Synthesis and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of Compounds Based on Toluquinol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of Compounds 2–15
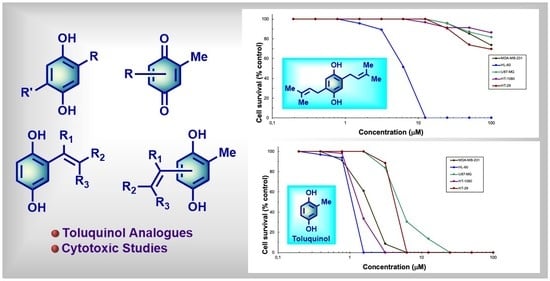
2.2. Antitumoral Properties of the Compounds
2.2.1. Antitumor Properties with Structure‒Activity Relationship (SAR) of 2-Substituted Hydroquinones 2–7
2.2.2. Antitumor Properties with SAR of 2,6-Disubstituted Hydroquinones 8–11
2.2.3. Antitumor Properties with SAR of 2,3-Disubstituted Hydroquinone 13 and 2,5-Disubstituted Hydroquinones 12 and 15
2.2.4. Antitumor Properties with SAR of Benzoquinones 14, 16, and Benzopyrane 19
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Techniques
3.2. Biological Material and Methods
3.3. Synthesis
3.3.1. 2-(Trifluoromethyl)benzene-1,4-diol (2)
3.3.2. 2-(3-Methylbut-2-en-1-yl)benzene-1,4-diol (3), 2,5-bis-(3-Methylbut-2-en-1-yl)benzene-1,4-diol (18) and 2,2-dimethyl-6-chromanol (19): Reaction of 17 with Prenol
3.3.3. Synthesis of Compounds 20 and 22
3.3.4. General Procedures for Suzuki Couplings: Synthesis of the 2-Substituted and 2,6-Disubstituted Hydroquinones 4–11
3.3.5. Synthesis of Compounds 23, 24, and 2,5-Disubstituted Hydroquinones 12 and 15
3.4. Cell Growth Assay
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sunassee, S.N.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Cytotoxic and antioxidant marine prenylated quinones and hydroquinones. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 513–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, P.A.; Hernández, Á.P.; San Feliciano, A.; Castro, M.A. Bioactive Prenyl- and Terpenyl-Quinones/Hydroquinones of Marine Origin. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordaliza, M. Cytotoxic terpene quinones from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2849–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, A.L.; Hill, R.T.; Place, A.R.; Hamann, M.T. The expanding role of marine microbes in pharmaceutical development. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhatnagar, I.; Kim, S.K. Immense essence of excellence: Marine microbial bioactive compounds. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2673–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Caballero, M.; Marí-Beffa, M.; Cañedo, L.; Medina, M.A.; Quesada, A.R. Toluquinol, a Marine Fungus Metabolite, is a New Angiosuppresor that Interferes the Akt Pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1727–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Caballero, M.; Blacher, S.; Paupert, J.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.A.; Noël,, A. Novel Application Assigned to Toluquinol: Inhibition of Lymphangiogenesis by Interfering with VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 Signalling Pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 1966–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-J.; Kirchmeier, R.L.; Shreeve, J.M. New Electrophilic Trifluoromethylating Agents. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 2656–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, M.; Aravena, J.; Vergara, A.; Taborga, L.; Baeza, E.; Catalán, K.; González, C.; Carvajal, M.; Carrasco, H.; Espinoza, L. Synthesis and DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity of Prenylated Phenol Derivatives. Molecules 2012, 17, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Bulger, P.G.; Sarlah, D. Palladium-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions in Total Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4442–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viault, G.; Grée, D.; Das, S.; Yadav, J.S.; Grée, R. Synthesis of a Focused Chemical Library Based on Derivatives of Embelin, a Natural Product with Proapoptotic and Anticancer Properties. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 2011, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbermann, F.; Mayer, P.; Trauner, D. Biomimetic Synthesis of (−)-Pycnanthuquinone C through the Diels-Alder Reaction of a Vinyl Quinone. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6199–6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutz, S.K.; Schmidt, A.; Knölker, H.