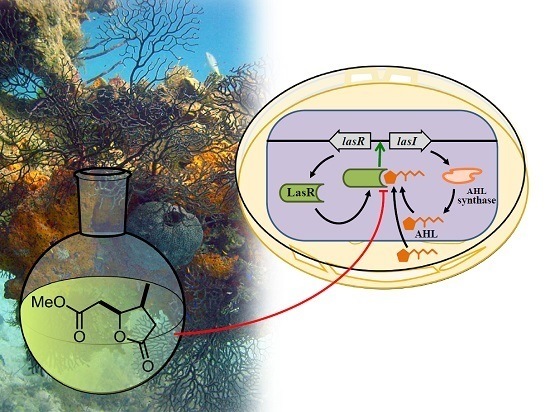
Plakofuranolactone as a Quorum Quenching Agent from the Indonesian Sponge Plakortis cf. lita
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Structural Elucidation of Plakofuranolactone (1)
2.2. Determination of Non-Inhibitory Concentration (NIC)
2.3. Quorum Quenching Activity of Plakofuranolactone (1)
2.3.1. Dose Dependent Quantification of Bioluminescence for the QQ Assay and Specificity to the LasI/LasR System
2.3.2. Inhibition of Virulence Factor Production—Pyocyanin and Total Protease Activity
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Collection, Extraction, and Isolation
3.3. Quantum Mechanical Calculation of the Optical Rotation of Plakofuranolactone (1)
3.4. Determination of Non-Inhibitory Concentration (NIC)
3.5. Dose Dependent QQ Assay
3.6. Inhibition of Virulence Factor Production—Pyocyanin and Protease
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coates, A.R.; Halls, G.; Hu, Y. Novel classes of antibiotics or more of the same? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 382–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Esposito, G.; Teta, R.; Miceli, R.; Ceccarelli, L.S.; Della Sala, G.; Camerlingo, R.; Irollo, E.; Mangoni, A.; Pirozzi, G.; Costantino, V. Isolation and Assessment of the in Vitro Anti-Tumor Activity of Smenothiazole A and B, Chlorinated Thiazole-Containing Peptide/Polyketides from the Caribbean Sponge, Smenospongia aurea. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 444–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A.; Perinu, C.; Cirino, G.; De Gruttola, L.; Roviezzo, F. Tedanol: A potent anti-inflammatory ent-pimaranediterpene from the Caribbean Sponge Tedania ignis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 7542–7547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, V.; D’Esposito, M.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Taramelli, D. Damicoside from Axinella damicornis: The influence of a glycosylated galactose 4-OH group on the immunostimulatory activity of α-galactoglycolsphingolipids. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 7411–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Mangoni, A.; Freigang, S.; Teyton, L. Glycolipids from Sponges. 18. Corrugoside, a New Immunostimulatory alpha-Galactoglycosphingolipid from the Marine Sponge Axinella corrugata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laport, M.S.; Santos, O.C.; Muricy, G. Marine sponges: Potential sources of new antimicrobial drugs. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009, 10, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Fusetani, N. Marine pharmacology in 2009–2011: Marine compounds with antibacterial, antidiabetic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2510–2573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fuqua, C.; Parsek, M.R.; Greenberg, E.P. Regulation of gene expression by cell-to-cell communication: Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2001, 35, 439–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, M.; Lostroh, C.P.; Ogi, T.; Greenberg, E.P. Identification, timing, and signal specificity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-controlled genes: A transcriptome analysis. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2066–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, V.E.; Bushnell, D.; Passador, L.; Brooks, A.I.; Iglewski, B.H. Microarray analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing regulons: Effects of growth phase and environment. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passador, L.; Cook, J.M.; Gambello, M.J.; Rust, L.; Iglewski, B.H. Expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes requires cell-to-cell communication. Science 1993, 260, 1127–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winson, M.K.; Camara, M.; Latifi, A.; Foglino, M.; Chhabra, S.R.; Daykin, M.; Bally, M.; Chapon, V.; Salmond, G.P.; Bycroft, B.W. Multiple N-acyl-l-homoserine lactone signal molecules regulate production of virulence determinants and secondary metabolites in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9427–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Delden, C.; Iglewski, B.H. Cell-to-cell signaling and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1998, 4, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentzer, M.; Givskov, M. Pharmacological inhibition of quorum sensing for the treatment of chronic bacterial infections. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saurav, K.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Haber, M.; Burgsdorf, I.; Oliviero, G.; Costantino, V.; Morgenstern, D.; Steindler, L. In Search of Alternative Antibiotic Drugs: Quorum-Quenching Activity in Sponges and their Bacterial Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindersoe, M.E.; Ettinger-Epstein, P.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Bjarnsholt, T.; de Nys, R.; Givskov, M. Quorum sensing antagonism from marine organisms. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skindersoe, M.; de Nys, R.; Kumar, N.; Read, R.; Givskov, M.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S. Evidence that halogenated furanones from Deliseapulchra inhibit acylated homoserine lactone (AHL)-mediated gene expression by displacing the AHL signal from its receptor protein. Microbiology 1999, 145, 283–291. [Google Scholar]
- Cafieri, F.; Fattorusso, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Di Rosa, M.; Ianaro, A. Metabolites from the sponge Plakortis simplex. Isolation of four bioactive lactone compounds and of a novel related amino acid. Tetrahedron 1999, 55, 13831–13840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; Isbrucker, R.A.; Longley, R.E.; Wright, A.E.; Pomponi, S.A.; Reed, J.K. Plakolide A, a New γ-Lactone from the Marine Sponge Plakortis sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Guzman, F.S.; Schimitz, F.J. Peroxy aliphatic esters from the sponge Plakortis lita. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.; Della Sala, G.; Mangoni, A.; Perinu, C.; Teta, R. Blurring the Boundary between Bio- and Geohopanoids: Plakohopanoid, a C32 Biohopanoid Ester from Plakortis cf. lita. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 5171–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinoa, E.; Kho, E.; Manes, L.V.; Crews, P.; Bakus, G.J. Heterocycles from the marine sponge Xestospongia sp. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 4260–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdani, S.; Gautun, O.R.; Koch, H.; Åstrand, P.O. Optical Rotation Calculations for a Set of Pyrrole Compounds. J. Phys. Chem. A 2016, 120, 7351–7360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09; Revision E. 01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, B.T.; Skindersoe, E.M.; Jarnsholt, B.T.; Phipps, K.R.; Christensen, B.K.; Jensen, P.O.; Andersen, J.B.; Koch, B.; Larsen, T.O.; Hentzer, M.; et al. Identity and effects of quorum-sensing inhibitors produced by Penicillium species. Microbiology 2005, 151, 1325–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skindersoe, M.E.; Alhede, M.; Phipps, R.; Yang, L.; Jensen, P.O.; Rasmussen, T.B. Effects of Antibiotics on Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 3648–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.Y.Y.; Chua, S.-L.; Chen, Y.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S.; Nielsen, T.E.; Yang, L.; Givskov, M. Identification of Five Structurally Unrelated Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from a Natural-Derivative Database. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5629–5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, J.C.; Teplitski, M.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Isolation and biological evaluation of 8-epi-malyngamide C from the Floridian marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobretsov, S.; Teplitski, M.; Alagely, A.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Paul, V.J. Malyngolide from the cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula interferes with quorum sensing circuitry. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2010, 2, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, J.C.; Meickle, T.; Ladwa, D.; Teplitski, M.; Paul, V.; Luesch, H. Lyngbyoic acid, a “tagged” fatty acid from a marine cyanobacterium, disrupts quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.-G.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-Y. Inhibiting N-acyl-homoserine lactone synthesis and quenching Pseudomonas quinolone quorum sensing to attenuate virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.D.; Joseph, P.; Gerdt, J.P.; Nora, R.; Eibergen, N.R.; Blackwell, H.E. Active efflux influences the potency of quorum sensing inhibitors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, M.A.; Helen, E.; Blackwell, H.E. Chemical probes of quorum sensing: From compound development to biological discovery. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 774–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. CLSI Document M100S17. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 17th Informational Supplement; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- McClean, K.H.; Winson, M.K.; Fish, L.; Taylor, A.; Chhabra, S.R.; Camara, M.; Daykin, M.; Lamb, J.H.; Swift, S.; Bycroft, B.W.; et al. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: Exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 1997, 143, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winson, M.K.; Swift, S.; Fish, L.; Throup, J.P.; Jørgensen, F.; Chhabra, S.R.; Bycroft, B.W.; Williams, P.; Stewart, G.S. Construction and analysis of luxCDABE-based plasmid sensors for investigating N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1998, 163, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pejin, B.; Talevska, A.; Ciric, A.; Glamoclija, J.; Nikolic, M.; Talevski, T.; Sokovic, M. Anti-quorum sensing activity of selected sponge extracts: A case study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 2330–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Foulya, M.Z.; Sharafb, A.M.; Shahina, A.A.M.; El-Bialya, H.A.; Omara, A.M.A. Biosynthesis of pyocyanin pigment by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2015, 8, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, A.B.; Riedel, K.; Eberl, L.; Flodgaard, L.R.; Molin, S.; Gram, L.; Givskov, M. Quorum-sensing-directed protein expression in Serratia proteamaculans B5a. Microbiology 2003, 149, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Bossier, P. Can bacteria evolve resistance to quorum sensing disruption? PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen, R.C.; Popat, R.; Diggle, S.P.; Brown, S.P. Targeting virulence: Can we make evolution-proof drugs? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Contreras, R.; Maeda, T.; Wood, T.K. Resistance to Quorum-Quenching Compounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 6840–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroche, M.; Imperatore, C.; Grozdanov, L.; Costantino, V.; Mangoni, A.; Hentschel, U.; Fattorusso, E. Cellular localisation of secondary metabolites isolated from the Caribbean sponge Plakortis simplex. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Pos. | δH [mult., J (Hz)] | δC [mult.] | COSY | HMBC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 172.2 (C) | ||||
| 2 | 2.71 (d, 7.1) | 35.7 (CH2) | 3, 8 | 1, 3, 4 | |
| 3 | 4.96 (q, 6.7) | 81.0 (CH) | 2, 4, 5a | 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7 | |
| 4 | 2.75 (m) | 33.8 (CH) | 3, 5a, 5b, 7 | 5, 6, 7 | |
| 5 | a | 2.79 (dd, 16.9, 8.0) | 37.5 (CH2) | 3, 4, 5b, 7 | 3, 4, 6, 7 |
| b | 2.24 (dd, 16.9, 4.4) | 4, 5a, 7 | 3, 4, 6, 7 | ||
| 6 | 178.7 (C) | ||||
| 7 | 1.01 (d, 7.1) | 14.0 (CH3) | 4, 5a, 5b | 3, 4, 5 | |
| 8 | 3.71 (s) | 52.3 (CH3) | 2 | 1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costantino, V.; Della Sala, G.; Saurav, K.; Teta, R.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Mangoni, A.; Steindler, L. Plakofuranolactone as a Quorum Quenching Agent from the Indonesian Sponge Plakortis cf. lita. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030059
Costantino V, Della Sala G, Saurav K, Teta R, Bar-Shalom R, Mangoni A, Steindler L. Plakofuranolactone as a Quorum Quenching Agent from the Indonesian Sponge Plakortis cf. lita. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(3):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030059
Chicago/Turabian StyleCostantino, Valeria, Gerardo Della Sala, Kumar Saurav, Roberta Teta, Rinat Bar-Shalom, Alfonso Mangoni, and Laura Steindler. 2017. "Plakofuranolactone as a Quorum Quenching Agent from the Indonesian Sponge Plakortis cf. lita" Marine Drugs 15, no. 3: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030059
APA StyleCostantino, V., Della Sala, G., Saurav, K., Teta, R., Bar-Shalom, R., Mangoni, A., & Steindler, L. (2017). Plakofuranolactone as a Quorum Quenching Agent from the Indonesian Sponge Plakortis cf. lita. Marine Drugs, 15(3), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030059