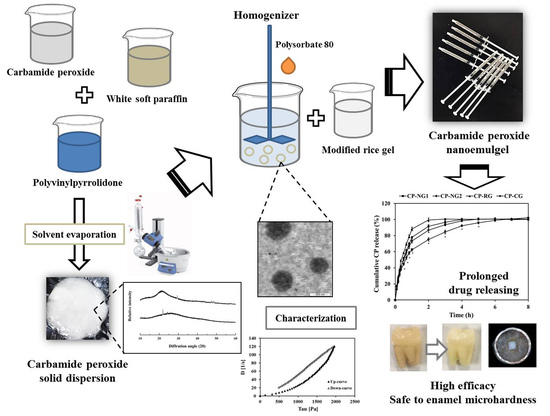
Development of Controlled-Release Carbamide Peroxide Loaded Nanoemulgel for Tooth Bleaching: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of CP Loaded Solid Dispersions (CP-SD)
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of CP Loaded NE (CP-NE)
2.3. Preparation of CP-NG
2.4. Characterization of CP-NG
2.4.1. Outer Appearance, Drug Content, and pH
2.4.2. Rheological Behavior and Viscosity
2.4.3. Adhesion Property
2.5. In Vitro Drug Release and Release Kinetics
2.6. Ex Vivo Bleaching Efficacy
2.7. Effect on Enamel Microhardness
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of CP-SD
3.3. Preparation and Characterization of CP-NE
3.4. Preparation of CP-NG
3.5. Characterization of CP-NG
3.5.1. Outer Appearance and pH
3.5.2. Determination of CP Content
3.5.3. HPLC Analysis
3.5.4. Rheological Behavior and Viscosity
3.5.5. Adhesion Study
3.6. In Vitro Release and Release Kinetics Study
3.7. Tooth Bleaching Efficacy and Enamel Microhardness
3.7.1. Tooth Preparation
3.7.2. Investigation of Bleaching Efficacy
3.7.3. Enamel Microhardness Test
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibiyemi, O.; Taiwo, J. Psychosocial aspect of anterior tooth discoloration among adolescents in igbo-ora, southwestern Nigeria. Ann. Ib. Postgrad. Med. 2011, 9, 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- Masterson, E.E.; Barker, J.C.; Hoeft, K.S.; Hyde, S. Shades of Decay: The Meanings of Tooth Discoloration and Deterioration to Mexican Immigrant Caregivers of Young Children. Hum. Organ. 2014, 73, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bizhang, M.; Seemann, R.; Duve, G.; Römhild, G.; Altenburger, M.J.; Jahn, K.R.; Zimmer, S. Demineralization Effects of 2 Bleaching Procedures on Enamel Surfaces with and Without Post-treatment Fluoride Application. Oper. Dent. 2006, 31, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.B. An overview of vital teeth bleaching. J. Interdiscip. Dent. 2016, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llena, C.; Esteve, I.; Forner, L.; Patil, S. Effect of Hydrogen and Carbamide Peroxide in Bleaching, Enamel Morphology, and Mineral Composition: In vitro Study. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2017, 18, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eimar, H.; Siciliano, R.; Abdallah, M.-N.; Nader, S.A.; Amin, W.M.; Martinez, P.-P.; Celemin, A.; Cerruti, M.; Tamimi, F. Hydrogen peroxide whitens teeth by oxidizing the organic structure. J. Dent. 2012, 40, e25–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ADA Council on Scientific Affairs Tooth Whitening/Bleaching. Treatment Considerations for Dentists and Their Patients; American Dental Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 2009; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz, K. Pretty painful: Why does tooth bleaching hurt? Med. Hypotheses 2010, 74, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oltu, U.; Gurgan, S. Effects of three concentrations of carbamide peroxide on the structure of enamel. J. Oral Rehabilitation 2000, 27, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökay, O.; Müjdeci, A.; Algın, E. Peroxide Penetration into the Pulp from Whitening Strips. J. Endod. 2004, 30, 887–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, N.; Chisci, E.; Giovannoni, R. The Role of Hydrogen Peroxide in Redox-Dependent Signaling: Homeostatic and Pathological Responses in Mammalian Cells. Cells 2018, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fugaro, J.; Nordahl, I.; Fugaro, O.J.; Matis, B.; Mjör, I.A. Pulp reaction to vital bleaching. Oper. Dent. 2004, 29, 363–368. [Google Scholar]
