Fish Synucleins: An Update
Abstract
:1. From Fish to Human: The Discovery of the Synuclein Family
2. Syn Isoforms in Agnathans and Fishes
| Class | Subclass | Order | Family | Species | Alpha synuclein (identity with human α-syn) | Beta synuclein (identity with human β-syn) | Gamma synuclein (identity with human γ-syn) | Synuclein-like (identity with human α-syn) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petromyzontida | Petromyzontiformes | Petromyzontidae | Petromyzon marinus | 67%1 | 53%2 | 52%3 | ||||||||||||
| Chondrichthyes | Holocephali | Chimaeriformes | Callorhinchidae | Callorhinchus milii | 74%4,5 | 78%6–8 | 61%9 | 54%10 | ||||||||||
| Elasmobranchii | Torpediniformes | Torpedinidae | Torpedo californica | 59%11 | ||||||||||||||
| Actinopterygii | Chondrostei | Acipenseriformes | Acipenseridae | Acipenser sturio | 94%12* | |||||||||||||
| Neopterygii | Lepisosteiformes | Lepisosteidae | Lepisosteus oculatus | 82%13 | 61%14 | |||||||||||||
| Neopterygii, Division Teleostei | Osteoglossiformes | Osteoglossidae | Scleropages formosus | 50%15 | ||||||||||||||
| Cypriniformes | Cyprinidae | Cyprinus carpio | 99%16* | |||||||||||||||
| Danio rerio | 71%17–20 | 50%21–23 | 52%24,25 | |||||||||||||||
| Characiformes | Characidae | Astyanax mexicanus | 55%26 | 35%27 | 60%28 | 53%29 | 28%30 | 52%31 | ||||||||||
| Siluriformes | Siluridae | Silurus glanis | 99%32* | |||||||||||||||
| Osmeriformes | Osmeridae | Osmerus mordax | 68%33 | |||||||||||||||
| Salmoniformes | Salmonidae | Salmo salar | 51%34,35 | 50%36,37 | 54%38 | 53%39,40 | 43%41 | |||||||||||
| Esociformes | Esocidae | Esox lucius | 52%42–44 | 46%45 | 51%46 | 56%47,48 | 56%49 | 55%50 | 54%51 | 58%52 | 53%53,54 | 43%55 | ||||||
| Beloniformes | Adrianichthyidae | Oryzias latipes | 61%56,57 | 57%58 | 59%59,60 | 49%61 | 50%62 | 55%63 | ||||||||||
| Cyprinodontiformes | Poeciliidae | Poecilia formosa | 62%64 | 46%65 | 61%66 | 55%67 | 46%68 | |||||||||||
| Poecilia reticulata | 62%69 | 46%70 | 62%71 | 55%72 | 46%73 | |||||||||||||
| Xiphophorus maculatus | 62%74 | 61%75,76 | 56%77 | 55%78 | 50%79 | |||||||||||||
| Scorpaeniformes | Anoplopomatidae | Anoplopoma fimbria | 59%80 | |||||||||||||||
| Perciformes | Cichlidae | Astatotilapia burtoni | 61%81 | 52%82 | 60%83 | 61%84,85 | 56%86 | |||||||||||
| Maylandia zebra | 61%87 | 61%88,89 | 55%90 | 53%91 | 57%92 | |||||||||||||
| Neolamprologus brichardi | 48%93 | 61%94 | 61%95,96 | 57%97 | ||||||||||||||
| Oreochromis niloticus | 60%98 | 57%99 | 52%100 | 60%101 | 61%102 | 61%103 | ||||||||||||
| Pundamilia nyererei | 61%104 | 52%105 | 60%106 | 61%107,108 | 57%109 | |||||||||||||
| Pomacentridae | Stegastes partitus | 50%110 | 54%111 | 61%112 | 51%113 | 50%114 | 50%115 | 56%116 | ||||||||||
| Nototheniidae | Notothenia coriceps | 43%117 | 58%118 | 58%119 | ||||||||||||||
| Sciaenidae | Larimichthys crocea | 61%120 | 62%121 | 53%122 | 57%123 | |||||||||||||
| Pleuronectiformes | Cynoglossidae | Cynoglossus semilaevis | 54%124,125 | 60%126 | 50%127 | 51%128 | 50%129 | 55%130 | ||||||||||
| Tetraodontiformes | Tetraodontidae | Takifugu rubripes | 61%131,132 | 61%133 | 60%134–136 | 55%137,138 | 52%129,140 | 52%141 | ||||||||||
| Sarcopterygii | Coelacanthimorpha | Coelacanthiformes | Latimeriidae | Latimeria chalumnae | 83%142 | 86%143 | 60%144 | |||||||||||

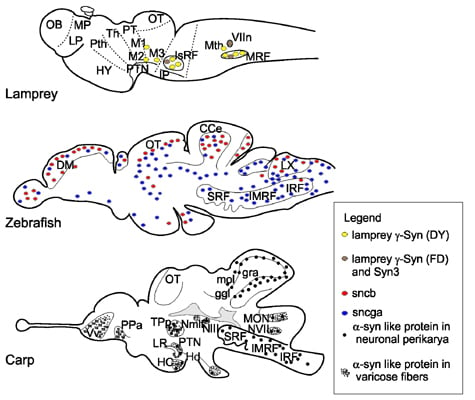
3. Gene Expression and Localization of Synucleins in Fish

4. Functions of Fish Synucleins
