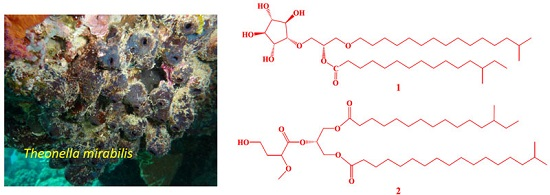
Mirabolides A and B; New Cytotoxic Glycerides from the Red Sea Sponge Theonella mirabilis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedure
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Spectral Data of the Compounds
3.5. Methanolysis of Compounds 1 and 2 and Methylation of Fatty Acids
3.6. Evaluation of the Cytotoxic Activities of Compounds 1–4
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Müller, W.E.G.; Brümmer, F.; Batel, R.; Müller, I.M.; Schröder, H.C. Molecular biodiversity. Case study: Porifera (sponges). Naturwissenschaften 2003, 90, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Soest, R.W.M.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Rützler, K.; de Voogd, N.J.; de Glasby, A.B.; Hajdu, E.; Pisera, A.B.; Manconi, R.; Schoenberg, C.; et al. World Porifera Database 2006. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org/porifera on 2016-04-03 (accessed on 16 June 2016).
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Hu, W.-P.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 35–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, C.A.; Faulkner, D.J. Lithistid sponges: Star performers or hosts to the stars. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2162–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, J.N.A.; van Soest, R.W.M. Systema Porifers: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges; Kluwer Academic: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- D’auria, M.V.; Zampella, A.; Zollo, F. The chemistry of Lithistid sponges: A spectacular source of new metabolites. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry, Volume 26: Bioactive Natural Products; Attar-ur-Rahman, Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002; Volume 26, pp. 1175–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Fusetani, N.; Matsunga, S. Bioactive sponge peptides. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1793–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winder, P.L.; Pomponi, S.A.; Wright, A.E. Natural products from the Lithistida: A Review of the literature since 2000. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2643–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-J.; Yi, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-W. Oxygenated 4-methylidene sterols from the South China Sea sponge Theonella swinhoei. Helv. Chim. Acta 2010, 93, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchingham, J. Dictionary of Natural Products on DVD v.20:1; CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Angawi, R.F.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Dien, H.A.; Fattorusso, E.; Scala, F.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O. Dehydroconicasterol and aurantoic acid, a chlorinated polyene derivative, from the Indonesian sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2195–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnayake, A.S.; Davis, R.A.; Harper, M.K.; Veltri, C.A.; Andjelic, C.D.; Barrows, L.R.; Ireland, C.M. Aurantosides G, H, and I: Three new tetramic acid glycosides from a Papua New Guinea Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piel, J. Bacterial symbionts: Prospects for the sustainable production of invertebrate-derived pharmaceuticals. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabayashi, J.; Itagaki, F.; Shigemori, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Takahashi, K.; Ogura, M.; Nagasawa, S.; Nakamura, T.; Hirota, H.; Ohta, T.; et al. Keramamides B–D, novel peptides from the Okinawan marine sponge Theonella sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 7812–7813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itagaki, F.; Shigemori, H.; Ishibashi, M.; Nakamura, T.; Sasaki, T.; Kabayashi, J. Keramamide F, a new thiazole-containing peptide from the Okinawan marine sponge Theonella sp. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 5540–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chill, L.; Kashman, Y.; Schleyer, M. Oriamide, a new cytotoxic cyclic peptide containing a novel amino acid from the marine sponge Theonella sp. Tetrahedron 1997, 53, 16147–16152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Lee, N.K.; Shibuya, H.; Momose, T.; Kitagawa, I. Marine natural products. XXVI. Biologically active tridecapeptide lactones from the Okinawan marine sponge Theonella swinhoei (Theonellidae). (2). Structures of theonellapeptolides Ia, Ib, Ic, and Ie. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 39, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, P.W.; Gustafson, K.R.; McKee, T.C.; Shigematsu, N.; Maurizi, L.K.; Pannell, L.K.; Williams, D.E.; de Silva, E.D.; Lassota, P.; Allen, T.M.; et al. Papuamides A–D, HIV-inhibitory and cytotoxic depsipeptides from the sponges Theonella mirabilis and Theonella swinhoei collected in Papua New Guinea. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 5899–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusetani, N.; Warabi, K.; Nogata, Y.; Nakao, Y.; Matsunaga, S. Koshikamide A1, a new cytotoxic linear peptide isolated from a marine sponge, Theonella sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 4687–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmely, S.; Kashman, Y. Structure of swinholide-A, a new macrolide from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Tetrahedron Lett. 1985, 26, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, J.; Murayama, T.; Ohizumi, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Ohta, T.; Nozoe, S. Theonelladins A–D, novel antineoplastic pyridine alkaloids from the Okinawan marin sponge Theonella swinhoei. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 4833–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Shimbo, K.; Kubota, T.; Mikami, Y.; Kobayashi, J. Two theonellapeptolide congeners from marine sponge Theonella sp. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 10305–10314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A. Isolation of five-membered cyclitol glycolipids, crasserides: Unique glycerides from the sponge Pseudoceratina crassa. J. Org. Chem. 1993, 58, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Mangoni, A. Glycolipids from sponges. 11. Isocrasserides, novel glycolipids with a five-membered cyclitol widely distributed in marine sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Shaala, L.A.; Mohamed, G.A.; Badr, J.M.; Bamanie, F.H.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. Theonellamide G, a potent antifungal and cytotoxic bicyclic glycopeptide from the Red Sea marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1911–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, D.T.A.; Mooberry, S.L. Hurghadolide A and swinholide I, potent actin-microfilament disrupters from the Red Sea sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugo, Y.; Inouye, Y.; Nakayama, N. Structures of nine oxygenated 4-methylene sterols from Hachijo marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Steroids 1995, 60, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeyama, A.; Shoji, N.; Enoki, M.; Arihara, S. Swinhosterol A–C, 4-methylene secosteroids from the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. J. Nat. Prod. 1997, 60, 296–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.I. A Text Book of Practical Organic Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Longmans and Green Co., Ltd.: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Skehan, P.; Storeng, R.; Scudiero, D.; Monks, A.; McMahom, J.; Vistica, D.; Warren, T.; Bokesch, H.; Kenney, S.; Boyd, M.R. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Position | δC (mult.) a | δH (mult., J in Hz) | HMBC (H→C) b |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 67.7 CH2 | 3.78, dd (10.8, 4.2) 3.73, dd (10.8, 6.6) | H-2, H2-3, H-1′ |
