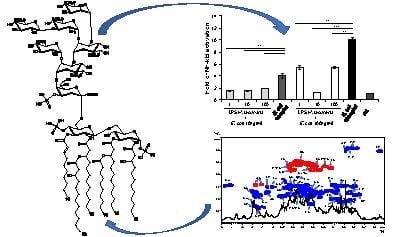
The Deep-Sea Polyextremophile Halobacteroides lacunaris TB21 Rough-Type LPS: Structure and Inhibitory Activity towards Toxic LPS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation, Purification, and Compositional Analyses of the R-LPS Isolated from H. lacunaris TB21
2.2. NMR Spectroscopy Structural Characterization of the R-LPS Core OS Isolated from H. lacunaris TB21
2.3. MALDI Mass Spectrometry Investigation of the Lipid A Isolated from H. lacunaris TB21 R-LPS.
2.4. Immunological Properties of Isolated H. lacunaris TB21 R-LPS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacteria Isolation and Growth
4.2. Isolation and Purification of the R-LPS from H. lacunaris TB21
4.3. Chemical Analyses
4.4. Isolation of the Core OS from the H. lacunaris TB21 R-LPS
4.5. NMR Spectroscopy
4.6. MALDI Mass Spectrometry
4.7. Cell Cultures
4.8. BMDMs Isolation and Culture
4.9. Cytokine Measurement
4.10. HEK 293 hTLR4/CD14/MD2 Cell Culture, Transfection, and Stimulation
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacElroy, R.D. Some comments on the evolution of the Extremophiles. Biosystems 1974, 6, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorty, D.; Shreshtha, A.K.; Babu, V.R.S.; Patra, S. Molecular evolution of Extremophiles. In Extremophiles: Sustainable Resources and Biotechnological Implications; Singh, Om V., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yakimov, M.M.; La Cono, V.; Spada, G.L.; Bortoluzzi, G.; Messina, E.; Smedile, F.; Arcadi, E.; Borghini, M.; Ferrer, M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; et al. Microbial community of the deep-sea brine Lake Kryos seawater-brine interface is active below the chaotropicity limit of life as revealed by recovery of mRNA. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 364–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Cono, V.; Smedile, F.; Bortoluzzi, G.; Arcadi, E.; Maimone, G.; Messina, E.; Borghini, M.; Oliveri, E.; Mazzola, S.; L’Haridon, S.; et al. Unveiling microbial life in new deep-sea hypersaline Lake Thetis. Part I: Prokaryotes and environmental settings. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 2250–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horikoshi, K. Barophiles deep-sea microorganisms adapted to an extreme environment. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1998, 1, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, Y.; Nakayama, A.; Ishihara, K.; Saito, H. Adaptive changes in membrane lipids of barophilic bacteria in response to changes in growth pressure. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raetz, C.R.; Whitfield, C. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2002, 71, 635–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lorenzo, F.; De Castro, C.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Silipo, A.; Molinaro, A. Lipopolysaccharides as microbe-associated molecular patterns: A structural perspective. In Carbohydrates in Drug Design and Discovery; Jimenez-Barbero, J., Javier Canada, F., Martıín-Santamaría, S., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC): London, UK, 2015; pp. 38–63. [Google Scholar]
- Poltorak, A.; He, X.; Smirnova, I.; Liu, M.Y.; Van Huffel, C.; Du, X.; Birdwell, D.; Alejos, E.; Silva, M.; Galanos, C.; et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: Mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 1998, 282, 2085–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafilou, M.; Triantafilou, K. Lipopolysaccharide recognition: CD14, TLRs and the LPS-activation cluster. Trends Immunol. 2002, 23, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.R.; Christ, W.J.; Bristol, J.R.; Kawata, T.; Rossignol, D.P. Agonistic and antagonistic activities of bacterially derived Rhodobacter sphaeroides lipid A: Comparison with activities of synthetic material of the proposed structure and analogs. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Lorenzo, F.; Billod, J.-M.; Martín-Santamaría, S.; Silipo, A.; Molinaro, A. Gram-negative Extremophile Lipopolysaccharides: Versatile molecules to survive in harsh habitats and promising source of inspiration for a new generation of endotoxin antagonists. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, O.; Jann, K. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides: Extraction with phenol-water and further applications of the procedure. Methods Carbohydr. Chem. 1965, 5, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kittelberger, R.; Hilbink, F. Sensitive silver-staining detection of bacterial lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1993, 26, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, O. Deacylation of lipopolysaccharides and isolation of oligosaccharide phosphates. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 145, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Silipo, A.; Leone, S.; Molinaro, A.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M. The Structure of the phosphorylated carbohydrate backbone of the lipopolysaccharide of the phytopathogen bacterium Pseudomonas tolaasii. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 2241–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silipo, A.; Sturiale, L.; Garozzo, D.; De Castro, C.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Grant, W.D.; Molinaro, A. Structure elucidation of the highly heterogeneous lipid a from the lipopolysaccharide of the gram-negative extremophile bacterium Halomonas magadiensis strain 21 M1. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 10, 2263–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Mangoni, A. Glycolipids from Sponges. 12. Ectyoceramide, the First Natural Hexofuranosylceramide from the Marine Sponge Ectyoplasia ferox. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 8, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Mangoni, A. J-coupling analysis for stereochemical assignments in furanosides: Structue elucidation of vesparioside B, a glycosphingolipid from the marine sponge Spheciospongia vesparia. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 6158–6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, G.I.; Roy, R.; Brisson, J.R.; Jennings, H.J. Conformations of ammonium 3-deoxy-d-manno-2-octulosonate (KDO) and methyl α-and β-ketopyranosides of KDO: X-ray structure and 1H NMR analyses. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 1987, 6, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, K.; Thomsen, J.U.; Kosma, P.; Christian, R.; Holst, O.; Brade, H. A nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic investigation of Kdo containing oligosaccharides related to the genus-specific epitope of Chlamydia lipopolysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 1992, 229, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertelt, C.; Lindner, B.; Skurnik, M.; Holst, O. Isolation and structural characterization of an R-form lipopolysaccharide from Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:8. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domon, B.; Costello, C.E. A systematic nomenclature for carbohydrate fragmentations in FAB-MS/MS spectra of glycoconjugates. Glycoconj. J. 1988, 5, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, G.; Fazio, L.L.; Martino, M.C.; Rossi, G.; Tattoli, I.; Liparoti, V.; De Castro, C.; Molinaro, A.; Philpott, D.J.; Bernardini, M.L. Muramylpeptide shedding modulates cell sensing of Shigella flexneri. Cell. Microbiol. 2008, 3, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinaro, A.; Holst, O.; Di Lorenzo, F.; Callaghan, M.; Nurisso, A.; D’Errico, G.; Zamyatina, A.; Peri, F.; Berisio, R.; Jerala, R.; et al. Martín-Santamaría, S. Chemistry of lipid A: At the heart of innate immunity. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 500–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohto, U.; Fukase, K.; Miyake, K.; Satow, Y. Crystal structures of human MD-2 and its complex with antiendotoxic lipid IVa. Science 2007, 316, 1632–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lorenzo, F.; Paciello, I.; Fazio, L.L.; Albuquerque, L.; Sturiale, L.; da Costa, M.S.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Garozzo, D.; Bernardini, M.L.; et al. Thermophiles as potential source of novel endotoxin antagonists: The full structure and bioactivity of the lipo-oligosaccharide from Thermomonas hydrothermalis. ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 2146–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ialenti, A.; Di Meglio, P.; Grassia, G.; Maffia, P.; Di Rosa, M.; Lanzetta, R.; Molinaro, A.; Silipo, A.; Grant, W.D.; Ianaro, A. A novel lipid A from Halomonas magadiensis inhibits enteric LPS-induced human monocyte activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Microorganisms. Available online: www.dsmz.de/microorganisms/medium/pdf/DSMZ_Medium141.pdf (accessed on 26 June 2017).