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Carlson, S.S.; Kelly, R.B. An antiserum specific for cholinergic synaptic vesicles from electric organ. J. Cell Boil. 1980, 87, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroteaux, L.; Campanelli, J.T.; Scheller, R.H. Synuclein: A neuron-specific protein localized to the nucleus and presynaptic nerve terminal. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 2804–2815. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, K.; Fukushima, H.; Masliah, E.; Xia, Y.; Iwai, A.; Yoshimoto, M.; Otero, D.A.; Kondo, J.; Ihara, Y.; Saitoh, T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding an unrecognized component of amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11282–11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobe, T.; Nakajo, S.; Tanaka, A.; Mitoya, A.; Omata, K.; Nakaya, K.; Tomita, M.; Nakamura, Y. Cloning and characterization of the cDNA encoding a novel brain-specific 14-kDa protein. J. Neurochem. 1992, 59, 1624–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajo, S.; Tsukada, K.; Omata, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakaya, K. A new brain-specific 14-kDa protein is a phosphoprotein. Its complete amino acid sequence and evidence for phosphorylation. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 217, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibayama-Imazu, T.; Okahashi, I.; Omata, K.; Nakajo, S.; Ochiai, H.; Nakai, Y.; Hama, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakaya, K. Cell and tissue distribution and developmental change of neuron specific 14 kDa protein (phosphoneuroprotein 14). Brain Res. 1993, 622, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. Identification of two distinct synucleins from human brain. FEBS Lett. 1994, 345, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Liu, Y.E.; Jia, T.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Xiao, G.; Joseph, B.K.; Rosen, C.; Shi, Y.E. Identification of a breast cancer-specific gene, BCSG1, by direct differential cDNA sequencing. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akopian, A.N.; Wood, J.N. Peripheral nervous system-specific genes identified by subtractive cDNA cloning. J. Boil. Chem. 1995, 270, 21264–21270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavedan, C.; Leroy, E.; Dehejia, A.; Buchholtz, S.; Dutra, A.; Nussbaum, R.L.; Polymeropoulos, M.H. Identification, localization and characterization of the human gamma-synuclein gene. Hum. Genet. 1998, 103, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campion, D.; Martin, C.; Heilig, R.; Charbonnier, F.; Moreau, V.; Flaman, J.M.; Petit, J.L.; Hannequin, D.; Brice, A.; Frebourg, T. The NACP/synuclein gene: Chromosomal assignment and screening for alterations in Alzheimer disease. Genomics 1995, 26, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; de Silva, H.A.; Pettenati, M.J.; Rao, P.N.; St George-Hyslop, P.; Roses, A.D.; Xia, Y.; Horsburgh, K.; Ueda, K.; Saitoh, T. The human NACP/alpha-synuclein gene: Chromosome assignment to 4q21.3-q22 and TaqI RFLP analysis. Genomics 1995, 26, 425–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibasaki, Y.; Baillie, D.A.; St Clair, D.; Brookes, A.J. High-resolution mapping of SNCA encoding alpha-synuclein, the non-A beta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor, to human chromosome 4q21.3→q22 by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1995, 71, 54–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavedan, C.; Dehejia, A.; Pike, B.; Dutra, A.; Leroy, E.; Ide, S.E.; Root, H.; Rubenstein, J.; Boyer, R.L.; Chandrasekharappa, S.; et al. Contig map of the Parkinson’s disease region on 4q21-q23. DNA Res. Int. J. Rapid Publ. Rep. Genes Genomes 1998, 5, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Divane, A.; Goedert, M. Assignment of human alpha-synuclein (SNCA) and beta-synuclein (SNCB) genes to chromosomes 4q21 and 5q35. Genomics 1995, 27, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavedan, C. The synuclein family. Genome Res. 1998, 8, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruening, W.; Giasson, B.I.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Godwin, A.K. Synucleins are expressed in the majority of breast and ovarian carcinomas and in preneoplastic lesions of the ovary. Cancer 2000, 88, 2154–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Dong, B.; Lu, A.; Qu, L.; Xing, X.; Meng, L.; Wu, J.; Eric Shi, Y.; Shou, C. Synuclein gamma predicts poor clinical outcome in colon cancer with normal levels of carcinoembryonic antigen. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Qu, L.; Dong, B.; Xing, X.; Ren, T.; Zeng, Y.; Jiang, B.; Meng, L.; Wu, J.; Shou, C. Combined phenotype of 4 markers improves prognostic value of patients with colon cancer. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 343, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibi, T.; Mori, T.; Fukuma, M.; Yamazaki, K.; Hashiguchi, A.; Yamada, T.; Tanabe, M.; Aiura, K.; Kawakami, T.; Ogiwara, A.; et al. Synuclein-gamma is closely involved in perineural invasion and distant metastasis in mouse models and is a novel prognostic factor in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2864–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchman, V.L.; Hunter, H.J.; Pinon, L.G.; Thompson, J.; Privalova, E.M.; Ninkina, N.N.; Davies, A.M. Persyn, a member of the synuclein family, has a distinct pattern of expression in the developing nervous system. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 9335–9341. [Google Scholar]
- Pfefferkorn, C.M.; Jiang, Z.; Lee, J.C. Biophysics of alpha-synuclein membrane interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikiy, I.; Eliezer, D. Folding and misfolding of alpha-synuclein on membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G. Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and multiple system atrophy are alpha-synucleinopathies. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 1999, 5, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.J.; West, A.B.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. Molecular pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 28, 57–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luk, K.C.; Lee, V.M. Modeling Lewy pathology propagation in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014, 20 (Suppl. 1), S85–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, D.J.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Parkinson’s disease dementia: Convergence of alpha-synuclein, tau and amyloid-beta pathologies. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, E.H.; Giasson, B.I.; Lee, V.M. Alpha-synuclein: Normal function and role in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr. Top. Dev. Boil. 2004, 60, 17–54. [Google Scholar]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, W.P.; Power, J.H.; Blumbergs, P.C.; Blessing, W.W. Multiple-system atrophy: A new alpha-synuclein disease? Lancet 1998, 352, 547–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, K.L.; Boyer, P.; Gomez-Tortosa, E.; Hobbs, W.; Hedley-Whyte, E.T.; Vonsattel, J.P.; Hyman, B.T. Alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity is present in axonal swellings in neuroaxonal dystrophy and acute traumatic brain injury. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 58, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cookson, M.R.; van der Brug, M. Cell systems and the toxic mechanism(s) of alpha-synuclein. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 209, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Dawson, V.L.; Dawson, T.M. What causes cell death in Parkinson’s disease? Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64 (Suppl 2), S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pals, P.; Lincoln, S.; Manning, J.; Heckman, M.; Skipper, L.; Hulihan, M.; van den Broeck, M.; de Pooter, T.; Cras, P.; Crook, J.; et al. alpha-Synuclein promoter confers susceptibility to Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 56, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajput, A.; Vilarino-Guell, C.; Rajput, M.L.; Ross, O.A.; Soto-Ortolaza, A.I.; Lincoln, S.J.; Cobb, S.A.; Heckman, M.G.; Farrer, M.J.; Rajput, A. Alpha-synuclein polymorphisms are associated with Parkinson’s disease in a Saskatchewan population. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2009, 24, 2411–2414. [Google Scholar]