- Da Costa, J.B.; Mazur, R.F. Effects of new formulas of bleaching gel and fluoride application on enamel microhardness: An in vitro study. Oper. Dent. 2007, 32, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvikl, B.; Lussi, A.; Moritz, A.; Flury, S. Enamel Surface Changes After Exposure to Bleaching Gels Containing Carbamide Peroxide or Hydrogen Peroxide. Oper. Dent. 2016, 41, E39–E47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grobler, S.R.; Hayward, R.; Wiese, S.; Moola, M.; Kotze, T.V.W. Spectrophotometric assessment of the effectiveness of Opalescence PF 10%: A 14-month clinical study. J. Dent. 2010, 38, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maran, B.M.; Vochikovski, L.; Hortkoff, D.R.D.A.; Stanislawczuk, R.; Loguercio, A.D.; Reis, A. Tooth sensitivity with a desensitizing-containing at-home bleaching gel—A randomized triple-blind clinical trial. J. Dent. 2018, 72, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzell, E.M.; Pallesen, U.; Thoresen, N.R.; Wallman, C.; Dahl, J.E. Side effects of external tooth bleaching: A multi-centre practice-based prospective study. Br. Dent. J. 2013, 215, E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, J.A.; Marchi, G.M.; Ambrosano, G.M.; Heymann, H.O.; Pimenta, L.A. Microhardness evaluation of in situ vital bleaching on human dental enamel using a novel study design. Dent. Mater. 2005, 21, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonogi, S.; Kaewpinta, A.; Junmahasathien, T.; Yotsawimonwat, S. Effect of rice variety and modification on antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Drug Discov. Ther. 2018, 12, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okonogi, S.; Khongkhunthian, S.; Jaturasitha, S. Development of mucoadhesive buccal films from rice for pharmaceutical delivery systems. Drug Discov. Ther. 2014, 8, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khongkhunthian, S.; Sastraruji, T.; Klayraung, S.; Okonogi, S. Efficacy of anesthetic rice nanogel on pain reduction in human oral cavity. Drug Discov. Ther. 2018, 12, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okonogi, S.; Kaewpinta, A.; Khongkhunthian, S.; Yotsawimonwat, S. Effect of rice variety on the physicochemical properties of the modified rice powders and their derived mucoadhesive gels. Drug Discov. Ther. 2015, 9, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaewpinta, A.; Khongkhunthian, S.; Chaijareenont, P.; Okonogi, S. Preparation and characterization of rice gels containing tooth bleaching agent. Drug Discov. Ther. 2018, 12, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, H.; Gorain, B.; Pandey, M.; Chatterjee, L.A.; Sengupta, P.; Das, A.; Molugulu, N.; Kesharwani, P. Recent Update on Nanoemulgel as Topical Drug Delivery System. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1736–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Kohli, K.; Ali, M. Formulation development of novel in situ nanoemulgel (NEG) of ketoprofen for the treatment of periodontitis. Drug Deliv. 2014, 23, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonogi, S.; Oguchi, T.; Yonemochi, E.; Puttipipatkhachorn, S.; Yamamoto, K. Improved dissolution of ofloxacin via solid dispersion. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 156, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panarin, E.F.; Kalninsh, K.; Pestov, D. Complexation of hydrogen peroxide with polyvinylpyrrolidone: Ab initio calculations. Eur. Polym. J. 2001, 37, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite-Silva, V.R.; Grice, J.E.; Mohammed, Y.; Moghimi, H.R.; Roberts, M.S. The Influence of Emollients on Dermal and Transdermal Drug Delivery. In Percutaneous Penetration Enhancers Drug Penetration into/through the Skin; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 37, pp. 77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ghadially, R.; Halkier-Sorensen, L.; Elias, P.M. Effects of petrolatum on stratum corneum structure and function. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1992, 26, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, C.L.-N.; Park, C.; Lee, B.-J. Current trends and future perspectives of solid dispersions containing poorly water-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, P.; De Marco, I. The Use of Poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone) in the Delivery of Drugs: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodorescu, M.; Bercea, M. Poly(vinylpyrrolidone)—A Versatile Polymer for Biomedical and Beyond Medical Applications. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2015, 54, 923–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholipourmalekabadi, M.; Zhao, S.; Harrison, B.S.; Mozafari, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Oxygen-Generating Biomaterials: A New, Viable Paradigm for Tissue Engineering? Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jog, R.; Burgess, D.J. Pharmaceutical Amorphous Nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.; Mittal, K.L. Handbook of Microemulsion Science and Technology; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 1–846. [Google Scholar]
- Nasr, M.; Younes, H.; Abdel-Rashid, R.S. Formulation and evaluation of cubosomes containing colchicine for transdermal delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurina, D.; Surov, O.V.; Voronova, M.I.; Zakharov, A.G.; Kiselev, M.G. Water Effects on Molecular Adsorption of Poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) on Cellulose Nanocrystals Surfaces: Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Materials 2019, 12, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Modi, J.D.; Patel, J.K. Nanoemulsion-based gel formulation of aceclofenac for topical delivery. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2011, 1, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos Ramos, E.V.; del Pilar Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Milovanovic, B.; Djekic, I.; Miocinovic, J.; Djordjevic, V.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Barba, F.J.; Mörlein, D.; Tomasevic, I. What Is the Color of Milk and Dairy Products and How Is It Measured? Foods 2020, 9, 1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aframian, D.J.; Davidowitz, T.; Benoliel, R. The distribution of oral mucosal pH values in healthy saliva secretors. Oral Dis. 2006, 12, 420–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumria, R.; Nair, A.; Goomber, G.; Gupta, S. Buccal films of prednisolone with enhanced bioavailability. Drug Deliv. 2014, 23, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.H.; Moturi, V.; Lee, Y. Thixotropic property in pharmaceutical formulations. J. Control. Release 2009, 136, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, M.Q. Tooth-bleaching procedures and their controversial effects: A literature review. Saudi Dent. J. 2014, 26, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Housiny, S.; Eldeen, M.A.S.; El-Attar, Y.A.; Salem, H.A.; Attia, D.; Bendas, E.R.; El-Nabarawi, M.A. Fluconazole-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles topical gel for treatment of pityriasis versicolor: Formulation and clinical study. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Kao, W.J. Drug release kinetics and transport mechanisms of non-degradable and degradable polymeric delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, P.; Pyo, Y.-C.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, S.-E.; Kim, J.-K.; Park, J.-S. Overview of the Manufacturing Methods of Solid Dispersion Technology for Improving the Solubility of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs and Application to Anticancer Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa, P.; Lobo, J.M.S. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Sahlin, J.J. A simple equation for the description of solute release. III. Coupling of diffusion and relaxation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 57, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A simple equation for description of solute release I. Fickian and non-fickian release from non-swellable devices in the form of slabs, spheres, cylinders or discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, M.L. Mathematical models of drug release. In Strategies to Modify the Drug Release from Pharmaceutical Systems; Bruschi, M.L., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 63–86. [Google Scholar]
