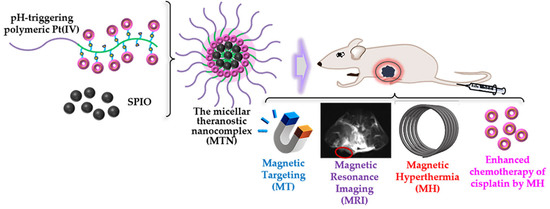
A Theranostic Nanocomplex Combining with Magnetic Hyperthermia for Enhanced Accumulation and Efficacy of pH-Triggering Polymeric Cisplatin(IV) Prodrugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Polymeric Pt(IV)
2.2. Characterization of Polymeric Pt(IV)-Based Micelles
2.3. Drug Release Studies
2.4. Antitumor Efficacy In Vitro
2.5. Efficient Tumor Diagnosis by a Combination of MT and MRI In Vivo
2.6. Antitumor Efficacy In Vivo
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Pt(IV) with Single Carboxyl
3.3. Preparation of Hydrophilic Block Copolymer mPEG-b-pHEMA
3.4. Preparation of Polymeric Pt(IV)
3.5. Characterization of Molecular Structures
3.6. Preparation of Polymeric Pt(IV) Micelles (PPMs) and MTNs
3.7. General Properties of PPM and MTN
3.8. Drug Release Studies
3.9. Cell Viability Assay In Vitro
3.10. Cellular Uptake Studies
3.11. Animal Protocol
3.12. Biodistribution of MTNs and MRI of Tumor In Vivo
3.13. In Vivo Tumor Inhibition Studies
3.14. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kelland, L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Yan, B.; Dempsey, E.M.; Song, W.; Qi, R.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; Jing, X.; Zhou, D.; Ding, J.; et al. Recent progress in polymer-based platinum drug delivery systems. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 87, 70–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, S.A.; Kerwood, D.J.; Goodisman, J.; Dabrowiak, J.C. Pt(IV) complexes as prodrugs for cisplatin. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 107, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, D.; Xu, S.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Yasen, W.; Wang, N.; Su, Y.; Qian, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; et al. Platinum(IV) complex-based two-in-one polyprodrug for a combinatorial chemo-photodynamic therapy. Biomaterials 2018, 177, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yin, W.; Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Zha, Z.; Ke, W.; Wang, Y.; He, C.; Ge, Z. Intracellular glutathione-depleting polymeric micelles for cisplatin prodrug delivery to overcome cisplatin resistance of cancers. J. Control. Release 2018, 273, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Miao, C.; Tang, L.; Liu, Y.; Ni, P.; Gong, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, F.; Feng, S. Homotypic Cancer Cell Membranes Camouflaged Nanoparticles for Targeting Drug Delivery and Enhanced Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Glioma. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Song, H.; Yang, Q.; Cai, H.; Qi, R.; Yan, L.; Liu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, T.; et al. A prodrug strategy to deliver cisplatin(IV) and paclitaxel in nanomicelles to improve efficacy and tolerance. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6507–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Shang, J.; Jiao, C.; Jiang, P.; Xiao, H.; Luo, L.; Liu, T. A core cross-linked polymeric micellar platium(IV) prodrug with enhanced anticancer efficiency. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golombek, S.K.; May, J.N.; Theek, B.; Appold, L.; Drude, N.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Tumor targeting via EPR: Strategies to enhance patient responses. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 130, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.W.; Bae, Y.H. Odyssey of a cancer nanoparticle: From injection site to site of action. Nano Today 2012, 7, 606–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dewhirst, M.W.; Secomb, T.W. Transport of drugs from blood vessels to tumor tissue. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, B.A.; Chimenti, M.; Jacobson, M.P.; Barber, D.L. Dysregulated pH: A perfect storm for cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuppusamy, P.; Li, H.; Ilangovan, G.; Cardounel, A.J.; Zweier, J.L.; Yamada, K.; Krishna, M.C.; Mitchell, J.B. Noninvasive imaging of tumor redox status and its modification by tissue gluta-thione levels. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Hagen, T.L.M.; Bolkestein, M.; Gasselhuber, A.; Yatvin, J.; Rhoon, G.C.; Eggermont, A.M.M.; Haemmerich, D.; Koning, G.A. Improved intratumoral nanoparticle extravasation and penetration by mild hyperthermia. J. Control. Release 2013, 167, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, A.A.; Lindner, L.H.; Landon, C.D.; Park, J.Y.; Simnick, A.J.; Dreher, M.R.; Das, S.; Hanna, G.; Park, W.; Chilkoti, A.; et al. Overcoming Limitations in Nanoparticle Drug Delivery: Triggered, Intravascular Release to Improve Drug Penetration into Tumors. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5566–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mantso, T.; Goussetis, G.; Franco, R.; Botaitis, S.