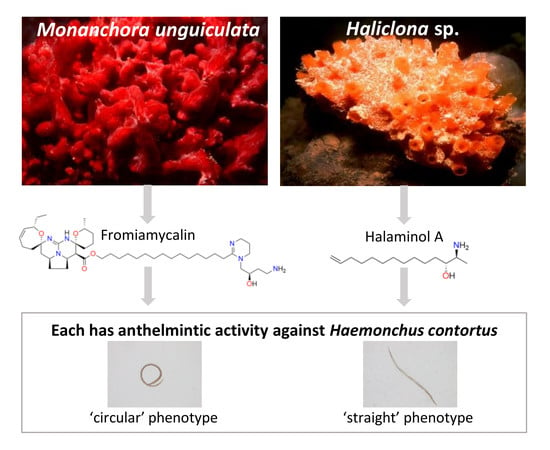
Identification of Fromiamycalin and Halaminol A from Australian Marine Sponge Extracts with Anthelmintic Activity against Haemonchus contortus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Three Extracts from Marine Sponges Exhibited Anthelmintic Activity Against Larval Stages of H. contortus
2.2. Bioassay Screening Identified Active Chromatographic Fractions from Three Marine Sponge Extracts
2.3. NMR, MS and Chiro-optical Data Analyses Identified Fromiamycalin in Active Fractions from Extract Mu-1
2.4. Fromiamycalin Inhibited the Motility and Development of Larvae of H. contortus, and had Moderate Toxicity on Fao Rat Hepatoma Cells
2.5. NMR, MS and Chiro-optical Analyses Identified Halaminol A in the Active Fractions of Extracts Ha-1 and Ha-2
2.6. Halaminol A Inhibited the Motility and/or Development of Larvae of H. contortus, and had Limited Toxicity on Fao Rat Hepatoma Cells
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Marine Sponge Material: Extraction, Fractionation and Compound Characterisation
3.2. Procurement of H. contortus, and Bioassays to Identify Active Extracts and Chromatographic Fractions
3.3. Assessment of the Potency of Extracts and Purified Compounds
3.4. Assessment of Cytotoxicity of Purified Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perdicaris, S.; Vlachogianni, T.; Valavanidis, A. Bioactive natural substances from marine sponges: new developments and prospects for future pharmaceuticals. Nat. Prod. Chem. Res. 2013, 1, 2329–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 122–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Proksch, P. Defensive roles for secondary metabolites from marine sponges and sponge-feeding nudibranchs. Toxicon. 1994, 32, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, N.G.M.; Dasari, R.; Chandra, S.; Kiss, R.; Kornienko, A. Marine invertebrate metabolites with anticancer activities: solutions to the “supply problem”. Mar. Drugs. 2016, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C. Marine natural products in medicinal chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Advanced tools in marine natural drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 42, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornburg, C.C.; Britt, J.R.; Evans, J.R.; Akee, R.K.; Whitt, J.A.; Trinh, S.K.; Harris, M.J.; Thompson, J.R.; Ewing, T.L.; Shipley, S.M.; et al. NCI program for natural product discovery: A publicly-accessible library of natural product fractions for high-throughput screening. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 2484–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.M.; McClean, C.J.; Veron, J.E.N.; Hawkins, J.P.; Allen, G.R.; McAllister, D.E.; Mittermeier, C.G.; Schueler, F.W.; Spalding, M.; Wells, F.; et al. Marine biodiversity hotspots and conservation priorities for tropical reefs. Science 2002, 295, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renema, W.; Bellwood, D.R.; Braga, J.C.; Bromfield, K.; Hall, R.; Johnson, K.G.; Lunt, P.; Meyer, C.P.; McMonagle, L.B.; Morley, R.J.; et al. Hopping hotspots: global shifts in marine biodiversity. Science 2008, 321, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 1999: compounds with antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anthelmintic, anti-inflammatory, antiplatelet, antiprotozoal and antiviral activities affecting the cardiovascular, endocrine, immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2002, 132, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodriguez, A.D.; Berlinck, R.G.; Hamann, M.T. Marine pharmacology in 2003-4: marine compounds with anthelmintic antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antimalarial, antiplatelet, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the cardiovascular, immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 145, 553–581. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Capon, R.J.; Skene, C.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Wadsworth, D.; Friedel, T. Geodin A magnesium salt: A novel nematocide from a southern Australian marine sponge, Geodia. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, D.; Capon, R.J.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Heiland, K.; Friedel, T. Onnamide F: A new nematocide from a southern Australian marine sponge, Trachycladus laevispirulifer. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 640–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Skene, C.; Liu, E.H.