- Pankratz, N.; Wilk, J.B.; Latourelle, J.C.; DeStefano, A.L.; Halter, C.; Pugh, E.W.; Doheny, K.F.; Gusella, J.F.; Nichols, W.C.; Foroud, T.; et al. Genomewide association study for susceptibility genes contributing to familial Parkinson disease. Hum. Genet. 2009, 124, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraganore, D.M.; de Andrade, M.; Elbaz, A.; Farrer, M.J.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Krüger, R.; Rocca, W.A.; Schneider, N.K.; Lesnick, T.G.; Lincoln, S.J.; et al. Collaborative analysis of α-synuclein gene promoter variability and Parkinson disease. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2006, 296, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polymeropoulos, M.H.; Lavedan, C.; Leroy, E.; Ide, S.E.; Dehejia, A.; Dutra, A.; Pike, B.; Root, H.; Rubenstein, J.; Boyer, R.; et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 1997, 276, 2045–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, R.; Kuhn, W.; Muller, T.; Woitalla, D.; Graeber, M.; Kosel, S.; Przuntek, H.; Epplen, J.T.; Schols, L.; Riess, O. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 1998, 18, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarranz, J.J.; Alegre, J.; Gomez-Esteban, J.C.; Lezcano, E.; Ros, R.; Ampuero, I.; Vidal, L.; Hoenicka, J.; Rodriguez, O.; Atares, B.; et al. The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann. Neurol. 2004, 55, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proukakis, C.; Dudzik, C.G.; Brier, T.; MacKay, D.S.; Cooper, J.M.; Millhauser, G.L.; Houlden, H.; Schapira, A.H. A novel alpha-synuclein missense mutation in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2013, 80, 1062–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appel-Cresswell, S.; Vilarino-Guell, C.; Encarnacion, M.; Sherman, H.; Yu, I.; Shah, B.; Weir, D.; Thompson, C.; Szu-Tu, C.; Trinh, J.; et al. Alpha-synuclein p.H50Q, a novel pathogenic mutation for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2013, 28, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesage, S.; Anheim, M.; Letournel, F.; Bousset, L.; Honore, A.; Rozas, N.; Pieri, L.; Madiona, K.; Durr, A.; Melki, R.; et al. G51D alpha-synuclein mutation causes a novel parkinsonian-pyramidal syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 73, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasanen, P.; Myllykangas, L.; Siitonen, M.; Raunio, A.; Kaakkola, S.; Lyytinen, J.; Tienari, P.J.; Poyhonen, M.; Paetau, A. Novel alpha-synuclein mutation A53E associated with atypical multiple system atrophy and Parkinson’s disease-type pathology. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 2180.e1–2180.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, K.A.; Harper, J.D.; Lansbury, P.T. Accelerated in vitro fibril formation by a mutant alpha-synuclein linked to early-onset Parkinson disease. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartier-Harlin, M.C.; Kachergus, J.; Roumier, C.; Mouroux, V.; Douay, X.; Lincoln, S.; Levecque, C.; Larvor, L.; Andrieux, J.; Hulihan, M.; et al. Alpha-synuclein locus duplication as a cause of familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2004, 364, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanez, P.; Bonnet, A.M.; Debarges, B.; Lohmann, E.; Tison, F.; Pollak, P.; Agid, Y.; Durr, A.; Brice, A. Causal relation between alpha-synuclein gene duplication and familial Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2004, 364, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, A.B.; Farrer, M.; Johnson, J.; Singleton, A.; Hague, S.; Kachergus, J.; Hulihan, M.; Peuralinna, T.; Dutra, A.; Nussbaum, R.; et al. alpha-Synuclein locus triplication causes Parkinson’s disease. Science 2003, 302, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giasson, B.I.; Duda, J.E.; Murray, I.V.; Chen, Q.; Souza, J.M.; Hurtig, H.I.