In Vitro and In Silico Approaches to Generating and Identifying Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme I Inhibitory Peptides from Green Macroalga Ulva lactuca
Abstract
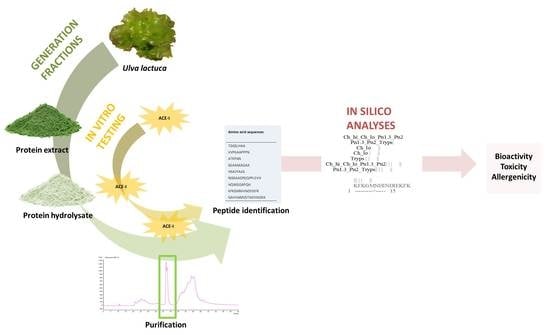
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Protein Extraction
2.2. Generation of Hydrolysates and Antihypertensive Activities In Vitro
2.3. Purification by Preparative Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC) and Antihypertensive Activity In Vitro
2.4. Identification of Peptides Using HPLC-MS/MS and Bitterness Estimation
2.5. In Silico Analyses
2.5.1. In Silico GI Enzymatic Digestion
2.5.2. In Silico Prediction of Allergenicity and Bioactivity
2.5.3. In Silico Prediction of Toxicity
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Biological Materials
3.2. Chemicals
3.3. Protein Extraction and Quantification
3.4. Protein Hydrolysis and Molecular Weight Cutoff Filtration
3.5. Preparative Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
3.6. In Vitro Antihypertensive Activities
3.6.1. ACE-I Inhibition Assay
3.6.2. Renin Inhibition Assay
3.7. Identification of Peptides by Mass Spectrometry
3.8. In Silico Analyses
3.9. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Callow, A.D. Cardiovascular disease 2005—The global picture. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 45, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaniak, A.; Minkiewicz, P.; Darewicz, M. Food-originating ACE inhibitors, including antihypertensive peptides, as preventive food components in blood pressure reduction. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, E.A.; Park, Y. Healthier meat products as functional foods. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, C.I. Franz Volhard Lecture. Renin-angiotensin system: A dual tissue and hormonal system for cardiovascular control. J. Hypert. 1992, 10, S13–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Trogdon, J.G.; Khavjou, O.A.; Butler, J.; Dracup, K.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Finkelstein, E.A.; Hong, Y.; Johnston, S.C.; Khera, A. Forecasting the future of cardiovascular disease in the United States: A policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011, 123, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarga, T.; Rai, D.K.; O’connor, P.; Hayes, M. Generation of bioactive hydrolysates and peptides from bovine hemoglobin with in vitro renin, angiotensin-I-converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activities. J. Food Biochem. 2016, 40, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, H.; Walsh, D.; Murray, B.; Fitzgerald, R. ACE inhibitory peptides, nutraceutical proteins and peptides in health and disease. In Nutraceutical Science and Technology; Mine, Y., Shahidi, F., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, W.O.; Hernandez-Diaz, S.; Arbogast, P.G.; Dudley, J.A.; Dyer, S.; Gideon, P.S.; Hall, K.; Ray, W.A. Major congenital malformations after first-trimester exposure to ACE inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pryde, P.G.; Sedman, A.B.; Nugent, C.E.; Barr, M. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor fetopathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1993, 3, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, H.-L.; Liu, D.; Ma, C.-B. Review on the angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor peptides from marine proteins. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 169, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, R.; Behare, P.; Rana, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Arora, S.; Morotta, F.; Jain, S.; Yadav, H. Bioactive peptides derived from milk proteins and their health beneficial potentials: An update. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeyrathne, E.; Lee, H.; Jo, C.; Nam, K.; Ahn, D. Enzymatic hydrolysis of ovalbumin and the functional properties of the hydrolysates. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 2678–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lafarga, T.; O’Connor, P.; Hayes, M. Identification of novel dipeptidyl peptidase-IV and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from meat proteins using in silico analysis. Peptides 2014, 59, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, C.N.; Mora-Soler, L.; Gallagher, E.; O’Connor, P.; Prieto, J.; Soler-Vila, A.; Hayes, M. Isolation and characterization of bioactive pro-peptides with in vitro renin inhibitory activities from the macroalga Palmaria palmata. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7421–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangopadhyay, N.; Wynne, K.; O’Connor, P.; Gallagher, E.; Brunton, N.P.; Rai, D.K.; Hayes, M. In silico and in vitro analyses of the angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory activity of hydrolysates generated from crude barley (Hordeum vulgare) protein concentrates. Food Chem. 2016, 203, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.-H.; Qu, M.-R.; Wan, J.-Z.; You, J.-M. Antihypertensive effect of rice protein hydrolysate with in vitro angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 16, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Hayes, M. Red and green macroalgae for fish and animal feed and human functional food development. Food Rev. Int. 2016, 32, 15–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Rajauria, G.; Tiwari, B.; Sweeney, T.; O’Doherty, J. Extraction and yield optimisation of fucose, glucans and associated antioxidant activities from Laminaria digitata by applying response surface methodology to high intensity ultrasound-assisted extraction. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Vaquero, M. Seaweed Proteins and Applications in Animal Feed. In Novel Proteins for Food, Pharmaceuticals, and Agriculture: Sources, Applications, and Advances; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 139. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, M.; Hanniffy, D.; Heesch, S.; Hernandez-Kantun, J.; Queguineur, B.; Ratcliff, J.; Soler-Vila, A.; Wan, A. Macroalgae Fact-Sheets; NUI: Galway, Ireland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fleurence, J.; Morançais, M.; Dumay, J. Seaweed proteins. In Proteins in Food Processing; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 245–262. [Google Scholar]
- Frikha, F.; Kammoun, M.; Hammami, N.; Mchirgui, R.; Belbahri, L.; Gargouri, Y.; Miled, N.; Ben-Rebah, F. Chemical composition and some biological activities of marine algae collected in Tunisia. Cienc. Mar. 2011, 37, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Lopez-Alonso, M.; Hayes, M. Assessment of the functional properties of protein extracted from the brown seaweed Himanthalia elongata (Linnaeus) SF Gray. Food Res. Int. 2017, 99, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, A. Enzymatic protein hydrolysates in human nutrition. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleakley, S.; Hayes, M.; O’Shea, N.; Gallagher, E.; Lafarga, T. Predicted release and analysis of novel ACE-I, renin, and DPP-IV inhibitory peptides from common oat (Avena sativa) protein hydrolysates using in silico analysis. Foods 2017, 6, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Aluko, R.E.; Nakai, S. Structural requirements of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides: Quantitative structure−activity relationship study of di-and tripeptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Aluko, R.E.; Nakai, S. Structural requirements of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides: Quantitative structure-activity relationship modeling of peptides containing 4-10 amino acid residues. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2006, 25, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.W.; Tran, A.D. Factors influencing the performance of peptide mapping by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1990, 499, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, H.