Clogging the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Machinery with Marine Natural Products: Last Decade Update
Abstract
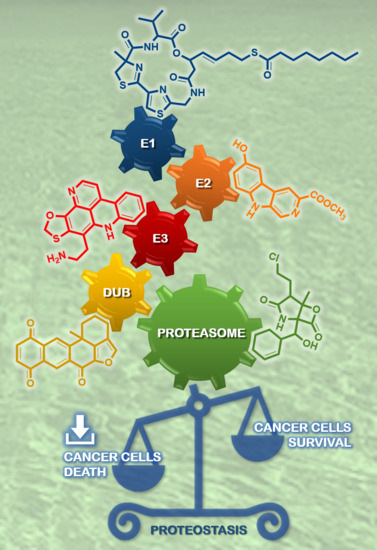
:1. Introduction
2. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway as a Target for Cancer Therapy
3. Salinosporamide A, a Milestone in Natural Product Drug Discovery

4. Inhibitors of the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway in the Last Decade (2007–2018)
4.1. Terpenes



4.2. Alkaloids


4.3. Peptides

4.4. Sphingolipids and Phospholipids


4.5. Sterols

4.6. Quinones


5. Resistance Mechanisms to Proteasome Inhibition
6. High-Throughput Screening for Discovery of Natural UPP Inhibitors
6.1. HTS Methods for Detection of Natural Proteasome Inhibitors
6.2. HTS Methods for Detection of Natural Inhibitors Targeting E1, E2, E3, and DUBs Enzymes
6.3. Indirect Methods to Detect Natural Products Targeting the UPP Pathways
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Advanced preclinical and clinical trials of natural products and related compounds from marine sources. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1693–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegley Kelly, L.; Haas, A.F.; Nelson, C.E. Ecosystem microbiology of coral reefs: Linking genomic, metabolomic, and miogeochemical dynamics from animal symbioses to reefscape processes. mSystems 2018, 3, e00162-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerwick, W.H.; Moore, B.S. Lessons from the past and charting the future of marine natural products drug discovery and chemical biology. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malve, H. Exploring the ocean for new drug developments: Marine pharmacology. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2016, 8, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, G.M.; Kehraus, S.S.; Seibert, F.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Müller, D. Natural Products from Marine Organisms and Their Associated Microbes. ChemBioChem 2006, 7, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.C.; Mori, T.; Rückert, C.; Uria, A.R.; Helf, M.J.; Takada, K.; Gernert, C.; Steffens, U.A.E.; Heycke, N.; Schmitt, S.; et al. An environmental bacterial taxon with a large and distinct metabolic repertoire. Nature 2014, 506, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Della Sala, G.; Hochmuth, T.; Teta, R.; Costantino, V.; Mangoni, A. Polyketide Synthases in the Microbiome of the Marine Sponge Plakortis halichondrioides: A Metagenomic Update. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5425–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulder, T.A.M.; Moore, B.S. Chasing the Treasures of the Sea—Bacterial Marine Natural Products. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, M.; Dittmann, E.; von Döhren, H. Cyanobacteria as a source of natural products. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 517, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manasanch, E.E.; Orlowski, R.Z. Proteasome inhibitors in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.B.; Crews, C.M. From Epoxomicin to Carfilzomib: Chemistry, Biology, and Medical Outcomes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 600–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudler, R. Manipulation of host proteasomes as a virulence mechanism of plant pathogens. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentschel, U.; Usher, K.M.; Taylor, M.W. Marine sponges as microbial fermenters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 55, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hentschel, U.; Fieseler, L.; Wehrl, M.; Gernert, C.; Steinert, M.; Hacker, J. Microbial Diversity of Marine Sponges. In Sponge (Porifera), 1st ed.; Muller, W.E.G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 37, pp. 59–88. ISBN 978-3-642-55519-0. [Google Scholar]
- Britstein, M.; Saurav, K.; Teta, R.; Della Sala, G.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Stoppelli, N.; Zoccarato, L.; Costantino, V.; Steindler, L. Identification and chemical characterization of N-acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing signals across sponge species and time. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, V.; Della Sala, G.; Saurav, K.; Teta, R.; Bar-shalom, R.; Mangoni, A.; Steindler, L. Plakofuranolactone as a Quorum Quenching Agent from the Indonesian Sponge Plakortis cf. lita. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, K.; Zhang, X.H. Quorum Quenching Agents: Resources for Antivirulence Therapy. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3245–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pawlik, J.R. Marine Invertebrate Chemical Defenses. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.R.; Garrone, R. Nutrition in marine sponges. Involvement of symbiotic bacteria in the uptake of dissolved carbon. In Nutrition in Lower Metazoa, 1st ed.; Smith, D., Tyffon, Y., Eds.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1980; pp. 157–161. ISBN 9780080259048. [Google Scholar]
