Amino Acid Composition, Antioxidant, and Cytoprotective Effect of Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Hydrolysate through the Inhibition of Caspase-3 Activation in Oxidative Stress-Mediated Endothelial Cell Injury
Abstract
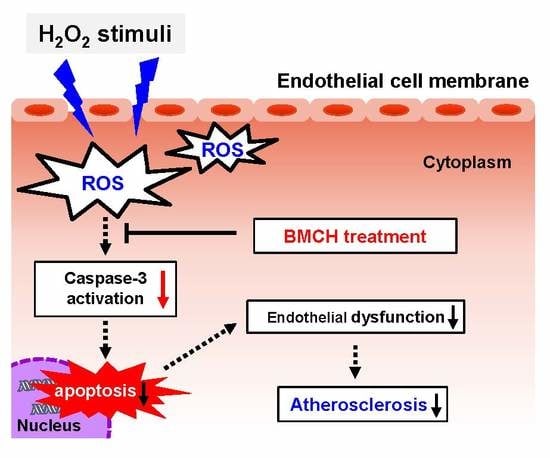
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antioxidant and Inhibitory Effect of BMHs on LDL Oxidation
2.2. The Protective Effect of BMCH against H2O2-Induced Cytotoxicity in HUVEC
2.3. BMCH Treatment Inhibits ROS Generation in H2O2-Induced HUVEC Injury
2.4. BMCH Enhanced the Levels of Intracellular GSH and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
2.5. Prevention of Apoptosis and Necrosis by BMCH Treatment in H2O2-Mediated HUVEC Injury
2.6. Modulation of Apoptosis-Related Genes by BMCH in H2O2-Induced HUVEC Injury
2.7. Supression Caspase-3 Activation in H2O2-Induced HUVEC Injury
2.8. Amino Acid Composition and Molecular Weight Distribution of BMCH
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Blue Mussel Hydrolysates
4.3. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
4.3.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
4.3.2. ABTS+ Radical Scavenging Assay
4.3.3. ORAC Assay
4.4. LDL Oxidation Inhibitory Activity
4.5. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.6. Determination of Cytoprotective Effect in H2O2-Mediated HUVEC Injury
4.6.1. Cell Viability Assay
4.6.2. Live/Dead Cell Assay
4.6.3. Measurement of Intracellular Glutathione (GSH) Levels
4.6.4. Intracellular ROS Measurement
4.6.5. Determination of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
4.6.6. Cellular Morphological Changes
4.6.7. Cell Apoptosis and Necrosis Analysis by Flow Cytometry
4.6.8. mRNA Expression by Real Time-qPCR
4.6.9. Western Blotting
4.7. Characterization of Blue Mussel Hydrolysates
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Blaha, M.J.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; Deo, R.; Floyd, J.; Fornage, M.; Gillespie, C.; Isasi, C. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 135, e146–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esper, R.J.; Nordaby, R.A.; Vilariño, J.O.; Paragano, A.; Cacharrón, J.L.; Machado, R.A. Endothelial dysfunction: A comprehensive appraisal. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2006, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudau, M.; Genis, A.; Lochner, A.; Strijdom, H. Endothelial dysfunction: The early predictor of atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2012, 23, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanassoulis, G.; Campbell, C.Y.; Owens, D.S.; Smith, J.G.; Smith, A.V.; Peloso, G.M.; Kerr, K.F.; Pechlivanis, S.; Budoff, M.J.; Harris, T.B. Genetic associations with valvular calcification and aortic stenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.B.; Mengi, S.A.; Xu, Y.-J.; Arneja, A.S.; Dhalla, N.S. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: A multifactorial process. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2002, 7, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Harrison, D.G. Endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: The role of oxidant stress. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonetti, P.O.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. Endothelial dysfunction: A marker of atherosclerotic risk. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davi, G.; Falco, A. Oxidant stress, inflammation and atherogenesis. Lupus 2005, 14, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foncea, R.; Carvajal, C.; Almarza, C.; Leighton, F. Endothelial cell oxidative stress and signal transduction. Biol. Res. 2000, 33, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.C.; Landau, W.M. Atherosclerosis and stroke. Ann. Neurol. 1990, 28, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, E. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47 (Suupl. 8), C7–C12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, D.-H.; Kim, S.-K. Marine bioactive peptides as potential antioxidants. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2013, 14, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamatsu, S.; Hodges, T.W.; Rajbhandari, I.; Gerwick, W.H.; Hamann, M.T.; Nagle, D.G. Marine natural products as novel antioxidant prototypes. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Wu, C.; Liu, D.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liao, B.; He, H.; Li, H. Overview of antioxidant peptides derived from marine resources: The sources, characteristic, purification, and evaluation methods. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1815–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Je, J.-Y.; Cha, J.-Y.; Cho, Y.-S.; Ahn, H.-Y.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, Y.-S.; Ahn, C.