Inhibition of FGFR2 Signaling by Cynaroside Attenuates Liver Fibrosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
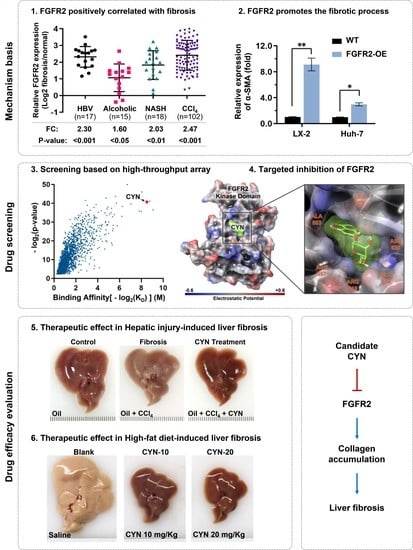
2.1. High Expression of FGFR2 Coincides with Liver Fibrosis
2.2. FGFR2 Drives the Process of Liver Fibrosis
2.3. Cynaroside (CYN) Blocks the Activity of FGFR2
2.4. CYN Blocks the Activation and Development of Liver Fibrosis
2.5. CYN Attenuates the Progression of Liver Fibrosis In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Mining and Clinical Samples
4.2. Molecular Evaluation
4.3. Cell Evaluation Procedure
4.4. High Throughput Screening of Drugs and Binding Affinity Verification
4.5. In Silico Docking and MD Simulation
4.6. Animal Experiments
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, Y.-S.; Kim, W.R. The Global Impact of Hepatic Fibrosis and End-Stage Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2008, 12, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, K.; Liu, J. Liver fibrosis is closely related to metabolic factors in metabolic associated fatty liver disease with hepatitis B virus infection. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practical Guidelines on the management of acute (fulminant) liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1047–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataller, R.; Brenner, D. Liver fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henson, J.B.; Simon, T.G.; Kaplan, A.; Osganian, S.; Masia, R.; Corey, K.E. Advanced fibrosis is associated with incident cardiovascular disease in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73 (Suppl. S1), 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thannickal, V.J.; Zhou, Y.; Gaggar, A.; Duncan, S.R. Fibrosis: Ultimate and proximate causes. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4673–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higashi, T.; Friedman, S.L.; Hoshida, Y. Hepatic stellate cells as key target in liver fibrosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 121, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Seki, E. Hepatic Stellate Cell–Macrophage Crosstalk in Liver Fibrosis and Carcinogenesis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2020, 40, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Gea, V.; Friedman, S.L. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2011, 6, 425–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewidar, B.; Meyer, C.; Dooley, S.; Meindl-Beinker, N. TGF-β in Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation and Liver Fibrogenesis—Updated 2019. Cells 2019, 8, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caja, L.; Dituri, F.; Mancarella, S.; Caballero-Diaz, D.; Moustakas, A.; Giannelli, G.; Fabregat, I. TGF-β and the Tissue Microenvironment: Relevance in Fibrosis and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, Z.; Sun, H.; Xue, T.; Gan, C.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ye, T. Liver Fibrosis: Therapeutic Targets and Advances in Drug Therapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 730176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhangdi, H.-J.; Su, S.-B.; Wang, F.; Liang, Z.-Y.; Yan, Y.-D.; Qin, S.-Y.; Jiang, H.-X. Crosstalk network among multiple inflammatory mediators in liver fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4835–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehlen, N.; Crouchet, E.; Baumert, T.F. Liver Fibrosis: Mechanistic Concepts and Therapeutic Perspectives. Cells 2020, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steiling, H.; Mühlbauer, M.; Bataille, F.; Schölmerich, J.; Werner, S.; Hellerbrand, C. Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells Express Keratinocyte Growth Factor in Chronic Liver Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 165, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Fan, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Disruption of FGF Signaling Ameliorates Inflammatory Response in Hepatic Stellate Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato-Matsubara, M.; Matsubara, T.; Daikoku, A.; Okina, Y.; Longato, L.; Rombouts, K.; Thuy, L.T.T.; Adachi, J.; Tomonaga, T.; Ikeda, K.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) regulates cytoglobin expression and activation of human hepatic stellate cells via JNK signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 18961–18972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seitz, T.; Freese, K.; Dietrich, P.; Thasler, W.E.; Bosserhoff, A.; Hellerbrand, C. Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 is expressed by activated hepatic stellate cells and promotes progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koledova, Z.; Sumbal, J. FGF signaling in mammary gland fibroblasts regulates multiple fibroblast functions and mammary epithelial morphogenesis. Development 2019, 146, dev185306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Zhang, X.; Qi, J.; Zhang, J.; Tong, Y.; Li, L.; Fu, L.; Qin, Y.