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Oxidative damage linked to neurodegeneration by selective alpha-synuclein nitration in synucleinopathy lesions. Science 2000, 290, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofaris, G.K.; Razzaq, A.; Ghetti, B.; Lilley, K.S.; Spillantini, M.G. Ubiquitination of alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies is a pathological event not associated with impairment of proteasome function. J. Boil. Chem. 2003, 278, 44405–44411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xilouri, M.; Stefanis, L. Autophagic pathways in Parkinson disease and related disorders. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2011, 13, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, A.; Masliah, E.; Yoshimoto, M.; Ge, N.; Flanagan, L.; de Silva, H.A.; Kittel, A.; Saitoh, T. The precursor protein of non-A beta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid is a presynaptic protein of the central nervous system. Neuron 1995, 14, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Gallardo, G.; Fernandez-Chacon, R.; Schluter, O.M.; Sudhof, T.C. Alpha-synuclein cooperates with CSPalpha in preventing neurodegeneration. Cell 2005, 123, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burre, J.; Sharma, M.; Tsetsenis, T.; Buchman, V.; Etherton, M.R.; Sudhof, T.C. Alpha-synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 2010, 329, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeliovich, A.; Schmitz, Y.; Farinas, I.; Choi-Lundberg, D.; Ho, W.H.; Castillo, P.E.; Shinsky, N.; Verdugo, J.M.; Armanini, M.; Ryan, A.; et al. Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 2000, 25, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.D.; Rueter, S.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Synucleins are developmentally expressed, and alpha-synuclein regulates the size of the presynaptic vesicular pool in primary hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3214–3220. [Google Scholar]
- George, J.M.; Jin, H.; Woods, W.S.; Clayton, D.F. Characterization of a novel protein regulated during the critical period for song learning in the zebra finch. Neuron 1995, 15, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Liu, Y.E.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.E. Stimulation of breast cancer invasion and metastasis by synuclein gamma. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Spence, M.J.; Zhang, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.E.; Shi, Y.E. Transcriptional suppression of synuclein gamma (SNCG) expression in human breast cancer cells by the growth inhibitory cytokine oncostatin M. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2000, 62, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiunova, A.A.; Anokhin, K.V.; Saha, A.R.; Schmidt, O.; Hanger, D.P.; Anderton, B.H.; Davies, A.M.; Ninkina, N.N.; Buchman, V.L. Chicken synucleins: Cloning and expression in the developing embryo. Mech. Dev. 2000, 99, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Craxton, M.; Jakes, R.; Zibaee, S.; Tavare, R.; Fraser, G.; Serpell, L.C.; Davletov, B.; Crowther, R.A.; Goedert, M. Synuclein proteins of the pufferfish Fugu rubripes: Sequences and functional characterization. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 2599–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, K.; Hedegaard, C.; Bertelsen, M.F.; Bendixen, C. Threonine 53 in alpha-synuclein is conserved in long-living non-primate animals. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 387, 602–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, B.A. Alpha-Synuclein A53T substitution associated with Parkinson disease also marks the divergence of Old World and New World primates. Genomics 2004, 83, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, E.M. The Physiology of Fishes; Evans, D.H., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; p. 592. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, J.S. Fishes of the World; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Busch, D.J.; Morgan, J.R. Synuclein accumulation is associated with cell-specific neuronal death after spinal cord injury. J. Comp. Neurol. 