of EP-80317, a Ghrelin Receptor Antagonist. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brighenti, V.; Pellati, F.; Steinbach, M.; Maran, D.; Benvenuti, S. Development of a New Extraction Technique and HPLC Method for the Analysis of Non-Psychoactive Cannabinoids in Fibre-Type Cannabis Sativa L. (Hemp). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 143, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellati, F.; Brighenti, V.; Sperlea, J.; Marchetti, L.; Bertelli, D.; Benvenuti, S. New Methods for the Comprehensive Analysis of Bioactive Compounds in Cannabis Sativa L. (Hemp). Molecules 2018, 23, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iseppi, R.; Brighenti, V.; Licata, M.; Lambertini, A.; Sabia, C.; Messi, P.; Pellati, F.; Benvenuti, S. Chemical Characterization and Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oils from Fibre-Type Cannabis Sativa L. (Hemp). Molecules 2019, 24, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Protti, M.; Brighenti, V.; Battaglia, M.R.; Anceschi, L.; Pellati, F.; Mercolini, L. Cannabinoids from Cannabis Sativa L.: A New Tool Based on HPLC–DAD–MS/MS for a Rational Use in Medicinal Chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brighenti, V.; Marchetti, L.; Anceschi, L.; Protti, M.; Verri, P.; Pollastro, F.; Mercolini, L.; Bertelli, D.; Zanardi, C.; Pellati, F. Separation and Non-Separation Methods for the Analysis of Cannabinoids in Cannabis Sativa L. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 206, 114346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, P.; Futoran, K.; Lewitus, G.M.; Mukha, D.; Benami, M.; Shlomi, T.; Meiri, D. A New ESI-LC/MS Approach for Comprehensive Metabolic Profiling of Phytocannabinoids in Cannabis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, B.F.; ElSohly, M.A. The Botany of Cannabis Sativa L. In The Analytical Chemistry of Cannabis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1–26. ISBN 978-0-12-804646-3. [Google Scholar]
- Appendino, G.; Chianese, G.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Cannabinoids: Occurrence and Medicinal Chemistry. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 1085–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Quispe, C.; Herrera-Bravo, J.; Martorell, M.; Sharopov, F.; Tumer, T.B.; Kurt, B.; Lankatillake, C.; Docea, A.O.; Moreira, A.C.; et al. A Pharmacological Perspective on Plant-Derived Bioactive Molecules for Epilepsy. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 2205–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrelly, A.M.; Vlachou, S.; Grintzalis, K. Efficacy of Phytocannabinoids in Epilepsy Treatment: Novel Approaches and Recent Advances. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina, L.T.S.; Guimarães, A.G.; da Santos, W.B.R.; Oliveira, M.A.; Rabelo, T.K.; Serafini, M.R. Monoterpenes as a Perspective for the Treatment of Seizures: A Systematic Review. Phytomedicine 2021, 81, 153422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, C.C.; de Oliveira, C.V.; Grigoletto, J.; Ribeiro, L.R.; Funck, V.R.; Grauncke, A.C.B.; de Souza, T.L.; Souto, N.S.; Furian, A.F.; Menezes, I.R.A.; et al. Anticonvulsant Activity of β-Caryophyllene against Pentylenetetrazol-Induced Seizures. Epilepsy Behav. 2016, 56, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Viana, G.S.B.; do Vale, T.G.; Silva, C.M.M.; de Matos, F.J.A. Anticonvulsant Activity of Essential Oils and Active Principles from Chemotypes of Lippia Alba (Mill.) N.E. Brown. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 23, 1314–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elisabetsky, E.; Silva Brum, L.F.; Souza, D.O. Anticonvulsant Properties of Linalool in Glutamate-Related Seizure Models. Phytomedicine 1999, 6, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, D.P.; Nóbrega, F.F.F.; Santos, C.C.M.P.; de Almeida, R.N. Anticonvulsant Activity of the Linalool Enantiomers and Racemate: Investigation of Chiral Influence. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1847–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, A.M.; Lucchi, C.; Simonini, C.; Rosal Lustosa, Í.; Biagini, G. Status Epilepticus Dynamics Predicts Latency to Spontaneous Seizures in the Kainic Acid Model. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 54, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.-M.; Lucchi, C.; Malkoç, A.; Rustichelli, C.; Biagini, G. Relationship between Delta Rhythm, Seizure Occurrence and Allopregnanolone Hippocampal Levels in Epileptic Rats Exposed to the Rebound Effect. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Guzman, P.; Inaba, Y.; Biagini, G.; Baldelli, E.; Mollinari, C.; Merlo, D.; Avoli, M. Subiculum Network Excitability Is Increased in a Rodent Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Hippocampus 2006, 16, 843–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antuono, M.; Benini, R.; Biagini, G.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Barbarosie, M.; Tancredi, V.; Avoli, M. Limbic Network Interactions Leading to Hyperexcitability in a Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. J. Neurophysiol. 2002, 87, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antuono, M.; Kawasaki, H.; Palmieri, C.; Curia, G.; Biagini, G.; Avoli, M. Antiepileptic Drugs and Muscarinic Receptor-Dependent Excitation in the Rat Subiculum. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarini-Lopes, W.; Do Val-da Silva, R.A.; da Silva-Júnior, R.M.P.; Silva-Cardoso, G.K.; Leite-Panissi, C.R.A.; Leite, J.P.; Garcia-Cairasco, N. Chronic Cannabidiol (CBD) Administration Induces Anticonvulsant and Antiepileptogenic Effects in a Genetic Model of Epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2021, 119, 107962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socała, K.; Wyska, E.; Szafarz, M.; Nieoczym, D.; Wlaź, P. Acute Effect of Cannabidiol on the Activity of Various Novel Antiepileptic Drugs in the Maximal Electroshock- and 6 Hz-Induced Seizures in Mice: Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Studies. Neuropharmacology 2019, 158, 107733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, B.; van Beelen, T.; Stijl, M.; van Someren, P.; Roessen, M.; van Dijk, J.G. A DC Attenuator Allows Common EEG Equipment to Record Fullband EEG, and Fits Fullband EEG into Standard European Data Format. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2010, 121, 1992–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Compound | Formula | MS (m/z) | MS/MS (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive ion mode | |||
| Cannflavin B | C21H20O6 | 369.1333 | 315.2315 |
| Dehydrocannabifuran-C5 (DCBF) | C21H24O2 | 309.1775 | 239.8728 |
| Epoxycannabigerol | C21H32O3 | 333.2424 | 315.2319 |
| Cannabinodiol (CBND) | C21H26O2 | 311.2006 | 293.1898 |
| Cannabidivarin (CBDV) | C19H26O2 | 287.0060 | 277.2160 |
| Hydroxycannabidiol (OH-CBD) | C21H30O3 | 331.2268 | 313.2160 |
| Cannabidiol-C4 (CBD-C4) | C20H28O2 | 301.2153 | 245.1530 |
| Cannflavin A | C26H28O6 | 437.1959 | 359.2211 |
| Cannabigerol (CBG) | C21H32O2 | 317.2475 | 245.1547 |
| Cannabidiol (CBD) | C21H30O2 | 315.2319 | 245.1547 |
| Cannabidiol monomethyl ether-C5 (CBDM) | C22H32O2 | 329.2474 | 313.1800 |
| Bisnor-cannabielsoin-C1 (CBEO) | C17H22O3 | 275.1635 | 207.1013 |
| Cannabinol (CBN) | C21H26O2 | 311.2006 | 293.1898 |
| Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9-THC) | C21H30O2 | 315.2321 | 245.1547 |
