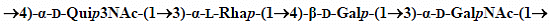Structural Studies of the Lipopolysaccharide from the Fish Pathogen Aeromonas veronii Strain Bs19, Serotype O16
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation of LPS and SDS-PAGE

2.2. Chemical and ESI FT-ICR Mass Spectrometric Analyses of LPS

| Species | Mmeasured water phase | Mmeasured phenol phase | Mcalculated | Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPStriI | 3042.219 | 3042.214 | 3042.203 | Hep5Hex3HexN3KdoP3[14:0(3-OH)]212:0 |
| LPStetraI | 3268.403 | 3268.400 | 3268.397 | Hep5Hex3HexN3KdoP3[14:0(3-OH)]312:0 |
| LPShexaI | 3676.765 | 3676.765 | 3676.757 | Hep5Hex3HexN3KdoP3[14:0(3-OH)]4(12:0)2 |
| SR-LPStriI | 3740.498 | 3740.498 | 3740.480 | 6dHex6dHexNHep5Hex4HexN4KdoP3Ac2[14:0(3-OH)]212:0 |
| SR-LPStetraI | 3966.695 | 3966.694 | 3966.671 | 6dHex6dHexNHep5Hex4HexN4KdoP3Ac2[14:0(3-OH)]312:0 |
| SR-LPShexaI | 4375.077 | 4375.077 | 4375.031 | 6dHex6dHexNHep5Hex4HexN4KdoP3Ac2[14:0(3-OH)]4(12:0)2 |
| LPStetraII | − | 2816.290 | 2816.300 | Hep4Hex2HexN3KdoP2[14:0(3-OH)]312:0-H2O |
| LPStetraIII | − | 2624.231 | 2624.240 | Hep3Hex2HexN3KdoP2[14:0(3-OH)]312:0-H2O |

| Species | Mmeasured water phase | Mmeasured phenol phase | Mcalculated | Composition |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YI | 1134.638 | 1134.639 | 1134.634 | HexN2P2[14:0(3-OH)]212:0 |
| YaI | 1162.673 | 1162.672 | 1162.665 | HexN2P2[14:0(3-OH)]214:0 |
| YII | 1360.830 | 1360.830 | 1360.827 | HexN2P2[14:0(3-OH)]312:0 |
| YaII | 1388.831 | 1388.832 | 1388.859 | HexN2P2[14:0(3-OH)]314:0 |
| YIII | 1769.193 | − | 1769.188 | HexN2P2[14:0(3-OH)]4(12:0)2 |
| BI | 1809.599 | 1809.598 | 1809.598 | Hep5Hex3HexNKdo-2H2O |
| BII | 1907.588 | 1907.588 | 1907.569 | Hep5Hex3HexNKdoP-H2O |
| BIII | 2507.880 | 2507.875 | 2507.866 | 6dHex6dHexNHep5Hex4HexN2KdoAc2-2H2O |
| BIV | 2605.869 | 2605.876 | 2605.843 | 6dHex6dHexNHep5Hex4HexN2KdoPAc2-H2O |
2.3. Structural Studies of the OPS

| Chemical Shifts (ppm) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sugar Residue | H-1 | H-2 | H-3 | H-4 | H-5 | H-6 | |
| C-1 | C-2 | C-3 | C-4 | C-5 | C-6 | ||
| →3)-α-d-GalpNAc-(1→ | A | 5.27 | 4.35 | 3.95 | 4.24 | 4.11 | 3.75 |
| 98.11 | 49.15 | 78.33 | 69.72 | 72.30 | 62.30 | ||
| →3)-α-l-Rhalp-(1→ | B | 5.21 | 4.28 | 3.87 | 3.61 | 3.78 | 1.33 |
| 102.46 | 68.34 | 77.14 | 71.21 | 70.71 | 18.00 | ||
| →4)-α-d-Quip3NAc-(1→ | C | 5.05 | 3.56 | 4.33 | 3.52 | 4.20 | 1.30 |
| 96.03 | 71.50 | 55.09 | 77.44 | 68.24 | 19.00 | ||
| →4)-β-d-Galp-(1→ | D | 4.47 | 3.54 | 3.77 | 4.03 | 3.74 | 3.75 |
| 106.02 | 71.45 | 74.17 | 77.04 | 76.06 | 62.30 | ||


| Species | Mmeasured | Mcalculated | Composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| C4 | 716.286 | 716.284 | [6dHexNAc6dHexHexHexNAc] |
| C5 | 903.372 | 903.369 | [6dHexNAc6dHexHexHexNAc] |
| C6 | 1049.433 | 1049.427 | [6dHexNAc6dHexHexHexNAc]6dHexNAc6dHex |
| C7 | 1211.486 | 1211.479 | [6dHexNAc6dHexHexHexNAc]6dHexNAc6dHexHex |
| C8 | 1414.576 | 1414.558 | [6dHexNAc6dHexHexHexNAc]2 |
| C9 | 1601.669 | 1601.643 | [6dHexNAc6dHexHexHexNAc]26dHexNAc |
| C10 | 1747.724 | 1747.700 | [6dHexNAc6dHexHexHexNAc]26dHexNAc6dHex |
| C12 | 2112.830 | 2112.831 | [6dHexNAc6dHexHexHexNAc]3 |
| Z10 | 1827.612 | 1827.603 | Hep5Hex3HexNKdo-H2O |
| Z12 | 2192.748 | 2192.734 | [HexHexNAc]Hep5Hex3HexNKdo-H2O |
| Z14 | 2525.895 | 2525.876 | [6dHexNAc6dHexHexHexNAc]Hep5Hex3HexNKdo-H2O |
| Z16 | 2891.010 | 2891.007 | [6dHexNAc6dHexHex2HexNAc2]Hep5Hex3HexNKdo-H2O |
| Z17 | 3037.077 | 3037.065 | [6dHexNAc6dHex2Hex2HexNAc2]Hep5Hex3HexNKdo-H2O |
| Z18 | 3224.159 | 3224.145 | [6dHexNAc6dHexHexHexNAc]2Hep5Hex3HexNKdo-H2O |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Bacterial Strain, Cultivation Conditions and Isolation of the LPS
3.2. Isolation of the OPS
3.3. Chemical Analyses
3.4. NMR Spectroscopy
3.5. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
3.6. SDS-PAGE
4. Conclusions
Abbreviations
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| ESI-MS | electrospray ionization mass spectrometry |
| FT-ICR | Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance |
| OPS | O-specific polysaccharide |
| ADP | adenosine diphosphate |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| ESI-FT-ICR | electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance |
| GC-MS | gas chromatography with mass spectrometry |
| DQF-COSY | double quantum filtered correlation spectroscopy |
