Bioactive Hydantoin Alkaloids from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Hemimycale arabica
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Purification of Compounds 1–3
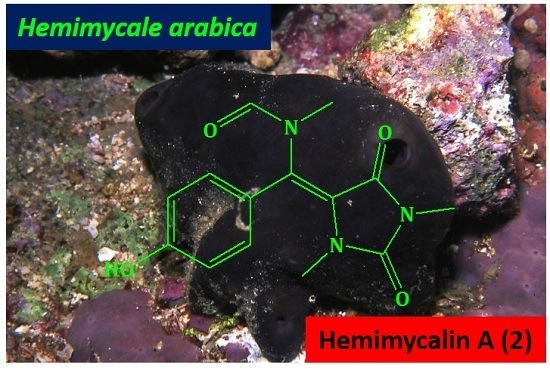
2.2. Structure Elucidation of Compound 1–3

| Position | δC | δH (m, J in Hz) | HMBC (H→C) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 155.7, qC | ||
| 4 | 165.7, qC | H-6 | |
| 5 | 125.3, qC | ||
| 6 | 109.2, CH | 6.33 (s) | H-8, H-12 |
| 7 | 123.8, qC | H-9, H-11 | |
| 8 | 131.2, CH | 7.46 (d, 9.0) | H-6 |
| 9 | 115.6, CH | 6.76 (d, 9.0) | |
| 10 | 158.0, qC | H-8, H-9, H-11, H-12 | |
| 11 | 115.6, CH | 6.76 (d, 9.0) | |
| 12 | 131.2, CH | 7.46 (d, 9.0) | H-6 |
| NH, OH | 10.0-10.5 (br s) |
| Position | δC | δH (m, J in Hz) | HMBC (H→C) a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 153.4, qC | H3-13, H3-14 | |
| 4 | 149.9, qC | H3-14 | |
| 5 | 93.8, qC | H3-13 | |
| 6 | 126.0, qC | H-8, H-12, H3-15 | |
| 7 | 124.6, qC | H-9, H-11 | |
| 8 | 131.1, CH | 7.44 (d, 8.4) | |
| 9 | 115.6, CH | 6.75 (d, 8.4) | |
| 10 | 159.4, qC | H-8, H-9, H-11, H-12 | |
| 11 | 115.6, CH | 6.75 (d, 8.4) | |
| 12 | 131.1, CH | 7.44 (d, 8.4) | |
| 13 | 31.2, CH3 | 2.77 (s) | |
| 14 | 29.3, CH3 | 3.23 (s) | |
| 15 | 33.5, CH3 | 2.80 (s) | H-16 |
| 16 | 166.1, CH | 7.89 (s) | H3-15 |
| OH | 10.88 (br s) |

| Position | δC | δH (m, J in Hz) | HMBC a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 156.6, qC | H3-13 | |
| 4 | 166.2, qC | H-6, H-13 | |
| 5 | 125.7, qC | H-6 | |
| 6 | 112.9, CH | 6.52 (s) | H-12 |
| 7 | 125.0, qC | H-6, H-9, H-11 | |
| 8 | 132.2, CH | 7.33 (d, 8.4) | H-6 |
| 9 | 117.0, CH | 6.83 (d, 8.4) | |
| 10 | 159.9, qC | H-8, H-9, H-11, H-12 | |
| 11 | 117.0, CH | 6.83 (d, 8.4) | |
| 12 | 132.2, CH | 7.33 (d, 8.4) | |
| 13 | 44.4, CH | 4.64 (m) | H3-17 |
| 14 | 47.0, CH2 | 3.35 b 3.00 (dd, 18.0, 6.0) | H3-16, H3-17 |
| 15 | 208.6, qC | H2-14, H3-16 | |
| 16 | 29.9, CH3 | 2.12 (s) | H3-15 |
| 17 | 18.7, CH3 | 1.36 (d, 7.2) | |
| NH | 10.47 (br hump) |
2.3. Biological Activities of the Isolated Compounds
| Compound | Antiproliferation Activity (IC50, μg/mL) | Antimicrobial Activity Inhibition Zone (mm) at 100 μg/disc | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HeLa Cell | S. aureus | E. coli | C. albicans | |
| Compound 1 | 28.3 | NI | 18 | 22 |
| Compound 2 | >50 | NI | 10 | 14 |
| Compound 3 | >50 | NI | 20 | 20 |
| Paclitaxel a | 0.0014 | - | - | - |
| Ciprofloxacin b | - | 22 | 30 | - |
| Ketoconazole c | - | - | - | 30 |
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Biological Materials

3.3. Purification of Compounds 1–3
3.4. Spectroscopic Data of Compounds 1–3
3.5. Biological Evaluation of Compounds 1–3
3.5.1. Determination of the Antimicrobial Activities Using the Disc Diffusion Assay
3.5.2. Evaluation of Antiproliferative and Cytotoxic Activities against HeLa Cells
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Marine natural products and related compounds in clinical and advanced preclinical trials. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1216–1238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 116–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebada, S.S.; Proksch, P. The Chemistry of Marine Sponges. In Handbook of Marine Natural Products; Fattorusso, E., Gerwick, W.H., Taglialatela-Scafati, O., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 191–293. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, R.W.M.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Vacelet, J.; Dohrmann, M.; Epenbeck, D.; de Voogd, N.J.; Santodomingo, N.; Vanhoorne, B.; Kelly, M.; Hooper, J.N.A. Global Diversity of Sponges (Porifera). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laport, M.S.; Santos, O.C.S.; Muricy, G. Marine sponges: Potential sources of new antimicrobial drugs. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009, 10, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Glaser, K.B.; Cuevas, C.; Jacobs, R.S.; Kem, W.; Little, R.D.; McIntosh, J. M.; Newman, D.J.; Potts, B.C.; Shuster, D.E. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: A current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, I.; Kusumi, T.; Kakisawa, H.; Kashman, Y.; Hirsh, S. Structure and chemical properties of ptilomycalin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 8472–8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashman, Y.; Hirsh, S.; McConnell, O.J.; Ohtani, I.; Kusumi, T.; Kakisawa, H. Ptilomycalin A: A novel polycyclic guanidine alkaloid of marine origin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 8925–8926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.A.; Lemke, T.L. (Eds.) Foye’s Principles of Medicinal Chemistry, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: New York, NY, USA, 2002.
- Kleemann, A.; Engel, J.; Kutscher, B.; Reichert, D. Pharmaceutical Substances: Synthesis, Patents, Applications, 4th ed.; Thieme Medical: Leipzig, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Malawska, B. New anticonvulsant agents. Curr. Topics Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrtus, H.; Obniska, J.; Czopek, A.; Kaminski, K.; Pawlowski, M. Synthesis and anticonvulsant activity of new N-Mannich bases derived from 5-cyclopropyl-5-phenyl- and 5-cyclopropyl-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-imidazolidine-2,4-diones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6149–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiallo, M.M.L.; Kozlowski, H.; Garnier-Suillerot, A. Mitomycin antitumor compounds. Part 1. CD studies on their molecular structure. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 12, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoriou, M.; Noble, M.E.M.; Watson, K.A.; Garman, E.F.; Krulle, T.M.; Delafuente, C.; Fleet, G.W.J.; Oikonomakos, N.G.; Johnson, L.N. The structure of a glycogen phosphorylase glucopyranose spirohydantoin complex at 1.8 angstrom resolution and 100 k—The role of the water structure and its contribution to binding. Protein Sci. 1998, 7, 915–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiozaki, M. Syntheses of hydantocidin and C-2 thioxohydantocidin. Carbohyd. Res. 2002, 337, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfar, M.A.; Hill, R.A.; Kaddoumi, A.; El Sayed, K.A. Discovery of novel GSK-3 beta inhibitors with potent in vitro and in vivo activities and excellent brain permeability using combined ligand- and structure-based virtual screening. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8534–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudit, M.; Khanfar, M.A.; Muralidharan, A.; Thomas, S.; Shah, G.V.; van Soest, R.W.; El Sayed, K.A. Discovery, design, and synthesis of anti-metastatic lead phenylmethylene hydantoins inspired by marine natural products. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1731–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanfar, M.A.; Abu Asal, B.; Mudit, M.; Kaddoumi, A.; El Sayed, K.A. The marine natural-derived inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3β phenylmethylene hydantoins: In vitro and in vivo activities and pharmacophore modeling. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6032–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Ang, K.; Jayachandran, H.; Fong, Y. Substituent effects in 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance correlations of chemical shifts in para-substituted 5-arylmethylenehydantoins. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1987, 2, 1043–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brastianos, H.C.; Vottero, E.; Patrick, B.O.; van Soest, R.; Matainaho, T.; Mauk, G.; Andersen, R.J. Exiguamine A, an indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) inhibitor isolated from the marine sponge Neopetrosia exigua. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16046–16047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balansa, W.; Islam, R.; Gilbert, D.F.; Fontaine, F.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H.; Piggott, A.M.; Lynch, J.W.; Capon, R.J. Australian marine sponge alkaloids as a new class of glycine-gated chloride channel receptor modulator. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 4420–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, X.; Luo, X.; de Voogd, N.J.; Li, P.; Li, G. (+)- and (−)-Spiroreticulatine, a pair of unusual spiro bisheterocyclic quinoline-imidazole alkaloids from the South China Sea sponge Fascaplysinopsis reticulata. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 3458–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preecha Phuwapraisirisan, P.; Shigeki Matsunaga, S.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Fusetani, N. Isolation of a new mycalolide from the marine sponge Mycale izuensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 942–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Keiichirou Koimaru, K.; Ohta, T. Secomycalolide A: A new proteasome inhibitor isolated from a marine sponge of the genus Mycale. Mar. Drugs 2005, 3, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiehlbauch, J.A.; Hannett, G.E.; Salfinger, M.; Archinal, W.; Monserrat, C.; Carlyn, C. Use of the national committee for clinical laboratory standards guidelines for disk diffusion susceptibility testing in New York state laboratories. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3341–3348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyd, M.R.; Paull, K.D. Some practical considerations and applications of the National Cancer Institute in vitro anticancer discovery screen. Drug Dev. Res. 1995, 34, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skehan, P.; Storeng, R.; Scudiero, D.; Monks, A.; McMahon, J.; Vistica, D.; Warren, J.T.; Bokesch, H.; Kenney, S.; Boyd, M.R. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risinger, A.L.; Jackson, E.M.; Polin, L.A.; Helms, G.L.; LeBoeuf, D.A.; Joe, P.A.; Hopper-Borge, E.; Ludueña, R.F.; Kruh, G.D.; Mooberry, S.L. The taccalonolides: Microtubule stabilizers that circumvent clinically relevant taxane resistance mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8881–8888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youssef, D.T.A.; Shaala, L.A.; Alshali, K.Z. Bioactive Hydantoin Alkaloids from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Hemimycale arabica. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6609-6619. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116609
Youssef DTA, Shaala LA, Alshali KZ. Bioactive Hydantoin Alkaloids from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Hemimycale arabica. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(11):6609-6619. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116609
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoussef, Diaa T. A., Lamiaa A. Shaala, and Khalid Z. Alshali. 2015. "Bioactive Hydantoin Alkaloids from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Hemimycale arabica" Marine Drugs 13, no. 11: 6609-6619. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116609
APA StyleYoussef, D. T. A., Shaala, L. A., & Alshali, K. Z. (2015). Bioactive Hydantoin Alkaloids from the Red Sea Marine Sponge Hemimycale arabica. Marine Drugs, 13(11), 6609-6619. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116609