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M. Effects of hyperthermia as a mitigation strategy in DNA damage-based cancer therapies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 37–38, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolik, S.; Delgado, J.A.; Pérez, A.; Anasagasti, L. Measurement of the Penetration Depths of Red and Near Infrared Light in Human “ex Vivo” Tissues. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2000, 57, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, J.; Leng, J.; Lin, C.; Shi, D. Enhanced magnetic fluid hyperthermia by micellar magnetic nanoclusters composed of MnxZn1-xFe2O4 nanoparticles for induced tumor cell apoptosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16867–16879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Li, J.; Ren, J.; Leng, J.; Lin, C.; Shi, D. Enhanced synergism of thermo-chemotherapy by combining highly efficient magnetic hyperthermia with magnetothermally-facilitated drug release. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 12408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarío, E.; Cañete, M.; Herranz, F.; Sánchez-Marcos, J.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Herrasti, P.; Menéndez, N. Highly Efficient T2 Cobalt Ferrite Nanoparticles Vectorized for Internalization in Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makharza, S.A.; Cirillo, G.; Vittorio, O.; Valli, E.; Voli, F.; Farfalla, A.; Curcio, M.; Iemma, F.; Nicoletta, F.P.; El-Gendy, A.A.; et al. Magnetic Graphene Oxide Nanocarrier for Targeted Delivery of Cisplatin: A Perspective for Glioblastoma Treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rieter, W.J.; Pott, K.M.; Taylor, K.M.L.; Lin, W. Nanoscale Coordination Polymers for Platinum-Based Anticancer Drug Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 11584–11585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Qi, R.; Liu, S.; Hu, X.; Duan, T.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jing, X. Biodegradable polymer-cisplatin(IV) conjugate as a pro-drug of cisplatin(II). Biomaterials 2011, 32, 7732–7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Wang, R.; Xiao, H.; Cai, H.; Zhang, W.; Xie, Z.; Huang, Y.; Jing, X.; Liu, T. A cross-linked polymeric micellar delivery system for cisplatin(IV) complex. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, R.K.; Dhar, S. A nanoparticle cocktail: Temporal release of predefined drug combinations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8324–8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.T.; Filla, D.; Shea, R. Functional Polymers from Novel Carboxyl-Terminated Trithiocarbonates as Highly Efficient RAFT Agents. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 6754–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, V.T.; Chen, G.; Souza, P.; Stenzel, M.H. Thiol-yne and Thiol-ene “Click” Chemistry as a Tool for a Variety of Platinum Drug Delivery Carriers, from Statistical Copolymers to Crosslinked Micelles. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1738–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Xiong, H.; Zhou, D.; Xie, Z.; Huang, Y.; Jing, X.; Sun, X. Co-Delivery of Oxaliplatin and Demethylcantharidin via a Polymer–Drug Conjugate. Macromol. Biosci. 2014, 14, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.K.; Basu, U.; Ahmad, A.; Sarkar, S.; Kumar, A.; Surnar, B.; Ansari, S.; Wilczek, K.; Ivan, M.E.; Marples, B.; et al. A designer bowtie combination therapeutic platform: An approach to resistant cancer treatment by simultaneous delivery of cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory agents and radiation. Biomaterials 2018, 187, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosensweig, R.E. Heating magnetic fluid with alternating magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 252, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H.; Rinna, A. Glutathione: Overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2009, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Chi, D.; Song, D.; Su, G.; Li, L.; Shao, L. Quantification of Glutathione in Plasma Samples by HPLC Using 4-Fluoro-7-nitrobenzofurazan as a Fluorescent Labeling Reagent. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2012, 50, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lyv, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhan, W.; Chen, H.; Chen, H.; Li, X. A theranostic prodrug delivery system based on Pt(IV) conjugated nano-graphene oxide with synergistic effect to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of Pt drug. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Xiao, M.; Wang, D.; Hou, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, J. In Situ Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Pt(IV) Prodrug to Conquer Cisplatin Resistance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottenberg, S.; Disler, C.; Perego, P. The rediscovery of platinum-based cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasawa, T.; Steyger, P.S. An integrated view of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 237, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, K.; Hu, X.; Ma, X.; Lan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Z. Theranostics of Malignant Melanoma with 64CuCl2. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imlimthan, S.; Moon, E.S.; Rathke, H.; Afshar-Oromieh, A.; Rösch, F.; Rominger, A.; Gourni, E. New Frontiers in Cancer Imaging and Therapy Based on Radiolabeled Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitors: A Rational Review and Current Progress. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barca, C.; Griessinger, C.M.; Faust, A.; Depke, D.; Essler, M.; Windhorst, A.D.; Devoogdt, N.; Brindle, K.M.; Schäfers, M.; Zinhardt, B. Expanding Theranostic Radiopharmaceuticals for Tumor Diagnosis and Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Yang, L.; Gao, J.; Chen, X. Structure-Relaxivity Relationships of Magnetic Nanoparticles for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1804567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Huang, G.; Hensley, C.; Huang, X.; Ma, X.; Zhao, T.; Sumer, B.D.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Gao, J. A nanoparticle-based strategy for the imaging of a broad range of tumours by non-linear amplification of microenvironment signals. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sykes, E.A.; Chen, J.; Zheng, G.; Chan, W.C.W. Investigating the Impact of Nanoparticle Size on Active and Passive Tumor Targeting Efficiency. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5696–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wu, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, J.; Xie, J.; Zang, F.; Ma, M.; Gu, N.; Zhang, Y. Magnetic targeting combined with active targeting of dual-ligand iron oxide nanoprobes to promote the penetration depth in tumors for effective magnetic resonance imaging and hyperthermia. Acta Biomater. 2019, 96, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Luo, L.; Xue, Y.; Han, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, T.; Wang, L.H.; Cun, D.; Gou, J.; et al. Cisplatin-loaded poly-meric complex micelles with a modulated drug/copolymer ratio for improved in vivo performance. Acta Biomater. 2019, 92, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Gao, M.; Tao, D.; Chen, Q.; Wang, H.; Dong, Z.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z. Cisplatin-Prodrug-Constructed Liposomes as a Versatile Theranostic Nanoplatform for Bimodal Imaging Guided Combination Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tao, Y.; Saw, P.E.; Cao, M.; Huang, H.; Xu, X. A polyprodrug-based nanoplatform for cisplatin prodrug delivery and combination cancer therapy. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 13987–13990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.J.; Lippard, S.J. Synthetic Methods for the Preparation of Platinum Anticancer Complexes. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4470–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandra, F.; Zaks, L.; Zhu, A. Survival Prolongation Index as a Novel Metric to Assess Anti-Tumor Activity in Xenograft Models. AAPS J. 2019, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, M.; Zhao, T.; Zhu, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Liu, H. A Theranostic Nanocomplex Combining with Magnetic Hyperthermia for Enhanced Accumulation and Efficacy of pH-Triggering Polymeric Cisplatin(IV) Prodrugs. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040480
Qu Y, Wang Z, Sun M, Zhao T, Zhu X, Deng X, Zhang M, Xu Y, Liu H. A Theranostic Nanocomplex Combining with Magnetic Hyperthermia for Enhanced Accumulation and Efficacy of pH-Triggering Polymeric Cisplatin(IV) Prodrugs. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(4):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040480
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Yang, Zhiqi Wang, Miao Sun, Tian Zhao, Xuanlei Zhu, Xiaoli Deng, Man Zhang, Ying Xu, and Hongfei Liu. 2022. "A Theranostic Nanocomplex Combining with Magnetic Hyperthermia for Enhanced Accumulation and Efficacy of pH-Triggering Polymeric Cisplatin(IV) Prodrugs" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 4: 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040480
APA StyleQu, Y., Wang, Z., Sun, M., Zhao, T., Zhu, X., Deng, X., Zhang, M., Xu, Y., & Liu, H. (2022). A Theranostic Nanocomplex Combining with Magnetic Hyperthermia for Enhanced Accumulation and Efficacy of pH-Triggering Polymeric Cisplatin(IV) Prodrugs. Pharmaceuticals, 15(4), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15040480