-B. Hepatoprotective effect of peptic hydrolysate from salmon pectoral fin protein byproducts on ethanol-induced oxidative stress in Sprague–Dawley rats. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyung, J.-H.; Ahn, C.-B.; Je, J.-Y. Blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) protein hydrolysate promotes mouse mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblasts through up-regulation of bone morphogenetic protein. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmadi, B.H.; Ismail, A. Antioxidative peptides from food proteins: A review. Peptides 2010, 31, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Li, L.; Chi, C.F.; Ma, J.H.; Luo, H.Y.; Xu, Y.F. Purification and characterisation of a novel antioxidant peptide derived from blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Ahn, C.-B.; Je, J.-Y. Partial purification and identification of three antioxidant peptides with hepatoprotective effects from blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) hydrolysate by peptic hydrolysis. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-L.; Qian, Y.; Meng, W.-F.; Pang, J.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Guan, Y.-Y.; Chen, S.-P.; Liu, J.; Pei, Z.; Wang, G.-L. A novel marine compound xyloketal B protects against oxidized LDL-induced cell injury in vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Luo, R.; Xiang, Q.; Xu, X.; Qiu, L.; Pang, J. Design and synthesis of novel xyloketal derivatives and their protective activities against H2O2-induced HUVEC injury. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 948–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, W.-W.; Kang, N.; Kim, E.-A.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, D.; Jeon, Y.-J. Protective effect of fucoxanthin isolated from Ishige okamurae against high-glucose induced oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and zebrafish model. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 11, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, Y.; Maruhashi, T.; Noma, K.; Kihara, Y. Oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction: Clinical evidence and therapeutic implications. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2014, 24, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiva, E.; Wehinger, S.; Guzmán, L.; Orrego, R. Role of Oxidized LDL in Atherosclerosis. In Hypercholesterolemia; InTech: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Liang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Huang, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J. Rice Bioactive Peptide Binding with TLR4 To Overcome H2O2-Induced Injury in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells through NF-κB Signaling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerksick, C.; Willoughby, D. The antioxidant role of glutathione and N-acetyl-cysteine supplements and exercise-induced oxidative stress. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2005, 2, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faucher, K.; Rabinovitch-Chable, H.; Cook-Moreau, J.; Barrière, G.; Sturtz, F.; Rigaud, M. Overexpression of human GPX1 modifies Bax to Bcl-2 apoptotic ratio in human endothelial cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2005, 277, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y.; Lin, J.K. Involvement of reactive oxygen species and caspase 3 activation in arsenite-induced apoptosis. J. Cell. Physiol. 1998, 177, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, C. Endothelial cell functions. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 196, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.-L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Hu, H.; Pan, Y.; Fan, X.-J.; Hu, X.-M.; Zou, W.-W. Inhibition of hydrogen peroxide-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells aging by allicin depends on Sirtuin1 activation. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, W.N.; Deng, J.; Ruan, X.Z.; Xu, Q. Reactive oxygen species generation and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, e41–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, U.; Jialal, I. Oxidative stress and atherosclerosis. Pathophysiology 2006, 13, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, D.; Griendling, K.K.; Landmesser, U.; Hornig, B.; Drexler, H. Role of oxidative stress in atherosclerosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstermann, U. Oxidative stress in vascular disease: Causes, defense mechanisms and potential therapies. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2008, 5, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victor, V.M.; Rocha, M.; Sola, E.; Banuls, C.; Garcia-Malpartida, K.; Hernandez-Mijares, A. Oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2988–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrulea, M.; Muresan, A.; Duncea, I. Oxidative stress and antioxidant status in hypo-and hyperthyroidism. In Antioxidant Enzyme; InTech: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Kang, J.