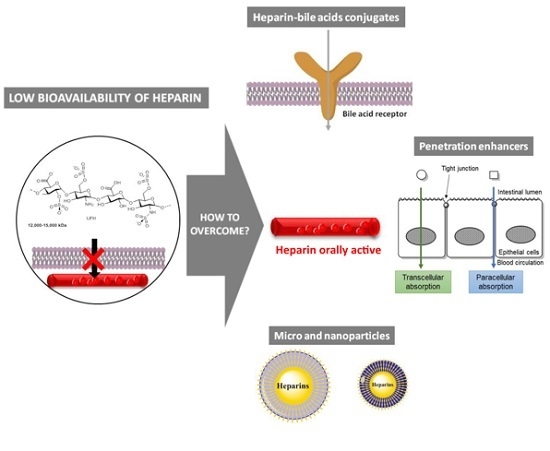
Strategies to Overcome Heparins’ Low Oral Bioavailability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Heparin Conjugates
3. Co-Administration with Penetration Enhancers
3.1. Paracellular Absorption
3.2. Transcellular Absorption
4. Micro and Nanoparticles
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATIII | Antithrombin III |
| DMC | N,N-Dimethyl chitosan |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| DOCA | Deoxycholic acid |
| DOCA-NH2 | N-Deoxycholylethylamine |
| FXa | Factor Xa |
| GA | 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| LMWHs | Low molecular weight heparins |
| MCC | Mono-N-carboxymethyl chitosan |
| PCP-Cys | Polycarbophil-cystein |
| SNAC | Sodium N-(8-[2-hydroxybenzoyl] amino) caprylate |
| SNAD | Sodium N-[10-(2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] decanoate |
| SNOCC | N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan |
| UFH | Unfractioned heparin |
| VKA | Vitamin K antagonists |
References
- Wardrop, D.; Keeling, D. The story of the discovery of heparin and warfarin. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 141, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, C. Heparin and related drugs: Beyond anticoagulant activity. ISRN Pharmacol. 2013, 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugemwa, F.; Shaikh, K.; Hochstedt, E. Facile and efficient acetylation of primary alcohols and phenols with acetic anhydride catalyzed by dried sodium bicarbonate. Catalysts 2013, 3, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone-Bay, A.; Paton, D.R.; Weidner, J.J. The development of delivery agents that facilitate the oral absorption of macromolecular drugs. Med. Res. Rev. 2000, 20, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, J.I. Low-molecular-weight heparins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hirsh, J.; Levine, M. Low molecular weight heparin. Blood 1992, 79, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McRae, S.J.; Ginsberg, J.S. Initial treatment of venous thromboembolism. Circulation 2004, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaques, L.B. Heparins-anionic polyelectrolyte drugs. Pharmacol. Rev. 1979, 31, 99–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Zhao, G.; Liu, D.; Shriver, Z.; Sundaram, M.; Sengupta, S.; Venkataraman, G.; Langer, R.; Sasisekharan, R. Delivery of therapeutic levels of heparin and low-molecular-weight heparin through a pulmonary route. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9867–9872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandik, K.A.; Kruep, D.; Cartier, M.; Linhardt, R.J. Accelerated stability studies of heparin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.Y.; Shin, K.H.; Kim, D.-H.; Jung, E.-A.; Toida, T.; Linhardt, R.J.; Kim, Y.S. Characterization of a bacteroides species from human intestine that degrades glycosaminoglycans. Can. J. Microbiol. 1998, 44, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, B.T.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, N.Y.; Han, M.J.; Shin, K.H.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, Y.S. Degradation of acharan sulfate and heparin by Bacteroides stercoris HJ-15, a human intestinal bacterium. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 1998, 21, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linker, A.; Hovingh, P. Isolation and characterization of oligosaccharides obtained from heparin by the action of heparinase. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, K.A. Pros and cons of new oral anticoagulants. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Progr. 2013, 2013, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, R.J. Therapeutic use of heparin beyond anticoagulation. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2009, 6, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varki, N.M.; Varki, A. Heparin inhibition of selectin-mediated interactions during the hematogenous phase of carcinoma metastasis: Rationale for clinical studies in humans. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2002, 28, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Brown, J.R.; Varki, A.; Esko, J.D. Heparin’s anti-inflammatory effects require glucosamine 6-O-sulfation and are mediated by blockade of l- and P-selectins. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.; Ahsan, F.; Meezan, E.; Pillion, D.J. Nasal administration of low molecular weight heparin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Mustafa, F.; Bai, S.; Ahsan, F. Pulmonary delivery of low molecular weight heparins. