Mutation-Based Antibiotic Resistance Mechanism in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of S. aureus Isolates
2.2. Characteristics of MRSA Isolates
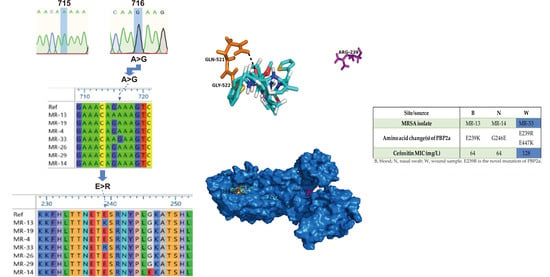
2.3. Genetic Polymorphism of mecA Gene
2.4. Structural Perspective of PBP2a with E239R Mutation on Cefoxitin Resistance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Isolates
4.2. Identification of S. aureus from Clinical Samples
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.4. Molecular Detection of mecA Gene
4.5. Genetic Polymorphism of mecA Gene
4.6. Protein Modeling and Protein-Ligand Docking
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fishovitz, J.; Rojas-Altuve, A.; Otero, L.H.; Dawley, M.; Carrasco-Lopez, C.; Chang, M.; Hermoso, J.A.; Mobashery, S. Disruption of allosteric response as an unprecedented mechanism of resistance to antibiotics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 9814–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, C.C.; Chen, C.C.; Lu, Y.C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Tang, H.J. The clinical significance of silent mutations with respect to ciprofloxacin resistance in MRSA. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gajdács, M. The continuing threat of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aswani, S.A.; Abdul-Aziz, A. The characterization of mecA gene and SCCmec typing in clinical samples of MRSA. Sci. Lett. 2019, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Namvar, A.E.; Bastarahang, S.; Abbasi, N.; Ghehi, G.S.; Farhadbakhtiarian, S.; Arezi, P.; Hosseini, M.; Baravati, S.Z.; Jokar, Z.; Chermahin, S.G. Clinical characteristics of Staphylococcus epidermidis: A systematic review. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control 2014, 9, Doc23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makgotlho, P.E.; Kock, M.M.; Hoosen, A.; Lekalakala, R.; Omar, S.; Dove, M.; Ehlers, M.M. Molecular identification and genotyping of MRSA isolates. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 57, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinho, M.G.; Filipe, S.R.; de Lencastre, H.; Tomasz, A. Complementation of the essential peptidoglycan transpeptidase function of penicillin-binding protein 2 (PBP2) by the drug resistance protein PBP2A in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 6525–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinho, M.G.; de Lencastre, H.; Tomasz, A. An acquired and a native penicillin-binding protein cooperate in building the cell wall of drug-resistant staphylococci. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10886–10891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekizuka, T.; Niwa, H.; Kinoshita, Y.; Uchida-Fujii, E.; Inamine, Y.; Hashino, M.; Kuroda, M. Identification of a mecA/mecC-positive MRSA ST1-t127 isolate from a racehorse in Japan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, K. Molecular evolution of MRSA. Microbiol. Immunol. 1995, 39, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, K.B.; Agrawal, P.; Kumar, S.; Kapila, K. Comparison of cefoxitin disc diffusion test, oxacillin screen agar, and PCR for mecA gene for detection of MRSA. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 27, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, Q. Identification of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) using simultaneous detection of mecA, nuc, and femB by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.K.; Ramaswamy, S.V.; Conradt, J.; Stemper, M.E.; Reich, R.; Reed, K.D.; Graviss, E.A. Novel polymorphisms in mec genes and a new mec complex type in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates obtained in rural Wisconsin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3080–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otero, L.H.; Rojas-Altuve, A.; Llarrull, L.I.; Carrasco-Lopez, C.; Kumarasiri, M.; Lastochkin, E.; Fishovitz, J.; Dawley, M.; Hesek, D.; Lee, M.; et al. How allosteric control of Staphylococcus aureus penicillin binding protein 2a enables methicillin resistance and physiological function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16808–16813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alm, R.A.; McLaughlin, R.E.; Kos, V.N.; Sader, H.S.; Iaconis, J.P.; Lahiri, S.D. Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates with reduced susceptibility to ceftaroline: An epidemiological and structural perspective. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schaumburg, F.; Peters, G.; Alabi, A.; Becker, K.; Idelevich, E.A. Missense mutations of PBP2a are associated with reduced susceptibility to ceftaroline and ceftobiprole in African MRSA. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, S.W.; Olsen, R.J.; Mehta, S.C.; Palzkill, T.; Cernoch, P.L.; Perez, K.K.; Musick, W.L.; Rosato, A.E.; Musser, J.M. PBP2a mutations causing high-level ceftaroline resistance in clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6668–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loganathan, A.; Manohar, P.; Eniyan, K.; Jayaraj, R.; Nachimuthu, R. Evaluation of various phenotypic methods with genotypic screening for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Asian Biomed. (Res. Rev. News) 2019, 13, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Hao, Y.; Yang, D.; Pang, B.; Wang, L. Fluorescent PCR detection of mecA in drug resistant MRSA: A methodological study. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 74, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests, 13th ed.; CLSI Standard M02; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mahasenan, K.V.; Molina, R.; Bouley, R.; Batuecas, M.T.; Fisher, J.F.; Hermoso, J.A.; Chang, M.; Mobashery, S. Conformational dynamics in penicillin-binding protein 2a of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, allosteric communication network and enablement of catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coppens, J.; Van Heirstraeten, L.; Ruzin, A.; Yu, L.; Timbermont, L.; Lammens, C.; Matheeussen, V.; McCarthy, M.; Jorens, P.; Ieven, M.; et al. Comparison of GeneXpert MRSA/SA ETA assay with semi-quantitative and quantitative cultures and nuc gene-based qPCR for detection of Staphylococcus aureus in endotracheal aspirate samples. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqib, A.I.; Ijaz, M.; Farooqi, S.H.; Ahmed, R.; Shoaib, M.; Ali, M.M.; Mehmood, K.; Zhang, H. Emerging discrepancies in conventional and molecular epidemiology of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine milk. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 116, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeeza, T.; Nadeem, A.; Nauman, J.; Afia, A.; Kunwal, R. Discrepancies in the diagnosis of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus among different hospitals in Lahore, Pakistan. Int. Med. J. 2009, 8, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- De Bonville, D. The impact of incorrect MRSA diagnoses. MLO Med. Lab. Obs. 2012, 44, 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sapkota, J.; Sharma, M.; Jha, B.; Bhatt, C.P. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from clinical samples in a tertiary care hospital: A descriptive cross-sectional study. JNMA J. Nepal Med. Assoc. 2019, 57, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.S.; Naqvi, A.; Sharaz, M. Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA); prevalence and susceptibility pattern of (MRSA) isolated from pus in tertiary care of district hospital of Rahim Yar Khan. Professional Med. J. 2019, 26, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Khanal, L.K.; Adhikari, R.P.; Guragain, A. Prevalence of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and antibiotic susceptibility pattern in a tertiary hospital in Nepal. J. Nepal Health Res. Counc. 2018, 16, 172–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perwaiz, S.; Barakzi, Q.; Farooqi, B.J.; Khursheed, N.; Sabir, N. Antimicrobial susceptibility pattern of clinical isolates of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2007, 57, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ariom, T.O.; Iroha, I.R.; Moses, I.B.; Iroha, C.S.; Ude, U.I.; Kalu, A.C. Detection and phenotypic characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from clinical and community samples in Abakaliki, Ebonyi State, Nigeria. Afr. Health Sci. 2019, 19, 2026–2035. [Google Scholar]
- Kelley, W.L.; Jousselin, A.; Barras, C.; Lelong, E.; Renzoni, A. Missense mutations in PBP2A affecting ceftaroline susceptibility detected in epidemic hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clonotypes ST228 and ST247 in Western Switzerland archived since 1998. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1922–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forbes, B.A.; Sahm, D.F.; Weissfeld, A.S. Study Guide for Bailey & Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology; Mosby: Maryland Heights, MO, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sarhan, S.R.; Hashim, H.O.; Al-Shuhaib, M.B.S. The Gly152Val mutation possibly confers resistance to β-lactam antibiotics in ovine Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Open Vet. J. 2020, 9, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brakstad, O.G.; Aasbakk, K.; Maeland, J.A. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction amplification of the nuc gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, G.S.; Cheon, S.H.; An, Y.J.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, K.J. Characterization of blaCMY-11, an AmpC-type plasmid-mediated β-lactamase gene in a Korean clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 49, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bressler, A.M.; Williams, T.; Culler, E.E.; Zhu, W.; Lonsway, D.; Patel, J.B.; Nolte, F.S. Correlation of penicillin binding protein 2a detection with oxacillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus and discovery of a novel penicillin binding protein 2a mutation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4541–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenti-Nineth Informational Supplement M100-S29; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Murakami, K.; Minamide, W.; Wada, K.; Nakamura, E.; Teraoka, H.; Watanabe, S. Identification of methicillin-resistant strains of staphylococci by polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 2240–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schymkowitz, J.; Borg, J.; Stricher, F.; Nys, R.; Rousseau, F.; Serrano, L. The FoldX web server: An online force field. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W382–W388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Pham, T.N.H.; Huy, N.T.; Bay, M.V.; Pham, M.Q.; Nam, P.C.; Vu, V.V.; Ngo, S.T. AutoDock Vina adopts more accurate binding poses but AutoDock 4 forms better binding affinity. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaillard, T. Evaluation of AutoDock and AutoDock Vina on the CASF-2013 benchmark. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2018, 58, 1697–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Staphylococcus aureus Isolate | Zone Diameter (mm) | Interpretive Category a |
|---|---|---|
| MR-1 | 13 | R |
| MR-2 | 20 | R |
| MR-3 | 13 | R |
| MR-4 | 13 | R |
| MR-5 | 16 | R |
| MR-6 | 13 | R |
| MR-7 | 13 | R |
| MR-8 | 17 | R |
| MR-9 | 16 | R |
| MR-10 | 15 | R |
| MR-11 | 20 | R |
| MR-12 | 19 | R |
| MR-13 | 4 | R |
| MR-14 | 4 | R |
| MR-15 | 34 | S |
| MR-16 | 13 | R |
| MR-17 | 16 | R |
| MR-18 | 13 | R |
| MR-19 | 14 | R |
| MR-20 | 23 | S |
| MR-21 | 17 | R |
| MR-22 | 17 | R |
| MR-23 | 18 | R |
| MR-24 | 16 | R |
| MR-25 | 15 | R |
| MR-26 | 14 | R |
| MR-27 | 18 | R |
| MR-28 | 29 | S |
| MR-29 | 17 | R |
| MR-30 | 14 | R |
| MR-31 | 16 | R |
| MR-32 | 17 | R |
| MR-33 | 3 | R |
| Site/Source | B | N | W |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRSA isolate | MR-13 | MR-14 | MR-33 |
| Amino acid change(s) of PBP2a | E239K | G246E | E239R E447K |
| Cefoxitin MIC (mg/L) | 64 | 64 | 128 |
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Fnuc | GCGATTGATGGTGATACGGTT | This study |
| Rnuc | AGCCAAGCCTTGACGAACTAAAGC | This study |
| 16sF | AGAGTTTGATCCTTGGCTAG | This study |
| 16sR | GCYTACCTTGTTACGACTT | This study |
| mecA_DF | AAAATCGATGGTAAAGGTTGGC | This study |
| mecA_DR | AGTTCTGCAGTACCGGATTTGC | This study |
| MF | AACCGAAGAAGTCGTGTCAG | This study |
| MR | CATCGTTACGGATTGCTTCG | |
| MecAR4 | GATACATTCTTTGGAACGATG | [36] |
| MecAF5 | ACAAGATGATACCTTCGTTCCACTT | |
| MecAF3 | GAAGATGGCTATCGTGTCAC | |
| MecAF4 | GGTAATATCGACTTAAAACAAG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, T.; Basit, A.; Karim, A.M.; Lee, J.-H.; Jeon, J.-H.; Rehman, S.u.; Lee, S.-H. Mutation-Based Antibiotic Resistance Mechanism in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050420
Ali T, Basit A, Karim AM, Lee J-H, Jeon J-H, Rehman Su, Lee S-H. Mutation-Based Antibiotic Resistance Mechanism in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(5):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050420
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Tanveer, Abdul Basit, Asad Mustafa Karim, Jung-Hun Lee, Jeong-Ho Jeon, Shafiq ur Rehman, and Sang-Hee Lee. 2021. "Mutation-Based Antibiotic Resistance Mechanism in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 5: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050420
APA StyleAli, T., Basit, A., Karim, A. M., Lee, J. -H., Jeon, J. -H., Rehman, S. u., & Lee, S. -H. (2021). Mutation-Based Antibiotic Resistance Mechanism in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates. Pharmaceuticals, 14(5), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050420