- Türkün, M.; Çelik, E.U.; Aladağ, A.; Gökay, N. One-Year Clinical Evaluation of the Efficacy of a New Daytime At-Home Bleaching Technique. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2010, 22, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.N.; Francci, C.; Medeiros, I.S.; De Godoy Froes Salgado, N.R.; Riehl, H.; Marasca, J.M.; Muench, A. Effect of light irradiation on tooth whitening: Enamel microhardness and color change. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2009, 21, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartak, R.; Menon, S.; Patki, M.; Billack, B.; Patel, K. Ebselen nanoemulgel for the treatment of topical fungal infection. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 148, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Otsuki, M.; Tagami, J. Effect of pH conditioners on tooth bleaching. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2019, 5, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, Y.; Momoi, Y. Bleaching using 30% hydrogen peroxide and sodium hydrogen carbonate. Dent. Mater. J. 2011, 30, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asmawati, A.; Rieuwpassa, I.E. Comparison of enamel hardness after dental bleaching agent application strawberry gel and carbamide peroxide 10%. J. Dentomaxillofacial Sci. 2018, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polydorou, O.; Hellwig, E.; Hahn, P. The Efficacy of Three Different In-office Bleaching Systems and Their Effect on Enamel Microhardness. Oper. Dent. 2008, 33, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunil, C.; Sujana, V.; Choudary, T.M.; Nagesh, B. In vitro action of various carbamide peroxide gel bleaching agents on the microhardness of human enamel. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2012, 3, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhani, R.; Sukmana, B.I.; Suhartono, E. Effect pH on demineralization dental erosion. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2015, 6, 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, A.; Norris, D.F.; Momeni, S.S.; Waldo, B.; Ruby, J.D. The pH of beverages in the United States. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2016, 147, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basting, R.T.; Rodrigues, A.L.; Serra, M.C. The effect of 10% carbamide peroxide, carbopol and/or glycerin on enamel and dentin microhardness. Oper. Dent. 2005, 30, 608–616. [Google Scholar]
- Okonogi, S.; Kaewpinta, A.; Yotsawimonwat, S.; Khongkhunthian, S. Preparation and characterization of lidocaine rice gel for oral application. Drug Discov. Ther. 2015, 9, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tayel, S.A.; El-Nabarawi, M.A.; Tadros, M.I.; Abd-Elsalam, W.H. Promising ion-sensitive in situ ocular nanoemulsion gels of terbinafine hydrochloride: Design, in vitro characterization and in vivo estimation of the ocular irritation and drug pharmacokinetics in the aqueous humor of rabbits. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 443, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimeno, P.; Bousquet, C.; Lassu, N.; Maggio, A.-F.; Civade, C.; Brenier, C.; Lempereur, L. High-performance liquid chromatography method for the determination of hydrogen peroxide present or released in teeth bleaching kits and hair cosmetic products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusayama, T.; Katayori, T.; Nomoto, S. Corrosion of Gold and Amalgam Placed in Contact with Each other. J. Dent. Res. 1963, 42, 1183–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonogi, S.; Kaewpinta, A.; Rades, T.; Müllertz, A.; Yang, M.; Khongkhunthian, S.; Chaijareenont, P. Enhancing Stability and Tooth Bleaching Activity of Carbamide Peroxide by Electrospun Nanofibrous Film. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Sample | Weight Ratio (g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CP | WSP | PVP | |