- Manasanch, E.E.; Korde, N.; Zingone, A.; Tageja, N.; de Larrea, F.; Bhutani, M.; Roschewski, M.; Landgren, O. The proteasome: Mechanisms of biology and markers of activity and response to treatment in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, B.S.; Eustáquio, A.S.; McGlinchey, R.P. Advances in and applications of proteasome inhibitors. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haglund, K.; Dikic, I. Ubiquitylation and cell signaling. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3353–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kane, R.C.; Farrell, A.T.; Sridhara, R.; Pazdur, R. United States Food and Drug Administration approval summary: Bortezomib for the treatment of progressive multiple myeloma after one prior therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 2955–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlowski, R.Z.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. NF-kappaB as a therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delic, J.; Masdehors, P.; Omura, S.; Cosset, J.M.; Dumont, J.; Binet, J.L.; Magdelénat, H. The proteasome inhibitor lactacystin induces apoptosis and sensitizes chemo- and radioresistant human chronic lymphocytic leukaemia lymphocytes to TNF-alpha-initiated apoptosis. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 77, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoreva, T.A.; Tribulovich, V.G.; Garabadzhiu, A.V.; Melino, G.; Barlev, N.A. The 26S proteasome is a multifaceted target for anti-cancer therapies. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24733–24749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hideshima, T.; Mitsiades, C.; Akiyama, M.; Hayashi, T.; Chauhan, D.; Richardson, P.; Schlossman, R.; Podar, K.; Munshi, N.C.; Mitsiades, N.; et al. Molecular mechanisms mediating antimyeloma activity of proteasome inhibitor PS-341. Blood 2003, 101, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenci, S.; Mezghrani, A.; Cascio, P.; Bianchi, G.; Cerruti, F.; Fra, A.; Lelouard, H.; Masciarelli, S.; Mattioli, L.; Oliva, L.; et al. Progressively impaired proteasomal capacity during terminal plasma cell differentiation. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diehl, J.A.; Fuchs, S.Y.; Koumenis, C. The Cell Biology of the Unfolded Protein Response. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, B.; Benavides, A.; Shi, Y.; Frost, P.; Lichtenstein, A. Effect of autophagy on multiple myeloma cell viability. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1974–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, G.W.; Ali, M.; Wood, T.E.; Wong, D.; Maclean, N.; Wang, X.; Gronda, M.; Skrtic, M.; Li, X.; Hurren, R.; et al. The ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of leukemia and multiple myeloma. Blood 2010, 115, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soucy, T.A.; Smith, P.G.; Milhollen, M.A.; Berger, A.J.; Gavin, J.M.; Adhikari, S.; Brownell, J.E.; Burke, K.E.; Cardin, D.P.; Critchley, S.; et al. An inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme as a new approach to treat cancer. Nature 2009, 458, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulvino, M.; Liang, Y.; Oleksyn, D.; DeRan, M.; Van Pelt, E.; Shapiro, J.; Sanz, I.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J. Inhibition of proliferation and survival of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells by a small-molecule inhibitor of the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Ubc13-Uev1A. Blood 2012, 120, 1668–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Raoof, D.A.; Wang, Z.; Lin, M.-Y.; Thomas, D.G.; Greenson, J.K.; Giordano, T.J.; Orringer, M.B.; Chang, A.C.; Beer, D.G.; et al. Expression and Effect of Inhibition of the Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme E2C on Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Neoplasia 2006, 8, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landré, V.; Rotblat, B.; Melino, S.; Bernassola, F.; Melino, G. Screening for E3-Ubiquitin ligase inhibitors: Challenges and opportunities. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 7988–8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndubaku, C.; Tsui, V. Inhibiting the deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs). J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1581–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; He, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X.; Chen-Kiang, S.; Jaffrey, S.R.; Xu, G. A novel effect of thalidomide and its analogs: Suppression of cereblon ubiquitination enhances ubiquitin ligase function. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 4829–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groll, M.; Huber, R.; Potts, B.C.M. Crystal structures of salinosporamide A (NPI-0052) and B (NPI-0047) in complex with the 20S proteasome reveal important consequences of β-lactone ring opening and a mechanism for irreversible binding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 5136–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manam, R.R.; McArthur, K.A.; Chao, T.H.; Weiss, J.; Ali, J.A.; Palombella, V.J.; Groll, M.; Lloyd, G.K.; Palladino, M.A.; Neuteboom, S.T.; et al. Leaving groups prolong the duration of 20S proteasome inhibition and enhance the potency of salinosporamides. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 6711–6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macherla, V.R.; Mitchell, S.S.; Manam, R.R.; Reed, K.A.; Chao, T.H.; Nicholson, B.; Deyanat-Yazdi, G.; Mai, B.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W.F.; et al. Structure-activity relationship studies of salinosporamide A (NPI-0052), a novel marine derived proteasome inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3684–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groll, M.; McArthur, K.A.; Macherla, V.R.; Manam, R.R.; Potts, B.C. Snapshots of the Fluorosalinosporamide/20S Complex Offer Mechanistic Insights for Fine Tuning Proteasome Inhibition. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 5420–5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, K.A.; Manam, R.R.; Mitchell, S.S.; Xu, J.; Teisan, S.; Chao, T.H.; Deyanat-Yazdi, G.; Neuteboom, S.T.; Lam, K.S.; Potts, B.C. Salinosporamides D–J from the marine actinomycete Salinispora tropica, bromosalinosporamide, and thioester derivatives are potent inhibitors of the 20S proteasome. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nett, M.; Gulder, T.A.M.; Kale, A.J.; Hughes, C.C.; Moore, B.S. Function-Oriented Biosynthesis of β-Lactone Proteasome Inhibitors in Salinispora tropica. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6163–6167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulder, T.A.M.; Moore, B.S. Salinosporamide Natural Products: Potent 20S Proteasome Inhibitors as Promising Cancer Chemotherapeutics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng. 2010, 49, 9346–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, K.S.; Sethi, G.; Chao, T.H.; Neuteboom, S.T.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Palladino, M.A.; Younes, A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Salinosporamide A (NPI-0052) potentiates apoptosis, suppresses osteoclastogenesis, and inhibits invasion through down-modulation of NF-κB–regulated gene products. Blood 2007, 110, 2286–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baritaki, S.; Yeung, K.; Palladino, M.; Berenson, J.; Bonavida, B. Pivotal roles of snail inhibition and RKIP induction by the proteasome inhibitor NPI-0052 in tumor cell chemoimmunosensitization. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8376–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baritaki, S.; Chapman, A.; Yeung, K.; Spandidos, D.A.; Palladino, M.; Bonavida, B. Inhibition of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in metastatic prostate cancer cells by the novel proteasome inhibitor, NPI-0052: Pivotal roles of Snail repression and RKIP induction. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3573–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.P.; Ban, K.; Dujka, M.E.; McConkey, D.J.; Munsell, M.; Palladino, M.; Chandra, J. NPI-0052, a novel proteasome inhibitor, induces caspase-8 and ROS-dependent apoptosis alone and in combination with HDAC inhibitors in leukemia cells. Blood 2007, 110, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Millward, M.; Price, T.; Townsend, A.; Sweeney, C.; Spencer, A.; Sukumaran, S.; Longenecker, A.; Lee, L.; Lay, A.; Sharma, G.; et al. Phase I clinical trial of the novel proteasome inhibitor marizomib with the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat in patients with melanoma, pancreatic and lung cancer based on in vitro assessments of the combination. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 2303–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.J.; Mainwaring, P.; Price, T.; Millward, M.J.; Padrik, P.; Underhill, C.R.; Cannell, P.K.; Reich, S.D.; Trikha, M.; Spencer, A. Phase I clinical trial of marizomib (NPI-0052) in patients with advanced malignancies including multiple myeloma: Study NPI-0052-102 final results. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4559–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, N.; Spencer, A.; Harrison, S.J.; Chauhan, D.; Burrows, F.J.; Anderson, K.C.; Reich, S.D.; Richardson, P.G.; Trikha, M. Marizomib irreversibly inhibits proteasome to overcome compensatory hyperactivation in multiple myeloma and solid tumour patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 174, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di, K.; Lloyd, G.K.; Abraham, V.; MacLaren, A.; Burrows, F.J.; Desjardins, A.; Trikha, M.; Bota, D.A. Marizomib activity as a single agent in malignant gliomas: Ability to cross the blood-brain barrier. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, B.C.; Lam, K.S. Generating a generation of proteasome inhibitors: From microbial fermentation to total synthesis of salinosporamide a (marizomib) and other salinosporamides. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 835–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Della Sala, G.; Teta, R.; Caso, A.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Pawlik, J.R.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Chlorinated Thiazole-Containing Polyketide-Peptides from the Caribbean Sponge Smenospongia conulosa: Structure Elucidation on Microgram Scale. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 2016, 2871–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teta, R.; Della Sala, G.; Glukhov, E.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Combined LC-MS/MS and molecular networking approach reveals new cyanotoxins from the 2014 cyanobacterial bloom in Green Lake, Seattle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14301–14310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, L.M.; Faulkner, D.J. Acanthosulfate, a Sulfated Hydroxyhydroquinone Sesterterpenoid from the Sponge Acanthodendrilla sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Xu, B.; Cui, J.; Deng, Z.; de Voogd, N.J.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Globostelletins A–I, cytotoxic isomalabaricane derivatives from the marine sponge Rhabdastrella globostellata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 4639–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Guo, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Deng, R.; Liu, J.; Feng, G.K.; Xiao, D.J.; Deng, S.Z.; Zhang, X.S.; et al. Rhabdastrellic Acid-A Induced Autophagy-Associated Cell Death through Blocking Akt Pathway in Human Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morceau, F.; Schumacher, M.; Cerella, C.; Eifes, S.; Jaspars, M.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Heteronemin, a spongean sesterterpene, inhibits TNF α-induced NF-κB activation through proteasome inhibition and induces apoptotic cell death. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 79, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margarucci, L.; Monti, M.C.; Tosco, A.; Riccio, R.; Casapullo, A. Chemical Proteomics Discloses Petrosapongiolide M, an Antiinflammatory Marine Sesterterpene, as a Proteasome Inhibitor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Eng. 2010, 49, 3960–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margarucci, L.; Tosco, A.; De Simone, R.; Riccio, R.; Monti, M.C. Modulation of Proteasome Machinery by Natural and Synthetic Analogues of the Marine Bioactive Compound Petrosaspongiolide M. ChemBioChem 2012, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, M.C.; Margarucci, L.; Riccio, R.; Bon, L.; Mozzicafreddo, M.; Maria, A.; Casapullo, A. Mechanistic insights on petrosaspongiolide M inhibitory effects on immunoproteasome and autophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1844, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, A.; Sakai, E.; Kato, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; De Voogd, N.J.; Yokosawa, H.; Tsukamoto, S. Strongylophorines, meroditerpenoids from the marine sponge Petrosia corticata, function as proteasome inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2650–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.A.; Kagiyama, I.; El-desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; De Voogd, N.J.; Ammar, N.M.; Hifnawy, M.S.; Tsukamoto, S. Sulawesins A–C, Furanosesterterpene Tetronic Acids That Inhibit USP7, from a Psammocinia sp. Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Nehira, T.; Matsuo, K.; Kawabata, T.; Kobashigawa, Y.; Morioka, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; De Voogd, N.J.; Yokosawa, H.; et al. Niphateolide A: Isolation from the marine sponge Niphates olemda and determination of its absolute configuration by an ECD analysis. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 6956–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, I.E.; Gross, H.; Pontius, A.; Kehraus, S.; Krick, A.; Kelter, G.; Maier, A.; Fiebig, H.H.; König, G.M. Epoxyphomalin A and B, Prenylated Polyketides with Potent Cytotoxicity from the Marine-Derived Fungus Phoma sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5014–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, I.E.; Kehraus, S.; Krick, A.; Ko, G.M.; Kelter, G.; Maier, A. Mode of Action of Epoxyphomalins A and B and Characterization of Related Metabolites from the Marine-Derived Fungus Paraconiothyrium sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 2053–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, X.-H.; Wang, S.-K.; Huang, Y.-H.; Huang, M.-J.; Duh, C.-Y. A High-Content Screening Assay for the Discovery of Novel Proteasome Inhibitors from Formosan Soft Corals. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Yamanokuchi, R.; Yoshitomi, M.; Sato, K.; Ikeda, T.; Rotinsulu, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.; de Voogd, N.J.; van Soest, R.W.; Yokosawa, H. Aaptamine, an alkaloid from the sponge Aaptos suberitoides, functions as a proteasome inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3341–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Venz, S.; Shubina, L.K.; Fedorov, S.N.; Walther, R.; Jacobsen, C.; Stonik, V.A.; Bokemeyer, C.; Balabanov, S.; Honecker, F. Activity of aaptamine and two derivatives, demethyloxyaaptamine and isoaaptamine, in cisplatin-resistant germ cell cancer. J. Proteom. 2014, 96, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Fedorov, S.N.; Shubina, L.K.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Bokemeyer, C.; Keller-von Amsberg, G.; Honecker, F. Aaptamines from the Marine Sponge Aaptos sp. Display Anticancer Activities in Human Cancer Cell Lines and Modulate AP-1-, NF-κB-, and p53-Dependent Transcriptional Activity in Mouse JB6 Cl41 Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 469309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, C.; Bowling, J.; Seth, A.; Ju, B.; Kahali, B.; Hamann, M.; Cunningham, L.C. An Evaluation of the Cytotoxic Effect of the Natural Product Aaptamine Against t(4;11) Leukemias. Blood 2016, 128, 1624. [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa, Y.; Ueoka, R.; Yamanokuchi, R.; Horiuchi, N.; Ikeda, T.; Rotinsulu, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.; Ukai, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Namikoshi, M.; et al. Isolation of Salsolinol, a Tetrahydroisoquinoline Alkaloid, from the Marine Sponge Xestospongia cf. vansoesti as a Proteasome Inhibitor. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mravec, B. Salsolinol, a derivate of dopamine, is a possible modulator of catecholaminergic transmission: A review of recent developments. Physiol. Res. 2006, 55, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamanokuchi, R.; Imada, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Kato, H.; Watanabe, T.; Fujimuro, M.; Saeki, Y.; Yoshinaga, S.; Terasawa, H.; Iwasaki, N.; et al. Hyrtioreticulins A–E, indole alkaloids inhibiting the ubiquitin-activating enzyme, from the marine sponge Hyrtios reticulatus. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 4437–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Hirota, H.; Imachi, M.; Fujimuro, M.; Onuki, H.; Ohta, T.; Yokosawa, H. Himeic acid A: A new ubiquitin-activating enzyme inhibitor isolated from a marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansdell, T.A.; Hewlett, N.M.; Skoumbourdis, A.P.; Fodor, M.D.; Seiple, I.B.; Su, S.; Baran, P.S.; Feldman, K.S.; Tepe, J.J. Palau’amine and Related Oroidin-alkaloids Dibromophakellin and Dibromophakellstatin Inhibit the Human 20S Proteasome. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Miyazaki, M.; Kodrasov, M.P.; Rotinsulu, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Yokosawa, H.; Nicholson, B.; Tsukamoto, S. Spongiacidin C, a pyrrole alkaloid from the marine sponge stylissa massa, functions as a USP7 inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3884–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Desoky, A.H.; Kato, H.; Eguchi, K.; Kawabata, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Takeya, M.; Yokosawa, H.; et al. Acantholactam and pre-neo-kauluamine, manzamine-related alkaloids from the Indonesian marine sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusato, A.; Kato, H.; Nehira, T.; Eguchi, K.; Kawabata, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Takeya, M.; et al. Acanthomanzamines A-E with new manzamine frameworks from the marine sponge Acanthostrongylophora ingens. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 3888–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, E.; Kato, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Yokosawa, H.; Tsukamoto, S. Variabines A and B: New β-carboline alkaloids from the marine sponge Luffariella variabilis. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 68, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, J.A.; Kitagaki, J.; Yang, Y.; Saucedo, C.J.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Weissman, A.M.; McKee, T.C.; McMahon, J.B. Discovery of New Pyridoacridine Alkaloids from Lissoclinum cf. badium that Inhibit the Ubiquitin Ligase Activity of Hdm2 and Stabilize p53. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 10022–10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funayama, S.; Cordell, G.A. Alkaloids Possessing the Porphine Skeleton. In Alkaloids; Funayama, S., Cordell, G.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 209–217. ISBN 9780124173026. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Li, M.; Xu, B.; Zhu, X.; Deng, Z.; Lin, W. Proteasome and NF-kappaB inhibiting phaeophytins from the green alga Cladophora fascicularis. Molecules 2007, 12, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krunic, A.; Vallat, A.; Mo, S.; Lantvit, D.D.; Swanson, S.M.; Orjala, J. Scytonemides A and B, Cyclic Peptides with 20S Proteasome Inhibitory Activity from the Cultured Cyanobacterium Scytonema hofmanii. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1927–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Luesch, H. Largazole: From Discovery to Broad-Spectrum Therapy. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungermannova, D.; Parker, S.J.; Nasveschuk, C.G.; Wang, W.; Quade, B.; Zhang, G.; Kuchta, R.D.; Phillips, A.J.; Liu, X. Largazole and Its Derivatives Selectively Inhibit Ubiquitin Activating Enzyme (E1). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.R.; Kale, A.J.; Fenley, A.T.; Byrum, T.; Debonsi, H.M.; Gilson, M.K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Moore, B.S.; Gerwick, W.H. The Carmaphycins, New Proteasome Inhibitors Exhibiting an α,β-Epoxyketone Warhead from a Marine Cyanobacterium. ChemBioChem 2012, 13, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivella, D.B.B.; Pereira, A.R.; Stein, M.L.; Kasai, Y.; Byrum, T.; Valeriote, F.A.; Tantillo, D.J.; Groll, M.; Gerwick, W.H.; Moore, B.S. Enzyme inhibition by hydroamination: Design and mechanism of a hybrid carmaphycin-syringolin enone proteasome inhibitor. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirrung, M.C.; Zhang, F.; Ambadi, S.; Rao, G. Total synthesis of the fellutamides, lipopeptide proteasome inhibitors. More sustainable peptide bond formation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 8367–8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, J.; Groll, M.; Fahnestock, M.; Crews, C.M. Proteasome Inhibition by Fellutamide B Induces Nerve Growth Factor Synthesis. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Ondeyka, J.; Harris, G.H.; Zink, D.; Kahn, J.N.; Wang, H.; Bills, G.; Platas, G.; Wang, W.; Szewczak, A.A.; et al. Isolation, structure, and biological activities of fellutamides C and D from an undescribed Metulocladosporiella (Chaetothyriales) using the genome-wide Candida albicans fitness test. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-M.; Dang, H.T.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Hong, J.-K.; Lee, C.-O.; Jung, J.-H. A Cytotoxic Fellutamide Analogue from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 3817–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Li, D.; Chidawanyika, T.; Nathan, C.; Li, H. Fellutamide B is a potent inhibitor of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis proteasome. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 501, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Rotinsulu, H.