Antiplasmodial Compounds from Deep-Water Marine Invertebrates
Abstract
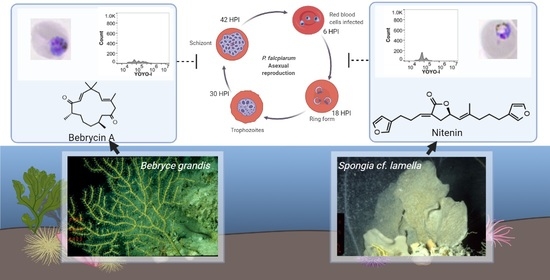
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemical Analysis
2.2. Biological Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Analysis
4.2. Biological Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation
- Bebrycin A (1); tan oil; [α]D20 = +5.0 (c 0.11 in MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 220 nm (4.1); 1H and 13C NMR (Table 1, Figures S4–S22); HRESIMS: C20H32O2 [m/z observed 327.2301 [M+Na]+, calculated 327.2300, Δ = –0.07 mmu], Figure S23.
- Nitenin (2); colorless oil; [α]D20 = -12.8 (c 0.054 in MeOH); UV (MeOH) λmax (log ε) 218 nm (3.5); 1H and 13C NMR (Table S26, Figures S27–S33); HRESIMS: C21H24O4 [m/z observed 341.1749 [M + H]+, calculated 341.1753, Δ = −0.4 mmu], Figure S34.
4.4. Biological Testing
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.; Rosenfeld, L.C.; Lim, S.S.; Andrews, K.G.; Foreman, K.J.; Haring, D.; Fullman, N.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Lopez, A.D. Global malaria mortality between 1980 and 2010: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2012, 379, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. World Malaria Report. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240015791 (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Cui, W. WHO urges the phasing out of artemisinin based monotherapy for malaria to reduce resistance. BMJ 2011, 342, d2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, E.A.; Dhorda, M.; Fairhurst, R.M.; Amaratunga, C.; Lim, P.; Suon, S.; Sreng, S.; Anderson, J.M.; Mao, S.; Sam, B.; et al. Spread of artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, L.; Straimer, J.; Gnadig, N.F.; Ralph, S.A.; Fidock, D.A. Artemisinin Action and Resistance in Plasmodium falciparum. Trends Parasitol. 2016, 32, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slater, H.C.; Griffin, J.T.; Ghani, A.C.; Okell, L.C. Assessing the potential impact of artemisinin and partner drug resistance in sub-Saharan Africa. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duru, V.; Khim, N.; Leang, R.; Kim, S.; Domergue, A.; Kloeung, N.; Ke, S.; Chy, S.; Eam, R.; Khean, C.; et al. Plasmodium falciparum dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine failures in Cambodia are associated with mutant K13 parasites presenting high survival rates in novel piperaquine in vitro assays: Retrospective and prospective investigations. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindequist, U. Marine-Derived Pharmaceuticals—Challenges and Opportunities. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Bardon, M.; Perez-Pertejo, Y.; Ordonez, C.; Sepulveda-Crespo, D.; Carballeira, N.M.; Tekwani, B.L.; Murugesan, S.; Martinez-Valladares, M.; Garcia-Estrada, C.; Reguera, R.M.; et al. Screening Marine Natural Products for New Drug Leads against Trypanosomatids and Malaria. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, F.C.; Gupta, R.; Geden, S.; Rohde, K.H.; Roberts, J.; Winder, P.; Pomponi, S.A.; Diaz, M.C.; Reed, J.K.; Wright, A.E. Selective Killing of Dormant Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Marine Natural Products. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00743-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, S.; Roberts, B.F.; Wright, A.E.; Chakrabarti, D. The bis(indolyl)imidazole alkaloid nortopsentin A exhibits antiplasmodial activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2362–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, D.; Wright, A. Screening Methods for Identifying Anti-Malarial Compounds from Marine Natural Products and Methods of Use Thereof for Treating Malaria. U.S. Patent US20140200226, 17 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fattorusso, E.; Minale, L.; Sodano, G.; Trivellone, E. Isolation and structure of nitenin and dihydronitenin, new furanoterpenes from Spongia nitens. Tetrahedron 1971, 27, 3909–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, A.; Albarella, L.; Scognamiglio, G.; Uriz, M.; Cimino, G. Structural and Stereochemical Studies of C-21 Terpenoids from Mediterranean Spongiidae Sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, T.; Kang, M.