-J. Palladium-Catalyzed Synthesis of Pyrayaquinones, Murraya-quinones, and Murrayafoline-B. Synthesis 2017, 49, 275–292. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson-Ajinwo, O.R.; Li, E.-W. Stable Isotope Dilution Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry for Quantification of Thymoquinone in Black Cumin Seed Oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5466–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, S.E.; Yi, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Hong, S.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. Hydroquinone Exhibits In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Cancer Activity in Cancer Cells and Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, B.M.; Clarkson, K.; Bernstein, R.L. Simple prenylated hydroquinone derivatives from the marine Urochordate Aplidium californicum. Natural anticancer and antimutagenic agents. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 4449–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertanha, C.S.; Januário, A.H.; Alvarenga, T.A.; Pimenta, L.P.; Silva, M.L.; Cunha, W.R.; Pauletti, P.M. Quinone and hydroquinone metabolites from the ascidians of the genus Aplidium. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3608–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisch, K.M.; Böhm, V.; Wright, A.D.; König, G.M. Antioxidative meroterpenoids from the brown alga Cystoseira crinita. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamel, M.S.; Assaf, M.H.; Hasanean, H.A.; Ohtani, K.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K. Monoterpene glucosides from Origanum syriacum. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sevindik, H.G.; Ozgen, U.; Atila, A.; Er, H.O.; Kazaz, C.; Duman, H. Phtytochemical Studies and Quantitative HPLC Analysis of Rosmarinic Acid and Luteolin 5-O-β-d-Glucopyranoside on Thymus praecox subsp. grossheimii var. grossheimii. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 63, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darakhshan, S.; Bidmeshki Pour, A.; Hosseinzadeh Colagar, A.; Sisakhtnezhad, S. Thymoquinone and its therapeutic potentials. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 95–96, 138–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Husain, A.; Mujeeb, M.; Khan, S.A.; Najmi, A.K.; Siddique, N.A.; Damanhouri, Z.A.; Anwar, F. A Review on Therapeutic Potential of Nigella sativa: A Miracle Herb. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2013, 3, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdalawieh, A.F.; Fayyad, M.W.; Nasrallah, G.K. Anti-cancer properties and mechanisms of action of thymoquinone, the major active ingredient of Nigella sativa. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3911–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaufi, O.M.; Noorwali, A.; Zahran, F.; Al-Abd, A.M.; Al-Attas, S. Cytotoxicity of Thymoquinone Alone or in Combination with Cisplatin (CDDP) against Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, T.; Cho, S.G.; Yi, Z.; Pang, X.; Rodriguez, M.; Wang, Y.; Sethi, G.; Aggarwal, B.B.; Liu, M. Thymoquinone inhibits tumor angiogenesis and tumor growth through suppressing AKT and extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways. Mol. Cancer. Ther. 2008, 7, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, L.; Liu, A.; Shen, Y.; Xu, H.Z.; Yang, S.Z.; Ying, X.Z.; Liao, W.; Liu, H.X.; Lin, Z.Q.; Chen, Q.Y.; et al. Antitumor and anti-angiogenesis effects of thymoquinone on osteosarcoma through the NF-κB pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkharfy, K.M.; Al-Daghri, N.M.; Al-Attas, O.S.; Alokail, M.S. The protective effect of thymoquinone against sepsis syndrome morbidity and mortality in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson-Ajinwo, O.R.; Ullah, I.; Mbye, H.; Richardson, A.; Horrocks, P.; Li, W.W. The synthesis and evaluation of thymoquinone analogues as anti-ovarian cancer and antimalarial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koka, P.S.; Mondal, D.; Schultz, M.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Agrawal, K.C. Studies on molecular mechanisms of growth inhibitory effects of thymoquinone against prostate cancer cells: Role of reactive oxygen species. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010, 235, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, Y.K.; Abdelrazek, H.M.A. Cancer: Thymoquinone antioxidant/pro-oxidant effect as potential anticancer remedy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 115, 108783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, H.; Khan, H.Y.; Sohail, A.; Azim, S.; Ullah, M.F.; Ahmad, A.; Sarkar, F.H.; Hadi, S.M. Redox cycling of endogenous copper by thymoquinone leads to ROS mediated DNA breakage and consequent cell death: Putative anticancer mechanism of antioxidants. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas, C.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.Á. Evaluation of the anti-angiogenic effect of aloe-emodin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 3083–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Structure | Compound | Tumor Cell Line | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDA-MB-231 [b] | HL-60 [c] | U87-MG [d] | HT-1080 [e] | HT-29 [f] | ||
 | Toluquinol (1) | 2.3 ± 0.8 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 5.6 ± 1.5 | 1.4 ± 0.6 | 4.1 ± 0.4 |
 | Compound 2 | 14.5 ± 1.8 | 13.9 ± 1.1 | 31.7 ± 5.6 | 41.2 ± 11.4 | 29.7 ± 7.1 |
 | Compound 3 | >100 | 50.0 ± 3.4 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
 | Compound 18 | >100 | 7.0 ± 1.2 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
 | Compound 4 | 4.1 ± 1.1 | 3.0 ± 0.7 | 10.4 ± 3.6 | 3.7 ± 1.8 | 7.9 ± 0.1 |
 | Compound 5 | 3.9 ± 1.5 | 5.3 ± 2.0 | 29.7 ± 4.9 | 8.4 ± 1.4 | 15.5 ± 4.5 |
 | Compound 6 | 6.7 ± 1.8 | 6.3 ± 1.3 | 15.9 ± 4.4 | 6.1 ± 2.5 | 12.3 ± 2.5 |
 | Compound 7 | 4.2 ± 1.8 | 6.2 ± 1.7 | 8.8 ± 0.8 | 3.2 ± 1.9 | 9.8 ± 3.2 |
 | Compound 8 | 2.2 ± 0.3 | 3.1 ± 1.7 | 10.0 ± 2.1 | 3.3 ± 0.1 | 8.1 ± 0.6 |
 | Compound 9 | 2.6 ± 1.3 | 3.6 ± 1.5 | 15.8 ± 2.3 | 5.5 ± 1.9 | 14.2 ± 4.3 |
 | Compound 10 | 3.2 ± 1.2 | 4.7 ± 0.8 | 16.0 ± 1.3 | 5.0 ± 1.5 | 15.6 ± 1.2 |
 | Compound 11 | 2.4 ± 0.3 | 3.1 ± 1.3 | 9.6 ± 1.3 | 2.9 ± 1.0 | 7.7 ± 1.6 |
 | Compound 12 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 2.9 ± 1.4 | 5.2 ± 1.2 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 7.9 ± 2.0 |
 | Compound 13 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 3.2 ± 1.6 | 5.1 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.3 | 6.5 ± 2.6 |
 | Thymoquinol (15) | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 10.2 ± 2.0 | 2.0 ± 1.1 | 8.2 ± 1.4 |
 | Thymoquinone (16) | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.9 | 15.1 ± 3.2 | 4.0 ± 0.9 | 12.9 ± 1.6 |
 | Toluquinone (14) | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 5.6 ± 1.9 | 8.8 ± 0.9 | 4.9 ± 1.7 | 9.5 ± 0.5 |
 | Compound 19 | >100 | 82.0 ± 5.9 | >100 | >100 | >100 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng-Sánchez, I.; Torres-Vargas, J.A.; Martínez-Poveda, B.; Guerrero-Vásquez, G.A.; Medina, M.Á.; Sarabia, F.; Quesada, A.R. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of Compounds Based on Toluquinol. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090492
Cheng-Sánchez I, Torres-Vargas JA, Martínez-Poveda B, Guerrero-Vásquez GA, Medina MÁ, Sarabia F, Quesada AR. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of Compounds Based on Toluquinol. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(9):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090492
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng-Sánchez, Iván, José A. Torres-Vargas, Beatriz Martínez-Poveda, Guillermo A. Guerrero-Vásquez, Miguel Ángel Medina, Francisco Sarabia, and Ana R. Quesada. 2019. "Synthesis and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of Compounds Based on Toluquinol" Marine Drugs 17, no. 9: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090492
APA StyleCheng-Sánchez, I., Torres-Vargas, J. A., Martínez-Poveda, B., Guerrero-Vásquez, G. A., Medina, M. Á., Sarabia, F., & Quesada, A. R. (2019). Synthesis and Antitumor Activity Evaluation of Compounds Based on Toluquinol. Marine Drugs, 17(9), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17090492