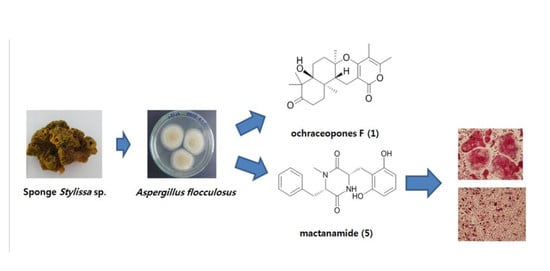
Suppression of RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by the Metabolites from the Marine Fungus Aspergillus flocculosus Isolated from a Sponge Stylissa sp.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Material and Fermentation
3.3. Isolation of Compounds
3.4. Cell Viability Assay
3.5. Osteoclastogenesis Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ihn, H.J.; Lee, T.; Kim, J.A.; Lee, D.; Kim, N.D.; Shin, H.I.; Bae, Y.C.; Park, E.K. OCLI-023, a novel pyrimidine compound, suppresses osteoclastogenesis in vitro and alveolar bone resorption in vivo. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, W.J.; Simonet, W.S.; Lacey, D.L. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 2003, 423, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H.; Nakahama, K.; Sato, T.; Tuchiya, T.; Asakawa, Y.; Maemura, T.; Tanaka, M.; Morita, M.; Morita, I. The role of Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) in osteoclast differentiation induced by receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3243–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, U.H. Osteoclast formation and resorption. Matrix Biol. 2000, 19, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsenty, G.; Wagner, E.F. Reaching a genetic and molecular understanding of skeletal development. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alliston, T.; Derynck, R. Medicine: Interfering with bone remodelling. Nature 2002, 416, 686–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneda, T.; Yoshida, H.; Nakajima, Y.; Toishi, M.; Nugroho, A.E.; Morita, H. Cyclolinopeptides, cyclic peptides from flaxseed with osteoclast differentiation inhibitory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 1760–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, N.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, W.; Pan, C.; Yin, P.; Yu, X.; Tang, M. Beta-Carotene suppresses osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption by suppressing NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2017, 174, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konig, G.M.; Kehraus, S.; Seibert, S.F.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Muller, D. Natural products from marine organisms and their associated microbes. Chembiochem 2006, 7, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aly, A.H.; Debbab, A.; Kjer, J.; Proksch, P. Fungal endophytes from higher plants: A prolific source of phytochemicals and other bioactive natural products. Fungal Divers. 2010, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.R.A.; Kavlekar, D.P.; LokaBharathi, P.A. Marine Drugs from Sponge-Microbe Association—A Review. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1417–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.W.; Radax, R.; Steger, D.; Wagner, M. Sponge-Associated Microorganisms: Evolution, Ecology, and Biotechnological Potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 295–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegl, A.; Bayer, K.; Kozytska, S.; Hentschel, U.; Schmitt, S. Sponges and Microbes-New frontiers in an ancient symbiosis. Vie Milieu 2008, 58, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Endophytic and epiphytic microbes as “sources” of bioactive agents. Front. Chem. 2015, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Natural products: A continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3670–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Bao, L.; Ren, J.; Bahadur Basnet, B.; Liu, R.; He, L.; Han, J.; Yin, W.-B.; Liu, H. Versicoamides F–H, Prenylated Indole Alkaloids from Aspergillus tennesseensis. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Zhu, W. Antimicrobial ergosteroids and pyrrole derivatives from halotolerant Aspergillus flocculosus PT05-1 cultured in a hypersaline medium. Extremophiles 2013, 17, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadury, P.; Mohammad, B.T.; Wright, P.C. The current status of natural products from marine fungi and their potential as anti-infective agents. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 33, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, S.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wu, A.A.; Gui, F.; Guo, K.; Yang, Y.; Cao, S.; Hu, Z.; et al. Aspertetranones A-D, Putative Meroterpenoids from the Marine Algal-Associated Fungus Aspergillus sp. ZL0-1b14. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2405–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, K.; Hosoe, T.; Itabashi, T.; Wakana, D.; Takizawa, K.; Yaguchi, T.; Kawai, K.-I. Novoamauromine and Cycloechinulin: Two New Diketopiperazine Derivatives from Aspergillus novofumigatus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbandy, M.; Shinde, P.B.; Hong, J.-K.; Bae, K.-S.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.-M.; Jung, J.H. α-Pyrones and yellow pigments from the sponge-derived fungus Paecilomyces lilacinus. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2009, 30, 188–192. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, P.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Mactanamide, A New Fungistatic Diketopiperazine Produced By A Marine Aspergillus sp. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1998, 12, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Qin, X.; Tian, X.; Liao, L.; Li, K.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, T.; et al. Antiviral Merosesquiterpenoids Produced by the Antarctic Fungus Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis SCSIO 05702. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellana, E.A.; Kasinski, A.L. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay in Cell Culture to Investigate Cell Proliferation. Bio-Protoc. 2016, 6, e1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afiyatullov, S.S.; Leshchenko, E.V.; Sobolevskaya, M.P.; Denisenko, V.A.; Kirichuk, N.N.; Khudyakova, Y.V.; Hoai, T.P.T.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Pislyagin, E.A.; et al. New eudesmane sesquiterpenes from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium thomii. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 14, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Position | 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J, Hz) | δC | HMBC | COSY | |
| 1 | - | 165.7 | ||
| 2 | - | 97.6 | ||
| 3 | - | 163.9 | ||
| 4 | - | 107.5 | ||
| 5 | - | 155.7 | ||
| 6 | 2.28, dd (16.5, 5.0) | 16.5 | 1, 2, 3, 8, 12 | 7 |
| 7 | 2.47, dd (13.0, 5.0) | 42.9 | 11, 12, 20 | 6 |
| 8 | 80.4 | |||
| 9a | 1.91, brt | 33.3 | 10 | |
| 9b | 2.18, overlap | 10 | ||
| 10a | 1.69, overlap | 24.5 | 12 | 9 |
| 10b | 2.01, overlap | 12 | 9 | |
| 11 | - | 78.2 | ||
| 12 | - | 40.4 | ||
| 13 | - | 53.1 | ||
| 14 | - | 218.0 | ||
| 15a | 2.49, m | 33.3 | 14, 16 | 16 |
| 15b | 2.64, m | 14, 16 | 16 | |
| 16a | 1.68, overlap | 32.4 | 15 | |
| 16b | 2.01, overlap | 15 | ||
| 17 | 1.88, s | 8.1 | 3, 4, 5 | |
| 18 | 2.23, s | 15.7 | 4, 5 | |
| 19 | 1.30, s | 19.3 | 7, 8, 9 | |
| 20 | 1.17, s | 17.3 | 7, 11, 12, 16 | |
| 21 | 1.21, s | 22.5 | 11, 13, 14, 22 | |
| 22 | 1.12, s | 20.9 | 11, 13, 14, 21 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, H.J.; Choi, B.-K.; Trinh, P.T.H.; Lee, H.-S.; Kang, J.S.; Van, T.T.T.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, J. Suppression of RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by the Metabolites from the Marine Fungus Aspergillus flocculosus Isolated from a Sponge Stylissa sp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010014
Shin HJ, Choi B-K, Trinh PTH, Lee H-S, Kang JS, Van TTT, Lee H-S, Lee JS, Lee Y-J, Lee J. Suppression of RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by the Metabolites from the Marine Fungus Aspergillus flocculosus Isolated from a Sponge Stylissa sp. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Hee Jae, Byeoung-Kyu Choi, Phan Thi Hoai Trinh, Hwa-Sun Lee, Jong Soon Kang, Tran Thi Thanh Van, Hyi-Seung Lee, Jong Seok Lee, Yeon-Ju Lee, and Jihoon Lee. 2018. "Suppression of RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by the Metabolites from the Marine Fungus Aspergillus flocculosus Isolated from a Sponge Stylissa sp." Marine Drugs 16, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010014
APA StyleShin, H. J., Choi, B. -K., Trinh, P. T. H., Lee, H. -S., Kang, J. S., Van, T. T. T., Lee, H. -S., Lee, J. S., Lee, Y. -J., & Lee, J. (2018). Suppression of RANKL-Induced Osteoclastogenesis by the Metabolites from the Marine Fungus Aspergillus flocculosus Isolated from a Sponge Stylissa sp. Marine Drugs, 16(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010014