| NOE | Nuclear Overhauser effect |
| ROESY | rotating frame Overhauser effect spectroscopy |
| TOCSY | total correlation spectroscopy |
| PCR-RFLP | polymerase chain reaction/restriction fragment length polymorphism |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janda, J.M.; Duffy, P.S. Mesophilic aeromonads in human diseases: current taxonomy, laboratory infection and infectious diseases spectrum. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1988, 10, 980–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M. Recent advances in the study of the taxonomy, pathogenicity and infectious syndromes with the genus Aeromonas. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1991, 4, 397–410. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, M.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, A.A.; Sung, K.; Tran, Q.; Kerdahi, K.; Steele, R. Detection and characterization of virulence genes and integrons in Aeromonas veronii isolated from catfish. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.M.; Arribas, R.M.; Pares, R. Distribution of Aeromonas species in waters with different levels of pollution. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1991, 71, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S. The genus Aeromonas: taxonomy, pathogenicity, and infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 35–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Colque-Navarro, P.; Kühn, I.; Huys, G.; Swings, J.; Möllby, R. Identification and characterization of pathogenic Aeromonas veronii bv. sobria associated with epizootic ulcerative syndrome in fish in Bangladesh. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.-H.; Wu, Z.-H.; Jian, J.-C.; Lu, Y.-S.; Tang, J.F. Characterization of pathogenic Aeromonas veronii bv. veronii associated with ulcerative syndrome from Chinese longsnout catfish (Leiocassis longirostris Günther). Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, S.D.; Schell, W.L.; Fanning, G.R.; Wachsmuth, I K.; Blake, P.A.; Brenner, D.J.; Farmer, J.J. Aeromonas intestinal infections in the United States. Ann. Intern. Med. 1986, 105, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Carnahan, A.M.; Altwegg, M.; Luthy-Hottenstein, J.; Joseph, S.W. Aeromonas bestiarum sp. nov. (formerly genomospecies DNA group 2 A. hydrophila), a new species isolated from non human sources. Med. Microbiol.Lett. 1996, 5, 156–165. [Google Scholar]
- Kahajanchi, B.K.; Fadl, A.A.; Borchardt, M.A.; Berg, R.L.; Horneman, A.J.; Stemper, M.E.; Joseph, S.W.; Moyer, N.P.; Sha, J.; Chopra, A.K. Distribution of virulence factors and molecular fingerprinting of Aeromonas species isolates from water and clinical samples: suggestive evidence of water-to-human transmission. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2313–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueras, M.J. Clinical relevance of Aeromonas spp. Rev. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 16, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Murcia, A.J.; Borrell, N.; Figureas, M.J. Typing of clinical and environmental Aeromonas veronii strains based on the 16S-23S rDNA spacers. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 28, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, J.S.G.; Lallier, R.; Shaw, D.H.; Trust, T.J. Electrophoretic and immunochemical analyses of the lipopolysaccharides from various strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 164, 263–269. [Google Scholar]
- Merino, S.; Rubires, X.; Aguillar, A.; Guillot, J.F.; Tomas, J.M. The role of the O-antigen lipopolysaccharide on the colonization in vivo of the germfree chicken gut by Aeromonas hydrophila serogroup O:34. Microb Pathog. 1996, 20, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, A.; Merino, S.; Rubires, X.; Tomas, J. Influence of osmolarity on lipopolysaccharides and virulence of Aeromonas hydrophila serotype O:34 strains grown at 37 degrees C. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Rabaan, A.A.; Gryllos, I.; Tomas, J.M.; Shaw, J.G. Motility and polar flagellum are required for Aeromonas caviae adherence to HEp-2 cells. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 4257–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garduno, R.A.; Moore, A.R.; Oliver, G.; Lizama, A.L.; Garduno, E.; Kay, W.W. Host cell invasion and intracellular resistance by Aeromonas salmonicida: role of the S-layer. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 46, 660–668. [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki, R.; Shimada, T. O-serogrouping for mesophilic Aeromonas strains. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. 1984, 37, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Nandapalan, N.; Chang, B.J. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Aeromonas sobria surface antigens. FEMS Microbiol. Immunol. 1989, 47, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francki, K.T.; Chang, B.J.; Mee, B.J.; Collignon, P.J.; Susai, V.; Keese, P.K. Identification of genes associated with copper tolerance in an adhesion-defective mutant of Aeromonas veronii biovar sobria. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 29, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman-Brenner, F.W.; MacDonald, K.L.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Fanning, G.R.; Brenner, D.J.; Farmer, J.J., III. Aeromonas veronii, a new ornithine decarboxylase-positive species that may cause diarrhea. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 900–906. [Google Scholar]
- Mencacci, A.; Cenci, E.; Mazzolla, R.; Farinella, S.; D’Alo, F.; Vitali, M.; Bistoni, F. Aeromonas veronii biovar veronii septicaemia and acute suppurative cholangitis in a patient with hepatitis B. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.T.M.; Enoch, D.A.; Harris, K.A.; Karas, J.A. Aeromonas veronii biovar sobria bacteraemia with septic arthritis confirmed by 16S rDNA PCR in an immunocompetent adult. J. Med. Microbiol. 2006, 55, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Dacanay, A.; Harrison, B.A.; Fast, M.; Colquhoun, D.J.; Lund, V.; Brown, L.L.; Li, J.; Altman, E. Carbohydrate analysis and serological classification of typical and atypical isolates of Aeromonas salmonicida: A rationale for the lipopolysaccharide-based classification of A. salmonicida. Fish Shellfish Immun. 2007, 23, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Merino, S.; Tomas, J.M. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide of Aeromonas hydrophila O:34; a case of random O-acetylation of 6-deoxy-L-talose. Carbohydr. Res. 2002, 337, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarenko, E.L.; Crawford, R.J.; Iwanowa, E.P. The structural diversity of carbohydrate antigens of selected Gram-negative marine bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1914–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Lindner, B.; Komaniecka, I.; Kozinska, A.; Pekala, A.; Choma, A.; Holst, O. Structural and immunochemical studies of the lipopolysaccharide from the fish pathogen, Aeromonas bestiarum strain K296, serotype O18. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1235–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozinska, A.; Pekala, A. Serotyping of Aeromonas species isolated from Polish fish farms in relation to species and virulence phenotype of the bacteria. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2010, 54, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Kozinska, A.; Russa, R.; Holst, O. The structure of the O-specific polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of Aeromonas bestiarum strain 207. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Guz, L.; Lindner, B.; Pietras, H.; Russa, R.; Holst, O. Structural characterization of the O-specific polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of fish pathogen Aeromonas bestiarum strain P1S. Carbohydr. Res. 2011, 346, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozinska, A.; Figueras, M.J.; Chacon, M.R.; Soler, L. Phenotypic characteristics of Aeromonas genomospecies isolated from common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 93, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, O.; Jann, K. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Extraction with phenol-water and further applications of the procedure. Meth. Carbohydr. Chem. 1965, 5, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Domon, B.; Costello, C.E. A systamatic nomenclature for carbohydrate fragmentations in FAB MS/MS spectra of glycoconjugates. Glycoconj. J. 1988, 5, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, L.L.; Perry, M.B. Structural characterization of the serotype O:5 O-polysaccharide antigen of the lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli O:5. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1997, 75, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Lindner, B.; Pekala, A.; Palusinska-Szysz, M.; Choma, A.; Russa, R.; Holst, O. Structural analysis of the O-specific polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of Aeromonas veronii bv. sobria strain K49. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 353, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leontein, K.; Lindberg, B.; Lönngren, J. Assignment of absolute configuration of sugars by GLC of their acetylated glycosides formed from chiral alcohols. Carbohydr. Res. 1978, 62, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkind, G.M.; Shashkov, A.S.; Knirel, Y.A.; Vinogradov, E.V.; Kochetkov, N.K. A computer-assisted structural analysis of regular polysaccharides on the basis of 13C-n.m.r. data. Carbohydr. Res. 1988, 175, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashkov, A.S.; Vinogradov, E.V.; Knirel, Y.A.; Nifant’ev, N.E.; Kochetkov, N.K.; Dabrowski, J.; Kholodkova, E.V.; Stanislavsky, E.S. Structure of the O-specific polysaccharide of Salmonella arizonae O45. Carbohydr. Res. 1993, 241, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashkov, A.S.; Paramonov, N.A.; Veremeychenko, S.P.; Grosskurth, H.; Zdorovenko, G.M.; Knirel, Y.A.; Kochetkov, N.K. Somatic antigens of pseudomonads: structure of the O-specific polysaccharide of Pseudomonas fluorescens biovar B, strain IMV 247. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 306, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senchenkova, S.N.; Shashkov, A.S.; Laux, P.; Knirel, Y.A.; Rudolph, K. The O-chain polysaccharide of Xanthomonas campestris pv. begoniae GSPB 525 is a partially l-xylosylated rhamnan. Carbohydr. Res. 1999, 319, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carillo, S.; Silipo, A.; Perino, V.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Molinaro, A. The structure of the O-specific polysaccharide from the lipopolysaccharide of Burkholderia anthina. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 1697–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzenellenbogen, E.; Romanowska, E.; Kocharova, N.A.; Knirel, Y.A.; Shashkov, A.S.; Kochetkov, N.K. Structure of a glycerol teichoic acid-like O-specific polysaccharide of Hafnia alvei 1205. Carbohydr. Res. 1992, 231, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silipo, A.; Leone, S.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Sturiale, L.; Garozzo, D.; Nazarenko, E.L.; Gorshkova, R.P.; Ivanova, E.P.; Gorshkova, N.M.; Molinaro, A. The complete structure of the lipooligosaccharide from the halophilic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas issachenkonii KMM 3549T. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 1985–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, P.E.; Kenne, L.; Widmalm, G. Computer-assisted structural analysis of polysaccharides with an extended version of CASPER using 1H- and 13C-NMR data. Carbohydr. Res. 1989, 188, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toukach, F.V.; Bartodziejska, B.; Senchenkova, S.N.; Wykrota, M.; Shashkov, A.S.; Rozalski, A.; Knirel, Y.A. Structure of a new acidic O-antigen of Proteus vulgaris O22 containing O-acetylated 3-acetamido-3,6-dideoxy-d-glucose. Carbohydr. Res. 1999, 318, 146–153. [Google Scholar]
- Vinogradov, E.V.; Petersen, B.O.; Thomas-Oates, J.E.; Duus, J.O.; Brade, H.; Holst, O. Characterization of a novel branched tetrasaccharide of 3-deoxy-d-manno-oct-2-ulopyranosonic acid. The structure of the carbohydrate backbone of the lipopolysaccharide from Acinetobacter baumannii strain NCTC 10303 (ATCC 17904). J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 28122–28131. [Google Scholar]
- Kumirska, J.; Szafranek, J.; Czerwicka, M.; Paszkiewicz, M.; Dziadziuszko, H.; Kunikowska, D.; Stepnowski, P. The structure of the O-specific polysaccharide isolated from the lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella Dakar (serogroup O:28). Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2138–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, L.L.; Vinogradov, E.; Perry, M.B. The structure of the antigenic O-polysaccharide in the lipopolysaccharide of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli serotype O71:H12. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2010, 88, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziadziuszko, H.; Kumirska, J.; Muża, S.; Czerwicka, M.; Lubecka, E.A.; Stepnowski, P.; Kunikowska, D. Immunochemical studies of Salmonella Dakar and Salmonella Telaviv O-antigens (serogroup O:28). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 326, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaniecka, I.; Choma, A.; Lindner, B.; Holst, O. The structure of a novel lipid A from the lipopolysaccharide of Bradyrhizobium elkanii containing three mannose units in the backbone. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 2922–2929. [Google Scholar]
