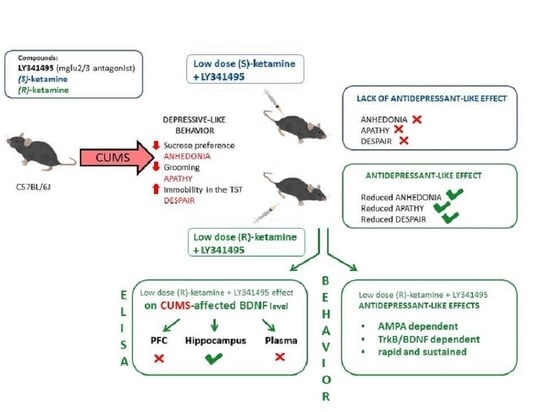
Combined Administration of (R)-Ketamine and the mGlu2/3 Receptor Antagonist LY341495 Induces Rapid and Sustained Effects in the CUMS Model of Depression via a TrkB/BDNF-Dependent Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Rapid Antidepressant-like Effects of (S)-Ketamine and (R)-Ketamine Coadministered with LY341495 in the TST
2.2. The Effects of (S)-Ketamine and (R)-Ketamine in the CUMS Model of Depression
2.3. The Effects of (S)-Ketamine and (R)-Ketamine Coadministered with LY341495 in the CUMS Model of Depression
2.4. Sustained Effects of (R)-Ketamine Coadministered with LY341495 in the CUMS Model of Depression
2.5. Mechanisms of the Effects of (R)-Ketamine Coadministered with LY341495 in the CUMS Model of Depression
2.6. The Effects of (S)-Ketamine and (R)-Ketamine Coadministered with LY341495 on the Locomotor Activity of Mice
2.7. The Effects of (R)-Ketamine Coadministered with LY341495 on BDNF Levels in the CUMS Model of Depression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Housing
4.2. Compounds
4.3. Tail Suspension Test
4.4. CUMS Procedure
4.5. Splash Test
4.6. Sucrose Preference Test
4.7. Locomotor Activity
4.8. BDNF Levels
4.9. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Singh, J.B.; Carlson, P.J.; Brutsche, N.E.; Ameli, R.; Luckenbaugh, D.A.; Charney, D.S.; Manji, H.K. A randomized trial of an NMDA antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 63, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahase, E. Esketamine is approved in Europe for treating resistant major depressive disorder. BMJ 2020, 367, l7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Vlisides, R.E. Ketamine: 50 years of modulating the mind. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zanos, P.; Moaddel, R.; Morris, P.J.; Riggs, L.M.; Highland, J.N.; Georgiou, P.; Pereira, E.F.R.; Albuquerque, E.X.; Thomas, C.J.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; et al. Ketamine and ketamine metabolite pharmacology: Insights into therapeutic mechanisms. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 621–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, L.; Zhang, K.; Pu, Y.; Qu, Y.; Wang, S.M.; Xiong, Z.; Ren, Q.; Dong, C.; Fujita, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Comparison of antidepressant and side effects in mice after intranasal administration of (R,S)-ketamine, (R)-ketamine, and (S)-ketamine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2019, 181, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafało-Ulińska, A.; Pałucha-Poniewiera, A. The effectiveness of (R)-ketamine and its mechanism of action differ from those of (S)-ketamine in a chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression in C57BL/6J mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 418, 113633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Shirayama, Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Ren, Q.; Yao, W.; Ma, M.; Dong, C.; Hashimoto, K. R-ketamine: A rapid-onset and sustained antidepressant without psychotomimetic side effects. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Zhang, J.C.; Yao, W.; Ren, Q.; Ma, M.; Yang, C.; Chaki, S.; Hashimoto, K. Rapid and sustained antidepressant action of the mGlu2/3 receptor antagonist MGS0039 in the social defeat stress model: Comparison with ketamine. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dwyer, J.M.; Lepack, A.E.; Duman, R.S. mGluR2/3 blockade produces rapid and long-lasting reversal of anhedonia caused by chronic stress exposure. J. Mol. Psychiatry 2013, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koike, H.; Fukumoto, K.; Iijima, M.; Chaki, S. Role of BDNF/TrkB signaling in antidepressant-like effects of a group II metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist in animal models of depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2013, 238, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepack, A.E.; Bang, E.; Lee, B.; Dwyer, J.M.; Duman, R.S. Fast-acting antidepressants rapidly stimulate ERK signaling and BDNF release in primary neuronal cultures. Neuropharmacology 2016, 111, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanos, P.; Highland, J.N.; Stewart, B.W.; Georgiou, P.; Jenne, C.E.; Lovett, J.; Morris, P.J.; Thomas, C.J.; Moaddel, R.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; et al. (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine exerts mGlu2 receptor-dependent antidepressant actions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 6441–6450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pałucha-Poniewiera, A.; Podkowa, K.; Pilc, A. Role of AMPA receptor stimulation and TrkB signaling in the antidepressant-like effect of ketamine co-administered with a group II mGlu receptor antagonist, LY341495, in the forced swim test in rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2019, 30, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podkowa, K.; Pochwat, B.; Brański, P.; Pilc, A.; Pałucha-Poniewiera, A. Group II mGlu receptor antagonist LY341495 enhances the antidepressant-like effects of ketamine in the forced swim test in rats. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 2901–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pałucha-Poniewiera, A.; Podkowa, K.; Rafało-Ulińska, A. The group II mGlu receptor antagonist LY341495 induces a rapid antidepressant-like effect and enhances the effect of ketamine in the chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression in C57BL/6J mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 109, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, B.; Mikkelsen, S.; Thorkildsen, C.; Borgbjerg, F.M. Norketamine, the main metabolite of ketamine, is a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist in the rat cortex and spinal cord. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 333, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ago, Y.; Tanabe, W.; Higuchi, M.; Tsukada, S.; Tanaka, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Igarashi, H.; Yokoyama, R.; Seiriki, K.; Kasai, A.; et al. (R)-Ketamine induces a greater increase in prefrontal 5-HT release than (S)-ketamine and ketamine metabolites via an AMPA receptor-independent mechanism. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 22, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ren, Q.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Ma, M.; Dong, C.; Hashimoto, K. Mechanistic target of rapamycin-independent antidepressant effects of (R)-ketamine in a social defeat stress model. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steru, L.; Chermat, R.; Thierry, B.; Simon, P. The tail suspension test: A new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology 1985, 85, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, P. The chronic mild stress (CMS) model of depression: History, evaluation and usage. Neurobiol. Stress 2017, 6, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Autry, A.E.; Adachi, M.; Nosyreva, E.; Na, E.S.; Los, M.F.; Cheng, P.F.; Kavalali, E.T.; Monteggia, L.M. NMDA receptor blockade at rest triggers rapid behavioural antidepressant responses. Nature 2011, 475, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castrén, E.; Monteggia, L.M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling in depression and antidepressant action. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 90, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepack, A.E.; Fuchikami, M.; Dwyer, J.M.; Banasr, M.; Duman, R.S. BDNF release is required for the behavioral actions of ketamine. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 18, pyu033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cryan, J.F.; Mombereau, C.; Vassout, A. The tail suspension test as a model for assessing antidepressant activity: Review of pharmacological and genetic studies in mice. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 571–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, M.; Gruca, P.; Łasoń-Tyburkiewicz, M.; Willner, P. Antidepressant, anxiolytic and procognitive effects of subacute and chronic ketamine in the chronic mild stress model of depression. Behav. Pharmacol. 2017, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.L.; Zhou, Z.Q.; Zhang, G.F.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.M.; Shen, J.C.; Hashimoto, K.; Yang, J.J. Role of hippocampal p11 in the sustained antidepressant effect of ketamine in the chronic unpredictable mild stress model. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cazorla, M.; Prémont, J.; Mann, A.; Girard, N.; Kellendonk, C.; Rognan, D. Identification of a low-molecular weight TrkB antagonist with anxiolytic and antidepressant activity in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1846–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monleon, S.; D’Aquila, P.; Parra, A.; Simon, V.M.; Brain, P.F.; Willner, P. Attenuation of sucrose consumption in mice by chronic mild stress and its restoration by imipramine. Psychopharmacology 1994, 117, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathomas, F.; Hartmann, M.N.; Seifritz, E.; Pryce, C.R.; Kaiser, S. The translational study of apathy—An ecological approach. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Willner, P.; Muscat, R.; Papp, M. Chronic mild stress-induced anhedonia: A realistic animal model of depression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1992, 16, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtholt-Gompf, A.J.; Smith, K.L.; John, C.S.; Kang, H.H.