-S.; Wang, F.-l.; Ondetti, M.A.; Sabo, E.F.; Cushman, D.W. Binding of peptide substrates and inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Importance of the COOH-terminal dipeptide sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 1980, 255, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.-L.; Chen, X.-L.; Wu, H.; Sun, C.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Zhou, B.-C. High throughput and rapid screening of marine protein hydrolysates enriched in peptides with angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity by capillary electrophoresis. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3499–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moayedi, A.; Mora, L.; Aristoy, M.-C.; Hashemi, M.; Safari, M.; Toldrá, F. ACE-inhibitory and antioxidant activities of peptide fragments obtained from tomato processing by-products fermented using Bacillus subtilis: Effect of amino acid composition and peptides molecular mass distribution. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 181, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Dziuba, J.; Iwaniak, A.; Dziuba, M.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP database and other programs for processing bioactive peptide sequences. J. AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 965–980. [Google Scholar]
- Grasso, S.; Brunton, N.; Lyng, J.; Lalor, F.; Monahan, F. Healthy processed meat products–Regulatory, reformulation and consumer challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 39, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ney, K. Voraussage der Bitterkeit von Peptiden aus deren Aminosäurezu-sammensetzung. Prediction of bitterness of peptides from their amino acid composition. Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch. 1971, 147, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.J.; Unklesbay, N.; Hsieh, F.-H.; Clarke, A.D. Hydrophobicity of bitter peptides from soy protein hydrolysates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5895–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, R.A.M.; Mendonça, S.; de Castro, L.Í.A.; Menezes, A.C.; Arêas, J.A.G. Major peptides from amaranth (Amaranthus cruentus) protein inhibit HMG-CoA reductase activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 4150–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushman, D.; Cheung, H.; Sabo, E.; Ondetti, M. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors: Evolution of a new class of antihypertensive drugs. In Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors. Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Implications; Urban & Schwarzenberg: Munich, Germany, 1981; pp. 3–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, V.T.T.; Ito, K.; Ohno, M.; Motoyama, T.; Ito, S.; Kawarasaki, Y. Analyzing a dipeptide library to identify human dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; De Mejia, E.G. A new frontier in soy bioactive peptides that may prevent age-related chronic diseases. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2005, 4, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) by proline containing casein-derived peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Ruiz, J.Á.; Ramos, M.; Recio, I. Identification of novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides from ovine milk proteins by CE-MS and chromatographic techniques. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 4202–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polikovsky, M.; Fernand, F.; Sack, M.; Frey, W.; Müller, G.; Golberg, A. In silico food allergenic risk evaluation of proteins extracted from macroalgae Ulva sp. with pulsed electric fields. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenta, R.; Hochwallner, H.; Linhart, B.; Pahr, S. Food allergies: The basics. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1120–1131.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO Panel). Scientific opinion on the assessment of allergenicity of GM plants and microorganisms and derived food and feed. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, I.; Bangov, I.; Flower, D.R.; Doytchinova, I. AllerTOP v. 2—A server for in silico prediction of allergens. J. Mol. Model. 2014, 20, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liao, W.; Udenigwe, C.C. Revisiting the mechanisms of ACE inhibitory peptides from food proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høst, A.; Halken, S. Hypoallergenic formulas—When, to whom and how long: After more than 15° years we know the right indication! Allergy 2004, 59, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygård, L.A.K.; Mundal, I.; Dahl, L.; Benth, J.Š.; Rokstad, A.M.M. Nutrition and physical performance in older people—Effects of marine protein hydrolysates to prevent decline in physical performance: A randomised controlled trial protocol. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e023845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shilov, I.V.; Seymour, S.L.; Patel, A.A.; Loboda, A.; Tang, W.H.; Keating, S.P.; Hunter, C.L.; Nuwaysir, L.M.; Schaeffer, D.A. The Paragon Algorithm, a next generation search engine that uses sequence temperature values and feature probabilities to identify peptides from tandem mass spectra. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2007, 6, 1638–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Kapoor, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Gautam, A.; Kumar, R.; Raghava, G.P. Open Source Drug Discovery Consortium. In silico approach for predicting toxicity of peptides and proteins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, C.; Haslam, N.J.; Pollastri, G.; Shields, D.C. Towards the improved discovery and design of functional peptides: Common features of diverse classes permit generalized prediction of bioactivity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Samples | Amino Acid Sequences | Modifications | Observed MW | Calculated MW | Observed m/z | Theoretical m/z | Charge (+) | Database | Accessions | Q-Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fr41 | TGGSLHAA | 712.41 | 712.35 | 357.21 | 357.18 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_005851095.1; EFN58993.1 | 607.5 | |
| VVPKAAPPPN | 988.76 | 988.57 | 495.39 | 495.29 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_005843189.1; EFN51087.1 | 1343 | ||
| ATKPAN | 600.41 | 600.32 | 301.21 | 301.17 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_001696486.1; XP_001696477.1 | 1001.67 | ||
| SGAASASGAA | 748.40 | 748.34 | 375.21 | 375.17 | 2 | NCBInr | RRRRRKXZ51346.1 | 377 | ||
| HSAVFAAS | 788.51 | 788.38 | 395.26 | 395.20 | 2 | NCBInr | GAX77766.1 | 883.75 | ||
| NGNAASPGQPPLEVH | 1486.84 | 1486.72 | 744.43 | 744.37 | 2 | NCBInr | RRRRRJAC80986.1 | 960 | ||
| HQWGGAPQH | 1016.69 | 1016.46 | 509.35 | 509.24 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_002500034.1; ACO61292.1 | 794.44 | ||
| KFKGMNHINDIEKFK | 1847.96 | 1847.97 | 616.99 | 617.00 | 3 | UniProt | sp|B9DRW5 | 1304 | ||
| GAVHAMVDTAKIHKGKK | 1789.95 | 1790.00 | 597.66 | 597.67 | 3 | UniProt | RRRRRsp|Q3TC72 | 1048.23 | ||
| Fr42 | AGGPNQPPN | 850.48 | 850.39 | 426.25 | 426.20 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_001694488.1; EDP02483.1 | 941.11 | |
| AANITVPAAN | 940.58 | 940.50 | 471.30 | 471.26 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_002957564.1; EFJ41334.1 | 1062 | ||
| DSLSAIGGAPDG | 1058.45 | 1058.49 | 530.23 | 530.25 | 2 | NCBInr | JAC65094.1 | 885.83 | ||
| SAGVLPWK | 856.50 | 856.48 | 429.26 | 429.25 | 2 | NCBInr | KXZ46138.1 | 1500 | ||
| DGLIDGL | 694.35 | 701.36 | 695.36 | 702.37 | 1 | UniProt | tr|A0A1C9C803|A0A1C9C803_9FLOR | 1270 | ||