- Russa, R.; Urbanik-Sypniewska, T.; Lindström, K.; Mayer, H. Chemical characterization of two lipopolysaccharide species isolated from Rhizobium loti NZP2213. Arch. Microbiol. 1995, 163, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakomori, S. A rapid permethylation of glycolipid and polysaccharide catalyzed by methylsulfinyl carbanion in dimethyl sulfoxide. J. Biochem. 1964, 55, 205–208. [Google Scholar]
- Pieretti, G.; Corsaro, M.M.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Vilches, S.; Merino, S.; Tomas, J.M. Structure of the core region from the lipopolysaccharide of Plesiomonas shigelloides strain 302-73 (serotype O1). Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 2009, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondakova, A.; Lindner, B. Structural characterization of complex bacterial glycolipids by Fourier transform ion cyclotron mass spectrometry. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 11, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, G.; Lindner, B.; Brabetz, W.; Brade, H.; Raina, S. Escherichia coli K-12 suppressor-free mutants lacking early glycosyltransferases and late acyltransferases: minimal lipopolysaccharide structure and induction of envelope stress response. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 15369–15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Palusinska-Szysz, M.; Russa, R. Structural studies of O-polysaccharide chain from the lipopolysaccharide of symbiotically enhanced mutant Mlo-13 of Mesorhizobium loti NZP2213. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raetz, C.R.H.; Whitfield, C. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 635–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, Q.; Cao, B.; He, X.; Li, K.; Feng, L.; Wang, L. Genetic analysis of the Cronobacter sakazakii O4 to O7 O-antigen gene clusters and development of a PCR assay for identification of all C. sakazakii O serotypes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3966–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knirel, Y.A.; Vinogradov, E.; Jimenez, N.; Merino, S.; Tomas, J.M. Structural studies on the R-type lipopolysaccharide of Aeromonas hydrophila. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, N.; Canals, R.; Lacasta, A.; Kondakova, A.; Lindner, B.; Knirel, Y.A.; Merino, S.; Regue, M.; Tomas, J.M. Molecular analysis of three Aeromonas hydrophila AH-3 (Serotype O34) lipopolysaccharide core biosynthesis gene clusters. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 3176–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Turska-Szewczuk, A.; Duda, K.A.; Schwudke, D.; Pekala, A.; Kozinska, A.; Holst, O. Structural Studies of the Lipopolysaccharide from the Fish Pathogen Aeromonas veronii Strain Bs19, Serotype O16. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1298-1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12031298
Turska-Szewczuk A, Duda KA, Schwudke D, Pekala A, Kozinska A, Holst O. Structural Studies of the Lipopolysaccharide from the Fish Pathogen Aeromonas veronii Strain Bs19, Serotype O16. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(3):1298-1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12031298
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurska-Szewczuk, Anna, Katarzyna A. Duda, Dominik Schwudke, Agnieszka Pekala, Alicja Kozinska, and Otto Holst. 2014. "Structural Studies of the Lipopolysaccharide from the Fish Pathogen Aeromonas veronii Strain Bs19, Serotype O16" Marine Drugs 12, no. 3: 1298-1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12031298
APA StyleTurska-Szewczuk, A., Duda, K. A., Schwudke, D., Pekala, A., Kozinska, A., & Holst, O. (2014). Structural Studies of the Lipopolysaccharide from the Fish Pathogen Aeromonas veronii Strain Bs19, Serotype O16. Marine Drugs, 12(3), 1298-1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12031298