Polyphenol-Rich Fraction of Ecklonia cava Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Reduction of Adiposity in G-CA-HFD Mice


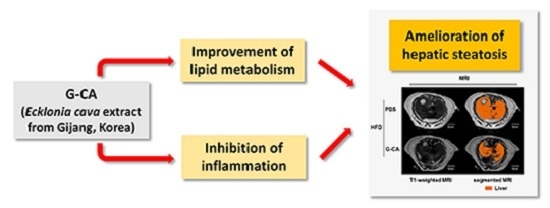
2.2. Reduced Liver Volume in G-CA-HFD Mice

2.3. Reduction of Intrahepatic Lipid Accumulation in G-CA-HFD Mice

2.4. Improvement of Liver Injury and Serum Lipid Levels in G-CA-HFD Mice


2.5. Effects of G-CA Extract on mRNA Expression of Inflammatory Genes, Hepatic Lipogenic Genes and Cholesterol Metabolism-Related Genes


3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Preparation of EtOAc Fraction of E. Cava Crude Extract
4.2. Animals
4.3. Induction of Fatty Liver and Treatment with CA Extract
4.4. Measurement of Body Composition
4.5. MRI and MRS
4.6. Serum Analysis
4.7. Analysis of mRNA Expression by Quantitative Real-Time PCR
| Target | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| TNFα | CCAACGGCATGGATCTCAAAGACA | AGATAGCAAATCGGCTGACGGTGT |
| IL-1β | CTACAGGCTCCGAGATGAACAAC | TCCATTGAGGTGGAGAGCTTTC |
| MCP-1 | TTAAAAACCTGGATCGGAACCAA | GCATTAGCTTCAGATTTACGGG |
| SREBP1c | GGAGCCATGGATTGCACATT | GGCCCGGGAAGTCACTGT |
| FAS | GCTGCGGAAACTTCAGGAAAT | AGAGACGTGTCACTCCTGGACTT |
| ACC1 | ACGCTCAGGTCACCAAAAAGAAT | GTAGGGTCCCGGCCACAT |
| CYP7A1 | AGCAACTAAACAACCTGCCAGTACTA | GTCCGGATATTCAAAGGATGCA |
| FXR | TCCGGACATTCAACCATCAC | TCACTGCACATCCCAGATCTC |
| SHP | AGGAACCTGCCGTTCCTTCTG | TGGCTTCCTCTAGCAGGATC |
| HNF4α | CCAACCTCAATTCATCCAACA | CCCGGTCCGCCACAGAT |
| LXRα | AGGAGTGTCGACTTCGCAAA | CTCTTCTTGCCGCTTCAGTTT |
| 18S rRNA | CCATCCAATCGGTAGTAGCG | GTAACCCGTTGAACCCCATT |
4.8. Oil-Red O Staining
4.9. Quantification of Liver Triglyceride Content
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Angulo, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesini, G.; Bugianesi, E.; Forlani, G.; Cerrelli, F.; Lenzi, M.; Manini, R.; Natale, S.; Vanni, E.; Villanova, N.; Melchionda, N.; Rizzetto, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver, steatohepatitis, and the metabolic syndrome. Hepatology 2003, 37, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, Y.; Younossi, Z.M. Obesity-associated nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 18, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, E.M.; Rinella, M.E. The role of diet and nutrient composition in nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, G.; Cassader, M.; de Michieli, F.; Rosina, F.; Orlandi, F.; Gambino, R. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis versus steatosis: Adipose tissue insulin resistance and dysfunctional response to fat ingestion predict liver injury and altered glucose and lipoprotein metabolism. Hepatology 2012, 56, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Iida, K.; Takahashi, K.; Yoshioka, S.; Fukuoka, H.; Takeno, R.; Imanaka, M.; Nishizawa, H.; Takahashi, M.; Seo, Y.; et al. Growth hormone reverses nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in a patient with adult growth hormone deficiency. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.H.; Husain, N.E.; Almobarak, A.O. Nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease and risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease: What is important for primary care physicians? J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2015, 4, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Zhao, S. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a potential risk factor of cardiovascular disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, W. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and carotid atherosclerosis: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 7673–7678. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Pecere, S.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ojetti, V. Physiology and pathophysiology of liver lipid metabolism. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 9, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratziu, V.; Goodman, Z.; Sanyal, A. Current efforts and trends in the treatment of NASH. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S65–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesinghe, W.A.; Jeon, Y.J. Exploiting biological activities of brown seaweed Ecklonia cava for potential industrial applications: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Jin, Y.B.; Lee, H.; Cha, M.; Sohn, E.T.; Moon, J.; Park, C.; Chun, S.; Jung, E.S.; Hong, J.S.; et al. Brown alga Ecklonia cava attenuates type 1 diabetes by activating AMPK and Akt signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Han, J.S.; Heo, S.J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Protective effects of dieckol isolated from Ecklonia cava against high glucose-induced oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Toxicol. Vitro 2010, 24, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eo, H.; Jeon, Y.J.; Lee, M.; Lim, Y. Brown Alga Ecklonia cava polyphenol extract ameliorates hepatic lipogenesis, oxidative stress, and inflammation by activation of AMPK and SIRT1 in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Min, K.H.; Han, J.S.; Lee, D.H.; Park, D.B.; Jung, W.K.; Park, P.J.; Jeon, B.T.; Kim, S.K.; Jeon, Y.J. Effects of brown alga, Ecklonia cava on glucose and lipid metabolism in C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice, a model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokogawa, K.; Matsui-Yuasa, I.; Tamura, A.; Terada, M.; Kojima-Yuasa, A. Inhibitory effects of Ecklonia cava extract on high glucose-induced hepatic stellate cell activation. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2793–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Satake, N.; Yamashita, H.; Tamura, A.; Sasaki, M.; Matsui-Yuasa, I.; Tabuchi, M.; Akahoshi, Y.; Terada, M.; Kojima-Yuasa, A. Ecklonia cava polyphenol protects the liver against ethanol-induced injury in rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, M.H.; Seo, Y.W.; Lee, J.I.; Jun, H.S. Polyphenol-rich fraction of brown alga ecklonia cava collected from gijang, korea, reduces obesity and glucose levels in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. ECAM 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.A.; Loomba, R. Management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2012, 2, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomonaco, R.; Ortiz-Lopez, C.; Orsak, B.; Webb, A.; Hardies, J.; Darland, C.; Finch, J.; Gastaldelli, A.; Harrison, S.; Tio, F.; et al. Effect of adipose tissue insulin resistance on metabolic parameters and liver histology in obese patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Nam, Y.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, H.R.; Park, E.S.; Chung, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Sohn, U.D.; Kim, H.C.; Oh, K.W.; et al. Beneficial effects of phosphatidylcholine on high-fat diet-induced obesity, hyperlipidemia and fatty liver in mice. Life Sci. 2014, 118, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.; Jang, M.K.; Jung, M.H. Vigna nakashimae extract prevents hepatic steatosis in obese mice fed high-fat diets. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larter, C.Z.; Yeh, M.M.; van Rooyen, D.M.; Brooling, J.; Ghatora, K.; Farrell, G.C. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha agonist, Wy 14,643, improves metabolic indices, steatosis and ballooning in diabetic mice with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.T.; Makishima, M.; Repa, J.J.; Schoonjans, K.; Kerr, T.A.; Auwerx, J.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Molecular basis for feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis by nuclear receptors. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, S.H. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Molecular mechanisms for the hepatic steatosis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2013, 19, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Wang, J.F.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.J.; Nagao, K.; Yanagita, T.; Xue, C.H. Dietary saponins of sea cucumber alleviate orotic acid-induced fatty liver in rats via PPARalpha and SREBP-1c signaling. Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghazadeh, S.; Amini, R.; Yazdanparast, R.; Ghaffari, S.H. Anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of Silybum marianum in treatment of experimental steatohepatitis. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2011, 63, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.P.; Ji, G. Natural products on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Kitade, H.; Ni, Y.; Ota, T. Roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in obesity-associated insulin resistance and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.W.; Adams, L.A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes mellitus: Pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargut, T.C.; Frantz, E.D.; Mandarim-de-Lacerda, C.A.; Aguila, M.B. Effects of a diet rich in n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on hepatic lipogenesis and beta-oxidation in mice. Lipids 2014, 49, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayek, T.; Ito, Y.; Azrolan, N.; Verdery, R.B.; Aalto-Setala, K.; Walsh, A.; Breslow, J.L. Dietary fat increases