-R.; Guan, X.; Zhang, L. Identification and characterization of FGFR2+ hematopoietic stem cell-derived fibrocytes as precursors of cancer-associated fibroblasts induced by esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, G.; O’Rourke, C.; Perrine, S.M.M.; Lu, N.; van Bakel, H.; Richtsmeier, J.T.; Jabs, E.W. Midface and upper airway dysgenesis in FGFR2-craniosynostosis involves multiple tissue-specific and cell cycle effects. Development 2018, 145, dev166488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Schéele, S.; Arman, E.; Haffner-Krausz, R.; Ekblom, P.; Lonai, P. Fibroblast Growth Factor Signaling and Basement Membrane Assembly Are Connected during Epithelial Morphogenesis of the Embryoid Body. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Shen, Y.-C.; Zhu, A.X. Targeting Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncology 2011, 81, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivapriya, P.M.; Singh, A.; Pandey, P.; Chhabra, N.; Sahoo, A.K.; Paital, B.; Varadwaj, P.K.; Samanta, S.K. Pathways in small cell lung cancer and its therapeutic perspectives. Front. Biosci. 2021, 26, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirica, A.E.; Gores, G.J.; Groopman, J.D.; Selaru, F.M.; Strazzabosco, M.; Wang, X.W.; Zhu, A.X. Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Continuing Challenges and Translational Advances. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Yang, C.; Jin, C.; Xie, R.; Wang, F.; McKeehan, W.L. Novel phosphotyrosine targets of FGFR2IIIb signaling. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Xu, C.-F.; Ma, J.; Eliseenkova, A.V.; Li, W.; Pollock, P.M.; Pitteloud, N.; Miller, W.T.; Neubert, T.A.; Mohammadi, M. A crystallographic snapshot of tyrosine trans -phosphorylation in action. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19660–19665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, A.M.; Singal, A.G.; Tapper, E.B. Contemporary Epidemiology of Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 2650–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.; Park, O.; Gao, B. Abrogation of the Antifibrotic Effects of Natural Killer Cells/Interferon-γ Contributes to Alcohol Acceleration of Liver Fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poynard, T.; McHutchison, J.; Manns, M.; Trepo, C.; Lindsay, K.; Goodman, Z.; Ling, M.; Albrecht, J. Impact of pegylated interferon alfa-2b and ribavirin on liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohamadnejad, M.; Malekzadeh, R.; Nasseri-Moghaddam, S.; Hagh-Azali, S.; Rakhshani, N.; Tavangar, S.M.; Sedaghat, M.; Alimohamadi, S.M. Impact of Immunosuppressive Treatment on Liver Fibrosis in Autoimmune Hepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2005, 50, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czaja, A. Hepatic inflammation and progressive liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efe, C.; Ozaslan, E.; Kav, T.; Purnak, T.; Shorbagi, A.; Ozkayar, O.; Berlot, A.H.; Sökmensuer, C.; Muratori, P. Liver fibrosis may reduce the efficacy of budesonide in the treatment of autoimmune hepatitis and overlap syndrome. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Yim, H.J.; Hwang, J.-W.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Jung, Y.K.; Yim, H.; Kim, B.-H.; Park, H.-C.; Seo, Y.S.; et al. Improved anti-fibrotic effects by combined treatments of simvastatin and NS-398 in experimental liver fibrosis models. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2022, 37, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Huang, L. Nano delivery of simvastatin targets liver sinusoidal endothelial cells to remodel tumor microenvironment for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanapirom, K.; Suksawatamnuay, S.; Tanpowpong, N.; Chaopathomkul, B.; Sriphoosanaphan, S.; Thaimai, P.; Srisoonthorn, N.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Komolmit, P. Non-invasive tests for liver fibrosis assessment in patients with chronic liver diseases: A prospective study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiji, H.; Nagoshi, S.; Akahane, T.; Asaoka, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Kawaguchi, T.; Kurosaki, M.; Sakaida, I.; Shimizu, M.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for Liver Cirrhosis 2020. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Chen, J.; Liang, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhu, L.; Liang, X.; Cai, X. Sorafenib: A potential therapeutic drug for hepatic fibrosis and its outcomes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 88, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Jiang, H. New insights into the antifibrotic effects of sorafenib on hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Wei, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Cai, S.; Fang, L. Sorafenib attenuates liver fibrosis by triggering hepatic stellate cell ferroptosis via HIF-1α/SLC7A11 pathway. Cell Prolif. 