Sanyin Formula Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Paclitaxel in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Metastases through the JAK/STAT3 Pathway in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
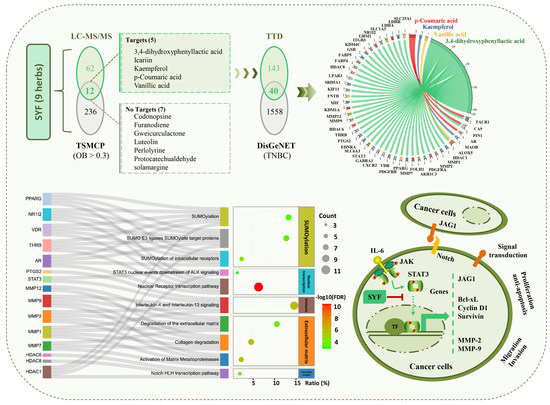
2.1. Main Compounds in SYF Extract
2.2. STAT3 Signalling Was Identified as the Potential Pathway
2.3. SYF Extract Reduced Cancer Cell Growth, Migration, and Invasion In Vitro
2.4. SYF Extract Reduced Cancer Cell Metastasis In Vivo
2.5. Candidate Compounds Bound Tightly to Candidate Target Proteins
2.6. SYF Extract Reduced Tumour Metastasis via STAT3 Signalling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Instruments
4.2. Traditional Chinese Medicines and Process for Extracting SYF Extract
4.3. HPLC-MS/MS Analysis
4.4. Cells and Cell Culture
4.5. Identification of Candidate Targets of SYF in TNBC
4.6. Bioinformatic Enrichment Analyses
4.7. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.8. Transwell Invasion and Migration Assays
4.9. Wound-Healing Migration Assay
4.10. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.11. Western Blotting (WB)
4.12. Animals and Xenograft Model Establishment
4.13. Haematoxylin-Eosin (HE), Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase (TRAP), and Giemsa Staining
4.14. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining and Semiquantitative Analysis
4.15. Molecular Docking
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareja, F.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Triple-negative breast cancers—A panoply of cancer types. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 347–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, T.G. Targeted Therapies for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2019, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malorni, L.; Shetty, P.B.; DE Angelis, C.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Rimawi, M.F.; Elledge, R.M.; Osborne, C.K.; De Placido, S.; Arpino, G. Clinical and biologic features of triple-negative breast cancers in a large cohort of patients with long-term follow-up. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonotto, M.; Gerratana, L.; Poletto, E.; Driol, P.; Giangreco, M.; Russo, S.; Minisini, A.M.; Andreetta, C.; Mansutti, M.; Pisa, F.E.; et al. Measures of Outcome in Metastatic Breast Cancer: Insights from a Real-World Scenario. Oncologist 2014, 19, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rapoport, B.L.; Nayler, S.; Demetriou, G.S.; Moodley, S.D.; Benn, C.A. Triple negative breast cancer pathologic diagnosis and current chemotherapy treatment options. Oncol. Hematol. Rev. 2014, 10, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchini, G.; Balko, J.M.; Mayer, I.A.; Sanders, M.E.; Gianni, L. Triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahmood, S.; Sapiezynski, J.; Garbuzenko, O.B.; Minko, T. Metastatic and triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and treatment options. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 1483–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergin, A.R.T.; Loi, S. Triple-negative breast cancer: Recent treatment advances. F1000Research 2019, 8, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, H.-T.; Lin, H.-S. Traditional Chinese medicine and cancer: History, present situation, and development. Thorac. Cancer 2015, 6, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, C.; He, F.; Zeng, J. Meta-analysis of effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine or its combination with western medicine in the treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.-W.; Qin, Y.-N.; Sun, C.-P.; Chen, J.-J.; Ruan, Y.-Y.; Chen, L.-X.; Liu, S.; Liu, G.-Y. Clinical observation on the effect of Chinese medicine-“TCM formula” intervention on recurrence and metastasis of triple negative breast cancer. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 52, 102456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Sun, C.; Liu, G.; Qin, Y.; Xue, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Ye, Z.; Li, Q.; et al. Effectiveness of the Sanyin Formula Plus Chemotherapy on Survival in Women with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-H.; Hwang, K.-A.; Choi, K.-C. Treatment with kaempferol suppresses breast cancer cell growth caused by estrogen and triclosan in cellular and xenograft breast cancer models. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2016, 28, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; An, Y.; Fang, G. The mechanism of anticancer action and potential clinical use of kaempferol in the treatment of breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xue, L. Kaempferol Suppresses Proliferation and Induces Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis, and DNA Damage in Breast Cancer Cells. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2019, 27, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arowosegbe, M.A.; Amusan, O.T.; Adeola, S.A.; Adu, O.B.; Akinola, I.A.; Ogungbe, B.F.; Omotuyi, O.I.; Saibu, G.M.; Ogunleye, A.J.; Kanmodi, R.I.; et al. Kaempferol as a Potential PAK4 Inhibitor in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Extra Precision Glide Docking and Free Energy Calculation. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2020, 17, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariadoss, A.V.A.; Saravanakumar, K.; Sathiyaseelan, A.; Karthikkumar, V.; Wang, M.-H. Smart drug delivery of p-Coumaric acid loaded aptamer conjugated starch nanoparticles for effective triple-negative breast cancer therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 195, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Cho, S.; Kang, J.; Park, W.; Lee, S.; Jung, Y.; Kang, M.