- Leontein, K.; Lindberg, B.; Lönngren, J. Assignment of absolute configuration of sugars by g.l.c. of their acetylated glycosides formed from chiral alcohols. Carbohydr. Res. 1978, 62, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciucanu, I.; Kerek, F. A simple and rapid method for the permethylation of carbohydrates. Carbohydr. Res. 1984, 131, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, C.; Parrilli, M.; Holst, O.; Molinaro, A. Microbe-associated molecular patterns in innate immunity: Extraction and chemical analysis of gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Methods Enzymol. 2010, 480, 89–115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rietschel, E.T. Absolute configuration of 3-hydroxy fatty acids present in lipopolysaccharides from various bacterial groups. Eur. J. Biochem. 1976, 64, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piantini, U.; Sorensen, O.W.; Ernst, R.R. Multiple quantum filters for elucidating NMR coupling networks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 6800–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rance, M.; Sorensen, O.W.; Bodenhausen, G.; Wagner, G.; Ernst, R.R.; Wuthrich, K. Improved spectral resolution in COSY 1H NMR spectra of proteins via double quantum filtering. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1983, 117, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- States, D.J.; Haberkorn, R.A.; Ruben, D.J. A two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser experiment with pure absorption phase in four quadrants. J. Magn. Reson. 1982, 48, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, A.S.; Li, K.B.; Hoch, J.C. Modern spectrum analysis in multidimensional NMR spectroscopy: Comparison of linear-prediction extrapolation and maximum-entropy reconstruction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 1982–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccheri, F.; Pozzi, C.; Avogadri, F.; Barozzi, S.; Faretta, M.; Fusi, P.; Rescigno, M. Bacteria-induced gap junctions in tumors favor antigen cross-presentation and antitumor immunity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 44ra57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Unit | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A 6-α-GlcN1P | 5.52 | 3.28 | 3.79 | 3.34 | 4.06 | 4.17/4.10 | - | - |
| 90.4 | 54.7 | 69.8 | 69.3 | 72.7 | 69.6 | - | - | |
| 3.55 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| B t-α-GlcN | 5.37 | 3.23 | 3.77 | 3.41 | 3.77 | 3.84/3.48 | - | - |
| 94.7 | 54.3 | 69.8 | 69.3 | 72.9 | 62.7 | - | - | |
| B’ 3-α-GlcN | 5.31 | 3.25 | 3.90 | 3.58 | 3.76 | 3.84/3.48 | - | - |
| 98.0 | 54.3 | 74.0 | 71.9 | 73.0 | 62.7 | - | - | |
| C 2,3-α-Hep | 5.15 | 4.14 | 4.13 | 3.71 | 3.63 | 3.87 | 3.61 | - |
| 100.8 | 78.7 | 74.0 | 71.3 | 71.2 | 68.4 | 63.0 | - | |
| D 2,3-α-Hep | 5.10 | 4.18 | 4.19 | 3.73 | 3.88 | 3.83 | 3.62 | - |
| 98.0 | 78.1 | 76.8 | 71.2 | 70.5 | 69.7 | 63.0 | - | |
| E t-α-Man | 5.07 | 4.05 | 4.00 | 3.75 | 3.70 | 3.81/3.61 | - | - |
| 102.2 | 70.1 | 70.3 | 66.2 | 73.3 | 61.0 | - | - | |
| F 6-β-GlcN4P | 4.83 | 2.95 | 3.75 | 3.63 | 3.43 | 3.60/3.43 | - | - |
| 99.3 | 55.6 | 72.8 | 74.0 | 75.2 | 62.3 | - | - | |
| - | - | - | 2.02 | - | - | - | - | |
| G t-β-GlcA | 4.35 | 3.24 | 3.40 | 3.38 | 3.63 | - | - | - |
| 102.3 | 72.4 | 75.2 | 72.4 | 77.3 | 175.8 | - | - | |
| H t-β-Glc | 4.28 | 3.16 | 3.24 | 3.20 | 3.32 | 3.75/3.66 | - | - |
| 102.8 | 73.2 | 75.8 | 69.8 | 76.2 | 60.6 | - | - | |
| K 5-α-Kdo4P | - | - | 1.91/2.09 | 4.44 | 4.18 | 3.82 | 3.68 | 3.81/3.53 |
| - | - | 34.4 | 69.7 | 72.2 | 73.2 | 71.4 | 63.2 | |
| - | - | - | −0.70 | - | - | - | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lorenzo, F.D.; Palmigiano, A.; Paciello, I.; Pallach, M.; Garozzo, D.; Bernardini, M.-L.; Cono, V.L.; Yakimov, M.M.; Molinaro, A.; Silipo, A. The Deep-Sea Polyextremophile Halobacteroides lacunaris TB21 Rough-Type LPS: Structure and Inhibitory Activity towards Toxic LPS. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15070201
Lorenzo FD, Palmigiano A, Paciello I, Pallach M, Garozzo D, Bernardini M-L, Cono VL, Yakimov MM, Molinaro A, Silipo A. The Deep-Sea Polyextremophile Halobacteroides lacunaris TB21 Rough-Type LPS: Structure and Inhibitory Activity towards Toxic LPS. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(7):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15070201
Chicago/Turabian StyleLorenzo, Flaviana Di, Angelo Palmigiano, Ida Paciello, Mateusz Pallach, Domenico Garozzo, Maria-Lina Bernardini, Violetta La Cono, Michail M. Yakimov, Antonio Molinaro, and Alba Silipo. 2017. "The Deep-Sea Polyextremophile Halobacteroides lacunaris TB21 Rough-Type LPS: Structure and Inhibitory Activity towards Toxic LPS" Marine Drugs 15, no. 7: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15070201
APA StyleLorenzo, F. D., Palmigiano, A., Paciello, I., Pallach, M., Garozzo, D., Bernardini, M. -L., Cono, V. L., Yakimov, M. M., Molinaro, A., & Silipo, A. (2017). The Deep-Sea Polyextremophile Halobacteroides lacunaris TB21 Rough-Type LPS: Structure and Inhibitory Activity towards Toxic LPS. Marine Drugs, 15(7), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15070201