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Heiland, K.; Friedel, T. Nematocidal thiocyanatins from a southern Australian marine sponge Oceanapia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Vuong, D.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H. (−)-Echinobetaine A: isolation, structure elucidation, synthesis, and SAR studies on a new nematocide from a southern Australian marine sponge, Echinodictyum sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Vuong, D.; McNally, M.; Peterle, T.; Trotter, N.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H. (+)-Echinobetaine B: isolation, structure elucidation, synthesis and preliminary SAR studies on a new nematocidal betaine from a southern Australian marine sponge, Echinodictyum sp. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, P.R.; Hodge, A.; Watson, T.G.; Seed, J.A.; Maeder, S.J. Field efficacy and safety of an oral formulation of the novel combination anthelmintic, derquantel-abamectin, in sheep in New Zealand. N. Z. Vet. J. 2010, 58, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.M.; Vidyashankar, A.N. An inconvenient truth: global worming and anthelmintic resistance. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, T. Haemonchus contortus: Applications in drug discovery. Adv. Parasitol. 2016, 93, 429–463. [Google Scholar]
- Kotze, A.C.; Prichard, R.K. Anthelmintic resistance in Haemonchus contortus: history, mechanisms and diagnosis. Adv. Parasitol. 2016, 93, 397–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Camp, D.; Davis, R.A.; Campitelli, M.; Ebdon, J.E.; Quinn, R.J. Drug-like properties: guiding principles for the design of natural product libraries. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 75, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Demerdash, A.; Moriou, C.; Martin, M.; de S. Rodrigues-Stien, A.; Petek, S.; Demoy-Schneider, M.; Hall, K.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Debitus, C.; Al-Mourabit, A. Cytotoxic guanidine alkaloids from a French Polynesian Monanchora n. sp. sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Demerdash, A.; Moriou, C.; Martin, M.; Petek, S.; Debitus, C.; Al-Mourabit, A. Unguiculins A-C: cytotoxic bis-guanidine alkaloids from the French Polynesian sponge, Monanchora n. sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Sorolla, A.; Fromont, J.; Blancafort, P.; Flematti, G. Crambescidin 800, isolated from the marine sponge Monanchora viridis, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, P.E.; Wolfender, J.; Queiroz, E.F.; Marcourt, L.; Al-Mourabit, A.; Frederich, M.; Bordignon, A.; de Voogd, N.; Illien, B.; Gauvin-Bialecki, A. Unguiculin A and ptilomycalins E-H, antimalarial guanidine alkaloids from the marine sponge Monanchora unguiculata. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.F.C.; Harper, P.M.; Williams, D.E.; Mesquita, J.T.; Pinto, E.G.; da Costa-Silva, T.A.; Hajdu, E.; Ferreira, A.G.; Santos, R.A.; Murphy, P.J.; et al. Anti-parasitic guanidine and pyrimidine alkaloids from the marine sponge Monanchora arbuscula. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Whittaker, N.F.; Bewley, C.A. Crambescidin 826 and dehydrocrambine A: new polycyclic guanidine alkaloids from the marine sponge Monanchora sp. that inhibit HIV-1 fusion. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takishima, S.; Ishiyama, A.; Iwatsuki, M.; Otoguro, K.; Yamada, H.; Omura, S.; Kobayashi, H.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Matsunaga, S. Merobatzelladines A and B, anti-infective tricyclic guanidines from a marine sponge Monanchora sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 2655–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazemi, M.; Salimi, M.A.; Salimi, P.A.; Motallebi, A.; Jahromi, S.T.; Ahmadzadeh, O. Antifungal and antibacterial activity of Haliclona sp. from the Persian Gulf, Iran. J. Mycol. Med. 2014, 24, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, V.; Srivastava, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Misra, S.; Verma, M.; Misra-Bhattacharya, S. In vitro and in vivo antifilarial potential of marine sponge, Haliclona exigua (Kirkpatrick), against human lymphatic filarial parasite Brugia malayi. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Misra, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Srivastava, S.; Srivastava, M.N.; Lakshmi, V.; Misra-Bhattacharya, S. Antifilarial activity of marine sponge Haliclona oculata against experimental Brugia malayi infection. Exp. Pasitol. 2012, 130, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dube, A.; Singh, N.; Saxena, A.; Lakshmi, V. Antileishmanial potential of a marine sponge, Haliclona exigua (Kirkpatrick) against experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarif, W.M.