| 2 | 69.3 CH | 5.17, quin (5.4) | H2-1, H2-3 |
| 3 | 67.1 CH2 | 3.57, dd (10.8, 5.4) 3.54, dd (10.8, 4.8) | H2-1, H-2, H2-1′′′, H2-2′′′ |
| 1′ | 80.3 CH | 3.66, t (6.0) | H2-1, H-2′, H-3′, H-4′, H-5′ |
| 2′ | 71.4 CH | 3.93, t (6.0) | H-1′, H-3′, H-4′, H-5′ |
| 3′ | 78.5 CH | 3.84, t (6.0) | H-1′, H-2′, H-4′, H-5′ |
| 4′ | 77.0 CH | 3.69, t (7.2) | H-1′, H-2′, H-3′, H-5′ |
| 5′ | 77.2 CH | 3.90, t (6.6) | H-1′, H-2′, H-3′, H-4′ |
| 1″ | 172.1 qC | - | H-2, H-1′, H2-2″, H2-3″ |
| 2″ | 32.5 CH2 | 2.33, t (7.8) | H2-3″ |
| 3″ | 23.0 CH2 | 1.60, quin (7.2) | H2-2″ |
| 4″–11″ | 20.8–35.1 CH2 | 1.25, m | |
| 12″ | 35.2 CH2 | 1.06, m | H2-11″, H-13″, H3-16″ |
| 13″ | 30.8 CH | 1.35, m | H2-12″, H3-15″, H3-16″ |
| 14″ | 30.0 CH2 | 1.25, m | H-13″, H3-15″, H3-16″ |
| 15″ | 12.2 CH3 | 0.88, t (6.6) | H-13″, H2-14″ |
| 16″ | 17.7 CH3 | 0.83, d (6.6) | H2-12″, H-13″, H2-14″ |
| 1′′′ | 70.0 CH2 | 3.45, dd (6.6, 2.4) 3.41, dd (6.6, 2.4) | H2-3′′′, H2-2′′′ |
| 2′′′ | 27.8 CH2 | 1.53, quin (7.2) | H2-1′′′, H2-3′′′ |
| 3′′′–12′′′ | 20.8–35.1 CH2 | 1.25, m | |
| 13′′′ | 37.1 CH2 | 1.15, m | H2-12′′′, H3-15′′′, H3-16′′′ |
| 14′′′ | 26.0 CH | 1.50, m | H2-13′′′, H3-15′′′, H3-16′′′ |
| 15′′′ | 20.7 CH3 | 0.85, d (6.6) | H2-12′′′, H2-13′′′, H-14′′′, H3-16′′′ |
| 16′′′ | 20.7 CH3 | 0.85, d (6.6) | H2-12′′′, H2-13′′′, H-14′′′, H3-15′′′ |
| Position | δC (mult.) a | δH (mult., J in Hz) | HMBC (H→C) b |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 70.5 CH2 | 3.60, m | H-2, H2-3 |
| 2 | 71.5 CH | 5.22, m | H2-1, H2-3 |
| 3 | 63.9 CH2 | 4.40, dd (12.0, 3.0) 4.16, dd (12.0, 7.2) | H2-1, H-2 |
| 1′ | 175.1 qC | - | H2-1, H2-2′, H2-3′ |
| 2′ | 35.0 CH2 | 2.30, m | H2-3′, H2-4′ |
| 3′ | 26.1 CH2 | 1.59, m | H2-2′, H2-4′ |
| 4′–11′ | 28.2–31.1 CH2 | 1.28, m | |
| 12′ | 38.2 CH2 | 1.10, m | H2-11′, H-13′, H2-14′, H3-16′ |
| 13′ | 35.7 CH | 1.31, m | H2-12′, H3-15′, H3-16′ |
| 14′ | 30.8 CH2 | 1.28, m | H2-12′, H-13′, H3-15′, H3-16′ |
| 15′ | 11.8 CH3 | 0.88, t (6.6 | H-13′, H2-14′ |
| 16′ | 19.6 CH3 | 0.85, d (6.6) | H2-12′, H-13′, H2-14′ |
| 1″ | 171.6 qC | - | H-2″, H2-3″, H2-4″ |
| 2″ | 77.5 CH | 3.70, brd (3.0) | MeO-2″, H2-3″, H2-4″ |
| 3″ | 29.1 CH2 | 2.08, m; 2.22, m | H-2″, H2-4″ |
| 4′′′ | 68.6 CH2 | 3.53, m; 3.67, m | H- 2″, H2-3″, OCH3-2″ |
| MeO-2″ | 52.4 CH3 | 3.20, s | H-2″ |
| 1′′′ | 174.7 qC | - | H2-3, H2-2′′′, H2-3′′′ |
| 2′′′ | 35.1 CH2 | 2.30, m | H2-3′′′, H2-4′′′ |
| 3′′′ | 26.1 CH2 | 1.59, m | H2-2′′′, H2-4′′′ |
| 4′′′–14′′′ | 28.2–31.1 CH2 | 1.28, m | |
| 15′′′ | 40.2 CH2 | 1.19, m | H2-14′′′, H-16′′′, H3-17′′′, H3-18′′′ |
| 16′′′ | 29.1 CH | 1.50, m | H3-17′′′, H3-18′′′ |
| 17′′′ | 23.1 CH3 | 0.87, d (6.6) | H2-14′′′, H2-15′′′, H-16′′′ |
| 18′′′ | 23.1 CH3 | 0.87, d (6.6) | H2-14′′′, H2-15′′′, H-16′′′ |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abou-Hussein, D.R.; Youssef, D.T.A. Mirabolides A and B; New Cytotoxic Glycerides from the Red Sea Sponge Theonella mirabilis. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14080155
Abou-Hussein DR, Youssef DTA. Mirabolides A and B; New Cytotoxic Glycerides from the Red Sea Sponge Theonella mirabilis. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(8):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14080155
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbou-Hussein, Dina R., and Diaa T. A. Youssef. 2016. "Mirabolides A and B; New Cytotoxic Glycerides from the Red Sea Sponge Theonella mirabilis" Marine Drugs 14, no. 8: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14080155
APA StyleAbou-Hussein, D. R., & Youssef, D. T. A. (2016). Mirabolides A and B; New Cytotoxic Glycerides from the Red Sea Sponge Theonella mirabilis. Marine Drugs, 14(8), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14080155