2022, 55, e13158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Ghufran, S.M.; Ghose, S.; Biswas, S. Cytoplasmic vacuolation with endoplasmic reticulum stress directs sorafenib induced non-apoptotic cell death in hepatic stellate cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hootegem, A.; Verslype, C.; Van Steenbergen, W. Sorafenib-Induced Liver Failure: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Hepatol. 2011, 2011, 941395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nissim, O.; Melis, M.; Diaz, G.; Kleiner, D.E.; Tice, A.; Fantola, G.; Zamboni, F.; Mishra, L.; Farci, P. Liver Regeneration Signature in Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)-Associated Acute Liver Failure Identified by Gene Expression Profiling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Affo, S.; Dominguez, M.; Lozano, J.J.; Sancho-Bru, P.; Rodrigo-Torres, D.; Morales-Ibanez, O.; Moreno, M.; Millán, C.; Loaeza-Del-Castillo, A.; Altamirano, J.; et al. Transcriptome analysis identifies TNF superfamily receptors as potential therapeutic targets in alcoholic hepatitis. Gut 2013, 62, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, M.; Ammerpohl, O.; von Schönfels, W.; Kolarova, J.; Bens, S.; Itzel, T.; Teufel, A.; Herrmann, A.; Brosch, M.; Hinrichsen, H.; et al. DNA Methylation Analysis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Suggests Distinct Disease-Specific and Remodeling Signatures after Bariatric Surgery. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuominen, I.; Fuqua, B.K.; Pan, C.; Renaud, N.; Wroblewski, K.; Civelek, M.; Clerkin, K.; Asaryan, A.; Haroutunian, S.G.; Loureiro, J.; et al. The Genetic Architecture of Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 11, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.; Fujiwara, N.; Koneru, B.; Ono, A.; Kubota, N.; Jajoriya, A.K.; Tung, M.G.; Crouchet, E.; Song, W.-M.; Marquez, C.A.; et al. Molecular Signature Predictive of Long-Term Liver Fibrosis Progression to Inform Antifibrotic Drug Development. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 1210–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.D.; Trinh, C.H.; Hubball, R.A.; Orritt, K.M.; Lin, C.-C.; Burns, J.E.; Knowles, M.A.; Fishwick, C.W.G. From Fragment to Lead: De Novo Design and Development toward a Selective FGFR2 Inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 1481–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Peinado, A.; Fructuoso-García, K.; Vásquez-Bochm, L.X.; González-Andrade, M. Bisindolylmaleimides New Ligands of CaM Protein. Molecules 2022, 27, 7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Madura, J.D. Relative free energy of binding and binding mode calculations of HIV-1 RT inhibitors based on dock-MM-PB/GS. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2004, 57, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollman, P.A.; Massova, I.; Reyes, C.; Kuhn, B.; Huo, S.; Chong, L.; Lee, M.; Lee, T.; Duan, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Calculating Structures and Free Energies of Complex Molecules: Combining Molecular Mechanics and Continuum Models. Accounts Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkin, I.T.; Xu, H.; Jensen, M.; Arbely, E.; Bennett, E.R.; Bowers, K.J.; Chow, E.; Dror, R.O.; Eastwood, M.P.; Flitman-Tene, R.; et al. Mechanism of Na+/H+ Antiporting. Science 2007, 317, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Q.; Luo, L.; Lei, M.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Su, Z.; et al. Inhibition of FGFR2 Signaling by Cynaroside Attenuates Liver Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040548
Meng Q, Luo L, Lei M, Chen Z, Sun Y, Chen X, Zhai Z, Zhang Y, Cao J, Su Z, et al. Inhibition of FGFR2 Signaling by Cynaroside Attenuates Liver Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(4):548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040548
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Qilin, Lin Luo, Minghua Lei, Zhiqi Chen, Yuanmeng Sun, Xue Chen, Zhaodong Zhai, Yibo Zhang, Jieqiong Cao, Zijian Su, and et al. 2023. "Inhibition of FGFR2 Signaling by Cynaroside Attenuates Liver Fibrosis" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 4: 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040548
APA StyleMeng, Q., Luo, L., Lei, M., Chen, Z., Sun, Y., Chen, X., Zhai, Z., Zhang, Y., Cao, J., Su, Z., Li, F., Li, J., Hong, A., & Chen, X. (2023). Inhibition of FGFR2 Signaling by Cynaroside Attenuates Liver Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals, 16(4), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040548