| GDLIDVA | 694.35 | 701.36 | 695.36 | 702.37 | 1 | UniProt | tr|M1VAH3|M1VAH3_CYAM1 | 1270 | ||
| NQVTNLIVA | 970.46 | 970.54 | 486.24 | 486.28 | 2 | UniProt | tr|A0A1G4NVL3|A0A1G4NVL3_9FLOR | 1091.11 | ||
| GSASGAFVY | 857.46 | 857.39 | 429.74 | 429.70 | 2 | UniProt | tr|M1V5F7|M1V5F7_CYAM1 | 972.22 | ||
| Fr43 | HGPPPPSPYRSAAGRAAL | 1800.90 | 1800.94 | 601.31 | 601.32 | 3 | NCBInr | XP_005846003.1; EFN53901.1 | 1297.22 | |
| EAEPAEAA | 786.37 | 786.34 | 394.19 | 394.18 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_005852249.1; EFN60147.1 | 898.75 | ||
| SIAGVAAFIG | 904.48 | 904.50 | 453.25 | 453.26 | 2 | NCBInr | JAC64130.1 | 1251 | ||
| YAAKMRK | 866.54 | 866.48 | 434.28 | 434.25 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_007512502.1; CCO17102.1 | 1337.14 | ||
| DDLKGTF | 794.38 | 794.38 | 398.20 | 398.20 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_003058074.1; EEH58025.1 | 1155.71 | ||
| GGVYGTSAR | 866.50 | 866.42 | 434.26 | 434.22 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_001700029.1; EDP07725.1 | 722.22 | ||
| GSECMWFAS | 1016.33 | 1016.37 | 509.17 | 509.19 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_001693035.1; EDP03604.1 | 923.33 | ||
| AGFSYFGESS | 1050.45 | 1050.43 | 526.23 | 526.22 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_002951597.1; EFJ47408.1 | 957 | ||
| DLLALRELDVACN | 1443.77 | 1443.74 | 722.89 | 722.88 | 2 | NCBInr | JAT73014.1 | 1167.69 | ||
| NGGDLPGAL | 812.42 | 812.40 | 407.22 | 407.21 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_003055625.1; EEH60877.1 | 968.89 | ||
| ALLQQQAQMAAALPLPP | 1759.90 | 1759.97 | 587.64 | 587.66 | 3 | NCBInr | XP_005847720.1; EFN55618.1 | 1299.41 | ||
| LTPCAVPE | 828.43 | 828.41 | 415.22 | 415.21 | 2 | NCBInr | KXZ44026.1 | 1383.75 | ||
| ERTGRVAM | 918.48 | 918.47 | 460.25 | 460.24 | 2 | NCBInr | KXZ43890.1 | 771.25 | ||
| LNCALK | 660.43 | 660.36 | 331.22 | 331.19 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_001416982.1; ABO95275.1 | 1176.67 | ||
| GAAPTPPSPPPATKPSTPPKPPT | 2190.15 | 2190.17 | 731.06 | 731.06 | 3 | NCBInr | XP_002958348.1; EFJ40570.1 | 1558.69 | ||
| IECCLLFALV | 1122.55 | 1122.58 | 562.28 | 562.30 | 2 | NCBInr | GAX82307.1 | 1585 | ||
| PVGCLPK | 712.40 | 712.39 | 357.21 | 357.20 | 2 | NCBInr | JAC75907.1 | 1550 | ||
| DEDESSFGK | 1012.47 | 1012.40 | 507.24 | 507.21 | 2 | UniProt | tr|R7QMS5|R7QMS5_CHOCR | 712.22 | ||
| GASPVTFVFT | 1024.49 | 1024.52 | 513.25 | 513.27 | 2 | UniProt | tr|M1VHB3|M1VHB3_CYAM1 | 1295 | ||
| AGDLGAYG | 722.39 | 722.32 | 362.20 | 362.17 | 2 | UniProt | tr|A0A1X6NU59|A0A1X6NU59_PORUM | 911.25 | ||
| RSARVRVGSTAT | 1259.69 | 1259.71 | 630.85 | 630.86 | 2 | UniProt | tr|A0A1X6NKL7|A0A1X6NKL7_PORUM | 665.83 | ||
| INNNKIITNL | Deamidated (N)@2 | 1156.65 | 1156.65 | 579.33 | 579.33 | 2 | UniProt | tr|A0A1Z1MP80|A0A1Z1MP80_9FLOR | 1323 | |
| DAVEIWRVK | 1114.58 | 1114.61 | 558.30 | 558.31 | 2 | UniProt | tr|R7QMS0|R7QMS0_CHOCR | 1488.89 | ||
| Fr44 | DEVIPGAL | 812.43 | 812.43 | 407.22 | 407.22 | 2 | NCBInr | GAX84002.1 | 1440 | |
| DATFCGDLDDA | 1141.54 | 1141.42 | 571.78 | 571.72 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_001697003.1; EDP00695.1 | 830 | ||
| PKPPALCN | 838.47 | 838.44 | 420.24 | 420.23 | 2 | NCBInr | KXZ44308.1 | 1562.5 | ||
| PPNPPNPPN | 942.56 | 942.46 | 472.29 | 472.24 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_002955492.1; EFJ43345.1 | 1743.33 | ||
| TPALVSQLH | 964.50 | 964.53 | 483.26 | 483.27 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_011396301.1; KFM23431.1 | 1195.56 | ||
| TMSDRFL | 868.51 | 868.41 | 435.26 | 435.21 | 2 | NCBInr | XP_002499460.1; ACO60718.1 | 1160 | ||
| AAGAAPLL | 682.44 | 682.40 | 342.23 | 342.21 | 2 | NCBInr | AAW51128.1 | 1297.5 | ||
| LIKELDSN | 930.62 | 930.50 | 466.32 | 466.26 | 2 | UniProt | tr|A0A1Z1MG56|A0A1Z1MG56_9FLOR | 1303.75 |
| Amino Acid Sequences | Bioactivity In Vitro * | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| AA | ACE-I inhibitor | Cushman et al. [37] |
