Chondroitin Sulfate-Rich Extract of Skate Cartilage Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Damage in Mice
Abstract
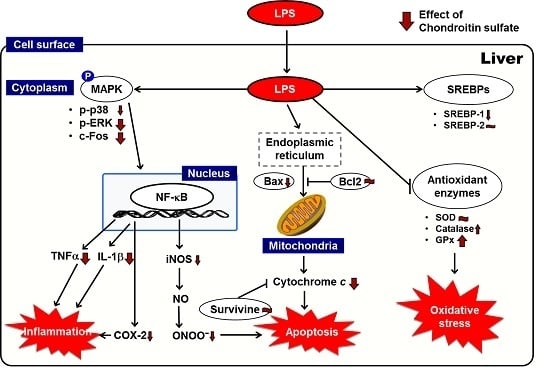
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Skate CSE on LPS-Induced Decrease in Body and Liver Weights
2.2. Effects of Skate CSE on LPS-Induced Peroxynitrite Radical Production, Serum Lipids, and Hepatic Function Parameters
2.3. Effects of Skate CSE on the Protein Expression of Antioxidant Enzymes in LPS-Induced Hepatic Tissue
2.4. Effects of Skate CSE on the Protein Expression of Proinflammatory Factors in LPS-Induced Hepatic Tissue
2.5. Effects of Skate CSE on the Protein Expression of Anti- and Pro-Apoptotic Mediators in LPS-Induced Hepatic Tissue
2.6. Effects of Skate CSE on the Protein Expression of Cell Signaling Transduction-Related Factors in LPS-Induced Hepatic Tissue
2.7. Effects of Skate CSE on the Protein Expression of Lipid Metabolism-Related Transcription Factors in LPS-Induced Hepatic Tissue
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chondroitin Sulfate-Rich Extract of Skate Cartilage
4.2. Animals and Experimental Protocol
4.3. Measurement of ONOO− Level in the Serum
4.4. Preparation of Nuclear and Post-Nuclear Fractions
4.5. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abe, S.; Obata, Y.; Oka, S.; Koji, T.; Nishino, T.; Izumikawa, K. Chondroitin sulfate prevents peritoneal fibrosis in mice by suppressing NF-κB activation. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2016, 49, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel-Pelletier, J.; Tat, S.K.; Pelletier, J.P. Effects of chondroitin sulfate in the pathophysiology of the osteoarthritic joint: A narrative review. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, S7–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpi, N. Disaccharide mapping of chondroitin sulfate of different origins by high-performance capillary electrophoresis and high-performance liquid chromatography. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 55, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, G.; Goemaere, S.; Veys, E.M. Systems to assess the progression of finger joint osteoarthritis and the effects of disease modifying osteoarthritis drugs. Clin. Rheumatol. 2002, 21, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, M.; Chevalier, X.; Henrotin, Y.; Hunter, D.J.; Uebelhart, D. Symptom and structure modification in osteoarthritis with pharmaceutical-grade chondroitin sulfate: What’s the evidence? Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2013, 29, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melgar-Lesmes, P.; Garcia-Polite, F.; Del-Rey-Puech, P.; Rosas, E.; Dreyfuss, J.L.; Montell, E.; Vergésd, J.; Edelmana, E.R.; Balcellsa, M. Treatment with chondroitin sulfate to modulate inflammation and atherogenesis in obesity. Atherosclerosis 2016, 245, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segarra, S.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Martínez-Puig, D.; Muñoz-Prieto, A.; Rodríguez-Franco, F.; Rodríguez-Bertos, A.; Allenspach, K.; Velasco, A.; Cerón, J. Oral chondroitin sulfate and prebiotics for the treatment of canine Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A randomized, controlled clinical trial. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergés, J.; Montell, E.; Herrero, M.; Perna, C.; Cuevas, J.; Dalmau, J.; Pérez, M.; Möller, I. Clinical and histopathological improvement of psoriasis with oral chondroitin sulfate: A serendipitous finding. Dermatol. Online J. 2005, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yi, D.; Hou, Y.; Wang, L.; Ding, B.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Long, M.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G. Dietary N-acetylcysteine supplementation alleviates liver injury in lipopolysaccharide-challenged piglets. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 111, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bélanger, M.; Desjardins, P.; Chatauret, N.; Rose, C.; Butterworth, R.F. Mild hypothermia prevents brain edema and attenuates up-regulation of the astrocytic benzodiazepine receptor in experimental acute liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, H.; Xue, B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, Z.; Luo, L. Protective effect of glutathione against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and mortality in rats. Inflamm. Res. 2006, 55, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.W.; Song, S.Z.; Wu, Y.L.; Lian, L.H.; Wan, Y.; Nan, J.X. Betulinic acid prevention of d-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide liver toxicity is triggered by activation of Bcl-2 and antioxidant mechanisms. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desagher, S.; Martinou, J.C. Mitochondria as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2000, 10, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Takada, Y.; Shishodia, S.; Gutierrez, A.M.; Oommen, O.V.; Ichikawa, H.; Baba, Y.; Kumar, A. Nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B: Role in biology and medicine. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 42, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shon, J.; Eo, J.H.; Hwang, S.J.; Eun, J.B. Effect of processing conditions on functional properties of collagen powder from skate (Raja kenojei) skins. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, J.A.; Rodríguez-Amado, I.; Montemayor, M.I.; Fraguas, J.; González, M.D.P.; Murado, M.A. Chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid and chitin/chitosan production using marine waste sources: Characteristics, applications and eco-friendly processes: A review. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 747–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Wu, W.; Xiao, C.; Liu, X. Carnosic acid attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in rats via fortifying cellular antioxidant defense system. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Gao, C.; Xing, M.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Yao, P. Quercetin prevents ethanol-induced dyslipidemia and mitochondrial oxidative damage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajuwon, O.R.; Oguntibeju, O.O.; Marnewick, J.L. Amelioration of lipopolysaccharide-induced liver (Aspalathus linearis) extract via inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Hayashi, S.; Harada, N.; Yamaji, R.; Nakano, Y.; Inui, H. Suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and amelioration of lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury by polyphenolic compounds in Eucalyptus globulus leaf extract. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Mouson, A.; Delzenne, N.M. Dietary supplementation with laminarin, a fermentable marine β (1–3) glucan, protects against hepatotoxicity induced by LPS in rat by modulating immune response in the hepatic tissue. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, T.; Kim, D.H.; Jo, J.E.; Lee, J.J.; Pyo, H.J.; Lim, B.O. Hepatoprotective activity of Haliotis discus hannai Ino extract on lipopolysaccharide-induced liver damage in rats. J. Food Biochem. 2015, 39, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, G.M.; Avenoso, A.; Campo, S.; D’Ascola, A.; Ferlazzo, A.M.; Calatroni, A. The antioxidant and antifibrogenic effects of the glycosaminoglycans hyaluronic acid and chondroitin-4-sulphate in a subchronic rat model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrogenesis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2004, 148, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, B.J. Oxidative stress in ovariectomy menopause and role of chondroitin sulfate. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.W.; Wang, J.H.; Park, H.J.; Choi, M.K.; Kim, H.G.; Son, C.G. Herbal formula CGX ameliorates LPS/D-galactosamine-induced hepatitis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1329–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Xiao, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, W.; Fu, L.; Xie, F.; Huang, W.; Deng, W. Melatonin suppresses proinflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated CRL1999 cells via targeting MAPK, NF-κB, c/EBPβ, and p300 signaling. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 53, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Kodama, N.; Arai, Y.; Kumamoto, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Chaichantipyuth, C.; Ishikawa, T.; Ueno, K.; Yano, S. Inhibitory effect of oxycoumarins isolated from the Thai medicinal plant Clausena guillauminii on the inflammation mediators, iNOS, TNF-α, and COX-2 expression in mouse macrophage RAW 264.7. J. Nat. Med. 2009, 63, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck-Palmer, O.M.; Unsinger, J.; Chang, K.C.; McDonough, J.S.; Perlman, H.; McDunn, J.E.; Hotchkiss, R.S. Modulation of the Bcl-2 family blocks sepsis-induced depletion of dendritic cells and macrophages. Shock 2009, 31, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, C.; Hou, L.; Sun, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Lv, Y.; Zhao, X. Anti-oxidation and antiapoptotic effects of chondroitin sulfate on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced injury through the up-regulation of Nrf2 and inhibition of mitochondria-mediated pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santin, I.; Moore, F.; Colli, M.L.; Gurzov, E.N.; Marselli, L.; Marchetti, P.; Eizirik, D.L. PTPN2, a candidate gene for type 1 diabetes, modulates pancreatic β-cell apoptosis via regulation of the BH3-only protein Bim. Diabetes 2011, 60, 3279–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uto, T.; Fujii, M.; Hou, D.X. 6-(Methylsulfinyl) hexyl isothiocyanate suppresses inducible nitric oxide synthase expression through the inhibition of Janus kinase 2-mediated JNK pathway in lipopolysaccharide-activated murine macrophages. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajizian, S.J.; English, B.K.; Meals, E.A. Specific inhibitors of p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways block inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor accumulation in murine macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide and interferon-γ. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 179, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bhat, N.R.; Zhang, P.; Lee, J.C.; Hogan, E.L. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 subgroups of mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-α gene expression in endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pearson, G.; Robinson, F.; Beers Gibson, T.; Xu, B.E.; Karandikar, M.; Berman, K.; Cobb, M.H. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions 1. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 153–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khovidhunkit, W.; Kim, M.S.; Memon, R.A.; Shigenaga, J.K.; Moser, A.H.; Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. Effects of infection and inflammation on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism: Mechanisms and consequences to the host. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 1169–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, M.; Shi, C.E.; Zhu, R.M.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H.; Wei, W.; Li, J.B.; Xu, D.X. Melatonin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic SREBP-1c activation and lipid accumulation in mice. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 51, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xue, C. Inhibitory effect of fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from the sea cucumber Acaudina molpadioides on adipogenesis is dependent on Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.L.; Li, A.L.; Jin, Z.Y.; Chen, M. Effects of oral chondroitin sulfate on lipid and antitoxidant metabolisms in rats fed a high-fat diet. J. Food Biochem. 2007, 31, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, A.R.; Sim, J.S.; Park, Y.; Hahn, B.S.; Toida, T.; Kim, Y.S. Isolation and characterization of chondroitin sulfates from the byproducts of marine organisms. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 18, 872–877. [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita, A.; Yamada, S.; Haslam, S.M.; Morris, H.R.; Dell, A.; Sugahara, K. Isolation and structural determination of novel sulfated hexasaccharides from squid cartilage chondroitin sulfate E that exhibits neuroregulatory activites. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 12654–12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falshaw, R.; Hubl, U.; Ofman, D.; Slim, G.C.; Tariq, M.A.; Watt, D.K.; Yorke, S.C. Comparison of the glycosaminoglycans isolated from the skin and head cartilage of Gould’s arrow squid (Nototodarus gouldi). Carbohydr. Polym. 2000, 41, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugahara, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Yamada, S.; Seno, N.; Kitagawa, H.; Haslam, S.M.; Morris, H.R.; Dell, A. Novel sulfated oligosaccharides containing 3-o-sulfated glucuronic acid from king crab cartilage chondroitin sulfate K unexpected degradation by chondroitinase ABC. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 26745–26754. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Sunwoo, H.H.; Li, X.; Price, M.A.; Jeong, S.S. Study of sulfated glycosaminoglycans from porcine skeletal muscle epimysium including analysis of iduronosyl and glucoronosyl residues in galactosaminoglycan fractions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 1424–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, B.J.; Lee, J.Y. The effect of chondroitin sulfate against CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooy, N.W.; Royall, J.A.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Beckman, J.S. Peroxynitrite-mediated oxidation of dihydrorhodamine 123. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 16, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S. Extraction of nuclear proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 355, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]







| Group | Body Weight | Liver Weight (g/100 mg Body Weight) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial (g) | Final (g) | Change (g/3 Days) | ||
| NC | 38.0 ± 0.5 | 40.2 ± 0.6 *** | 1.9 ± 0.3 *** | 8.1 ± 0.3 *** |
| LPS | 37.8 ± 0.6 | 33.3 ± 0.7 | −3.9 ± 0.4 | 5.6 ± 0.1 |
| CS | 37.7 ± 0.5 | 34.4 ± 0.5 | −2.8 ± 0.3 * | 7.2 ± 0.2 *** |
| CSE | 37.7 ± 0.6 | 35.0 ± 0.5 | −3.0 ± 0.1 * | 6.6 ± 0.4 * |
| Group | Peroxynitrite (Fluorescence/mL) | Triglyceride (mg/dL) | Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NC | 93.5 ± 1.5 ** | 166.4 ± 13.9 * | 86.6 ± 2.7 * |
| LPS | 139.1 ± 13.0 | 236.0 ± 27.6 | 94.8 ± 1.8 |
| CS | 96.6 ± 2.8 * | 151.8 ± 9.6 * | 74.2 ± 3.8 ** |
| CSE | 97.7 ± 3.7 * | 125.1 ± 13.4 ** | 70.5 ± 5.3 ** |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.O.; Kim, M.; Woo, M.; Baek, J.-M.; Kang, K.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Roh, S.-S.; Park, C.H.; Jeong, K.-S.; Noh, J.-S. Chondroitin Sulfate-Rich Extract of Skate Cartilage Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Damage in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060178
Song YO, Kim M, Woo M, Baek J-M, Kang K-H, Kim S-H, Roh S-S, Park CH, Jeong K-S, Noh J-S. Chondroitin Sulfate-Rich Extract of Skate Cartilage Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Damage in Mice. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(6):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060178
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yeong Ok, Mijeong Kim, Minji Woo, Jang-Mi Baek, Keon-Hee Kang, Sang-Ho Kim, Seong-Soo Roh, Chan Hum Park, Kap-Seop Jeong, and Jeong-Sook Noh. 2017. "Chondroitin Sulfate-Rich Extract of Skate Cartilage Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Damage in Mice" Marine Drugs 15, no. 6: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060178
APA StyleSong, Y. O., Kim, M., Woo, M., Baek, J. -M., Kang, K. -H., Kim, S. -H., Roh, S. -S., Park, C. H., Jeong, K. -S., & Noh, J. -S. (2017). Chondroitin Sulfate-Rich Extract of Skate Cartilage Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Liver Damage in Mice. Marine Drugs, 15(6), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15060178