-C.; Phan, C.-S.; Zanil, I.I.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Vairappan, C.S. Bioactive cembranoids from the soft coral genus Sinularia sp. in Borneo. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stothers, J.B. Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy (Organic Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 24); Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1972; pp. 434–453. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.W.; Langer, C.; Goodman, C.D.; McFadden, G.I.; Beeson, J.G. Defining the timing of action of antimalarial drugs against Plasmodium falciparum. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.M.; Kang, S.-W.; Lee, E.A.; Seo, E.-K.; Song, J.-I.; Pan, C.-H. Analysis of carotenoids in 25 indigenous Korean coral extracts. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2013, 56, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qi, S.-H.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, Z.-H.; Li, Q.-X. Bebrycoside, a new steroidal glycoside from the Chinese gorgonian coral Bebryce indica. Pharmazie 2007, 62, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aknin, M.; Rudi, A.; Kashman, Y.; Gaydou, E.M. Bebryazulene, a New Guaiane Metabolite from the Indian Ocean Gorgonian Coral, Bebryce grandicalyx. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1286–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkel, J.; Dickschat, J.S. Characterization of Micromonocyclol Synthase from the Marine Actinomycete Micromonospora marina. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 9442–9445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, A.; Gavagnin, M.; Mollo, E.; Trivellone, E.; Ortea, J.; Cimino, G. Chemical studies of Cadlina mollusks from the Cantabrian Sea (Atlantic Ocean). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 111B, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyer, C.; Thomas, O.P.; Becerro, M.A. Patterns of chemical diversity in the Mediterranean sponge Spongia lamella. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20844. [Google Scholar]
- Rueda, A.; Zubia, E.; Ortega, M.J.; Carballo, J.L.; Salva, J. New metabolites from the sponge Spongia agaricina. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deichmann, E. The Alcyonaria of the western part of the Atlantic Ocean. Mem. Mus. Comp. Zool. 1936, 53, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, F.M.; Cairns, S.D. (Eds.) The Unpublished Plates for A.E. Verrill’s Unfinished Report on the Alcyonaria of the “Blake” Expeditions: With Revised Explanations of the Figures Transcribed from A.E. Verrill’s Original Typescript; Department of Zoology, National Museum of Natural History: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Schulze, F.E. Untersuchungen über den Bau und die Entwicklung der Spongien. Siebente Mittheilung. Die Familie der Spongidae. Z. Wiss. Zool. 1879, 32, 593–660. [Google Scholar]
- Pronzato, R.; Manconi, R. Mediterranean commercial sponges: Over 5000 years of natural history and cultural heritage. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 29, 146–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.B. In vitro culture of Plasmodium parasites. Methods Mol. Med. 2002, 72, 477–488. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, D.; Schuster, S.M.; Chakrabarti, R. Cloning and characterization of subunit genes of ribonucleotide reductase, a cell-cycle-regulated enzyme, from Plasmodium falciparum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 12020–12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.D.; Dennull, R.A.; Gerena, L.; Lopez-Sanchez, M.; Roncal, N.E.; Waters, N.C. Assessment and continued validation of the malaria SYBR green I-based fluorescence assay for use in malaria drug screening. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1926–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, T.N.; Paguio, M.; Gligorijevic, B.; Seudieu, C.; Kosar, A.D.; Davidson, E.; Roepe, P.D. Novel, rapid, and inexpensive cell-based quantification of antimalarial drug efficacy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1807–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smilkstein, M.; Sriwilaijaroen, N.; Kelly, J.X.; Wilairat, P.; Riscoe, M. Simple and inexpensive fluorescence-based technique for high-throughput antimalarial drug screening. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1803–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, B.F.; Iyamu, I.D.; Manetsch, R.; Lee, S.; Lee, E.; Ayong, L.; Kyle, D.E.; Yuan, Y.; Chakrabarti, D. Spirocyclic chromanes exhibit antiplasmodial activities and inhibit all intraerythrocytic life cycle stages. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2016, 6, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Cantero, L.; Sanz, L.; Rodriguez, M.S.; Lafuente, M.J. Magnetic isolation of Plasmodium falciparum schizonts iRBCs to generate a high parasitaemia and synchronized in vitro culture. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambros, C.; Vanderberg, J.P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J. Parasitol. 1979, 65, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, B.F.; Zheng, Y.; Cleaveleand, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, E.; Ayong, L.; Yuan, Y.; Chakrabarti, D. 4-Nitro styrylquinoline is an antimalarial inhibiting multiple stages of Plasmodium falciparum asexual life cycle. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2017, 7, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Position | δC, type | δH (J in Hz) | COSY | HMBC 1 | NOESY | 1D-nOe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 39.1, qC | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | 157.3, CH | 6.83, d (15.8) | 3 | 1, 3, 4, 15, 16 | 5, 16/17 | 5, 15ab, 16/17 |
| 3 | 126.9, CH | 6.10, d (15.8) | 2 | 1, 4 | 5, 16/17 | 5w, 16/17 |
| 4 | 206.7, qC | - | - | - | - | - |
| 5 | 45.3, CH | 2.84, m | 6ab, 18 | 6 | - | 2, 3, 6abw, 18 |
| 6a | 35.2, CH2 | 1.59, m | 5, 6b, 7ab | - | - | - |
| 6b | - | 1.46, m | 6, 6a, 7ab | 7 | - | 6a,18w |
| 7a | 24.9, CH2 | 1.13, m | 6ab, 8ab | - | - | - |
| 7b | - | 1.08, m | - | - | - | - |
| 8a | 37.7, CH2 | 1.23, m | 7a, 8b, 9 | 7, 19w | - | 9w, 19w |
| 8b | - | 1.08 m | 8a, 9 | - | - | - |
| 9 | 29.3, CH | 1.92, m | 8ab, 10ab, 19 | - | 19,8 or 7, 10a | 8abw, 10aw, 12bw, 19 |
| 10a | 48.6, CH2 | 2.59, dd (17.2, 6.2) | 9, 10b | 8, 9, 11, 19 | - | 7abw, 12aw, 19 |
| 10b | - | 2.05, dd (17.2, 6.9) | 9, 10a | 8, 9, 11, 19 | - | 8bw, 10a,12aw, 19 |
| 11 | 211.8, qC | - | - | - | - | - |
| 12a | 54.5, CH2 | 3.00, d (12.4) | 12b | 11, 13, 14, 20 | 14w | 10aw, 14w, 20w |
| 12b | - | 2.92, d (12.4) | 12a | 11, 13, 14, 20 | 14w | 14, 20w |
| 13 | 132.8, qC | - | - | - | - | - |
| 14 | 126.5, CH | 5.22, tq (6.9, 1.4) | 15ab, 20 | 12, 15, 20 | 12ab, 16/17 | 2, 12ab, 15ab, 16/ 17 |
| 15ab | 41.7, CH2 | 2.18, m, 2H | 14 | 1, 2, 13, 14, 16, 17 | 20, 16/17 | 14, 16/17, 20 |
| 16 | 27.4, CH3 | 1.12, s | - | 1, 2, 15, 17 | 2, 3, 15ab | 2, 3, 14, 15ab |
| 17 | 26.6, CH3 | 1.08, s | - | 1, 2, 15, 16 | 2, 3, 15ab | - |
| 18 | 16.7, CH3 | 1.01, d (6.9) | 5 | 4, 5, 6 | - | 5, 6ab |
| 19 | 21.3, CH3 | 0.87, d (6.9) | 9 | 8, 9, 10 | - | 8ab 9,10ab |
| 20 | 17.3, CH3 | 1.62, s | 14 | 12, 13, 14 | 15ab | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wright, A.E.; Collins, J.E.; Roberts, B.; Roberts, J.C.; Winder, P.L.; Reed, J.K.; Diaz, M.C.; Pomponi, S.A.; Chakrabarti, D. Antiplasmodial Compounds from Deep-Water Marine Invertebrates. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040179
Wright AE, Collins JE, Roberts B, Roberts JC, Winder PL, Reed JK, Diaz MC, Pomponi SA, Chakrabarti D. Antiplasmodial Compounds from Deep-Water Marine Invertebrates. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(4):179. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040179
Chicago/Turabian StyleWright, Amy E., Jennifer E. Collins, Bracken Roberts, Jill C. Roberts, Priscilla L. Winder, John K. Reed, Maria Cristina Diaz, Shirley A. Pomponi, and Debopam Chakrabarti. 2021. "Antiplasmodial Compounds from Deep-Water Marine Invertebrates" Marine Drugs 19, no. 4: 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040179
APA StyleWright, A. E., Collins, J. E., Roberts, B., Roberts, J. C., Winder, P. L., Reed, J. K., Diaz, M. C., Pomponi, S. A., & Chakrabarti, D. (2021). Antiplasmodial Compounds from Deep-Water Marine Invertebrates. Marine Drugs, 19(4), 179. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19040179