| AG | ACE-I inhibitor | Cheung, Wang, Ondetti, Sabo and Cushman [29] |
| AS | DPP IV inhibitor | Lan et al. [38] |
| DG | ACE-I inhibitor | Meisel, Walsh, Murray and Fitzgerald [7] |
| GA | ACE-I inhibitor | Cheung, Wang, Ondetti, Sabo and Cushman [29] |
| GD | ACE-I inhibitor | Cheung, Wang, Ondetti, Sabo and Cushman [29] |
| GGV | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor | Soares, Mendonça, de Castro, Menezes and Arêas [36] |
| GK | ACE-I inhibitor | Cheung, Wang, Ondetti, Sabo and Cushman [29] |
| GM | ACE-I inhibitor | Cheung, Wang, Ondetti, Sabo and Cushman [29] |
| IG | ACE-I inhibitor | Cheung, Wang, Ondetti, Sabo and Cushman [29] |
| IH | DPP IV inhibitor | Lan, Ito, Ohno, Motoyama, Ito and Kawarasaki [38] |
| NH | DPP IV inhibitor | Lan, Ito, Ohno, Motoyama, Ito and Kawarasaki [38] |
| PK | DPP IV inhibitor | Lan, Ito, Ohno, Motoyama, Ito and Kawarasaki [38] |
| TM | DPP IV inhibitor | Lan, Ito, Ohno, Motoyama, Ito and Kawarasaki [38] |
| VK | DPP IV inhibitor | Lan, Ito, Ohno, Motoyama, Ito and Kawarasaki [38] |
| ACE-I inhibitor | Wang and De Mejia [39] | |
| VR | DPP IV inhibitor | Nongonierma and FitzGerald [40] |
| ACE-I inhibitor | Gómez-Ruiz et al. [41] |
| Amino Acid Sequence | MW (Da) | SVM Scores a | PeptideRanker Scores b | Nearest Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AANITVPAAN | 940.4978 | −1.3 | 0.144457 | NCBI GI number 2154734 |
| AAPPPN | 565.627 | −0.46 | 0.792864 | NCBI GI number 33323477 |
| AGD | 261.235 | −0.8 | 0.283992 | UniProtKB accession number O01949 |
| AGGPNQPPN | 850.3933 | −0.72 | 0.621643 | NCBI GI number 33323477 |
| CGD | 293.295 | −0.79 | 0.646691 | NCBI GI number 102834 |
| DD | 248.192 | −0.79 | 0.098852 | UniProtKB accession number Q17282 |
| DDA | 319.271 | −0.8 | 0.127455 | UniProtKB accession number O01949 |
| DEVIPGA | 699.759 | −0.45 | 0.185675 | NCBI GI number 543491 |
| EVH | 383.404 | −0.82 | 0.0380427 | NCBI GI number 21465915 |
| GASPVT | 530.579 | −0.97 | 0.247962 | NCBI GI number 2500822 |
| GESS | 378.339 | −0.76 | 0.0716116 | NCBI GI number 32363197 |
| GGAPQH | 565.586 | −0.86 | 0.388533 | UniProtKB accession number P86254 |
| GSASGA | 448.433 | −0.93 | 0.250858 | NCBI GI number 543482 |
| GSECM | 525.592 | −0.42 | 0.554283 | NCBI GI number 162927 |
| IDVA | 416.475 | −0.84 | 0.0871288 | NCBI GI number 539716 |
| IECC | 466.568 | −0.25 | 0.448357 | NCBI GI number 14285595 |
| IITN | 459.543 | −0.84 | 0.106012 | UniProtKB accession number Q93YG7 |
| IK | 259.349 | −0.8 | 0.0974139 | NCBI GI number 157829757 |
| INNNK | 601.66 | −0.81 | 0.0938778 | NCBI GI number 1083651 |
| NGNAASPGQPPL | 1122.203 | −0.78 | 0.505873 | NCBI GI number 33323477 |
| NQVTN | 574.591 | −1.01 | 0.0559664 | UniProtKB accession number P00709 |
| SAIGGAPDG | 743.771 | −0.67 | 0.397354 | NCBI GI number 285005077 |
| SAR | 332.36 | −0.81 | 0.278711 | NCBI GI number 81890324 |
| TGR | 332.36 | −0.8 | 0.276659 | UniProtKB accession number Q7M1M4 |
| TPAL | 400.475 | −0.8 | 0.342157 | NCBI GI number 18203509 |
| VAM | 319.419 | −0.8 | 0.264259 | NCBI GI number 9072 |
| VSQ | 332.357 | −0.83 | 0.0492778 | NCBI GI number 2147092 |
| VVPK | 441.571 | −0.88 | 0.0810705 | NCBI GI number 2133755 |
| Amino Acid Sequence | MW (Da) | SVM Scores a | PeptideRanker Scores b | Nearest Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAAL | 344.411 | −0.84 | 0.28869 | UniProtKB accession number A9UGV6 |
| AAGAAP | 456.499 | −1.01 | 0.352249 | UniProtKB accession number Q7M1V0 |
| AAK | 288.347 | −0.77 | 0.113614 | UniProtKB accession number P27807 |
| AAL | 273.332 | −0.84 | 0.310569 | UniProtKB accession number A9UGV6 |
| AAS | 247.251 | −0.82 | 0.123531 | UniProtKB accession number A2WQG7 |
| AM | 220.287 | −0.8 | 0.74549 | UniProtKB accession number Q8IWT0 |
| ATKPAN | 600.32312 | −0.88 | 0.129647 | UniProtKB accession number Q8WYQ3 |