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Cohen, B.M.; Ongür, D. CD-1 and Balb/cJmice do not show enduring antidepressant-like effects of ketamine in tests of acute antidepressant efficacy. Psychopharmacology 2011, 215, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sałat, K.; Siwek, A.; Starowicz, G.; Librowski, T.; Nowak, G.; Drabik, U.; Gajdosz, R.; Popik, P. Antidepressant-like effects of ketamine, norketamine and dehydronorketamine in forced swim test: Role of activity at NMDA receptor. Neuropharmacology 2015, 99, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, K.; Toki, H.; Iijima, M.; Hashihayata, T.; Yamaguchi, J.I.; Hashimoto, K.; Chaki, S. Antidepressant potential of (R)-ketamine in rodent models: Comparison with (S)-Ketamine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 361, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanos, P.; Moaddel, R.; Morris, P.J.; Georgiou, P.; Fischell, J.; Elmer, G.I.; Alkondon, M.; Yuan, P.; Pribut, H.J.; Singh, N.S.; et al. NMDAR inhibition-independent antidepressant actions of ketamine metabolites. Nature 2016, 533, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, A.; Fujita, Y.; Pu, Y.; Chang, L.; Hashimoto, K. MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in mouse brain is attenuated after subsequent intranasal administration of (R)-ketamine: A role of TrkB signaling. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Qu, Y.; Chang, L.; Pu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Hashimoto, K. Phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficits in mice are ameliorated by subsequent repeated intermittent administration of (R)-ketamine, but not (S)-ketamine: Role of BDNF-TrkB signaling. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 188, 172839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Shan, J.; Wang, S.; Chang, L.; Pu, Y.; Wang, X.; Tan, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Hashimoto, K. Rapid-acting and long-lasting antidepressant-like action of (R)-ketamine in Nrf2 knock-out mice: A role of TrkB signaling. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 271, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosyreva, E.; Szabla, K.; Autry, A.E.; Ryazanov, A.G.; Monteggia, L.M.; Kavalali, E.T. Acute suppression of spontaneous neurotransmission drives synaptic potentiation. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 6990–7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, P.Y.; Ma, Z.Z.; Mahgoub, M.; Kavalali, E.T.; Monteggia, L.M. A synaptic locus for TrkB signaling underlying ketamine rapid antidepressant action. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, A.; Dalmagro, A.P.; Wolin, I.A.V.; Siteneski, A.; Zeni, A.L.B.; Rodrigues, A.L.S. A low-dose combination of ketamine and guanosine counteracts corticosterone-induced depressive-like behavior and hippocampal synaptic impairments via mTORC1 signaling. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 111, 110371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Veldman, E.R.; Tiger, M.; Ekman, C.J.; Lundberg, J.; Svenningsson, P. Plasma levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and S100B in relation to antidepressant response to ketamine. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 698633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arosio, B.; Guerini, F.R.; Voshaar, R.C.O.; Aprahamian, I. Blood brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and major depression: Do we have a translational perspective? Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 626906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pałucha-Poniewiera, A.; Podkowa, K.; Rafało-Ulińska, A.; Brański, P.; Burnat, G. The influence of the duration of chronic unpredictable mild stress on the behavioural responses of C57BL/6J mice. Behav. Pharmacol. 2020, 31, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strekalova, T.; Steinbusch, H.W. Measuring behavior in mice with chronic stress depression paradigm. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 34, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rafało-Ulińska, A.; Brański, P.; Pałucha-Poniewiera, A. Combined Administration of (R)-Ketamine and the mGlu2/3 Receptor Antagonist LY341495 Induces Rapid and Sustained Effects in the CUMS Model of Depression via a TrkB/BDNF-Dependent Mechanism. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020125
Rafało-Ulińska A, Brański P, Pałucha-Poniewiera A. Combined Administration of (R)-Ketamine and the mGlu2/3 Receptor Antagonist LY341495 Induces Rapid and Sustained Effects in the CUMS Model of Depression via a TrkB/BDNF-Dependent Mechanism. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(2):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020125
Chicago/Turabian StyleRafało-Ulińska, Anna, Piotr Brański, and Agnieszka Pałucha-Poniewiera. 2022. "Combined Administration of (R)-Ketamine and the mGlu2/3 Receptor Antagonist LY341495 Induces Rapid and Sustained Effects in the CUMS Model of Depression via a TrkB/BDNF-Dependent Mechanism" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 2: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020125
APA StyleRafało-Ulińska, A., Brański, P., & Pałucha-Poniewiera, A. (2022). Combined Administration of (R)-Ketamine and the mGlu2/3 Receptor Antagonist LY341495 Induces Rapid and Sustained Effects in the CUMS Model of Depression via a TrkB/BDNF-Dependent Mechanism. Pharmaceuticals, 15(2), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020125