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Ukai, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Namikoshi, M.; Ohta, T.; Yokosawa, H. Leucettamol A: A new inhibitor of Ubc13-Uev1A interaction isolated from a marine sponge, Leucetta aff. Microrhaphis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 6319–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Kato, H.; Nishikawa, T.; Iwasaki, N.; Suwa, Y.; Rotinsulu, H.; Losung, F.; Maarisit, W.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; Morioka, H.; et al. Siladenoserinols A–L: New sulfonated serinol derivatives from a tunicate as inhibitors of p53-Hdm2 interaction. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushiyama, S.; Umaoka, H.; Kato, H.; Suwa, Y.; Morioka, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.; de Voogd, N.J.; Yokosawa, H.; et al. Manadosterols A and B, sulfonated sterol dimers inhibiting the Ubc13-Uev1A interaction, isolated from the marine sponge Lissodendryx fibrosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanokashira, N.; Kukita, S.; Kato, H.; Nehira, T.; Angkouw, E.D.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Tsukamoto, S. Petroquinones: trimeric and dimeric xestoquinone derivatives isolated from the marine sponge Petrosia alfiani. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 5530–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakuma, M.; Kato, H.; Matsuo, K.; El-Desoky, A.H.; Kawabata, T.; Losung, F.; Mangindaan, R.E.P.; de Voogd, N.J.; Yokosawa, H.; Tsukamoto, S. 1-Hydroxyethylhalenaquinone: A New Proteasome Inhibitor from the Marine Sponge Xestospongia sp. Heterocycles 2014, 89, 2605–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Zhu, W.; Shu, Y.; Liu, P. Efficacy of therapy with bortezomib in solid tumors: A review based on 32 clinical trials. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 1795–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attar, E.C.; Amrein, P.C.; Fraser, J.W.; Fathi, A.; McAfee, S.; Wadleigh, M.; Deangelo, D.J.; Steensma, D.P.; Stone, R.M.; Foster, J.; et al. Phase I Dose Escalation Study of Bortezomib in Combination with Lenalidomide in Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenci, S.; Oliva, L.; Cerruti, F.; Milan, E.; Bianchi, G.; Raule, M.; Mezghrani, A.; Pasqualetto, E.; Sitia, R.; Cascio, P. Pivotal Advance: Protein Synthesis Modulates Responsiveness of Differentiating and Malignant Plasma Cells to Proteasome Inhibitors. J. Leuk. Biol. 2012, 92, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, C.M.; Davis, R.E.; Demchenko, Y.; Bellamy, W.; Gabrea, A.; Zhan, F.; Lenz, G.; Hanamura, I.; Wright, G.; Xiao, W.; et al. Frequent engagement of the classical and alternative NF-κB pathways by diverse genetic abnormalities in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, S.; Schubert, U.; Neubert, K.; Herrmann, K.; Burger, R.; Gramatzki, M.; Hahn, S.; Schreiber, S.; Wilhelm, S.; Herrmann, M.; et al. Extensive immunoglobulin production sensitizes myeloma cells for proteasome inhibition. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lü, S.; Yang, J.; Chen, Z.; Gong, S.; Zhou, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Different mutants of PSMB5 confer varying bortezomib resistance in T lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia cells derived from the Jurkat cell line. Exp. Hematol. 2009, 37, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruckrich, T.; Kraus, M.; Gogel, J.; Beck, A.; Ovaa, H.; Verdoes, M.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Kalbacher, H.; Driessen, C. Characterization of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in bortezomib-adapted cells. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Fu, J.; Chen, P.; Ge, X.; Li, Y.; Kuiatse, I.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Orlowski, R.Z. The Nuclear Factor (Erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 and Proteasome Maturation Protein Axis Mediate Bortezomib Resistance in Multiple Myeloma. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29854–29868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.-D.; Baladandayuthapani, V.; Lin, H.; Mulligan, G.; Li, B.; Esseltine, D.-L.W.; Qi, L.; Xu, J.; Hunziker, W.; Barlogie, B.; et al. Tight Junction Protein 1 Modulates Proteasome Capacity and Proteasome Inhibitor Sensitivity in Multiple Myeloma via EGFR/JAK1/STAT3 Signaling. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsiades, C.S.; Mitsiades, N.S.; McMullan, C.J.; Poulaki, V.; Kung, A.L.; Davies, F.E.; Morgan, G.; Akiyama, M.; Shringarpure, R.; Munshi, N.C.; et al. Antimyeloma activity of heat shock protein-90 inhibition. Blood 2006, 107, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, J.J.; Chowdhury, R.D. Molecular crosstalk between the proteasome, aggresomes and autophagy: Translational potential and clinical implications. Cancer Lett. 2012, 325, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung-Hagesteijn, C.; Erdmann, N.; Cheung, G.; Keats, J.J.; Stewart, A.K.; Reece, D.; Chung, K.C.; Tiedemann, R.E. Xbp1s-Negative Tumor B Cells and Pre-Plasmablasts Mediate Therapeutic Proteasome Inhibitor Resistance in Multiple Myeloma. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, D.J.; Berkova, Z.; Jones, R.J.; Woessner, R.; Bjorklund, C.C.; Ma, W.; Davis, R.E.; Lin, P.; Wang, H.; Madden, T.L.; et al. Targeting the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor to overcome bortezomib resistance in preclinical models of multiple myeloma. Blood 2012, 120, 3260–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williamson, M.J.; Silva, M.D.; Terkelsen, J.; Robertson, R.; Yu, L.; Xia, C.; Hatsis, P.; Bannerman, B.; Babcock, T.; Cao, Y.; et al. The relationship among tumor architecture, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and efficacy of bortezomib in mouse xenograft models. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 3234–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weyburne, E.S.; Wilkins, O.M.; Sha, Z.; Williams, D.A.; Pletnev, A.A.; de Bruin, G.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Goldberg, A.L.; Cole, M.D.; Kisselev, A.F. Inhibition of the proteasome β2 site sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer cells to β5 inhibitors through a mechanism involving Nrf1 suppression. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, M.L.; Groll, M. Applied techniques for mining natural proteasome inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Götze, S.; Saborowski, R. NanoDrop fluorometry adopted for microassays of proteasomal enzyme activities. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 413, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, M.L.; Beck, P.; Kaiser, M.; Dudler, R.; Becker, C.F.W.; Groll, M. One-shot NMR analysis of microbial secretions identifies highly potent proteasome inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18367–18371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sasiela, C.A.; Stewart, D.H.; Kitagaki, J. Identification of inhibitors for MDM2 ubiquitin ligase activity from natural product extracts by a novel high-throughput electrochemiluminescent screen. J. Biomol. Screen. 2008, 13, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berndsen, C.E.; Wolberger, C. A spectrophotometric assay for conjugation of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 418, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldenberg, S.J.; McDermott, J.L.; Butt, T.R.; Mattern, M.R.; Nicholson, B. Strategies for the Identification of novel inhibitors of deubiquitinating enzymes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantuma, N.P.; Lindsten, K.; Glas, R.; Jellne, M.; Masucci, M.G. Short-lived green fluorescent proteins for quantifying ubiquitin/proteasome-dependent proteolysis in living cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ausseil, F.; Samson, A.; Aussagues, Y.; Vandenberghe, I.; Creancier, L.; Pouny, I.; Kruczynski, A.; Massiot, G.; Bailly, C. High-throughput bioluminescence screening of ubiquitin-proteasome pathway inhibitors from chemical and natural sources. J. Biomol. Screen. 2007, 12, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Della Sala, G.; Agriesti, F.; Mazzoccoli, C.; Tataranni, T.; Costantino, V.; Piccoli, C. Clogging the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Machinery with Marine Natural Products: Last Decade Update. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16120467
Della Sala G, Agriesti F, Mazzoccoli C, Tataranni T, Costantino V, Piccoli C. Clogging the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Machinery with Marine Natural Products: Last Decade Update. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(12):467. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16120467
Chicago/Turabian StyleDella Sala, Gerardo, Francesca Agriesti, Carmela Mazzoccoli, Tiziana Tataranni, Valeria Costantino, and Claudia Piccoli. 2018. "Clogging the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Machinery with Marine Natural Products: Last Decade Update" Marine Drugs 16, no. 12: 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16120467
APA StyleDella Sala, G., Agriesti, F., Mazzoccoli, C., Tataranni, T., Costantino, V., & Piccoli, C. (2018). Clogging the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Machinery with Marine Natural Products: Last Decade Update. Marine Drugs, 16(12), 467. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16120467