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betz, G.; Nowbakht, P.; Imboden, R.; Imanidis, G. Heparin penetration into and permeation through human skin from aqueous and liposomal formulations in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 228, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Orellana, I. Strategies to improve oral drug bioavailability. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, E.; Lee, Y.-K.; Kim, C.Y.; Moon, H.T.; Byun, Y. Absorption study of deoxycholic acid-heparin conjugate as a new form of oral anti-coagulant. J. Control. Release 2007, 120, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Jeon, O.C.; Kim, S.K.; Al-Hilal, T.A.; Moon, H.T.; Kim, C.Y.; Byun, Y. Anticoagulant efficacy of solid oral formulations containing a new heparin derivative. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, J.S.; Koh, K.S.; Al-Hilal, T.A.; Park, J.W.; Jeon, O.C.; Moon, H.T.; Byun, Y. Antithrombotic efficacy of an oral low molecular weight heparin conjugated with deoxycholic asset on microsurgical anastomosis in rats. Thromb. Res. 2010, 126, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, R.; Paliwal, S.R.; Agrawal, G.P.; Vyas, S.P. Biomimetic solid lipid nanoparticles for oral bioavailability enhancement of low molecular weight heparin and its lipid conjugates: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Nam, J.H.; Shin, H.C.; Byun, Y. Conjugation of low-molecular-weight heparin and deoxycholic acid for the development of a new oral anticoagulant agent. Circulation 2001, 104, 3116–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, C.-Y.; Shin, H.-C.; Moon, H.T.; Byun, Y. Efficacy of orally active chemical conjugate of low molecular weight heparin and deoxycholic acid in rats, mice and monkeys. J. Control. Release 2006, 111, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Park, K.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, I.C.; Choi, K.; Kim, C.-Y.; Byun, Y. Evaluation of absorption of heparin-doca conjugates on the intestinal wall using a surface plasmon resonance. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2005, 39, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatun, Z.; Nurunnabi, M.; Cho, K.J.; Lee, Y.-K. Imaging of the GI tract by QDs loaded heparin–deoxycholic acid (DOCA) nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, C.Y.; Nam, J.H.; Moon, H.T.; Byun, Y. A newly developed oral heparin derivative for deep vein thrombosis: Non-human primate study. J. Control. Release 2007, 123, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Vaishali, B.; Lee, E.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.-K.; Kumar, T.S.; Moon, H.T.; Byun, Y. Oral delivery of chemical conjugates of heparin and deoxycholic acid in aqueous formulation. Thromb. Res. 2006, 117, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-K.; Kim, S.; Byun, Y. Oral delivery of new heparin derivatives in rats. Pharm. Res. 2000, 17, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.Y.; Byun, Y. Preparation and characterization of self-assembled nanoparticles of heparin-deoxycholic acid conjugates. Langmuir 2004, 20, 11726–11731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Lee, E.H.; Vaishali, B.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.-K.; Kim, C.-Y.; Moon, H.T.; Byun, Y. Tricaprylin microemulsion for oral delivery of low molecular weight heparin conjugates. J. Control. Release 2005, 105, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hylemon, P.B.; Zhou, H.; Pandak, W.M.; Ren, S.; Gil, G.; Dent, P. Bile acids as regulatory molecules. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notman, R.; Noro, M.; O’Malley, B.; Anwar, J. Molecular basis for dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) action on lipid membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 13982–13983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hilal, T.A.; Park, J.; Alam, F.; Chung, S.W.; Park, J.W.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, I.-S.; Kim, S.Y.; Byun, Y. Oligomeric bile acid-mediated oral delivery of low molecular weight heparin. J. Control. Release 2014, 175, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hilal, T.A.; Chung, S.W.; Alam, F.; Park, J.; Lee, K.E.; Jeon, H.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, I.-S.; Kim, S.Y.; et al. Functional transformations of bile acid transporters induced by high-affinity macromolecules. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, S.A.; Petersen, L.J. Anti-cancer properties of low-molecular-weight heparin: Preclinical evidence. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.; Park, K.; Kim, S.K.; Park, R.W.; Kwon, I.C.; Kim, S.Y.; Byun, Y. Antimetastatic effect of an orally active heparin derivative on experimentally induced metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 2841–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, M.; Chang, H.W.; Moon, H.T.; Byun, Y.; Kim, S.Y. Antiangiogenic activity of orally absorbable heparin derivative in different types of cancer cells. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Son, D.H.; Nam, J.H.; Kim, I.S.; Park, R.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Byun, Y. Suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth by orally active deoxycholic acid-heparin conjugate. J. Control. Release 2007, 118, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatun, Z.; Nurunnabi, M.; Reeck, G.R.; Cho, K.J.; Lee, Y.-K. Oral delivery of taurocholic acid linked heparin-docetaxel conjugates for cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2013, 170, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatun, Z.; Nurunnabi, M.; Cho, K.J.; Byun, Y.; Bae, Y.H.; Lee, Y.-K. Oral absorption mechanism and anti-angiogenesis effect of taurocholic acid-linked heparin-docetaxel conjugates. J. Control. Release 2014, 177, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Al-Hilal, T.A.; Chung, S.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Ryu, G.H.; Son, W.C.; Byun, Y. Antiangiogenic and anticancer effect of an orally active low molecular weight heparin conjugates and its application to lung cancer chemoprevention. J. Control. Release 2015, 199, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, F.; Al-Hilal, T.A.; Chung, S.W.; Seo, D.; Mahmud, F.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Byun, Y. Oral delivery of a potent anti-angiogenic heparin conjugate by chemical conjugation and physical complexation using deoxycholic acid. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6543–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolle-Sander, S.; Lentz, K.A.; Maeda, D.Y.; Coop, A.; Polli, J.E. Increased acyclovir oral bioavailability via a bile acid conjugate. Mol. Pharm. 2004, 1, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Kumar, T.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, Y.-K.; Byun, Y. Synthesis and biological properties of insulin-deoxycholic acid chemical conjugates. Bioconj. Chem. 2005, 16, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, B.S.; Wynder, E.L. Large-bowel carcinogenesis: Fecal constituents of populations with diverse incidence rates of colon cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1973, 50, 1437–1442. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reddy, B.S.; Wynder, E.L. Metabolic epidemiology of colon cancer: Fecal bile acids and neutral sterols in colon cancer patients and patients with adenomatous polyps. Cancer 1977, 39, 2533–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajouz, H.; Mukherji, D.; Shamseddine, A. Secondary bile acids: An underrecognized cause of colon cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 12, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hilal, T.A.; Alam, F.; Byun, Y. Oral drug delivery systems using chemical conjugates or physical complexes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 845–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W.; Kim, S.K.; Al-Hilal, T.A.; Jeon, O.C.; Moon, H.T.; Byun, Y. Strategies for oral delivery of macromolecule drugs. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2010, 15, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aungst, B.J. Intestinal permeation enhancers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlekar, N.A.; Srivenugopal, K.S.; Wachtel, M.S.; Youan, B.B. Modulation of gastrointestinal permeability of low-molecular-weight heparin by l-arginine: In vivo and in vitro evaluation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motlekar, N.A.; Srivenugopal, K.S.; Wachtel, M.S.; Youan, B.B.C. Evaluation of the oral bioavailability of low molecular weight heparin formulated with glycyrrhetinic acid as permeation enhancer. Drug Dev. Res. 2006, 67, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, T.; Sakai, M.; Ohtake, H.; Azuma, H.; Otagiri, M. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the enhancing activity of glycyrrhizin on the intestinal absorption of drugs. Pharm. Res. 1999, 16, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisamitsu Pharmaceutical. Products. Available online: http://www.hisamitsu.co.jp/english/products/ (accessed on 24 February 2016).
- Jiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Shen, S.; Xiao, T.; Li, Y. Discovery of glycyrrhetinic acid as an orally active, direct inhibitor of blood coagulation factor xa. Thromb. Res. 2014, 133, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Greimel, A. Thiomers. Am. J. Drug Deliv. 2005, 3, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanou, M.; Nihot, M.; Jansen, M.; Verhoef, J.C.; Junginger, H. Mono-N-carboxymethyl chitosan (MCC), a polyampholytic chitosan derivative, enhances the intestinal absorption of low molecular weight heparin across intestinal epithelia in vitro and in vivo. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanou, M.; Henderson, S.; Kydonieus, A.; Elson, C. N-sulfonato-N,O-carboxymethylchitosan: A novel polymeric absorption enhancer for the oral delivery of macromolecules. J. Control. Release 2007, 117, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, P.V.A.; Souza, P.R.; Follmann, H.D.M.; Pereira, A.G.B.; Martins, A.F.; Rubira, A.F.; Muniz, E.C. N,N-dimethyl chitosan/heparin polyelectrolyte complex vehicle for efficient heparin delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 75, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Mi, J.; Huo, Y.; Huang, X.; Xing, J.; Yamamoto, A.; Gao, Y. Absorption enhancing effects of chitosan oligomers on the intestinal absorption of low molecular weight heparin in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 466, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kast, C.E.; Guggi, D.; Langoth, N.; Bernkop-Schnurch, A. Development and in vivo evaluation of an oral delivery system for low molecular weight heparin based on thiolated polycarbophil. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanou, M.; Verhoef, J.C.; Nihot, M.T.; Verheijden, J.H.; Junginger, H.E. Enhancement of the intestinal absorption of low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) in rats and pigs using carbopol 934P. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 1638–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanou, M.; Verhoef, J.; Junginger, H. Oral drug absorption enhancement by chitosan and its derivatives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 52, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, T.; Leitner, V.M.; Bernkop-Schnurch, A. Oral heparin delivery: Design and in vivo evaluation of a stomach-targeted mucoadhesive delivery system. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Matsuura, A.; Rama Prasad, Y.V.; Takada, K. Studies on the intestinal absorption of low molecular weight heparin using saturated fatty acids and their derivatives as an absorption enhancer in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama Prasad, Y.V.; Minamimoto, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Shibata, N.; Mori, S.; Matsuura, A.; Takada, K. In situ intestinal absorption studies on low molecular weight heparin in rats using labrasol as absorption enhancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 271, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Kusawake, T.; Prasad, Y.V.R.; Sugioka, N.; Shibata, N.; Takada, K. Preparation and evaluation of oral solid heparin using emulsifier and adsorbent for in vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 317, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkov, D.; Wang, H.Z.; Dinh, S.; Gomez-Orellana, I. Pathway of oral absorption of heparin with sodium N-[8-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)amino] caprylate. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineo, G.; Hull, R.; Marder, V. Oral delivery of heparin: SNAC and related formulations. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2004, 17, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkowitz, S.D.; Marder, V.J.; Kosutic, G.; Baughman, R.A. Oral heparin administration with a novel drug delivery agent (SNAC) in healthy volunteers and patients undergoing elective total hip arthroplasty. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 1, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salartash, K.; Gonze, M.D.; Leone-Bay, A.; Baughman, R.; Sternbergh, W.C., III; Money, S.R. Oral low-molecular weight heparin and delivery agent prevents jugular venous thrombosis in the rat. J. Vasc. Surg. 1999, 30, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emisphere Technologies. Emisphere Technologies Announces Clinical Data on Solid Oral Heparin Formulations. Available online: http://ir.emisphere.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=356222 (accessed on 22 February 2016).
- Baughman, R.A.; Kapoor, S.C.; Agarwal, R.K.; Kisicki, J.; Catella-Lawson, F.; FitzGerald, G.A. Oral delivery of anticoagulant doses of heparin: A randomized, double-blind, controlled study in humans. Circulation 1998, 98, 1610–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, S.A.; Zhang, F.; Aljada, A.; Chaturvedi, S.; Takieddin, M.; Zhang, H.; Chi, L.; Castelli, M.C.; Friedman, K.; Goldberg, M.M.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral heparin solid dosage form in healthy human subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 47, 1508–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emisphere Technologies. Emisphere Technologies Presents First Analysis of Protect Trial at the Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology. Available online: http://ir.emisphere.com/releasedetail.cfm?ReleaseID=356230 (accessed on 3 April 2016).