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Al-Lihaibi, S.S.; Ayyad, S.N.; Badria, F.A. A new cytotoxic brominated acetylenic hydrocarbon from the marine sponge Haliclona sp. with a selective effect against human breast cancer. Z. Naturforsch. 2013, 68, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento-Neto, L.G.; Cabral, M.G.; Carneiro, R.F.; Silva, Z.; Arruda, F.V.S.; Nagano, C.S.; Fernandes, A.R.; Sampaio, A.H.; Teixeira, E.H.; Videira, P.A. Halilectin-3, a lectin from the marine sponge Haliclona caerulea, induces apoptosis and autophagy in human breast cancer MCF7 cells through caspase-9 pathway and LC3-II protein expression. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarisit, W.; Abdjul, D.B.; Yamazaki, H.; Kato, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Sumilat, D.A.; Kapojos, M.M.; Ukai, K.; Namikoshi, M. Anti-mycobacterial alkaloids, cyclic 3-alkyl pyridinium dimers, from the Indonesian marine sponge Haliclona sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3503–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegelmann, C.; Parker, J.; Ooi, T.; Clements, C.; Abbott, G.; Young, L.; Kennedy, J.; Dobson, A.D.W.; Edrada-Ebel, R. Isolation and identification of antitrypanosomal and antimycobacterial active steroids from the sponge Haliclona simulans. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2937–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palagiano, E.; de Marino, S.; Minale, L.; Riccio, R.; Zollo, F.; Iorizzi, M.; Carre, J.B.; Debitus, C.; Lucarain, L.; Provost, J. Ptilomycalin A, crambescidin 800 and related new highly cytotoxic guanidine alkaloids from the starfishes Fromia monilis and Celerina heffernani. Tetrahedron. 1995, 51, 3675–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laville, R.; Thomas, O.P.; Berrue, F.; Marquez, D.; Vacelet, J.; Amade, P. Bioactive guanidine alkaloids from two Caribbean marine sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1589–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallimore, W.A.; Kelly, M.; Scheuer, P.J. Alkaloids from the sponge Monanchora unguifera. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1420–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensemhoun, J.; Bombarda, I.; Aknin, M.; Vacelet, J.; Gaydou, E.M. Ptilomycalin D, a polycyclic guanidine alkaloid from the marine sponge Monanchora dianchora. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 2033–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzii, A.G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Stonik, V.A. Monanchocidin: A new apoptosis-inducing polycyclic guanidine alkaloid from the marine sponge Monanchora pulchra. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4292–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Tabakmaher, K.M.; Guzii, A.G.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Shubina, L.K.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Lee, H.; Stonik, V.A. Monanchocidins B-E: polycyclic guanidine alkaloids with potent antileukemic activities from the sponge Monanchora pulchra. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1952–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Tabakmaher, K.M.; Guzii, A.G.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Lee, H.; Stonik, V.A. Monanchomycalins A and B, unusual guanidine alkaloids from the sponge Monanchora pulchra. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 4228–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakmakher, K.M.; Denisenko, V.A.; Guzii, A.G.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Lee, H.; Makarieva, T.N. Monanchomycalin C, a new pentacyclic guanidine alkaloid from the far-eastern marine sponge Monanchora pulchra. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Tavares, R.; Hajdu, E.; Van Soest, R.W.M. Novel polycyclic guanidine alkaloids from two marine sponges of the genus Monanchora. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabakmakher, K.M.; Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Guzii, A.G.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Stonik, V.A. Normonanchocidins A, B and D, new pentacyclic guanidine alkaloids from the far-eastern marine sponge Monanchora pulchra. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 913–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, J.E.H.; Nitcheu, J.; Mahmoudi, N.; Ibana, J.A.; Mangalindan, G.C.; Black, G.P.; Howard-Jones, A.G.; Moore, C.G.; Thomas, D.A.; Mazier, D. Antimalarial activity of crambescidin 800 and synthetic analogues against liver and blood stage of Plasmodium sp. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashman, Y.; Hirsh, S.; McConnell, O.J.; Ohtani, I.; Kusumi, T.; Kakisawa, H. Ptilomycalin A: A novel polycyclic guanidine alkaloid of marine origin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 8925–8926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.J.; Garson, M.J.; Hooper, J.N.A. Antifungal alkyl amino alcohols from the tropical marine sponge Haliclona n. sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1568–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, K.E.; Beamish, H.; Garson, M.J.; Skilleter, G.A.; Gegnan, B.M. Convergent antifouling activities of structurally distinct bioactive compounds synthesized within two sympatric Haliclona demosponges. Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.A.; Duffy, S.; Fletcher, S.; Avery, V.M.; Quinn, R.J. Thiaplakortones A-D: Antimalarial thiazine alkaloids from the Australian marine sponge Plakortis lita. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 9608–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, S.; Jabbar, A.; Nowell, C.; Joachim, A.; Ruttkowski, B.; Baell, J.; Cardno, T.; Korhonen, P.K.; Piedrafita, D.R.E.; Ansell, B.R.; et al. Low cost whole-organism screening of compounds for anthelmintic activity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sommerville, R.I. The development of Haemonchus contortus to the fourth stage in vitro. J. Parasitol. 1966, 52, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwka, L.; Wiktorska, K.; Suchocki, P.; Milczarek, M.; Mielczarek, S.; Lubelska, K.; Cierpial, T.; Lyzwa, P.; Kielbasinski, P.; Jaromin, A.; et al. The comparison of MTT and CVS assays for the assessment of anticancer agent interactions. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0155772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Extract Control Compound | xL3 Motility (IC50 in µge/µL) | L4 Development (IC50 in µge/µL) |
|---|---|---|
| 72 h | 7 days | |
| Monanchora unguiculata (Mu-1) | 0.7 ± 0.01 | 0.6 ± 0.17 |
| Haliclona sp. (Ha-1) | ~ 3.0 a | 0.6 ± 0.18 |
| Haliclona sp. (Ha-2) | ~ 3.0 a | 0.6 ± 0.15 |
| Monepantel b | 6.6 10−5 ± 0.06 | 1.4 10−5 ± 0.00 |
| Moxidectin b | 1.9 10−5 ± 0.06 | 2.6 10−6 ± 0.00 |
| Test Compound Control Compound | xL3 Motility (IC50 in µM) | L4 Motility (IC50 in µM) | L4 Development (IC50 in µM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 72 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | 7 days | |
| Fromiamycalin | > 100 | 52.4 ± 3.34 | 31.9 ± 3.74 | 39.4 ± 4.83 | 26.6 ± 0.74 |
| Monepantel | 0.1 ± 0.06 | 1.6 ± 0.73 | 0.2 ± 0.00 | 0.1–0.2 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 |
| Moxidectin | 0.03 ± 0.06 | 0.06 ± 0.05 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.008 a | 0.004 ± 0.00 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herath, H.M.P.D.; Preston, S.; Jabbar, A.; Garcia-Bustos, J.; Taki, A.C.; Addison, R.S.; Hayes, S.; Beattie, K.D.; McGee, S.L.; Martin, S.D.; et al. Identification of Fromiamycalin and Halaminol A from Australian Marine Sponge Extracts with Anthelmintic Activity against Haemonchus contortus. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110598
Herath HMPD, Preston S, Jabbar A, Garcia-Bustos J, Taki AC, Addison RS, Hayes S, Beattie KD, McGee SL, Martin SD, et al. Identification of Fromiamycalin and Halaminol A from Australian Marine Sponge Extracts with Anthelmintic Activity against Haemonchus contortus. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(11):598. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110598
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerath, H. M. P. Dilrukshi, Sarah Preston, Abdul Jabbar, Jose Garcia-Bustos, Aya C. Taki, Russell S. Addison, Sasha Hayes, Karren D. Beattie, Sean L. McGee, Sheree D. Martin, and et al. 2019. "Identification of Fromiamycalin and Halaminol A from Australian Marine Sponge Extracts with Anthelmintic Activity against Haemonchus contortus" Marine Drugs 17, no. 11: 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110598
APA StyleHerath, H. M. P. D., Preston, S., Jabbar, A., Garcia-Bustos, J., Taki, A. C., Addison, R. S., Hayes, S., Beattie, K. D., McGee, S. L., Martin, S. D., Ekins, M. G., Hooper, J. N. A., Chang, B. C. H., Hofmann, A., Davis, R. A., & Gasser, R. B. (2019). Identification of Fromiamycalin and Halaminol A from Australian Marine Sponge Extracts with Anthelmintic Activity against Haemonchus contortus. Marine Drugs, 17(11), 598. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17110598