-W.; Kwak, H.; Um, J.-Y. Vanillic Acid Improves Comorbidity of Cancer and Obesity through STAT3 Regulation in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese and B16BL6 Melanoma-Injected Mice. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lee, K.Y.; Park, B. Icariin abrogates osteoclast formation through the regulation of the RANKL-mediated TRAF6/NF-κB/ERK signaling pathway in Raw264.7 cells. Phytomedicine 2018, 51, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.B.; Lin, S.-H.; Mahalakshmi, B.; Lo, Y.-S.; Lin, C.-C.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Hsieh, M.-J.; Chen, M.-K. Sodium Danshensu Inhibits Oral Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion by Modulating p38 Signaling Pathway. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 568436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, B.; Jun, S.Y.; Seo, H.; Youn, H.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, W.; Kim, H.K.; Kang, C.; Youn, B. Inhibitory effect of traditional oriental medicine-derived monoamine oxidase B inhibitor on radioresistance of non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Chen, X.; Mi, L.; Liu, C.; Zhu, S.; Yang, T.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, H.; Liang, X. Icariin-induced inhibition of SIRT6/NF-κB triggers redox mediated apoptosis and enhances anti-tumor immunity in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 4242–4256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, D.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, L.; Dong, T.; Chen, T.; Yu, Z. Icariin induces apoptosis in breast cancer MCF-7 cells by regulating the MELK mediated PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2021, 42, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Tan, S.; Duan, F.; Yuan, Q.; Li, Q.; Deng, G. Icariin induces apoptosis by suppressing autophagy in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cell line MCF-7/TAM. Breast Cancer 2019, 26, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, P.H.; Kourghi, M.; Pei, J.V.; Nourmohammadi, S.; Yool, A.J. 5-Hydroxymethyl-Furfural and Structurally Related Compounds Block the Ion Conductance in Human Aquaporin-1 Channels and Slow Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Mol. Pharmacol. 2020, 98, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okon, E.; Kukula-Koch, W.; Halasa, M.; Jarzab, A.; Baran, M.; Dmoszynska-Graniczka, M.; Angelis, A.; Kalpoutzakis, E.; Guz, M.; Stepulak, A.; et al. Magnoflorine-isolation and the anticancer potential against NCI-H1299 lung, MDA-MB-468 breast, T98G glioma, and TE671 rhabdomyosarcoma cancer cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.A.; Xie, X.B.; Cao, P.C. Magnoflorine improves sensitivity to doxorubicin (DOX) of breast cancer cells via inducing apoptosis and autophagy through AKT/mTOR and p38 signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Tan, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Furanodiene, a natural small molecule suppresses metastatic breast cancer cell migration and invasion in vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 737, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.-F.; Qiang, W.-A.; Wang, C.-M.; Tan, W.; Wang, Y.-T. Furanodiene enhances the anti-cancer effects of doxorubicin on ERα-negative breast cancer cells in vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 774, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.-F.; Tan, W.; Tian, K.; Yu, H.; Qiang, W.-A.; Wang, Y.-T. Combined effects of furanodiene and doxorubicin on the migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells in vitro. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.; Jiang, X.; Jeong, J.B.; Lee, S.-H. Anticancer Activity of Protocatechualdehyde in Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) as a Cancer Biomarker and MMP-9 Biosensors: Recent Advances. Sensors 2018, 18, 3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Dai, Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, C.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z. Association between expression of MMP-7 and MMP-9 and pelvic lymph node and para-aortic lymph node metastasis in early cervical cancer. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2018, 44, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauro, M.; Lynch, C. Cutting to the Chase: How Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Activity Controls Breast-Cancer-to-Bone Metastasis. Cancers 2018, 10, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Martino, J.S.; Akhter, T.; Bravo-Cordero, J.J. Remodeling the ECM: Implications for Metastasis and Tumor Dormancy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ye, Y.; Zhu, X. MMP-9 secreted by tumor associated macrophages promoted gastric cancer metastasis through a PI3K/AKT/Snail pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Tao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhu, M.; Ji, W.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Hu, X. Exosomal MMP-1 transfers metastasis potential in triple-negative breast cancer through PAR1-mediated EMT. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 193, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.S.; Hostetter, G.; Tang, L.; Frank, S.B.; Saboda, K.; Mehra, R.