| CP-SD1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| CP-SD2 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| CP-SD3 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| CP-SD4 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Sample | Weight Ratio (g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP-SD | Polysorbate 80 | Water | |||
| CP | WSP | PVP | |||
| CP-NE1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 1.80 |
| CP-NE2 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 2.29 |
| BL-NE1 | - | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 2.80 |
| BL-NE2 | - | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 3.29 |
| Sample | Particle Size (nm) * | PdI * | Zeta Potential (mV) * | Conductivity (μS/cm) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP-NE1 | 262.87 ± 5.50 c | 0.22 ± 0.04 b | −15.50 ± 1.10 c | 103.2 ± 9.2 c |
| CP-NE2 | 409.10 ± 1.93 a | 0.24 ± 0.05 ab | −20.73 ± 1.02 b | 173.6 ± 2.8 b |
| BL-NE1 | 111.06 ± 5.73 d | 0.27 ± 0.02 ab | −20.67 ± 2.16 b | 153.7 ± 3.4 d |
| BL-NE2 | 330.63 ± 2.65 b | 0.29 ± 0.01 a | −25.20 ± 1.50 a | 202.5 ± 2.1 a |
| Sample | Adhesion * |
|---|---|
| Detachment Length (cm) | |
| CP-NE1 | 23.8 ± 1.0 a |
| CP-NE2 | 20.9 ± 1.5 b |
| CP-CG | 2.4 ± 0.3 c |
| Formulations | Color Parameters * | Transmittance (%) * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆L* | ∆a* | ∆b* | ∆E* | ||
| CP-NG1 | 2.86 ± 0.19 b | −0.36 ± 0.03 b | −0.06 ± 0.05 c | 2.88 ± 0.18 b | 30.32 ± 0.40 d |
| CP-NG2 | 5.25 ± 0.10 a | −0.54 ± 0.04 c | −0.16 ± 0.04 d | 5.28 ± 0.09 a | 16.88 ± 0.26 e |
| CP-RG | 1.37 ± 0.09 c | −0.03 ± 0.05 a | 0.51 ± 0.02 a | 1.46 ± 0.08 c | 85.20 ± 0.79 b |
| CP-CG | 1.50 ± 0.50 c | 0.08 ± 0.06 a | 0.13 ± 0.03 b | 1.51 ± 0.50 c | 84.59 ± 0.66 b |
| Gel base | 1.04 ± 0.21 c | 0.02 ± 0.03 a | 0.55 ± 0.05 a | 1.18 ± 0.19 c | 80.32 ± 0.40 c |
| Control | - | - | - | - | 99.91 ± 0.03 a |
| Formulation | Drug Content (%) | pH * | Viscosity (Pas) * | Adhesion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detachment Length (cm) * | ||||
| CP-NG1 | 99.13 ± 0.37 | 6.83 ± 0.01 b | 93.55 ± 2.50 b | 1.60 ± 0.18 b |
| CP-NG2 | 99.32 ± 0.11 | 6.94 ± 0.01 b | 79.50 ± 1.12 c | 1.72 ± 0.15 b |
| CP-RG | 99.35 ± 0.34 | 5.88 ± 0.02 d | 92.60 ± 1.45 b | 2.00 ± 0.20 a |
| CP-CG | 99.19 ± 0.50 | 6.55 ± 0.01 c | 91.30 ± 1.35 b | 2.09 ± 0.20 a |
| Gel base | - | 7.20 ± 0.02 a | 97.69 ± 1.34 a | 1.50 ± 0.15 b |
| Formulation | Zero-Order | First-Order | Higuchi | Korsmeyer–Peppas | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r2 | k0 | r2 | k1 | r2 | kH | r2 | kKP | n | |
| CP-NG1 | 0.78 | 29.09 | 0.98 | 1.19 | 0.94 | 52.93 | 0.99 | 1.88 | 0.65 |
| CP-NG2 | 0.80 | 16.18 | 0.97 | 0.75 | 0.94 | 44.54 | 0.98 | 1.84 | 0.71 |
| CP-RG | 0.79 | 48.17 | 0.98 | 2.50 | 0.96 | 78.56 | 0.98 | 1.94 | 0.52 |
| CP-CG | 0.78 | 30.77 | 0.99 | 1.47 | 0.94 | 58.14 | 0.99 | 1.91 | 0.62 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okonogi, S.; Kaewpinta, A.; Khongkhunthian, S.; Chaijareenont, P. Development of Controlled-Release Carbamide Peroxide Loaded Nanoemulgel for Tooth Bleaching: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020132
Okonogi S, Kaewpinta A, Khongkhunthian S, Chaijareenont P. Development of Controlled-Release Carbamide Peroxide Loaded Nanoemulgel for Tooth Bleaching: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Studies. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(2):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020132
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkonogi, Siriporn, Adchareeya Kaewpinta, Sakornrat Khongkhunthian, and Pisaisit Chaijareenont. 2021. "Development of Controlled-Release Carbamide Peroxide Loaded Nanoemulgel for Tooth Bleaching: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Studies" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 2: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020132
APA StyleOkonogi, S., Kaewpinta, A., Khongkhunthian, S., & Chaijareenont, P. (2021). Development of Controlled-Release Carbamide Peroxide Loaded Nanoemulgel for Tooth Bleaching: In Vitro and Ex Vivo Studies. Pharmaceuticals, 14(2), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14020132