-S.; Park, J.H.Y.; Lee, Y.-J.; Choi, J.-S.; Kang, Y.-H. Polyphenolic flavonoids differ in their antiapoptotic efficacy in hydrogen peroxide–treated human vascular endothelial cells. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, U.; Groscurth, P. Morphological features of cell death. Physiology 2004, 19, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redza-Dutordoir, M.; Averill-Bates, D.A. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2016, 1863, 2977–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyak, K.; Xia, Y.; Zweier, J.L.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature 1997, 389, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.W.; Lv, C.; Shi, Z.R.; Zeng, R.T.; Dong, X.Y.; Zhang, W.D.; Liu, R.H.; Shan, L.; Shen, Y.H. Abieslactone induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinomas through the mitochondrial pathway and the generation of reactive oxygen species. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotem, J.; Peled-Kamar, M.; Groner, Y.; Sachs, L. Cellular oxidative stress and the control of apoptosis by wild-type p53, cytotoxic compounds, and cytokines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 9166–9171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valen, G. The basic biology of apoptosis and its implications for cardiac function and viability. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2003, 75, S656–S660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Yan, X.; Genders, A.J.; Granata, C.; Bishop, D.J. An overview of technical considerations when using quantitative real-time PCR analysis of gene expression in human exercise research. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.; Ahn, C.B.; Yoon, N.Y.; Nam, K.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Je, J.Y. Protective effect of enzymatic hydrolysates from seahorse (Hippocampus abdominalis) against H2O2-mediated human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, A.G.; Jänicke, R.U. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ismail, N.A.; Okasha, S.H.; Dhawan, A.; Abdel-Rahman, A.O.; Shaker, O.G.; Sadik, N.A. Antioxidant enzyme activities in hepatic tissue from children with chronic cholestatic liver disease. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, P.J.; Kim, C.H. Extraction of polyphenols from apple peel using cellulase and pectinase and estimation of antioxidant activity. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 38, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulueta, A.; Esteve, M.J.; Frígola, A. ORAC and TEAC assays comparison to measure the antioxidant capacity of food products. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poot, M.; Verkerk, A.; Koster, J.F.; Jongkind, J.F. De novo synthesis of glutathione in human fibroblasts during in vitro ageing and in some metabolic diseases as measured by a flow cytometric method. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 1986, 883, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C T method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, Y.; Ahn, C.-B.; Nam, K.-H.; Kim, Y.-K.; Yoon, N.Y.; Je, J.-Y. Amino Acid Composition, Antioxidant, and Cytoprotective Effect of Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Hydrolysate through the Inhibition of Caspase-3 Activation in Oxidative Stress-Mediated Endothelial Cell Injury. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020135
Oh Y, Ahn C-B, Nam K-H, Kim Y-K, Yoon NY, Je J-Y. Amino Acid Composition, Antioxidant, and Cytoprotective Effect of Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Hydrolysate through the Inhibition of Caspase-3 Activation in Oxidative Stress-Mediated Endothelial Cell Injury. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(2):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020135
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Yunok, Chang-Bum Ahn, Ki-Ho Nam, Yeon-Kye Kim, Na Young Yoon, and Jae-Young Je. 2019. "Amino Acid Composition, Antioxidant, and Cytoprotective Effect of Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Hydrolysate through the Inhibition of Caspase-3 Activation in Oxidative Stress-Mediated Endothelial Cell Injury" Marine Drugs 17, no. 2: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020135
APA StyleOh, Y., Ahn, C. -B., Nam, K. -H., Kim, Y. -K., Yoon, N. Y., & Je, J. -Y. (2019). Amino Acid Composition, Antioxidant, and Cytoprotective Effect of Blue Mussel (Mytilus edulis) Hydrolysate through the Inhibition of Caspase-3 Activation in Oxidative Stress-Mediated Endothelial Cell Injury. Marine Drugs, 17(2), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020135