| Cannabichromene (CBC) | C21H30O2 | 315.2321 | 245.1547 |
| Negative ion mode | |||
| Hydroxycannabidiolic acid (OH-CBDA) | C22H30O5 | 373.2028 | 345.2076 |
| Cannabidiolic acid-C4 (CBDA-C4) | C21H28O4 | 343.1932 | 325.1845 |
| Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) | C22H30O4 | 357.2021 | 313.2176 |
| Cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) | C22H32O4 | 359.2228 | 331.2285 |
| Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (Δ9-THCA) | C22H30O4 | 357.2021 | 313.2177 |
| Cannabichromenic acid (CBCA) | C22H30O4 | 357.2021 | 313.2177 |
| Peak Number | tR (min) | Compound | Hemp Oil 1 (K1) | Hemp Oil 2 (K2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11.6 | CBDA | 0.34 ± 0.01 | <LOQ |
| 2 | 13.4 | CBGA | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| 3 | 14.9 | CBG | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 0.20 ± 0.10 |
| 4 | 15.4 | CBD | 4.78 ± 0.23 | 4.24 ± 0.05 |
| 5 | 19.8 | CBN | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.14 ± 0.01 |
| 6 | 21.6 | ∆9-THC | 0.42 ± 0.02 | 0.29 ± 0.01 |
| 7 | 23.6 | ∆9-THCA | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| Peak Number | tR (min) | Compound | Formula | MW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.6 | α-Pinene | C10H16 | 136.23 |
| 2 | 9.3 | Camphene | C10H16 | 136.23 |
| 3 | 10.7 | β-Pinene | C10H16 | 136.23 |
| 4 | 11.5 | β-Myrcene | C10H16 | 136.23 |
| 5 | 12.2 | α-Phellandrene | C10H16 | 136.23 |
| 6 | 12.4 | ∆3-Carene | C10H16 | 136.23 |
| 7 | 12.5 | Limonene | C10H16 | 136.23 |
| 8 | 17.0 | α-Terpinolene | C10H16 | 136.23 |
| 9 | 17.9 | Linalool | C10H18O | 154.25 |
| 10 | 23.3 | p-Cymen-8-ol | C10H14O | 150.22 |
| 11 | 33.4 | Ylangene | C15H2 | 204.35 |
| 12 | 34.9 | β-Caryophyllene | C15H24 | 204.35 |
| 13 | 35.5 | α-Bergamotene | C15H24 | 204.35 |
| 14 | 36.0 | α-Humulene | C15H24 | 204.35 |
| 15 | 38.6 | trans-Nerolidol | C15H26O | 222.37 |
| 16 | 39.8 | Caryophyllene oxide | C15H24O | 220.35 |
| Compound | Hemp Oil 1 (K1) | Hemp Oil 2 (K2) |
|---|---|---|
| α-Pinene | 3.48 ± 0.18 | 11.65 ± 0.98 |
| β-Pinene | <LOQ | <LOQ |
| β-Myrcene | <LOQ | 7.29 ± 0.19 |
| Limonene | <LOQ | 8.99 ± 0.46 |
| Linalool | <LOD | 5.29 ± 0.24 |
| β-Caryophyllene | <LOQ | 26.61 ± 3.00 |
| α-Humulene | <LOQ | 9.74 ± 1.08 |
| trans-Nerolidol | <LOQ | 4.15 ± 0.77 |
| Caryophyllene oxide | <LOQ | 8.25 ± 1.55 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, A.-M.; Senn, L.; Anceschi, L.; Brighenti, V.; Pellati, F.; Biagini, G. Antiseizure Effects of Fully Characterized Non-Psychoactive Cannabis sativa L. Extracts in the Repeated 6-Hz Corneal Stimulation Test. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121259
Costa A-M, Senn L, Anceschi L, Brighenti V, Pellati F, Biagini G. Antiseizure Effects of Fully Characterized Non-Psychoactive Cannabis sativa L. Extracts in the Repeated 6-Hz Corneal Stimulation Test. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(12):1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121259
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Anna-Maria, Lara Senn, Lisa Anceschi, Virginia Brighenti, Federica Pellati, and Giuseppe Biagini. 2021. "Antiseizure Effects of Fully Characterized Non-Psychoactive Cannabis sativa L. Extracts in the Repeated 6-Hz Corneal Stimulation Test" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 12: 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121259
APA StyleCosta, A. -M., Senn, L., Anceschi, L., Brighenti, V., Pellati, F., & Biagini, G. (2021). Antiseizure Effects of Fully Characterized Non-Psychoactive Cannabis sativa L. Extracts in the Repeated 6-Hz Corneal Stimulation Test. Pharmaceuticals, 14(12), 1259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14121259