2012, 520, 1751–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Zhao, Y. Evolutionary aspects of the synuclein super-family and sub-families based on large-scale phylogenetic and group-discrimination analysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amores, A.; Force, A.; Yan, Y.L.; Joly, L.; Amemiya, C.; Fritz, A.; Ho, R.K.; Langeland, J.; Prince, V.; Wang, Y.L.; et al. Zebrafish hox clusters and vertebrate genome evolution. Science 1998, 282, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaillon, O.; Aury, J.M.; Brunet, F.; Petit, J.L.; Stange-Thomann, N.; Mauceli, E.; Bouneau, L.; Fischer, C.; Ozouf-Costaz, C.; Bernot, A.; et al. Genome duplication in the teleost fish Tetraodon nigroviridis reveals the early vertebrate proto-karyotype. Nature 2004, 431, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Gitler, A.D. Discovery and characterization of three novel synuclein genes in zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2008, 237, 2490–2495. [Google Scholar]
- Milanese, C.; Sager, J.J.; Bai, Q.; Farrell, T.C.; Cannon, J.R.; Greenamyre, J.T.; Burton, E.A. Hypokinesia and reduced dopamine levels in zebrafish lacking beta- and gamma1-synucleins. J. Boil. Chem. 2012, 287, 2971–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Cheng, C.H.; Chen, G.D.; Hung, C.C.; Yang, C.H.; Hwang, S.P.; Kawakami, K.; Wu, B.K.; Huang, C.J. Recapitulation of zebrafish sncga expression pattern and labeling the habenular complex in transgenic zebrafish using green fluorescent protein reporter gene. Dev. Dyn. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Anat. 2009, 238, 746–754. [Google Scholar]
- Vaccaro, R.; Toni, M.; Casini, A.; Vivacqua, G.; Yu, S.; D’Este, L.; Cioni, C. Localization of alpha-synuclein in teleost central nervous system: Immunohistochemical and Western blot evidence by 3D5 monoclonal antibody in the common carp, Cyprinus carpio. J. Comp. Neurol. 2015, 523, 1095–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivacqua, G.; Casini, A.; Vaccaro, R.; Fornai, F.; Yu, S.; D’Este, L. Different sub-cellular localization of alpha-synuclein in the C57BL6J mouse’s central nervous system by two novel monoclonal antibodies. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2011, 41, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rink, E.; Wullimann, M.F. The teleostean (zebrafish) dopaminergic system ascending to the subpallium (striatum) is located in the basal diencephalon (posterior tuberculum). Brain Res. 2001, 889, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, H.; Lipkin, L.E.; Aronson, S.M. Diffuse intracytoplasmic ganglionic inclusions (Lewy type) associated with progressive dementia and quadriparesis in flexion. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1961, 20, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar, M.; Chou, H.T.; Luhrs, T.; Maji, S.K.; Riek-Loher, D.; Verel, R.; Manning, G.; Stahlberg, H.; Riek, R. The fold of alpha-synuclein fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8637–8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanaan, N.M.; Manfredsson, F.P. Loss of functional alpha-synuclein: A toxic event in Parkinson’s disease? J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2011, 2, 249–267. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toni, M.; Cioni, C. Fish Synucleins: An Update. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6665-6686. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116665
Toni M, Cioni C. Fish Synucleins: An Update. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(11):6665-6686. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116665
Chicago/Turabian StyleToni, Mattia, and Carla Cioni. 2015. "Fish Synucleins: An Update" Marine Drugs 13, no. 11: 6665-6686. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116665
APA StyleToni, M., & Cioni, C. (2015). Fish Synucleins: An Update. Marine Drugs, 13(11), 6665-6686. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116665