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Keller, E.T.; Miranti, C.K. Notch3 promotes prostate cancer-induced bone lesion development via MMP-3. Oncogene 2020, 39, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Ma, P.; Ye, Z.; Guo, L.; Xu, S.; Xu, L.; Liu, T.; et al. MicroRNA-429 inhibits bone metastasis in breast cancer by regulating CrkL and MMP-9. Bone 2019, 130, 115139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manore, S.G.; Doheny, D.L.; Wong, G.L.; Lo, H.-W. IL-6/JAK/STAT3 Signaling in Breast Cancer Metastasis: Biology and Treatment. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 866014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Grande, F.; Neamati, N. Small molecule inhibitors of Stat3 signaling pathway. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2007, 7, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.-J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.-D. STAT3 as a potential therapeutic target in triple negative breast cancer: A systematic review. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Du, X.; Huang, K.; Zhang, T.; Teng, Z.; Niu, W.; Wang, C.; Xia, G. Rac1 modulates the formation of primordial follicles by facilitating STAT3-directed Jagged1, GDF9 and BMP15 transcription in mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.H.; Qi, J.; Lin, S.Q.; Zhang, C.Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Xie, W.D.; Li, X. STAT3 targets ERR-α to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration, and invasion in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 2184–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.W.; Saadalla, A.; Ewida, A.H.; Al-Katranji, K.; Al-Saoudi, G.; Giaccone, Z.T.; Gounari, F.; Zhang, M.; Frank, D.A.; Khazaie, K. The STAT3 inhibitor pyrimethamine displays anti-cancer and immune stimulatory effects in murine models of breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 67, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ji, M.; Zhang, S.; Xue, N.; Xu, H.; Lin, S.; Chen, X. Bt354 as a new STAT3 signaling pathway inhibitor against triple negative breast cancer. J. Drug Target. 2018, 26, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, W.; Cai, G.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Guo, J.; Yin, G.; Chen, C.; Kong, L. A new synthetic derivative of cryptotanshinone KYZ3 as STAT3 inhibitor for triple-negative breast cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medina, P.J.; Goodin, S. Lapatinib: A dual inhibitor of human epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Clin. Ther. 2008, 30, 1426–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Zhao, K.; Jiang, W.; Bai, W.; Liu, J.; Yin, J. Syntenin1/MDA-9 (SDCBP) induces immune evasion in triple-negative breast cancer by upregulating PD-L1. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 171, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.S.; Toor, S.M.; Ali, B.R.; Elkord, E. Dual inhibition of STAT1 and STAT3 activation downregulates expression of PD-L1 in human breast cancer cells. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhu, J.; Gao, X. Genomic and GeneChip expression profiling reveals the inhibitory effects of Amorphophalli Rhizoma in TNBC cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, K.; Sun, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, B.; Huang, C. Systematic screening and characterization of the major bioactive components of Poria cocos and their metabolites in rats by LC-ESI-MS(n). Biomed. Chromatogr. 2012, 26, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, M.; Yang, Z.; Xu, C.; Yu, Q.; Song, J.; Wang, M.; Gao, X. Amorphophalli Rhizoma inhibits breast cancer growth, proliferation, migration, and invasion via the PI3K/AKT pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 286, 114926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Estimating the Maximum Safe Starting Dose in Initial Clinical Trials for Therapeutics in Adult Healthy Volunteers. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/estimating-maximum-safe-starting-dose-initial-clinical-trials-therapeutics-adult-healthy-volunteers (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Zheng, S.; Epstein, P.N. CD45 Immunohistochemistry in Mouse Kidney. BIO-PROTOCOL 2021, 11, e4230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac-Lam, M.F. Molecular modeling of the interaction of ligands with ACE2-SARS-CoV-2 spike protein complex. In Silico Pharmacol. 2021, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Sun, C.; Han, X.; Ye, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liu, S. Sanyin Formula Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Paclitaxel in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Metastases through the JAK/STAT3 Pathway in Mice. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010009
Wu C, Sun C, Han X, Ye Y, Qin Y, Liu S. Sanyin Formula Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Paclitaxel in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Metastases through the JAK/STAT3 Pathway in Mice. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chunyu, Chenping Sun, Xianghui Han, Yiyi Ye, Yuenong Qin, and Sheng Liu. 2023. "Sanyin Formula Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Paclitaxel in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Metastases through the JAK/STAT3 Pathway in Mice" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010009
APA StyleWu, C., Sun, C., Han, X., Ye, Y., Qin, Y., & Liu, S. (2023). Sanyin Formula Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of Paclitaxel in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Metastases through the JAK/STAT3 Pathway in Mice. Pharmaceuticals, 16(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010009