- Hayes, P.Y.; Ross, B.P.; Thomas, B.G.; Toth, I. Polycationic lipophilic-core dendrons as penetration enhancers for the oral administration of low molecular weight heparin. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.K.; Byun, Y. Lipophilic complexation of heparin based on bile acid for oral delivery. J. Control. Release 2007, 123, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahim, A.S.; Ziora, Z.M.; Bergeon, J.A.; Moss, A.R.; Toth, I. Design and synthesis of a series of novel, cationic liposaccharide derivatives as potential penetration enhancers for oral drug delivery. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 9436–9442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Kast, C.; Guggi, D. Permeation enhancing polymers in oral delivery of hydrophilic macromolecules: Thiomer/GSH systems. J. Control. Release 2003, 93, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffart, V.; Lamprecht, A.; Maincent, P.; Lecompte, T.; Vigneron, C.; Ubrich, N. Oral bioavailability of a low molecular weight heparin using a polymeric delivery system. J. Control. Release 2006, 113, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffart, V.; Ubrich, N.; Lamprecht, A.; Bachelier, K.; Vigneron, C.; Lecompte, T.; Hoffman, M.; Maincent, P. Microencapsulation of low molecular weight heparin into polymeric particles designed with biodegradable and nonbiodegradable polycationic polymers. Drug Deliv. 2003, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffart, V.; Ubrich, N.; Simonin, C.; Babak, V.; Vigneron, C.; Hoffman, M.; Lecompte, T.; Maincent, P. Low molecular weight heparin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles: Formulation, characterization, and release characteristics. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2002, 28, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Ubrich, N.; Hoffart, V.; Marchand-Arvier, M.; Vigneron, C.; Hoffman, M.; Maincent, P. Anticoagulant activity of heparin following oral administration of heparin-loaded microparticles in rabbits. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.; Ubrich, N.; Marchand-Arvier, M.; Vigneron, C.; Hoffman, M.; Lecompte, T.; Maincent, P. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of oral heparin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles in rabbits. Circulation 2002, 105, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.Y.; Ubrich, N.; Hoffart, V.; Marchand-Arvier, M.; Vigneron, C.; Hoffman, M.; Maincent, P. Preparation and characterization of heparin-loaded polymeric microparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2002, 28, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, Y.Y.; Ubrich, N.; Marchand-Arvier, M.; Vigneron, C.; Hoffman, M.; Maincent, P. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of heparin-loaded polymeric nanoparticles. Drug Deliv. 2001, 8, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, M.M.; Linhardt, R.J. Heparin-based nanoparticles. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 2, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alf, L.; Petra, K.; Nathalie, U.; Philippe, M.; Dirk, N. Low molecular weight heparin nanoparticles: Mucoadhesion and behaviour in Caco-2 cells. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3673. [Google Scholar]
- Lamprecht, A.; Ubrich, N.; Maincent, P. Oral low molecular weight heparin delivery by microparticles from complex coacervation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.C.; Wong, H.S.; Lin, K.J.; Chen, H.L.; Wey, S.P.; Sonaje, K.; Lin, Y.H.; Chu, C.Y.; Sung, H.W. The characteristics, biodistribution and bioavailability of a chitosan-based nanoparticulate system for the oral delivery of heparin. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6629–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagre, A.P.; Jain, K.; Jain, N.K. Alginate coated chitosan core shell nanoparticles for oral delivery of enoxaparin: In vitro and in vivo assessment. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paliwal, R.; Paliwal, S.R.; Agrawal, G.P.; Vyas, S.P. Chitosan nanoconstructs for improved oral delivery of low molecular weight heparin: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 422, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saupe, A.; Rades, T. Solid lipid nanoparticles. In Nanocarrier Technologies; Mozafari, M.R., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 41–50. [Google Scholar]
- Viehof, A.; Lamprecht, A. Oral delivery of low molecular weight heparin by polyaminomethacrylate coacervates. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 1990–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, M.; Gomez-Orellana, I. Challenges for the oral delivery of macromolecules. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Neves, A.R.; Correia-da-Silva, M.; Sousa, E.; Pinto, M. Strategies to Overcome Heparins’ Low Oral Bioavailability. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9030037
Neves AR, Correia-da-Silva M, Sousa E, Pinto M. Strategies to Overcome Heparins’ Low Oral Bioavailability. Pharmaceuticals. 2016; 9(3):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleNeves, Ana Rita, Marta Correia-da-Silva, Emília Sousa, and Madalena Pinto. 2016. "Strategies to Overcome Heparins’ Low Oral Bioavailability" Pharmaceuticals 9, no. 3: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9030037
APA StyleNeves, A. R., Correia-da-Silva, M., Sousa, E., & Pinto, M. (2016). Strategies to Overcome Heparins’ Low Oral Bioavailability. Pharmaceuticals, 9(3), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph9030037