| CN | 235.258 | −0.8 | 0.63423 | UniProtKB accession number P01052 |
| DAT | 305.288 | −0.81 | 0.0954274 | UniProtKB accession number Q9NNX6 |
| DAVEI | 545.59 | −0.93 | 0.0603561 | UniProtKB accession number Q9T2R4 |
| DEDESS | 680.58 | −0.78 | 0.0365686 | UniProtKB accession number Q9S8K0 |
| DS | 220.182 | −0.8 | 0.0878061 | UniProtKB accession number O75366 |
| DSN | 334.286 | −0.78 | 0.104772 | UniProtKB accession number P31358 |
| DVACN | 520.558 | −0.68 | 0.203726 | UniProtKB accession number Q7M2H1 |
| EAEPAEAA | 394.193 | −0.99 | 0.0830328 | UniProtKB accession number Q9S8F6 |
| ER | 303.318 | −0.8 | 0.0704548 | UniProtKB accession number Q9T2R8 |
| GAAPTPPSPPPATKPSTPPKPPT | 731.0588 | −0.69 | 0.378489 | UniProtKB accession number Q9S8M0 |
| GAVH | 382.42 | −0.77 | 0.173142 | UniProtKB accession number Q9S8I6 |
| GPPPPSP | 647.729 | −0.11 | 0.870562 | UniProtKB accession number Q7M1V1 |
| GTF | 323.349 | −0.8 | 0.84905 | UniProtKB accession number P04234 |
| GTSAR | 490.517 | −0.89 | 0.151592 | UniProtKB accession number Q7M282 |
| IDG | 303.315 | −0.78 | 0.288785 | UniProtKB accession number P86001 |
| INDIEK | 730.816 | −0.97 | 0.0849714 | UniProtKB accession number P86006 |
| IVA | 301.386 | −0.79 | 0.0757333 | UniProtKB accession number Q9S8N5 |
| NCA | 306.337 | −0.77 | 0.425512 | UniProtKB accession number A6N1B4 |
| NGGDL | 474.471 | −0.76 | 0.567577 | UniProtKB accession number P55857 |
| PGA | 243.263 | −0.81 | 0.674335 | UniProtKB accession number Q9S906 |
| PKPPAL | 621.778 | −0.7 | 0.715386 | UniProtKB accession number Q7M1U2 |
| PLPP | 422.525 | −1.04 | 0.876691 | UniProtKB accession number Q7M1V1 |
| PPNPPNPPN | 942.455933 | −0.4 | 0.855282 | UniProtKB accession number Q9S8M0 |
| PVGCL | 487.615 | −0.63 | 0.734232 | UniProtKB accession number P83184 |
| QQQAQM | 732.809 | −0.92 | 0.216075 | UniProtKB accession number Q9UL45 |
| SAAGR | 460.49 | −0.85 | 0.341095 | UniProtKB accession number P80825 |
| SAGVL | 445.516 | −0.99 | 0.38464 | UniProtKB accession number A9UGV7 |
| SAV | 275.305 | −0.82 | 0.0814653 | UniProtKB accession number Q09Y74 |
| SDR | 376.37 | −0.83 | 0.242439 | UniProtKB accession number Q9BXJ1 |
| SGAASASGAA | 748.335144 | −1.17 | 0.2792 | UniProtKB accession number Q7M1V0 |
| SIAGVAA | 587.674 | −1.28 | 0.134975 | UniProtKB accession number A9UGV6 |
| TGGS | 320.302 | −0.77 | 0.17105 | UniProtKB accession number Q15517 |
| TPCAVPE | 715.819 | −0.88 | 0.224438 | UniProtKB accession number Q9T2Q0 |
| VDTAK | 532.594 | −0.34 | 0.0513549 | UniProtKB accession number Q9T2R4 |
| VGSTAT | 534.567 | −1.03 | 0.0691571 | UniProtKB accession number Q10ST8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Mora, L.; Hayes, M. In Vitro and In Silico Approaches to Generating and Identifying Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme I Inhibitory Peptides from Green Macroalga Ulva lactuca. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040204
Garcia-Vaquero M, Mora L, Hayes M. In Vitro and In Silico Approaches to Generating and Identifying Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme I Inhibitory Peptides from Green Macroalga Ulva lactuca. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(4):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040204
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia-Vaquero, Marco, Leticia Mora, and Maria Hayes. 2019. "In Vitro and In Silico Approaches to Generating and Identifying Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme I Inhibitory Peptides from Green Macroalga Ulva lactuca" Marine Drugs 17, no. 4: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040204
APA StyleGarcia-Vaquero, M., Mora, L., & Hayes, M. (2019). In Vitro and In Silico Approaches to Generating and Identifying Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme I Inhibitory Peptides from Green Macroalga Ulva lactuca. Marine Drugs, 17(4), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040204