high density lipoprotein (HDL) levels both by increasing the transport rates and decreasing the fractional catabolic rates of HDL cholesterol ester and apolipoprotein (Apo) A-I. Presentation of a new animal model and mechanistic studies in human Apo A-I transgenic and control mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wanless, I.R.; Shiota, K. The pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and other fatty liver diseases: A four-step model including the role of lipid release and hepatic venular obstruction in the progression to cirrhosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2004, 24, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lake, A.D.; Novak, P.; Hardwick, R.N.; Flores-Keown, B.; Zhao, F.; Klimecki, W.T.; Cherrington, N.J. The adaptive endoplasmic reticulum stress response to lipotoxicity in progressive human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 137, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiroga, A.D.; Lehner, R. Liver triacylglycerol lipases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, H.Y.; Miller, C.; Bitterman, K.J.; Wall, N.R.; Hekking, B.; Kessler, B.; Howitz, K.T.; Gorospe, M.; de Cabo, R.; Sinclair, D.A. Calorie restriction promotes mammalian cell survival by inducing the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 2004, 305, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashiri, A.; Tavallaee, G.; Li, L.; Ng, D.S. Emerging role of cellular cholesterol in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2013, 24, 275–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Matozel, M.; Boehme, S.; Kong, B.; Nilsson, L.M.; Guo, G.; Ellis, E.; Chiang, J.Y. Overexpression of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase promotes hepatic bile acid synthesis and secretion and maintains cholesterol homeostasis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Owsley, E.; Matozel, M.; Hsu, P.; Novak, C.M.; Chiang, J.Y. Transgenic expression of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase in the liver prevents high-fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Hepatology 2010, 52, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Pandak, W.M.; Hylemon, P.B. LXR alpha is the dominant regulator of CYP7A1 transcription. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 293, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Nagayama, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Nakamura, T. Inhibitory activity of brown algal phlorotannins against hyaluronidase. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kong, C.S.; Lee, J.I.; Kim, H.; Baek, S.; Seo, Y. Evaluation of inhibitory effect of phlorotannins from Ecklonia cava on triglyceride accumulation in adipocyte. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 8541–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laufs, A.; Livingstone, R.; Nowotny, B.; Nowotny, P.; Wickrath, F.; Giani, G.; Bunke, J.; Roden, M.; Hwang, J.H. Quantitative liver 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 3T on a clinical scanner. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingstone, R.S.; Begovatz, P.; Kahl, S.; Nowotny, B.; Strassburger, K.; Giani, G.; Bunke, J.; Roden, M.; Hwang, J.H. Initial clinical application of modified Dixon with flexible echo times: hepatic and pancreatic fat assessments in comparison with (1)H MRS. Magma 2014, 27, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, E.-Y.; Choi, H.; Yoon, J.-Y.; Lee, I.-Y.; Seo, Y.; Moon, H.-S.; Hwang, J.-H.; Jun, H.-S. Polyphenol-Rich Fraction of Ecklonia cava Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6866-6883. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116866
Park E-Y, Choi H, Yoon J-Y, Lee I-Y, Seo Y, Moon H-S, Hwang J-H, Jun H-S. Polyphenol-Rich Fraction of Ecklonia cava Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(11):6866-6883. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116866
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Eun-Young, Hojung Choi, Ji-Young Yoon, In-Young Lee, Youngwan Seo, Hong-Seop Moon, Jong-Hee Hwang, and Hee-Sook Jun. 2015. "Polyphenol-Rich Fraction of Ecklonia cava Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice" Marine Drugs 13, no. 11: 6866-6883. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116866
APA StylePark, E. -Y., Choi, H., Yoon, J. -Y., Lee, I. -Y., Seo, Y., Moon, H. -S., Hwang, J. -H., & Jun, H. -S. (2015). Polyphenol-Rich Fraction of Ecklonia cava Improves Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Marine Drugs, 13(11), 6866-6883. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13116866